What are the different ways to cure leukemia?
Mar 04, 2022 · Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) are anticancer drugs that kill leukemia cells, stop the leukemia cells from dividing, or help the leukemia cells mature into white blood cells. These drugs are used in the treatment of a subtype of AML called acute promyelocytic leukemia .
What would be the most likely treatment for leukemia?
Jul 09, 2019 · Before discovering new avenues for treatment, Dr. Sauvageau and his team first faced the enormous task of identifying the genes associated with myeloid leukemia. Working together with researchers at the Quebec Leukemia Cell Bank, particularly its director Josée Hébert, also a professor in UdeM’s Faculty of Medicine, they were able to ...
How to cure leukemia naturally?
Apr 06, 2021 · Chemotherapy is the primary treatment for nearly all cases of acute lymphocytic leukemia and the main treatment for acute myeloid leukemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Chemotherapy drugs circulate throughout the body, so they are effective at targeting cancers like leukemia which proliferate in the bloodstream and lymphatic system.
Is there a known treatment and cure for leukemia?
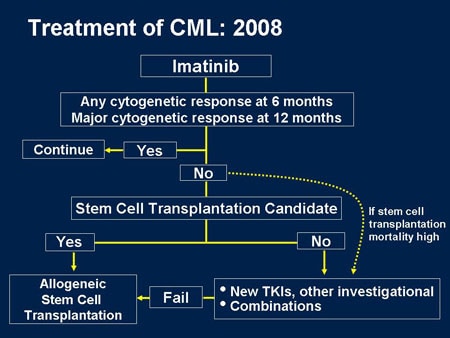
Treating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia by Phase Chronic phase. The standard treatment for chronic phase CML is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) like imatinib... Monitoring treatment results. Monitoring the patient to see how they respond to treatment …
What is the latest treatment for leukemia?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved two new treatments for some adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML): enasidenib (Idhifa®), a drug that targets aberrant forms of the IDH2 protein; and liposomal cytarabine-daunorubicin CPX-351 (Vyxeos™), a two-drug chemotherapy combination encapsulated ...Aug 28, 2017
What is the best medicine for leukemia?
Drugs Approved for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)Purixan (Mercaptopurine)Rubidomycin (Daunorubicin Hydrochloride)Rylaze (Asparaginase Erwinia Chrysanthemi [Recombinant]-rywn)Sprycel (Dasatinib)Tisagenlecleucel.Trexall (Methotrexate Sodium)Vincristine Sulfate.Vincristine Sulfate Liposome.More items...•Dec 3, 2021
How successful is treatment for leukemia?
The cure rates and survival outcomes for patients with ALL have improved over the past few decades. Today, nearly 90 percent of adults diagnosed with ALL achieve a complete remission, which means that leukemia cells can no longer be seen in the bone marrow with a microscope.
What are the 4 main types of leukemia?
There are 4 main types of leukemia, based on whether they are acute or chronic, and myeloid or lymphocytic:Acute myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (AML)Chronic myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (CML)Acute lymphocytic (or lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL)Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)Jun 19, 2018
How many rounds of chemo is needed for leukemia?
You'll usually be given a combination of 2 or more chemotherapy drugs. Most people have 2 rounds of induction chemotherapy. The treatment will be carried out in hospital or in a specialist centre, as you'll need very close medical and nursing supervision. You may be able to go home between treatment rounds.
Which type of leukemia is most fatal?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most fatal type of leukemia. The five-year survival rate (how many people will be alive five years after diagnosis) for AML is 29.5%. Leukemia is a cancer that usually affects white blood cells, though it can start in other types of blood cells.Feb 23, 2022
What are the 5 stages of leukemia?
What are the stages of CLL?Stage 0. The blood has too many white blood cells called lymphocytes. This is called lymphocytosis. ... Stage I. The blood has too many lymphocytes. ... Stage II. The blood has too many lymphocytes. ... Stage III. The blood has too many lymphocytes. ... Stage IV. The blood has too many lymphocytes.
What is survival rate for leukemia?
Survival rates are pretty even across all ages, and the relative survival rate for all ages is 69.9% . This form of leukemia mostly affects adults over the age of 55. The relative 5-year survival rate for people of all ages with this form of leukemia is 87.2% .Aug 18, 2021
What is the treatment for acute myeloid leukemia?
