
What is medical shock?
Shock is a life-threatening medical condition as a result of insufficient blood flow throughout the body. Shock often accompanies severe injury or illness. Medical shock is a medical emergency and can lead to other conditions such as lack of oxygen in the body's tissues , heart attack (cardiac arrest) or organ damage. It requires immediate ...
What is cardiogenic shock treatment?
Cardiogenic shock treatment focuses on reducing the damage from lack of oxygen to your heart muscle and other organs. Most people who have cardiogenic shock need extra oxygen. If necessary, you'll be connected to a breathing machine (ventilator).
What is the treatment for shock?
Tests will determine the cause and severity. Usually IV fluids are administered in addition to medications that raise blood pressure . Septic shock is treated with antibiotics and fluids. Anaphylactic shock is treated with diphenhydramine ( Benadryl ), epinephrine (an "Epi-pen"), and steroid medications ( solu-medrol ).
What is a cardiac cardioverter shock?
The shock interrupts the abnormal electrical rhythm and restores a normal heart rhythm. It may take several shocks to get the rhythm back to normal. Cardioverter: Attached to restoreone sticky patch placed on the normalcenter of your back and one on your chest.
What is the procedure called when they shock your heart?
Cardioversion is a procedure used to return an abnormal heartbeat to a normal rhythm. This procedure is used when the heart is beating very fast or irregular. This is called an arrhythmia. Arrhythmias can cause problems such as fainting, stroke, heart attack, and even sudden cardiac death.
What is the difference between cardioversion and shock?
Cardioversion is used on patients who have an irregular or unstable pulse. Cardioversion shocks the heart back into a normal rhythm without interrupting the heart's own important cycles. It syncs up with the heart to deliver the shock at the best possible moment.
What is the success rate of cardioversion?
The success rate of cardioversion with atrial fibrillation is generally better than 90 percent. Chances of success are lower when the atrial fibrillation has been present for more than several months or when the left atrium is very enlarged. In general, there are two ways that a cardioversion procedure for AF can fail.
How long is the hospital stay for a cardioversion?
You'll receive drugs, such as dofetilide or sotalol, used to treat heart rhythm problems. If your heart doesn't regain a normal rhythm from this treatment, your doctor may recommend an electrical cardioversion. An electrical cardioversion is an outpatient procedure. Most patients are at the hospital around three hours.
Is ablation better than cardioversion?
Conclusion: In patients with AF, there is a small periprocedural stroke risk with ablation in comparison to cardioversion. However, over longer-term follow-up, ablation is associated with a slightly lower rate of stroke.
How many times can you have cardioversion?
There is really no limit to the number of cardioversions that people can have but at some point of time, we figure out that either it is a futile strategy or patients tend to get frustrated. But when it is a necessity that our patients who've had 20, 25 cardioversions also.
Is there a risk of death from cardioversion?
Results. Electrical cardioversion success rate was 90.4%. Within a year after cardioversion one patient (0.6%) suffered myocardial infarction, three patients (1.9%) had a stroke/transitory ischemic attack (TIA), three patients (1.6%) died and three patients (1.9%) had a bleeding event that required hospitalization.
What happens when cardioversion fails?
If external cardioversion fails, then internal cardioversion may be done and involves delivering the jolt of energy through catheters inside the heart. Once you wake up following the electrical cardioversion, you can go home, but will need to have someone drive you.
Is cardioversion safe for elderly?
Electrical cardioversion can be performed safely in older patients, under sedation and continuous monitoring of blood pressure and oximetry. Available temporary pacing is mandatory to avoid unnecessary bradycardia episodes.
Can you go home after cardioversion?
You'll most likely go home the same day as your cardioversion. However, you can't drive for 24 hours because you'll be sleepy from the anesthesia. You'll be able to eat and drink after your procedure. Ask your provider when you can go back to work.
What are the side effects of having your heart shocked?
Potential risks of electric cardioversion include:Dislodged blood clots. Some people who have irregular heartbeats, such as A-fib, have blood clots form in the heart. ... Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmia). Rarely, some people develop other irregular heartbeats during or after cardioversion. ... Skin burns.
What should you not do after cardioversion?
As you have been given a short general anaesthetic for the procedure, you should not drive for the next 24 hours (your insurance will not cover you). For the next 24 hours: do not go to work • do not operate machinery • do not make important decisions • do not sign legally binding documents • do not drink alcohol.
