Medication
Jan 30, 2017 · Antibiotics used during the treatment will kill the bacteria that cause leprosy. But while the treatment can cure the disease and prevent it from getting worse, it does not reverse nerve damage or physical disfiguration that may have occurred before the diagnosis.
Procedures
Feb 10, 2017 · Hansen’s disease is treated with multidrug therapy (MDT) using a combination of antibiotics depending on the form of the disease: Paucibacillary form – 2 antibiotics are used at the same time, daily dapsone and rifampicin once per month Multibacillary form – daily clofazimine is added to rifampicin ...
Nutrition
Jun 19, 2004 · The regimens recommended by the World Health Organization of six or 24 months' multidrug treatment (rifampicin, dapsone, and clofazimine) produce good clinical responses and low rates of relapse. The long term outcome for shorter regimens and other drug combinations, however, is not known.
What is the life expectancy for someone with leprosy?
Treatment of leprosy has undergone considerable changes over decades, from chaulmoogra oil in 1915 to dapsone monotherapy in 1946, then eventually to multidrug therapy (MDT) in 1982.
What are the chances for recovery from leprosy?
There has been a good, effective cure for leprosy since the 1980s when it was discovered that Multiple Drug Therapy (MDT), taken for between 6 and 12 months would ensure a permanent cure of the disease. It consists of three drugs (Rifampicin, Clofazamine and Dapsone).
How do you cure leprosy?
6 rows · Jun 05, 2020 · Treatment includes nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and high-dose steroids. ...
How did they cure leprosy?
Feb 03, 2022 · These antibiotics include: dapsone (Aczone) rifampin (Rifadin) clofazimine (Lamprene) minocycline (Minocin) ofloxacin (Ocuflux)

Which is the most common treatment for leprosy?
Multidrug therapy (MDT) is a common treatment for leprosy that combines antibiotics. That means you'll take two or more medications, often antibiotics: Paucibacillary leprosy: You'll take two antibiotics, such as dapsone each day and rifampicin once a month.Sep 28, 2020
How is leprosy cured today?
How is leprosy cured? Antibiotics can cure leprosy. They work by killing the bacteria that cause leprosy. While antibiotics can kill the bacteria, they cannot reverse damage caused by the bacteria.
What was the first treatment for leprosy?
Promin, a sulfone drug, was introduced as a treatment for leprosy. It was first identified and used at Carville.
Is leprosy treatable with antibiotics?
Hansen's disease is treated with multidrug therapy (MDT) using a combination of antibiotics depending on the form of the disease: Paucibacillary form – 2 antibiotics are used at the same time, daily dapsone and rifampicin once per month. Multibacillary form – daily clofazimine is added to rifampicin and dapsone.Feb 10, 2017
Was Hawaii a leper colony?
The remote Kalaupapa peninsula on the Hawaiian island of Molokai housed a settlement for Leprosy patients from 1866 to 1969. When it was closed, many residents chose to remain. Over the years, more than 8,000 leprosy patients lived on the settlement.Sep 9, 2015
Are there still leper colonies in the United States?
The first leprosarium in the continental United States existed in Carville, Louisiana from 1894-1999 and Baton Rouge, Louisiana is the home of the only institution in the United States that is exclusively devoted to leprosy consulting, research, and training.
When did Alice ball find the cure for leprosy?
Alice Augusta Ball (July 24, 1892 – December 31, 1916) was an American chemist who developed the "Ball Method", the most effective treatment for leprosy during the early 20th century....Alice Ball.Alice Augusta BallScientific careerFieldsChemistry7 more rows
Is there a vaccine for leprosy?
There are two leprosy vaccine candidates, MIP in India (82) and LepVax (66), and the TB vaccine pipeline is much more advanced and diverse than the one for leprosy.Feb 26, 2018
What is leprosy called today?
Hansen's disease (also known as leprosy) is an infection caused by slow-growing bacteria called Mycobacterium leprae.
Can penicillin cure leprosy?
They concluded that, except for the healing of nonleprous ulcers, penicillin, in doses even larger than those found adequate in the treatment of syphilis, is ineffective in the treatment of leprosy.
What is the recommended standard treatment duration for leprosy?
For adults the standard regimen is: Rifampicin: 600 mg once a month Dapsone: 100 mg daily Clofazimine: 300 mg once a month and 50 mg daily Duration= 12 months.
What are the 3 main symptoms of leprosy?
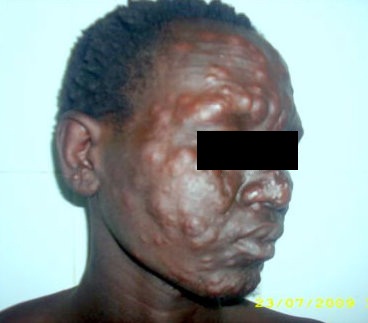
Signs and SymptomsDiscolored patches of skin, usually flat, that may be numb and look faded (lighter than the skin around)Growths (nodules) on the skin.Thick, stiff or dry skin.Painless ulcers on the soles of feet.Painless swelling or lumps on the face or earlobes.Loss of eyebrows or eyelashes.