Treatment of adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) during the remission phase depends on the subtype of AML and may include the following: Combination chemotherapy. High-dose chemotherapy, with or without radiation therapy, and stem cell transplant using the patient's stem cells . High-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplant using donor stem ...
What is the name of the drug that kills leukemia cells?
Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) are anticancer drugs that kill leukemia cells, stop the leukemia cells from dividing, or help the leukemia cells mature into white blood cells. These drugs are used in the treatment of a subtype of AML called acute promyelocytic leukemia.
What is the difference between AML and AML?
Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated.
What is the subtype of AML?
Most AML subtypes are based on how mature (developed) the cancer cells are at the time of diagnosis and how different they are from normal cells. Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is a subtype of AML that occurs when parts of two genes stick together.
What is the extent of cancer?
In adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the subtype of AML and whether the leukemia has spread outside the blood and bone marrow are used instead of the stage to plan treatment.
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the cancer. Total-body irradiation sends radiation toward the whole body. It is a type of external radiation that may be used to prepare the body for a stem cell transplant when the leukemia has recurred.
What is PDQ cancer?
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of adult acute myeloid leukemia. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
What is the first line of treatment for leukemia?
The first-line therapy for leukemia depends on the type of leukemia. For some leukemias, first-line therapy is chemotherapy, drugs designed to kill cancer cells. For others, the first-line medication will be targeted therapy drugs that home in on a unique genetic characteristic of the cancer cells. Other medications include antibodies to amplify the immune system’s response to cancer cells, differentiation agents to help cancerous cells in the bloodstream mature, and growth factors that provide an alternative to blood transfusions by stimulating red blood cell production in the bone marrow.
What is the best treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia?
Chemotherapy is the primary treatment for nearly all cases of acute lymphocytic leukemia and the main treatment for acute myeloid leukemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Chemotherapy drugs circulate throughout the body, so they are effective at targeting cancers like leukemia which proliferate in the bloodstream and lymphatic system.
What is the cause of leukemia?
Leukemia is a type of cancer that primarily affects the white blood cells. Formed from hematopoietic cells, or “blood-making cells”, white blood cells are mainly produced in the bone marrow. Changes to the genetic material in these cells can cause them to grow out of control.
How many people in the US have CLL?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (chronic lymphoblastic leukemia). Approximately 22,000 people in the U.S. will be diagnosed with CLL each year, mostly adults, and the average age at diagnosis is 70. The five-year survival rate is 85%. Chronic myeloid leukemia (chronic myelogenous leukemia).
What is the survival rate for children with leukemia?
The most common cancer in children, ALL represents about 15% of all leukemia cases. The five-year survival rate for children with ALL is 89% and the long-term survival rate is good.
How is leukemia determined?
Since leukemia does not produce tumors, leukemia stages are determined by the type of cancer cells that are found in the bloodstream and bone marrow. As leukemia progresses, the cancerous cells in the bone marrow crowd out the healthy bone marrow cells.
Does leukemia have symptoms?
Weakness. Unexplained weight loss. Chronic leukemia, however, frequently has no or only mild symptoms. A definitive diagnosis will be made by a hematologist, a specialist in blood diseases and disorders, or an oncologist, a specialist in cancer.
How to get immune system to fight leukemia?
One way to do this is by slowly lowering the doses or stopping the immune suppressing drugs they are taking. This is done very carefully in order to have an anti-leukemia effect without getting too much GVHD. Patients are watched closely during this time. Another approach that helps some patients is an infusion of lymphocytes taken from the person who donated the stem cells for the transplant (called donor lymphocyte infusion ). This can induce an immune reaction against the leukemia. Other drugs may also be helpful. Most experts agree that these patients should take part in a clinical trial.
What is the treatment for CML?
The standard treatment for chronic phase CML is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) like imatinib (Gleevec), nilotinib (Tasigna), dasatinib (Sprycel), or bosutinib (Bosulif). If the first drug stops working or it never really worked well at all, the dose may be increased or another TKI might be tried.
What happens when CML is in accelerated phase?
When CML is in accelerated phase, leukemia cells begin to build up in the body quickly, causing symptoms. The leukemia cells often acquire new gene mutations, which help them grow and might make treatments less effective.
Can TKI be used for CML?
But patients with accelerated phase CML are less likely to have a long-term response to any treatment. If the patient hasn’t had any treatment, a TKI will be used. Imatinib (often at higher doses than used for chronic phase CML) is an option for most people.