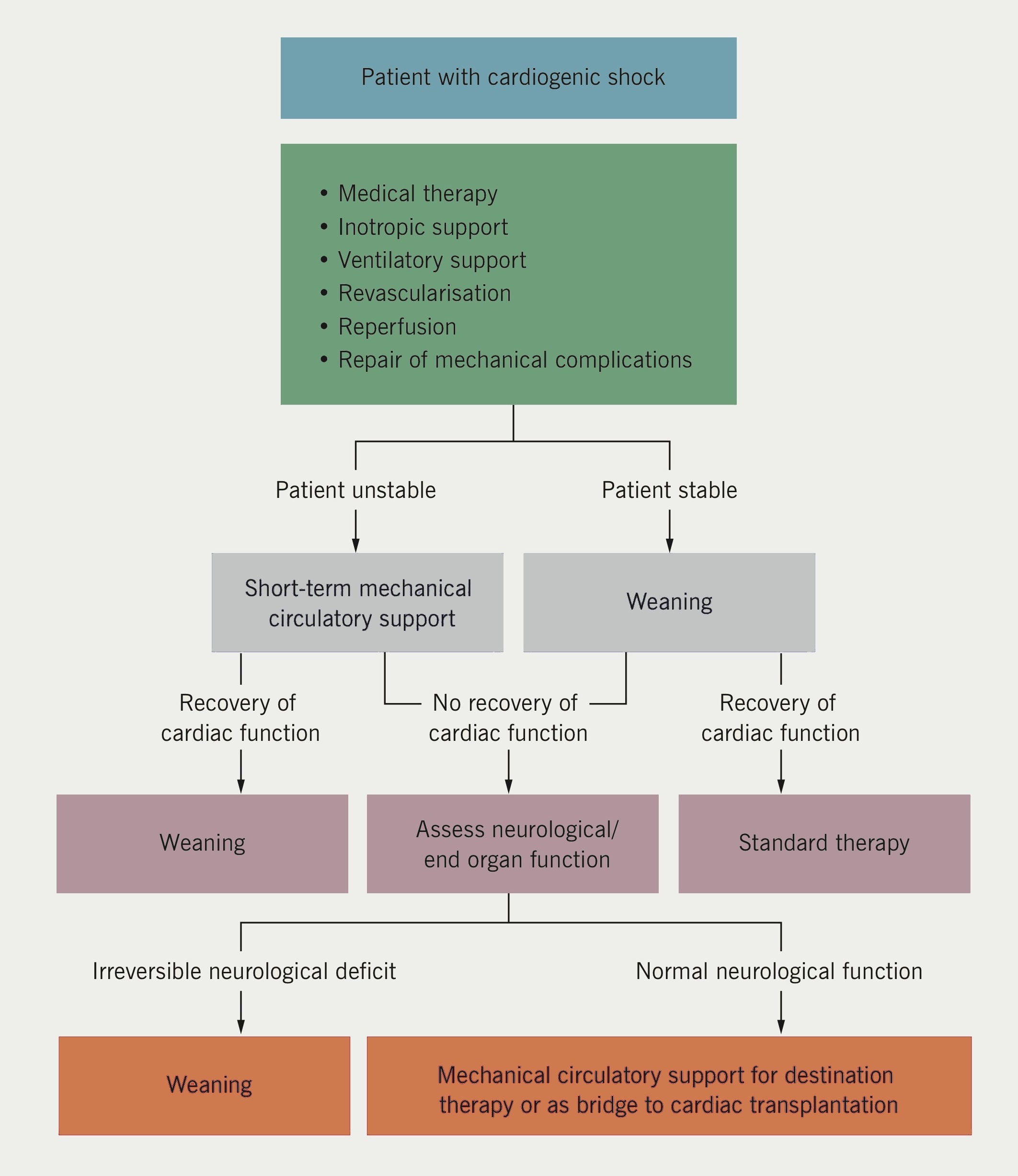
How to treat cardiogenic shock?
