
Streptomycin is bactericidal and broad-spectrum antibiotic. It is active against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Streptomycin is inhibitory for several species of Mycobacterium and is an effective antibiotic for treatment of tuberculosis caused by M. tuberculosis.
What is streptomycin used to treat?
Sep 29, 2021 · As with all aminoglycosides, streptomycin is bactericidal and provides interference with ribosomal peptide/protein synthesis. It binds to a side of 16S rRNA located on the smaller 30S component of the bacterial ribosome, inhibiting its functionality and halting further protein synthesis through inhibition of peptide bond formation.
What antibiotics are used to treat tuberculosis?
The antibiotic streptomycin is widely used in the treatment of microbial infections. The primary mechanism of action is inhibition of translation by binding to the ribosome, ... .
What does streptomycin do to ribosomes?
Mechanism of Action of Streptomycin: Streptomycin, like other aminoglycosidic antibiotics (e.g., gentamycin, neomycin, kanamycin, tobramycin), inhibits protein synthesis in bacterial cells by binding to the 30S subunit of ribosomes.
How is streptomycin excreted from the body?
Feb 26, 2021 · Streptomycin side effects. Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction (hives, difficult breathing, swelling in your face or throat) or a severe skin reaction (fever, sore throat, burning eyes, skin pain, red or purple skin rash with blistering and peeling).. Call your doctor at once if you have: headache, nausea, vomiting;. severe dizziness, spinning …
How does streptomycin work against tuberculosis?
What is streptomycin antibiotic used for?
Is streptomycin still used to treat tuberculosis?
What is work of streptomycin injection?
Is streptomycin safe for babies?
Use during pregnancy may result in permanent deafness in the developing baby. Use appears to be safe while breastfeeding. It is not recommended in people with myasthenia gravis or other neuromuscular disorders. Streptomycin is an aminoglycoside.
Is streptomycin safe for myasthenia gravis?
It is not recommended in people with myasthenia gravis or other neuromuscular disorders. Streptomycin is an aminoglycoside. It works by blocking the ability of 30S ribosomal subunits to make proteins, which results in bacterial death. Albert Schatz first isolated streptomycin in 1943 from Streptomyces griseus.
Is streptomycin a penicillin?
However streptomycin is approved for this purpose only by the US Food and Drug Administration. In veterinary medicine, streptomycin is the first-line antibiotic for use against gram negative bacteria in large animals ( horses, cattle, sheep, etc.). It is commonly combined with procaine penicillin for intramuscular injection.
What is streptomycin used for?
Pesticide. Streptomycin also is used as a pesticide, to combat the growth of bacteria beyond human applications. Streptomycin controls bacterial diseases of certain fruit, vegetables, seed, and ornamental crops. A major use is in the control of fireblight on apple and pear trees.
What is the effect of streptomycin on bacterial ribosomes?
This leads to codon misreading, eventual inhibition of protein synthesis and ultimately death of microbial cells through mechanisms that are still not understood. Speculation on this mechanism indicates that the binding of the molecule to the 30S subunit interferes with 50S subunit association with the mRNA strand. This results in an unstable ribosomal-mRNA complex, leading to a frameshift mutation and defective protein synthesis; leading to cell death. Humans have ribosomes which are structurally different from those in bacteria, so the drug does not have this effect in human cells. At low concentrations, however, streptomycin only inhibits growth of the bacteria by inducing prokaryotic ribosomes to misread mRNA. Streptomycin is an antibiotic that inhibits both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, and is therefore a useful broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Does streptomycin inhibit ribosomes?
At low concentrations, however, streptomycin only inhibits growth of the bacteria by inducing prokaryotic ribosomes to misread mRNA. Streptomycin isomer B is a peptidoglycan synthesis inhibitor much like lysozyme. It binds to the glycosidic linkages and breaks them through a SN2 mechanism.
When was streptomycin first discovered?