How long does clofazimine last?
Multibacillary form – daily clofazimine is added to rifampicin and dapsone. Treatment usually lasts between one to two years. The illness can be cured if treatment is completed as prescribed. In the U.S., people with the disease may be treated at special clinics run by the National Hansen’s Disease Program. External.
What is Hansen's disease?
Hansen’s disease is treated with multidrug therapy (MDT) using a combination of antibiotics depending on the form of the disease: 1 Paucibacillary form – 2 antibiotics are used at the same time, daily dapsone and rifampicin once per month 2 Multibacillary form – daily clofazimine is added to rifampicin and dapsone.
What is the most effective treatment for leprosy?
US regimens emphasize the use of rifampin, which is the most bactericidal drug used to treat leprosy. Corticosteroids have been used to treat nerve damage associated with leprosy, but a recent review of 3 randomized controlled trials shows no significant long-term effect. [ 19] .
How long does rifampicin last?
For rifampicin-resistant leprosy, the WHO recommends treatment with at least two of clarithromycin, minocycline, and quinolone, in addition to clofazimine daily for six months, followed by clofazimine and one of the above drugs for an additional 18 months. In cases of both rifampicin and ofloxacin resistance, the recommended treatment is ...
What is the type 2 reaction?
Type 2 reaction. Erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL), also known as lepra type 2 reaction, is a complication of lepromatous leprosy. It is characterized by the development of inflamed subcutaneous nodules accompanied at times by fever, lymphadenopathy, and arthralgias.
What is the Lucio phenomenon?
Lucio phenomenon. Lucio phenomenon is a severe complication of multibacillary leprosy that is marked by blue hemorrhagic plaques and necrotic ulcerations. The bacilli may extend to the endothelial cells along with the appearance of necrotic epidermis and vasculitis with thrombus formation and endothelial proliferation.
What causes a clawed hand?
Claw fingers and Z-thumbs caused by ulnar nerve paralysis are among the most common deformities. Clawed hands are repaired with arthrodesis or with a tendon transfer to 1 of 4 insertion sites on the finger: interosseus tendons, proximal phalanx, dorsal extensor expansion, or flexor sheath annular pulleys.
How long does it take to cure rifampicin resistance?
In cases of both rifampicin and ofloxacin resistance, the recommended treatment is clarithromycin, minocycline, and clofazimine for 6 months, followed by clarithromycin or minocycline and clofazimine for an additional 18 months. See Table 2.
When did the WHO start using multidrug regimens?
In response to the increased incidence of dapsone resistance, the WHO introduced a multidrug regimen in 1981 that includes rifampicin, dapsone, and clofazimine. Some clinical studies have also shown that certain quinolones, minocycline, and azithromycin have activity against M leprae. The WHO recommends the use of the long-term multidrug regimens ...
What is the cause of leprosy?
What is leprosy? Leprosy is a chronic, progressive bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. It primarily affects the nerves of the extremities, the skin, the lining of the nose, and the upper respiratory tract. Leprosy is also known as Hansen’s disease.
What are the three types of leprosy?
There are three systems for classifying leprosy. 1. Tuberculoid leprosy vs. lepromatous leprosy vs. borderline leprosy. The first system recognizes three types of leprosy: tuberculoid, lepromatous, and borderline . A person’s immune response to the disease determines which of these types of leprosy they have:
How do you know if you have leprosy?
The main symptoms of leprosy include: muscle weakness. numbness in the hands, arms, feet, and legs. skin lesions. The skin lesions result in decreased sensation to touch, temperature, or pain. They don’t heal, even after several weeks.
When was leprosy first discovered?
Leprosy is one of the oldest diseases in recorded history. The first known written reference to leprosy is from around 600 B.C. Leprosy is common in many countries, especially those with tropical or subtropical climates. It’s not very common in the United States.
Is lepromatous leprosy contagious?
The disease is mild and only mildly contagious. In lepromatous leprosy, the immune response is poor. This type also affects the skin, nerves, and other organs. There are widespread lesions, including nodules (large lumps and bumps). This form of disease is more contagious.
Does leprosy regress?
Many lesions with bacteria; hair loss; more severe nerve involvement with peripheral nerve thickening; limb weakness; disfigurement. Doesn’t regress. There’s also a form a leprosy called indeterminate leprosy that isn’t included in the Ridley-Jopling classification system.
Why is early treatment important?
Early treatment prevents further tissue damage, stops the spread of the disease, and prevents serious health complications. The outlook is typically worse when diagnosis occurs at a more advanced stage, after an individual has significant disfigurement or disability.
Why did Western countries isolate leprosy?