Medical procedures to treat cardiogenic shock usually focus on restoring blood flow through your heart. They include: 1 Angioplasty and stenting. If a blockage is found during a cardiac catheterization, your doctor can insert a long, thin tube (catheter) equipped with a special balloon through an artery, usually in your leg, to a blocked artery in your heart. Once in position, the balloon is briefly inflated to open the blockage.#N#A metal mesh stent might be inserted into the artery to keep it open over time. In most cases, you doctor will place a stent coated with a slow-releasing medication to help keep your artery open. 2 Balloon pump. Your doctor inserts a balloon pump in the main artery off of your heart (aorta). The pump inflates and deflates within the aorta, helping blood flow and taking some of the workload off your heart. 3 Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). ECMO helps improve blood flow and supplies oxygen to the body. Blood is pumped outside of your body to a heart-lung machine that removes carbon dioxide and sends oxygen-filled blood back to tissues in the body.
What are the drugs that help the heart pump?
They include dopamine, epinephrine (Adrenaline, Auvi-Q), norepinephrine (Levophed) and others. Inotropic agents. These medications, which help improve the pumping function of the heart, may be given until other treatments start to work. They include dobutamine, dopamine and milrinone.
What is the procedure to remove carbon dioxide from the body?
If medications and other procedures don't work to treat cardiogenic shock, your doctor might recommend surgery. Coronary artery bypass surgery.
How is plasma given in cardiogenic shock?
Fluids and plasma are given through an IV. Medications to treat cardiogenic shock are given to increase your heart's pumping ability and reduce the risk of blood clots.
Why do you take aspirin when you have a heart attack?
Aspirin. Aspirin is usually given immediately to reduce blood clotting and keep blood moving through a narrowed artery. Take an aspirin yourself while waiting for help to arrive only if your doctor has previously told you to do so for symptoms of a heart attack.
What is the best medicine for clots?
Antiplatelet medication. Emergency room doctors might give you drugs similar to aspirin to help prevent new clots from forming. These medications include clopidogrel (Plavix), tirofiban (Aggrastat) and eptifibatide (Integrilin). Other blood-thinning medications.
What is the best way to repair a heart injury?
Surgery to repair an injury to your heart. Sometimes an injury, such as a tear in one of your heart's chambers or a damaged heart valve, can cause cardiogenic shock. Surgery might correct the problem.
What is cardioversion in medical terms?
Cardioversion is a medical procedure that restores a normal heart rhythm in people with certain types of abnormal heartbeats (arrhythmias). Cardioversion is usually done by sending electric shocks to your heart ...
Why do you need an IV for shock?
You'll be given medications through an IV to make you sleep during the procedure so that you won't feel any pain from the shocks. You may receive other medications through the IV to help restore your heart rhythm.
How is cardioversion done?
Cardioversion is usually done by sending electric shocks to your heart through electrodes placed on your chest. It's also possible to do cardioversion with medications. Cardioversion is usually a scheduled procedure that's performed in a hospital. You should be able to go home the same day as your procedure.
How long does it take for blood clots to break free?
If your doctor finds blood clots, your cardioversion procedure will be delayed for three to four weeks.
What is the name of the machine that records your heart rhythm?
A nurse or technician places several large patches called electrodes on your chest. The electrodes connect to a cardioversion machine (defibrillator) using wires. The machine records your heart rhythm and delivers shocks to your heart to restore a normal heart rhythm. This machine can also correct your heart's rhythm if it beats too slowly after cardioversion.
What to do before cardioversion?
If necessary, your doctor may prescribe blood-thinning medications before the procedure or will check for blood clots in your heart before cardioversion.
How long does it take to do electric cardioversion?
Once you're sedated, electric cardioversion usually takes only a few minutes to complete.
What is the treatment for cardiogenic shock?
Possibilities include surgery to repair or replace a faulty valve, mechanical circulatory support (devices that assist the heart's pumping action) or heart transplantation.
What is the procedure to create a new route that allows blood to flow around a narrowed or blocked?
Coronary bypass surgery – a procedure to create a new route that allows blood to flow around a narrowed or blocked artery
What is ECMO in medical terms?
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) – An external device is used to pump and oxygenate your blood, allowing your heart and lungs to rest.
What is cardioversion in medicine?
Cardioversion – Medication or a brief electric shock resets the heart and restores a normal heartbeat.
What is the best medicine for clots?
Anticlotting medicines – such as aspirin, clopidogrel or heparin – to prevent new clots
How is cardiogenic shock treated?
Cardiogenic shock is treated by identifying and treating the underlying cause. Hypovolemic shock is treated with fluids (saline) in minor cases, and blood transfusions in severe cases. Neurogenic shock is the most difficult to treat as spinal cord damage is often irreversible.
What are the main treatments for shock?
