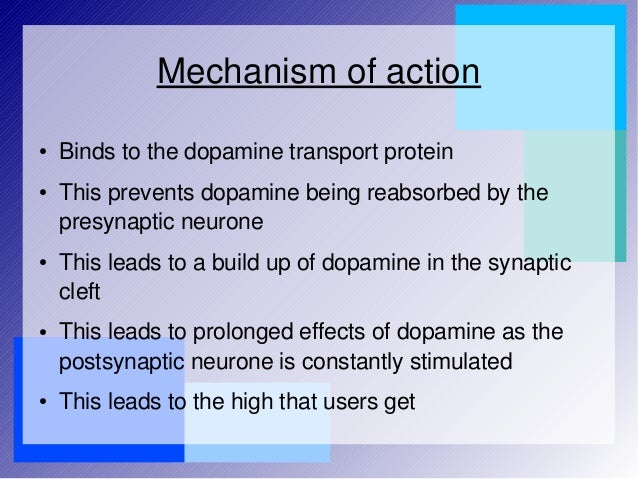
Its mechanism of action is by increasing the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma -aminobutyric acid (GABA). Diazepam was patented in 1959 by Hoffmann-La Roche. It has been one of the most frequently prescribed medications in the world since its launch in 1963.
Full Answer
What is the mechanism of action of diazepam?
Diazepam, first marketed as Valium, is a medicine of the benzodiazepine family that acts as an anxiolytic. It is commonly used to treat a range of conditions, including anxiety, seizures, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome, muscle spasms, insomnia, and restless legs syndrome. It may also be used to cause memory loss during certain medical …
What is the long-term use of diazepam for epilepsy?
Nov 10, 2021 · A comparison of cyamemazine to bromazepam after 3 month treatment with benzodiazepines. Cyamemazine was found to be as effective as bromazepam in treating withdrawal symptoms: Standardized counselling protocols: Comparison of a slow taper to counselling on the dangers of benzodiazepines and alternatives to treatment.
What is Valium (diazepam)?
GABA is the most common neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, found in high concentrations in the cortex and limbic system. GABA is inhibitory in nature and thus reduces the excitability of neurons. GABA produces a calming effect on the brain. 2 The 3 GABA receptors are designated A, B, and C.
What is the chemical name and structural formula of diazepam?
Abstract. Insomnia is a condition with sleep problems and many people suffered from it. Chronic insomnia can last for long time and it will severely affect people's health and the quality of life. In conventional medicine, the most commonly used the medicine is benzodiazepine. It is effective but also has significant side effects.

What is the mechanism of action of diazepam in the treatment of insomnia?
What is the mechanism of action of diazepam in the treatment of insomnia? Benzodiazepine agonists and other agonist ligands at the benzodiazepine site achieve their therapeutic effects by enhancing the actions of the inhibitory Âneurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at its receptor.Oct 15, 2015
How does diazepam work for sleep?
GABA is a neurotransmitter that acts as a natural 'nerve-calming' agent. It helps keep the nerve activity in the brain in balance, and is involved in reducing anxiety, relaxing muscles and inducing sleepiness. By increasing the activity of GABA in the brain, diazepam increases these calming effects.Jul 7, 2020
Why diazepam is used in insomnia?
Valium is used off-label to treat insomnia; it is approved to treat anxiety, seizures, muscle spasms, and symptoms of alcohol withdrawal. Ambien and Valium belong to different drug classes. Ambien is a sedative/hypnotic and Valium is a benzodiazepine.
What is the mechanism of action for diazepam?
Diazepam is a benzodiazepine that exerts anxiolytic, sedative, muscle- relaxant, anticonvulsant and amnestic effects. Most of these effects are thought to result from a facilitation of the action of gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system.
What is diazepam used to treat?
Diazepam is used to relieve anxiety and to control agitation caused by alcohol withdrawal.May 15, 2021
Can diazepam cause insomnia?
Symptoms usually only occur after extended use and can include return of insomnia, anxiety, sweating, headache, palpitations and panic attacks. Reducing the dose of diazepam slowly may make these symptoms less severe.