Streptomycin was first isolated on October 19, 1943, by Albert Schatz, a PhD student in the laboratory of Selman Abraham Waksman at Rutgers University in a research project funded by Merck and Co. Waksman and his laboratory staff discovered several antibiotics, including actinomycin, clavacin, streptothricin, streptomycin, grisein, neomycin, fradicin, candicidin, and candidin. Of these, streptomycin and neomycin found extensive application in the treatment of numerous infectious diseases. Streptomycin was the first antibiotic cure for tuberculosis (TB). In 1952 Waksman was the recipient of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in recognition "for his discovery of streptomycin, the first antibiotic active against tuberculosis". Waksman was later accused of playing down the role of Schatz who did the work under his supervision, claiming that Elizabeth Bugie had a more important role in its development.
Is streptomycin a fungicide?
It is an antibiotic antifungal drug, an antibiotic fungicide and a member of streptomycins.
Is streptomycin a hepatotoxic drug?
Streptomycin is usually used in combination with agents that are known to be hepatotoxic and the role of streptomycin in liver injury has been difficult to assess, but most information suggests that strepto mycin is not hepatotoxic.
What is the purpose of streptomycin?
Streptomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that works by binding to the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit, causing misreading of t-RNA, leaving the bacterium unable to synthesize proteins vital to its growth. Aminoglycosides are useful primarily in infections involving aerobic, Gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, and Enterobacter. In addition, some mycobacteria, including the bacteria that cause tuberculosis, are susceptible to aminoglycosides. Infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria can also be treated with aminoglycosides, but other types of antibiotics are more potent and less damaging to the host. In the past the aminoglycosides have been used in conjunction with penicillin -related antibiotics in streptococcal infections for their synergistic effects, particularly in endocarditis. Aminoglycosides are mostly ineffective against anaerobic bacteria, fungi and viruses.
What is the aminoglycoside of streptomycin?
Streptomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic derived from Streptomyces griseus with antibacterial activity. Streptomycin irreversibly binds to the 16S rRNA and S12 protein within the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit.
Does streptomycin interfere with ribosomes?
Streptomycin irreversibly binds to the 16S rRNA and S12 protein within the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit. As a result, this agent interferes with the assembly of initiation complex between mRNA and the bacterial ribosome, thereby inhibiting the initiation of protein synthesis. In addition, streptomycin induces misreading ...
How is streptomycin excreted?
Small amounts are excreted in milk, saliva, and sweat. Streptomycin is excreted by glomerular filtration. Following intramuscular injection of 1 g of streptomycin as the sulfate, a peak serum level of 25 to 50 ug/mL is reached within 1 hour, diminishing slowly to about 50 percent after 5 to 6 hours.
How long does it take for streptomycin to be absorbed?
Following IM administration of a single 1-g dose of streptomycin in adults with normal renal function, peak serum streptomycin concentrations are attained within 1 hour and range from 25-50 ug/mL; serum concentrations decrease 50% by 5-6 hours after the dose.
What is the antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis?
Streptomycin. Streptomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic indicated to treat multi-drug resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis and various non-tuberculosis infections. Streptomycin, an antibiotic derived from Streptomyces griseus, was the first aminoglycoside to be discovered and used in practice in the 1940s.
What was the first antibiotic?
Streptomycin , an antibiotic derived from Streptomyces griseus, was the first aminoglycoside to be discovered and used in practice in the 1940s. 3, 5 Selman Waksman and eventually Albert Schatz were recognized with the Nobel Prize in Medicine for their discovery of streptomycin and its antibacterial activity. 3, 6 Although streptomycin was the first antibiotic determined to be effective against mycobacterium tuberculosis, it has fallen out of favor due to resistance and is now primarily used as adjunctive treatment in cases of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis. 3
What was the first antibiotic to be used in the 1940s?