Immobilization, anti-inflammatories such as steroids and surgery are the main treatments. Shock prevention includes learning ways to prevent heart disease, injuries, dehydration, and other causes of shock.
What are the different types of shock?
There are several types of shock: septic shock caused by bacteria, anaphylactic shock caused by hypersensitivity or allergic reaction, cardiogenic shock from heart damage, hypovolemic shock from blood or fluid loss, and neurogenic shock from spinal cord trauma. Treatment for shock depends on the cause.
What is the treatment for septic shock?
Usually, IV fluids are administered in addition to medications that raise blood pressure. Septic shock is treated with antibiotics and fluids. Anaphylactic shock is treated with diphenhydramine ( Benadryl ), epinephrine (an "Epi-pen"), and steroid medications (solumedrol).
What happens when the heart is damaged and unable to supply sufficient blood to the body?
Cardiogenic shock happens when the heart is damaged and unable to supply sufficient blood to the body. This can be the end result of a heart attack or congestive heart failure.
How serious is septic shock?
Septic shock is a serious condition with a mortality rate of 24% to 50% according to some estimates. The sooner the infection is treated and fluids are administered, the greater the chances of success. Hospitals are now developing and utilizing specific protocols to identify and aggressively treat septic shock patients.
What causes anaphylactic shock?
Common causes of this are pneumonia, urinary tract infections, skin infections ( cellulitis ), intra-abdominal infections (such as a ruptured appendix ), and meningitis . Anaphylactic shock is a type of severe hypersensitivity or allergic reaction. Causes include allergy to insect stings, medicines, or foods (nuts, berries, seafood), etc.
What is the name of the condition that causes sudden cardiac death?
This is called an arrhythmia . Arrhythmias can cause problems such as fainting, stroke, heart attack, and even sudden cardiac death. With electrical cardioversion, a high-energy shock is sent to the heart to reset a normal rhythm. It is different from chemical cardioversion, in which medicines are used to try to restore a normal rhythm.
What are the risks of a heart attack?
Rarely, the procedure causes a more dangerous heart rhythm. If that happens, someone will give you medicines or a stronger electric shock to stop this rhythm. Some other risks are: 1 Other less dangerous abnormal rhythms 2 Temporary low blood pressure 3 Heart damage (usually temporary and without symptoms) 4 Heart failure 5 Skin damage 6 Dislodged blood clot, which can cause stroke, pulmonary embolism, or other problems
Why is cardioversion important?
Cardioversion upsets the abnormal signaling and lets the heart to reset itself back into a normal rhythm. Cardioversion is usually a scheduled procedure. But sometimes healthcare providers need to do it as an emergency . This is done if symptoms are severe.
How to check for blood clots in the heart?
Your healthcare provider may want a transesophageal echocardiography test before the procedure. This test is a special kind of ultrasound. A thin, flexible tube is put down your throat and into your esophagus. Here, the tube is close to your heart. It lets your healthcare provider see if you have any blood clots in the heart. Your cardioversion will be delayed if a clot is found. You'll likely need to take blood thinner medicine for a while until your risk of clots is low. It's important to take this medicine (such as warfarin) exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
How does a cardioversion machine work?
You will receive medicine through a vein in your arm to make you fall asleep. Using the cardioversion machine, a programmed high-energy shock is sent to your heart. This should convert your heart back to a normal rhythm.
How to reset heart rate before cardioversion?
Before trying electrical cardioversion, your healthcare provider may try to reset the heart rate in other ways. This might include the Valsalva maneuver. This is a method where you hold your breath and increase the pressure in your belly.
Is cardioversion the same as defibrillation?
You will be given medicine to put you to sleep before delivering the shocks. Cardioversion is not the same as defibrillation. Both use shocks to reset the heart. But defibrillation uses a stronger shock to stop very severe rhythms that can cause sudden death.
What is cardioversion in heart?
Cardioversion is a procedure that can be used to correct many types of fast or irregular heart rhythms. The most common of these are atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. Cardioversion is also used to correct ventricular tachycardia, which is a very fast, life-threatening heart rhythm that starts in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles).
What is EKG in medical terms?
ECG/EKG: Keeps track of your heart’s electrical activity. Several sticky patches (electrodes) are attached to your chest, and wires carry the information to a machine that creates a graph.
How does a defibrillator work?