What type of medication is used for short term management of insomnia?
Benzodiazepines. Benzodiazepines are one of the most widely used drug classes for the short-term treatment of insomnia. These agents bind to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the central nervous system (CNS), causing inhibition of neuronal excitation.Jan 20, 2011
How does medication affect sleep?
Prescription Medicines Beta-blockers treat high blood pressure, heart rhythm problems, and chest pain. They also appear to lower your body's level of melatonin, a hormone that helps control your sleep cycle. That can make you wake up at night and give you nightmares.Jul 20, 2021
How does diazepam make you feel?
Diazepam acts on nerve cells to calm abnormal electrical activity within the brain. Diazepam calms and sedates and may be used in the treatment of anxiety, as an anticonvulsant, as a muscle relaxant, or for its sedative effects.Jan 29, 2021
What receptors does diazepam act?
GABAA receptorThat the GABAA receptor is the main target for the central actions of benzodiazepines has been known for several decades (Costa et al., 1975; Haefely et al., 1975). The mechanism by which benzodiazepines, such as diazepam (DZP), enhance GABA receptor function has been termed allosteric.
What are the metabolites of diazepam?
Diazepam is metabolized to nordiazepam, oxazepam, and temazepam; all may be detected after diazepam use.
What are the indications of diazepam?
Diazepam is a benzodiazepine medication that is FDA approved for the management of anxiety disorders, short-term relief of anxiety symptoms, spasticity associated with upper motor neuron disorders, adjunct therapy for muscle spasms, preoperative anxiety relief, management of certain refractory epilepsy patients, and ...Sep 14, 2021
How long does it take for diazepam to absorb?
Lorazepam is well absorbed after sublingual administration, reaching peak levels in 60 minutes.2.
How long does diazepam last?
These metabolites and their actions account for diazepam's long elimination half-life, which increases approximately 1 hour for each year of age over 40 (eg, the diazepam elimination half-life in a 75-year-old would be approximately 75 hours).
What receptors are involved in calming the brain?
GABA produces a calming effect on the brain.2The 3 GABA receptors are designated A, B, and C. This article focuses primarily on the GABA-A receptor, with which BZDs interact. The GABA-A receptor complex is composed of 5 glycoprotein subunits, each with multiple isoforms (Figure 1).
What is the clinically appropriate use of BZDs?
Clinically appropriate use of BZDs requires prudence and the understanding of pharmacology.
What is the pharmacokinetics of benzodiazepine?
Benzodiazepine Pharmacokinetics. The pharmacokinetic properties of a drug determine its onset of action and the duration of its effect. Specifically, pharmacokinetics describes the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of a drug (ie, what the body does to the drug).
How many subunits are in the Gaba receptor?
GABA-A receptors contain 2 α subunits, 2 β subunits, and 1 γ subunit. Each receptor complex has 2 GABA-binding sites but only 1 BZD-binding site. The benzodiazepine binding site is in a specific pocket at the pairing (intersection) of the α and γ subunits.
What are the characteristics of a drug?
Characteristics of the drug—including lipid solubility, binding to plasma proteins, and molecular size—influence the volume of distribution. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacologic drug effects are described in terms of dose-response curves that depict the relationship between the dose and the resulting pharmacologic effect.
What is the most commonly used hypnotic herb in Chinese medicine?
Based on the clinical data, several herbs were identified as most frequently used sedative and hypnotic herbs in Chinese herbal medicine including Suanzaoren (Ziziphus spinose ), Fuling (Poria cocos ), and Gancao ( Glycyrrhiza uralensis ).
What is the best medicine for insomnia?
In conventional medicine, the most commonly used the medicine is benzodiazepine. It is effective but also has significant side effects. Patients try to use some kinds of alternative medicines. Chinese medicinal herbs and formulas have been ...
What is the mechanism of action of sedatives?
The major pharmacological action mechanisms shared by most of the sedative herbs are to act through the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) or via stimulation of GABAAAreceptor. Some herbs exert sedative activities via inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor.