Streptomycin , an antibiotic derived from Streptomyces griseus, was the first aminoglycoside to be discovered and used in practice in the 1940s. 3, 5 Selman Waksman and eventually Albert Schatz were recognized with the Nobel Prize in Medicine for their discovery of streptomycin and its antibacterial activity. 3, 6 Although streptomycin was the first antibiotic determined to be effective against mycobacterium tuberculosis, it has fallen out of favor due to resistance and is now primarily used as adjunctive treatment in cases of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis. 3
How long does streptomycin stay in your urine?
Approximately 50% of streptomycin is eliminated in the urine within 24 hours after intravenous or intramuscular administration. 7. Half-life. Streptomycins serum half-life is estimated to be 2.5 hours. 2. Clearance.
What are the symptoms of streptomycin overdose?
The most common symptoms of streptomycin overdose are ototoxicity and vestibular impairment. 2 Streptomycin is also associated with nephrotoxicity which presents as mild elevations in blood urea, mild proteinuria, and excess cellular excretion.
Does Adefovir lower the excretion rate of Streptomycin?
Adefovir dipivoxil may decrease the excretion rate of Streptomycin which could result in a higher serum level. Albutrepenonacog alfa. Streptomycin may decrease the excretion rate of Albutrepenonacog alfa which could result in a higher serum level.
Does streptomycin lower the excretion rate of synthetic conjugated estrogens?
Streptomycin may decrease the excretion rate of Synthetic Conjugated Estrogens, A which could result in a higher serum level. Synthetic Conjugated Estrogens, B. Streptomycin may decrease the excretion rate of Synthetic Conjugated Estrogens, B which could result in a higher serum level. Tacrolimus.
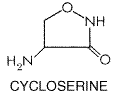
What is the structure of streptomycin?
Structure of Streptomycin: Streptomycin is characterised chemically as an aminoglycoside antibiotic. It consists of three components linked glycosidically (by ether bonds): (i) Streptidine (inositol with two guanido groups), (iii) Streptoscamine (N-methyl-L-glycosamine) as shown in Fig. 45.9.
Is streptomycin an aminoglycoside?
Streptomycin is characterised chemically as an aminoglycoside antibiotic. It consists of three components linked glycosidically (by ether bonds): (i) Streptidine (inositol with two guanido groups), (iii) Streptoscamine (N-methyl-L-glycosamine) as shown in Fig. 45.9.
Is streptomycin a broad spectrum antibiotic?
Streptomycin is bactericidal and broad-spectrum antibiotic. It is active against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Streptomycin is inhibitory for several species of Mycobacterium and is an effective antibiotic for treatment of tuberculosis caused by M. tuberculosis.
Is streptomycin gram positive or negative?
It is active against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Streptomycin is inhibitory for several species of Mycobacterium and is an effective antibiotic for treatment of tuberculosis caused by M. tuberculosis. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is the mechanism of action of streptomycin?
Mechanism of Action of Streptomycin: Streptomycin, like other aminoglycosidic antibiotics (e.g., gentamycin, neomycin, kanamycin, tobramycin), inhibits protein synthesis in bacterial cells by binding to the 30S subunit of ribosomes.
Which antibiotic inhibits protein synthesis in bacterial cells?
Streptomycin, like other aminoglycosidic antibiotics (e.g., gentamycin, neomycin, kanamycin, tobramycin), inhibits protein synthesis in bacterial cells by binding to the 30S subunit of ribosomes.
Does streptomycin interfere with codon-anticodon interaction?
By doing so, the streptomycin causes a structural change which interferes with the recognition site of codon-anticodon interaction resulting in misreading of the genetic message carried by messenger RNA (mRNA). The mechanism of inhibition of protein synthesis by streptomycin is schematically shown in Fig. 45.10.
How long does streptomycin last?
Some infections may need to be treated with streptomycin for several weeks. Follow your doctor's dosing instructions very carefully. Use this medicine for the full prescribed length of time, even if your symptoms quickly improve. Skipping doses can increase your risk of infection that is resistant to medication.