What happens in the blast phase of CML?
In the blast phase of CML, the leukemia cells become more abnormal. The disease acts like an acute leukemia, with blood counts getting higher and symptoms appearing or getting worse. For people with blast phase CML who haven't been treated before, high-dose imatinib may be helpful.
Can stem cells be used for leukemia?
An allogeneic stem cell transplant may be the best option for most patients who are young and healthy enough to have this treatment . Most doctors prefer that the leukemia be controlled, preferably in remission, before starting the transplant procedure. To achieve this, chemo will often be used.
Can CML be cured?
Because most patients with blast phase CML can't be cured, palliative treatment (intended to relieve symptoms rather than cure the disease) is important. For instance, radiation therapy can help shrink an enlarged spleen or reduce pain from areas of bone damaged by leukemia.
What are the different types of leukemia?
Types of leukemia. The major types of leukemia are: Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). This is the most common type of leukemia in young children. ALL can also occur in adults. Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). AML is a common type of leukemia. It occurs in children and adults.
How is leukemia classified?
How leukemia is classified. Doctors classify leukemia based on its speed of progression and the type of cells involved. The first type of classification is by how fast the leukemia progresses: Acute leukemia. In acute leukemia, the abnormal blood cells are immature blood cells (blasts).
What is the cancer of the lymphatic system?
Leukemia is cancer of the body's blood-forming tissues, including the bone marrow and the lymphatic system. Many types of leukemia exist. Some forms of leukemia are more common in children. Other forms of leukemia occur mostly in adults. Leukemia usually involves the white blood cells.
How does leukemia occur?
In general, leukemia is thought to occur when some blood cells acquire changes (mutations) in their genetic material or DNA. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. Normally, the DNA tells the cell to grow at a set rate and to die at a set time.
What are the factors that increase the risk of developing leukemia?
Factors that may increase your risk of developing some types of leukemia include: Previous cancer treatment. People who've had certain types of chemotherapy and radiation therapy for other cancers have an increased risk of developing certain types of leukemia. Genetic disorders.
Does smoking cause leukemia?
Smoking. Smoking cigarettes increases the risk of acute myelogenous leukemia. Family history of leukemia.
What are the causes of leukemia?
Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, some chemicals (such as benzene ), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome.
What are the symptoms of leukemia?
Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown.
What is the name of the cancer that causes blood cells to be abnormal?
Leukemia, also spelled leukaemia, is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called blasts or leukemia cells. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections.
How long do you live with leukemia?
The success of treatment depends on the type of leukemia and the age of the person. Outcomes have improved in the developed world. Five-year survival rate is 57% in the United States. In children under 15, the five-year survival rate is greater than 60% or even 90%, depending on the type of leukemia.
Who first described leukemia?
Leukemia was first described by anatomist and surgeon Alfred-Armand-Louis-Marie Velpeau in 1827. A more complete description was given by pathologist Rudolf Virchow in 1845. Around ten years after Virchow's findings, pathologist Franz Ernst Christian Neumann found that the bone marrow of a deceased person with leukemia was colored "dirty green-yellow" as opposed to the normal red. This finding allowed Neumann to conclude that a bone marrow problem was responsible for the abnormal blood of people with leukemia.
How long does it take for leukemia to develop?
Chronic leukemia is characterized by the excessive buildup of relatively mature, but still abnormal, white blood cells. Typically taking months or years to progress, the cells are produced at a much higher rate than normal, resulting in many abnormal white blood cells.
Can leukemia cause headaches?
If the leukemic cells invade the central nervous system, then neurological symptoms (notably headaches) can occur. Uncommon neurological symptoms like migraines, seizures, or coma can occur as a result of brain stem pressure. All symptoms associated with leukemia can be attributed to other diseases.
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- A diagnosis of leukemia may be devastating — especially for the family of a newly diagnosed child. With time you'll find ways to cope with the distress and uncertainty of cancer. Until then, you may find it helps to: 1. Learn enough about leukemia to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor about your leukemia, including your treatment options and, if you like, your prognosis. As …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Start by seeing your family doctor if you have signs or symptoms that worry you. If your doctor suspects you have leukemia, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in diseases of the blood and bone marrow (hematologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of information to discuss, it's a good idea to be prepared. Here's some information to …