Why is it important to review published research papers?
It is very important and very helpful to review the published research papers to gather the available information for a critical analysis. This chapter evaluated the data from both of clinical studies and pharmacological researches on the therapeutic formulas and on some key herbs used in the treatment of insomnia.
Does leptin help with insomnia?
Another mechanism shown by some herbs is to upregulate the expression of orexin-A, leptin, orexin receptor-1, and leptin receptor in the brain, reducing insomnia-induced negative consequences, and thus indirectly help improvement of insomnia.
Is Chinese medicine used in Western countries?
In recent decades, Chinese herbal medicine has been widely used in the Western countries. Many clinical studies including randomized controlled clinical trials and research on pharmacological action mechanisms of the herbs for treatment of insomnia have been conducted.
Is benzodiazepine effective for insomnia?
Chronic insomnia can last for long time and it will severely affect people's health and the quality of life. In conventional medicine, the most commonly used the medicine is benzodiazepine. It is effective but also has sig ….
How long does it take for a benzodiazepine to withdraw?
Protracted withdrawal syndrome associated with benzodiazepines is characterized by anxiety, cognitive impairment, depression, insomnia, formication, motor symptoms (e.g., weakness, tremor, muscle twitches), paresthesia, and tinnitus that persists beyond 4 to 6 weeks after initial benzodiazepine withdrawal. Protracted withdrawal symptoms may last weeks to more than 12 months. As a result, there may be difficulty in differentiating withdrawal symptoms from potential re-emergence or continuation of symptoms for which the benzodiazepine was being used.
How to reduce withdrawal reactions from Valium?
To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue Valium or reduce the dosage (a patient-specific plan should be used to taper the dose) (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Discontinuation or Dosage Reduction of Valium ).
How long does it take for diazepam to absorb?
After oral administration >90% of diazepam is absorbed and the average time to achieve peak plasma concentrations is 1 – 1.5 hours with a range of 0.25 to 2.5 hours. Absorption is delayed and decreased when administered with a moderate fat meal. In the presence of food mean lag times are approximately 45 minutes as compared with 15 minutes when fasting. There is also an increase in the average time to achieve peak concentrations to about 2.5 hours in the presence of food as compared with 1.25 hours when fasting. This results in an average decrease in C max of 20% in addition to a 27% decrease in AUC (range 15% to 50%) when administered with food.
What are the risks of using benzodiazepines with opioids?
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including Valium, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
What is Valium used for?
Valium is indicated for the management of anxiety disorders or for the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety. Anxiety or tension associated with the stress of everyday life usually does not require treatment with an anxiolytic.
How long does a full term infant's elimination half life last?
In full term infants, elimination half-lives around 30 hours have been reported, with a longer average half-life of 54 hours reported in premature infants of 28 - 34 weeks gestational age and 8 - 81 days post-partum. In both premature and full term infants the active metabolite desmethyldiazepam shows evidence of continued accumulation compared to children. Longer half-lives in infants may be due to incomplete maturation of metabolic pathways.
Is Valium a diazepam?
Valium is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to diazepam and, because of lack of sufficient clinical experience, in pediatric patients under 6 months of age. Valium is also contraindicated in patients with myasthenia gravis, severe respiratory insufficiency, severe hepatic insufficiency, and sleep apnea syndrome. It may be used in patients with open-angle glaucoma who are receiving appropriate therapy, but is contraindicated in acute narrow-angle glaucoma.
What are the symptoms of sertraline overdose?
The most common signs and symptoms associated with a non-fatal sertraline overdose are somnolence, vomiting, tachycardia, nausea, dizziness, agitation, and tremor. 21 No cases of fatal overdose with only sertraline have been reported.
What is the route of elimination for sertraline?
Route of elimination. Since sertraline is extensively metabolized, excretion of unchanged drug in the urine is a minor route of elimination, with 12-14% of unchanged sertraline excreted in the feces. 6, 7, 21.
What is the function of serum albumin?
Its main function is the regulation of the colloid...
What is the role of the serotonin reuptake inhibitor?