Can streptomycin make your urine less acidic?
If you use streptomycin long term, you may be given medicine to make your urine less acidic. Keep using these medicines for as long as your doctor has prescribed. Follow all directions on your prescription label and read all medication guides or instruction sheets. Use the medicine exactly as directed.
What are the symptoms of streptomycin?
headache, nausea, vomiting; severe dizziness, spinning sensation, balance problems; hearing loss, a feeling of fullness in your ears, a ringing or roaring sound in your ears (during or after treatment with streptomycin); vision problems, eye pain; problems with memory or concentration, changes in personality or behavior;
Does streptomycin harm the kidneys?
Streptomycin can harm your nerves and kidneys, especially if you also use certain medicines for infections, cancer, osteoporosis, organ transplant rejection, bowel disorders, or pain or arthritis (including Advil, Motrin, and Aleve ).
What is streptomycin used for?
Streptomycin is an antibiotic that is used to treat moderate to severe tuberculosis, pneumonia, E. coli, influenza, plague and other infections caused by certain bacteria. Streptomycin may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
Can streptomycin cause hearing loss?
Streptomycin may cause nerve damage or hearing loss, especially if you have kidney disease or use certain other medicines. Tell your doctor right away if you have severe dizziness, hearing problems, vision problems, balance problems, trouble concentrating, muscle weakness, numbness, or tingling.
Can you take streptomycin if you are allergic to it?
You should not be treated with streptomycin if you are allergic to streptomycin or similar antibiotics, such as: amikacin; gentamicin, kanamycin; neomycin; paromomycin; or. tobramycin. Tell your doctor if you have ever had: hearing problems;
Is ethambutol safe to administer during pregnancy?
The patient has been prescribed ethambutol. The patient says to the nurse, "I heard that most antitubercular drugs are not safe to administer during pregnancy.". What appropriate response does the nurse provide the patient? "Ethambutol is a first-line drug and belongs to category B, so it is safe to administer.".
What is chest radiography?
Chest radiography. The nurse is caring for a patient who has tuberculosis. The patient has been treated with isoniazid and then with rifampin and isoniazid combination therapy with no improvement in symptoms.
What is rifampin prescribed for?
Administers 600 mg of medication to the patient by the oral route. A patient is prescribed rifampin for the treatment of tuberculosis. While checking the patient's history, the nurse finds that the patient is on oral contraceptive therapy. What advice on the safe use of rifampin does the nurse give to the patient?
What is the nurse's job in pulmonary tuberculosis?
The nurse is caring for a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis who has been prescribed para-aminosalicylic acid and isoniazid. The nurse finds that the patient has rhinitis caused by an allergy. What will the nurse do in this situation? Request an order to administer diphenhydramine to the patient.
Is ethambutol a first line drug?
B) "Ethambutol is a first-line drug and belongs to category B, so it is safe to administer.". The nurse is caring for a patient with tuberculosis who was prescribed rifampin 10 mg/kg PO. Before administering the medication, the nurse checks the patient's weight and finds that it is 60 kg. What does the nurse implement for safe administration ...
What is the nurse's role in treating HIV?
The nurse is caring for a patient with advanced human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. The primary health care provider prescribed an antitubercular drug to prevent the tuberculosis caused by Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare bacteremia. Which medication will the nurse expect to administer to this patient?
What is a nurse caring for?
The nurse is caring for a patient who has tuberculosis. The patient has been treated with isoniazid and then with rifampin and isoniazid combination therapy with no improvement in symptoms.
How to cure MDR TB?
To cure MDR TB, healthcare providers must turn to a combination of second-line drugs, several of which are shown here. Second-line drugs may have more side effects, the treatment may last much longer, and the cost may be up to 100 times more than first-line therapy. MDR TB strains can also grow resistant to second-line drugs, ...
Is second line TB treatment more expensive than first line?