The shock interrupts the abnormal electrical rhythm and restores a normal heart rhythm. It may take several shocks to get the rhythm back to normal.
Where is cardioversion done?
The cardioversion will likely be done in the electrophysiology (EP) lab.
What is the tool that measures oxygen in blood?
Oximeter : A small clip on your finger measures the amount of oxygen in your blood.
Is cardioversion part of a plan of care?
Cardioversion is only one part of your plan of care. It is also important for you to take your medications, a heart-healthy lifestyle and keep your follow-up appointments. Please talk to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns.
What is electrical cardioversion?
Electrical cardioversion– the rhythm reset. Electrical cardioversion is a procedure in which a patient receives an electrical shock on the outside of the chest (while under mild anesthesia) using either paddles or patches. The shock can be used to “reset” the heart to a normal rhythm.
How does an ablation procedure work?
A catheter (thin, flexible tube) is inserted into the patient’s blood vessels and is gently guided to the heart. The physician carefully destroys malfunctioning tissue using the catheter to deliver energy (such as radiofrequency, laser or cryotherapy) to scar the problematic areas. The scarred areas will no longer send abnormal signals. If successful, the heart will return to a normal rhythm. But in some cases, atrial fibrillation may return. Sometimes the ablation procedure may need to be tried multiple times. This minimally invasive procedure usually has a short recovery period. Patients are generally placed on a short course of anti-arrhythmic drugs while the procedure takes full effect.
What are the different types of ablation?
Common types of ablation for AF include: 1 Pulmonary vein isolation ablation (PVI ablation or PVA). In some AF patients, fibrillation is triggered by extra electrical currents in the pulmonary veins. During this procedure, the catheter tip is used to destroy the tissue that is sending the extra currents and, in most cases, normal heart rhythm returns. 2 AV node ablation with pacemakers. In other AF patients, the trigger for their AF occurs in the AV node (the place where the electrical signals pass from the atria to the ventricles). The catheter is placed near the AV node and a small area of tissue is destroyed. A pacemaker is then implanted to restore and maintain the heart’s normal rhythm.
When is ablation used?
Ablation is used for cardiac arrhythmias when long-term medications or electrical cardioversion are either not preferred or were not effective. Before ablation surgery, electrical mapping of the heart is performed.
Can you take blood thinners before cardioversion?
For this reason, your healthcare provider may recommend that you take a *blood thinner before having an electrical cardioversion procedure. Electrical cardioversion often successfully restores regular heart rhythm, but for some patients their atrial fibrillation may return. In many instances, anti-arrhythmia medications are needed indefinitely to keep the heart’s rhythm and rate in the best range.

Overview
Why It's Done
- Cardioversion can correct a heartbeat that's too fast (tachycardia) or irregular (fibrillation). Cardioversion is usually done to treat people who have atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. These conditions occur when the electrical signals that normally make your heart beat at a regular rate don't travel properly through the upper chambers of your heart. Cardioversion is usually schedul…
Risks
- Complications of electric cardioversion are uncommon. Your doctor can take steps to reduce your risk. Major risks of cardioversion include: 1. Dislodged blood clots. Some people who have irregular heartbeats have blood clots in their hearts. Electric cardioversion can cause these blood clots to move to other parts of your body. This can cause life-threatening complications, such a…
How You Prepare
- Cardioversion procedures are usually scheduled in advance. However, if your symptoms are severe, you may need to have cardioversion in an emergency setting. You typically can't eat or drink anything for about eight hours before your procedure. Your doctor will tell you whether to take any of your regular medications before your procedure. If you do take medications before y…
What You Can Expect
- During the procedure
You'll be given medications through an IV to make you sleep during the procedure so that you won't feel any pain from the shocks. You may receive other medications through the IV to help restore your heart rhythm. A nurse or technician places several large patches called electrodes o… - After the procedure
Electric cardioversion is done on an outpatient basis, meaning you can go home the same day your procedure is done. You'll spend an hour or so in a recovery room being closely monitored for complications. You'll need someone to drive you home, and your ability to make decisions may b…
Results
- For most people, cardioversion can quickly restore a regular heartbeat. It's possible you'll need additional procedures to keep a normal heart rhythm. Your doctor may suggest lifestyle changes to improve your heart health and prevent or treat conditions that can cause arrhythmias, such as high blood pressure. 1. Avoid or limit caffeine and alcohol 2. Eat heart-healthy foods 3. Increase …
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.