Responsible for the metabolism of many drugs and environmental chemicals that it oxidizes. It is involved in the metabolism of drugs such as antiarrhythmics, adrenoceptor antagonists, and tricyclic... Baumann P: Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationship of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Which cytochrome is responsible for the metabolism of a number of therapeutic agents?
3. Cytochrome P450 2C19. Responsible for the metabolism of a number of therapeutic agents such as the anticonvulsant drug S-mephenytoin, omeprazole, proguanil, certain barbiturates, diazepam, propranolol, citalopram and im...
Does sertraline increase bleeding?
The risk or severity of bleeding can be increased when Sertraline is combine d with Oxyphenbutazone. Sertraline may increase the central nervous system depressant (CNS depressant) activities of Oxyphencyclimine. Sertraline may increase the central nervous system depressant (CNS depressant) activities of Oxyphenonium.
Can Sertraline be combined with Olodaterol?
Oliceridine. The risk or severity of hypotension, sedation, death, somnolence, and respiratory depression can be increased when Sertraline is combined with Oliceridine. Olodaterol. The metabolism of Olodaterol can be decreased when combined with Sertraline.
What is the NCI Thesaurus?
NCI Thesaurus (NCIt) Loratadine and its metabolic derivative desloratadine are second generation antihistamines that are used for the treatment of allergic rhinitis, angioedema and chronic urticaria. Loratadine and desloratadine have been linked to rare, isolated instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury.
What is 7.2 liver tox?
Loratadine and desloratadine have been linked to rare, isolated instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury.
What is the clearance of loratadine?
The clearance of loratadine after single oral doses of 20 mg and 40 mg are 12 L/h/kg and 9 L/h/kg respectively. P-glycoprotein is involved in the clearance of many 2nd generation antihistamines, including loratadine, from the central nervous system. 1st generation antihistamines are not cleared by P-glycoprotein, which may help explain why they have a different central nervous system adverse effect profile compared to their 2nd generation counterparts. It appears that an antihistamine with higher affinity for p-glycoprotein will have a lower incidence of CNS adverse effects.
What is antihistamine?
A class of non-sedating drugs that bind to but do not activate histamine receptors (DRUG INVERSE AGONISM), thereby blocking the actions of histamine or histamine agonists. These antihistamines represent a heterogenous group of compounds with differing chemical structures, adverse effects, distribution, and metabolism. Compared to the early (first generation) antihistamines, these non-sedating antihistamines have greater receptor specificity, lower penetration of BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER, and are less likely to cause drowsiness or psychomotor impairment. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H1 Antagonists, Non-Sedating .)
Can loratadine be eliminated by hemodialysis?
If vomiting is unsuccessful, or contraindicated, gastric lavage should be performed with normal saline. Saline cathartics may also be of value for rapid dilution of bowel contents. Loratadine is not eliminated by hemodialysis. It is not known if loratadine is eliminated by peritoneal dialysis.
Does loratadine cause rash?
Second generation antihistamines such as loratadine have very few adverse effects; however, insomnia, headache, fatigue, drowsiness and rash have been reported. Symptoms of loratadine overdose include gastrointestinal side effects, agitation, drowsiness, tachycardia, and headache. It is advised to obtain an ECG in the event of loratadine overdose.
What is the second generation H1 antagonist?
Further glucuronidation of 3-hydroxydesloratadine facilitates excretion. The second generation H1 antagonists astemizole, loratadine,and terfenadine are rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and metabolized in the liver to active metabolites by the hepatic microsomal p450 system.
How long does loratadine stay in your system?
Over a 10 day period, 40% of loratadine is excreted in the urine, and 42% is eliminated in the faeces. 17. Half-life. The elimination half life is approximately 10 hours for loratadine and 20 hours for descarboethoxyloratadine. 6. Clearance.
What is a 2nd generation antihistamine?
Pharmacology. Loratadine is a 2nd generation antihistamine and is used to manage symptoms of allergic rhinitis, wheal formation, urticaria, and other allergic dermatologic conditions. 5 6 17. With our commercial data, access important information on dangerous risks, contraindications, and adverse effects.