Though leprosy in Europe was again on the decline by the 1860s, Western countries embraced isolation treatment out of fear of the spread of disease from developing countries, minimal understanding of bacteriology, lack of diagnostic ability or knowledge of how contagious the disease was, and missionary activity. Growing imperialism and pressures of the industrial revolution resulted in a Western presence in countries where leprosy was endemic, namely the British presence in India. Isolation treatment methods were observed by Surgeon-Mayor Henry Vandyke Carter of the British Colony in India while visiting Norway, and these methods were applied in India with the financial and logistical assistance of religious missionaries. Colonial and religious influence and associated stigma continued to be a major factor in the treatment and public perception of leprosy in endemic developing countries until the mid-twentieth century.
What is the disease of Hansen's disease?
209,000 (2018) Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease ( HD ), is a long-term infection by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae or Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Infection can lead to damage of the nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve damage may result in a lack of ability to feel pain, which can lead to the loss of parts ...
How long does it take for leprosy to show up?
Leprosy symptoms may begin within one year, but, for some people, symptoms may take 20 years or more to occur. Leprosy is spread between people, although extensive contact is necessary. Leprosy has a low pathogenicity, and 95% of people who contract M. leprae do not develop the disease.
Where is leprosy most common?
Although the number of cases worldwide continues to fall, there are parts of the world where leprosy is more common, including Brazil, South Asia (India, Nepal, Bhutan), some parts of Africa (Tanzania, Madagascar, Mozambique), and the western Pacific. About 150 to 250 cases are diagnosed in the United States each year.
Is leprosy a disease?
Although leprosy has been curable since the mid-20th century, left untreated it can cause permanent physical impairments and damage to a person's nerves, skin, eyes, and limbs. Despite leprosy not being very infectious and having a low pathogenicity, there is still significant stigma and prejudice associated with the disease. Due to this stigma, leprosy can affect a person's participation in social activities and may also affect the lives of their family and friends. People with leprosy are also at a higher risk for problems with their mental well being. The social stigma may contribute to problems obtaining employment, financial difficulties, and social isolation. Efforts to reduce discrimination and reduce the stigma surrounding leprosy may help improve outcomes for people with leprosy.
What are the symptoms of leprosy?
Common symptoms present in the different types of leprosy include a runny nose; dry scalp; eye problems; skin lesions; muscle weakness; reddish skin; smooth, shiny, diffuse thickening of facial skin, ear, and hand; loss of sensation in fingers and toes; thickening of peripheral nerves; a flat nose due to destruction of nasal cartilage; and changes in phonation and other aspects of speech production. In addition, atrophy of the testes and impotence may occur.
How long does paucibacillary leprosy last?
Treatment for multibacillary leprosy uses the same medications for 12 months. A number of other antibiotics may also be used.
How long does leprosy last?
Leprosy (also called Hanses's disease) is usually treated with oral antibiotics for six months to two years, although the duration of treatment depends on the clinical circumstances and the choice of regimen. In the United States, the National Hansen's disease Program operates clinics that specialize in leprosy, ...
How to prevent leprosy?
The most effective way to prevent leprosy is to treat infected patients and thus render them noncontagious. The bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine has had variable efficacy in clinical trials and is not in widespread use to prevent leprosy.
Why does my skin feel numb?
The affected area of skin may feel numb because of nerve damage underneath. Tuberculoid leprosy is less contagious than other forms. Lepromatous. A more severe form of the disease. It brings widespread skin bumps and rashes (multibacillary leprosy), numbness, and muscle weakness.
What is the name of the nerve that carries blood to the brain?
Leprosy primarily affects your skin and nerves outside your brain and spinal cord, called the peripheral nerves . It may also strike your eyes and the thin tissue lining the inside of your nose.
How many people are infected with leprosy?
Today, about 208,000 people worldwide are infected with leprosy, according to the World Health Organization, most of them in Africa and Asia. About 100 people are diagnosed with leprosy in the U.S. every year, mostly in the South, California, Hawaii, and some U.S. territories.
Is leprosy contagious?
Leprosy has been around since ancient times. Outbreaks have affected people on every continent. But leprosy, also known as Hanson’s disease, isn’t that contagious.
What is MB in medical terms?
Multibacillary (MB): Six or more lesions. Leprosy Diagnosis. If you have a skin sore that might be leprosy, the doctor will remove a small sample of it and send it to a lab to be examined. This is called a skin biopsy. Your doctor may also do a skin smear test.
How long does it take for leprosy to show?
It usually takes about 3 to 5 years for symptoms to appear after coming into contact with the bacteria that causes leprosy. Some people do not develop symptoms until 20 years later. The time between contact with the bacteria and the appearance of symptoms is called the incubation period.
Can leprosy be cured?
If you do have a reaction, you may have tuberculoid or borderline tuberculoid leprosy. People who don’t have leprosy or who have lepromatous leprosy won’t have a reaction to this test. Leprosy can be cured. In the last 2 decades, 16 million people with leprosy have been cured.