Second-line drugs may have more side effects, the treatment may last much longer, and the cost may be up to 100 times more than first-line therapy. MDR TB strains can also grow resistant to second-line drugs, further complicating treatment. Credit.
What is the new drug for TB?
Bedaquiline and Delamanid are new drugs. Ethambutol, Pyrazinamide, Thioamides, Cycloserine, Para-aminosalicylic acid, Streptomycin, and Clofazimine are possibly effective. Kanamycin, Capreomycin and Amikacin are injectable second-line. XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, ...
Is kanamycin a second line drug?
Kanamycin, Capreomycin and Amikacin are injectable second-line. XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, two of the most powerful first-line drugs, as well as key drugs of the second line regimen—any fluoroquinolone and at least one of the three injectable drugs shown above.
Is XDR TB resistant to isoniazid?
NIAID. XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, two of the most powerful first-line drugs, as well as key drugs of the second line regimen—any fluoroquinolone and at least one of the three injectable drugs shown above. XDR TB strains may also be resistant to additional drugs, ...
What is XDR TB?
XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, two of the most powerful first-line drugs, as well as key drugs of the second line regimen—any fluoroquinolone and at least one of the three injectable drugs shown above.
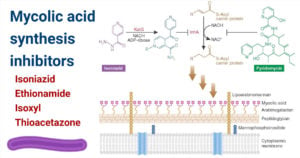
What drugs target DNA?
Rifamycins, Oxazolidinones and Macrolides act on DNA. Tuberculosis drugs target various aspects of Mycobacterium tuberculosis biology, including inhibition of cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, or nucleic acid synthesis. For some drugs, the mechanisms of action have not been fully identified.
Overview
Mechanism of action
Streptomycin has two mechanism of action depending on what conformation (isomer) is at in the system in which it will work. Isomer A functions as a protein synthesis inhibitor. It binds to the small 16S rRNA of the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome irreversibly, interfering with the binding of formyl-methionyl-tRNA to the 30S subunit. This leads to codon misreading, eventual inhibition of protein synthesis and ultimately death of microbial cells through mechanisms that …
Uses
• Infective endocarditis: An infection of the endocardium caused by enterococcus; used when the organism is not sensitive to gentamicin
• Tuberculosis: Used in combination with other antibiotics. For active tuberculosis it is often given together with isoniazid, rifampicin, and pyrazinamide. It is not the first-line treatment, except in medically under-served populations where the cost of more expensive treatments is prohibitive. It may be useful in cases where resistance to other drugs is …
Side effects
The most concerning side effects, as with other aminoglycosides, are kidney toxicity and ear toxicity. Transient or permanent deafness may result. The vestibular portion of cranial nerve VIII (the vestibulocochlear nerve) can be affected, resulting in tinnitus, vertigo, ataxia, kidney toxicity, and can potentially interfere with diagnosis of kidney malfunction.
Common side effects include vertigo, vomiting, numbness of the face, fever, and rash. Fever and …
History
Streptomycin was first isolated on October 19, 1943, by Albert Schatz, a PhD student in the laboratory of Selman Abraham Waksman at Rutgers University in a research project funded by Merck and Co. Waksman and his laboratory staff discovered several antibiotics, including actinomycin, clavacin, streptothricin, streptomycin, grisein, neomycin, fradicin, candicidin, and candidin. Of these, streptomycin and neomycin found extensive application in the treatment of n…
See also
• Philip D'Arcy Hart – The British medical researcher and pioneer in tuberculosis treatment in the early twentieth century.
Further reading
• Kingston W (July 2004). "Streptomycin, Schatz v. Waksman, and the balance of credit for discovery". Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences. 59 (3): 441–462. doi:10.1093/jhmas/jrh091. PMID 15270337. S2CID 27465970.
• Mistiaen V (November 2, 2002). "Time, and the great healer". The Guardian.. The history behind the discovery of streptomycin.
External links
• "Streptomycin". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.