What is DB00455 used for?
DB00455. Background. Loratadine is a second generation antihistamine used to manage symptoms of allergic rhinitis. 5 A lack of sedative and CNS adverse effects make loratadine, along with other second generation antihistamines, preferable over their 1st generation counterparts in many clinical situations. 7. Type.
Which anticholinergic drugs increase the excretion rate of loratadine?
Umeclidinium may increase the anticholinergic activities of Loratadine. Ursodeoxycholic acid. Ursodeoxycholic acid may decrease the excretion rate of Loratadine which could result in a higher serum level. Vecuronium. Vecuronium may increase the anticholinergic activities of Loratadine. Velpatasvir.
Which acid form decreases the excretion rate of Indocyanine green acid form?
Indocyanine green acid form. Loratadine may decrease the excretion rate of Indocyanine green acid form which could result in a higher serum level. Indomethacin. Indomethacin may decrease the excretion rate of Loratadine which could result in a higher serum level.
What is the cytochrome P450?
Cytochrome P450 2C19. Responsible for the metabolism of a number of therapeutic agents such as the anticonvulsant drug S-mephenytoin, omeprazole, proguanil, certain barbiturates, diazepam, propranolol, citalopram and im...
Is loratadine a selective antihistamine?
Pharmacodynamics. Like other 2nd generation antihistamines, loratadine is selective for peripheral H1 receptors. 9 Loratadine does not penetrate effectively into the central nervous system and has poor affinity for CNS H1-receptors. 9 These qualities result in a lack of CNS depressant effects such as drowsiness, sedation, ...
What is the pregnancy exposure registry?
Pregnancy Exposure Registry#N#There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to AEDs, such as Oxcarbazepine tablets, during pregnancy. Encourage women who are taking Oxcarbazepine tablets during pregnancy to enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry by calling 1-888-233-2334 or visiting http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/.
How long does it take for Oxcarbazepine to be converted to monotherapy?
The concomitant AEDs should be completely withdrawn over 3 to 6 weeks, while the maximum dose of Oxcarbazepine tablets should be reached in about 2 to 4 weeks. Oxcarbazepine tablets may be increased as clinically indicated by a maximum increment of 600 mg/day at approximately weekly intervals to achieve the maximum recommended daily dose of 2400 mg/day. A daily dose of 1200 mg/day has been shown in one study to be effective in patients in whom monotherapy has been initiated with Oxcarbazepine tablets. Patients should be observed closely during this transition phase.
How many mg is oxycarbazepine?
Oxcarbazepine is an antiepileptic drug available as 150 mg, 300 mg, and 600 mg film-coated tablets for oral administration. Oxcarbazepine is 10,11-Dihydro-10-oxo-5 H- dibenz [b,ƒ]azepine-5-carboxamide, and its structural formula is:
What are the side effects of oxycarbazepine?
Adjunctive Therapy/Monotherapy in Adults Previously Treated with Other AEDs#N#The most common (≥10% more than placebo for adjunctive or low dose for monotherapy) adverse reactions with Oxcarbazepine tablets: dizziness, somnolence, diplopia, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, ataxia, abnormal vision, headache, nystagmus tremor, and abnormal gait.
Can you give Oxcarbazepine to other people?
Do not use Oxcar bazepine tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Oxcarbazepine tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
Does oxycarbazepine affect CYP3A4/5?
Oxcarbazepine can inhibit CYP2C19 and induce CYP3A4/5 with potentially important effects on plasma concentrations of other drugs. In addition, several AEDs that are cytochrome P450 inducers can decrease plasma concentrations of Oxcarbazepine and MHD. No autoinduction has been observed with Oxcarbazepine tablets.
Is oxycarbazepine monotherapy?
Oxcarbazepine tablets is also indicated as monotherapy for partial-onset seizures in patients aged 4 to 16 years. The safety and effectiveness for use as monotherapy for partial-onset seizures in pediatric patients below the age of 4 have not been established.