
Maintenance therapy in AML: The past, the present and the future Abstract Curative treatment in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) depends on successful induction therapy to achieve a complete remission (CR), and subsequent post-remission therapy to prevent relapse.
Full Answer
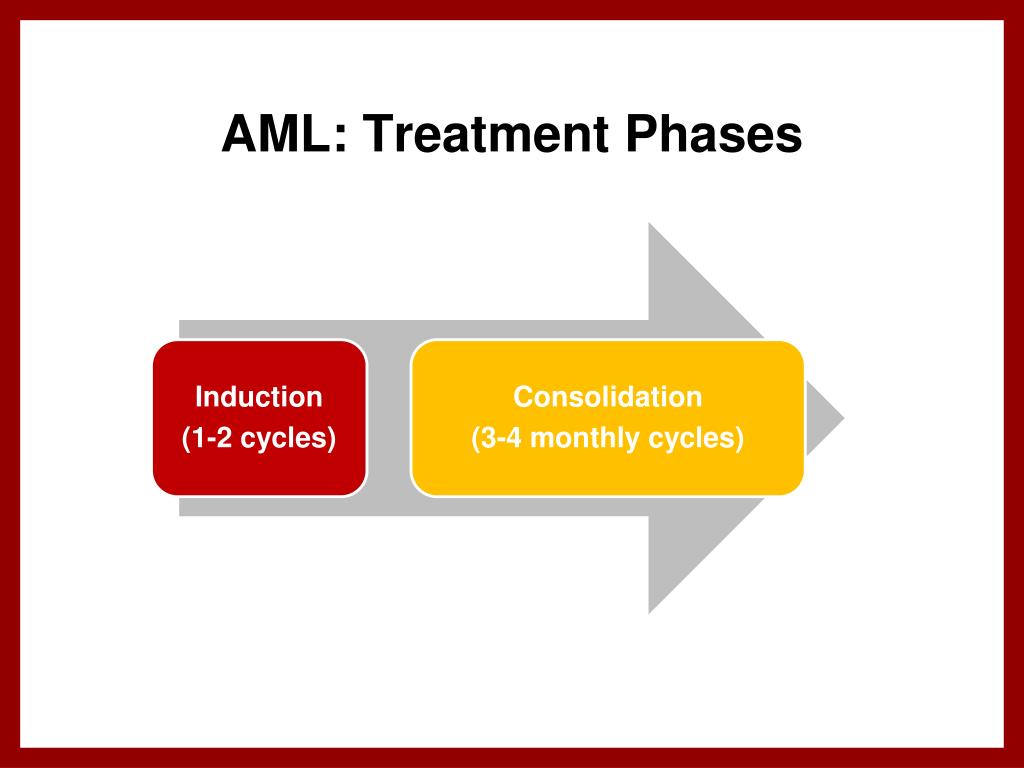
What are the phases of AML treatment?
There are two main phases of treating AML: induction and consolidation. Induction therapy is the first treatment given that tries to eliminate the bulk of the disease.
Can maintenance therapy prolong the remission interval in post-consolidation AML?
Effective maintenance therapy could play an important role in prolonging the remission interval in the post-consolidation setting, especially in high risk AML patients.
What is the maintenance phase of leukaemia treatment?
The maintenance phase of treatment takes up most of this time. The aim of the induction phase is to destroy the leukaemia cells. If there is no sign of leukaemia in your blood and bone marrow after treatment it is called a complete remission (CR). You start treatment quite quickly after being diagnosed. The main treatment is chemotherapy.
Is Interleukin-2 approved for remission maintenance in adults with AML?
Based on these data, in 2008, interleukin-2 was approved for remission maintenance in adults with AML in CR1 by the European Medicines Agency. Lenalidomide has been widely employed in clinical trials due to its immunomodulation-based antileukemic effect.
How many people die from AML?
What is AML in blood smear?
About this website

How long is maintenance therapy for AML?
Among 28 patients, with a median follow-up of 22.3 months, the median CR duration was 18.7 months and the 2-year OS was 63%, surpassing historical controls (78). The benefit was most pronounced in patients with non-secondary AML and those who had undetectable MRD (78).
What is maintenance therapy for leukemia?
Maintenance. If the leukemia remains in remission after induction and consolidation, maintenance therapy can begin. Most treatment plans use daily 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) and weekly methotrexate, given as pills, often along with vincristine, which is given into a vein (IV), and a steroid (prednisone or dexamethasone).
How long is a round of chemo for AML?
AML chemotherapy usually starts with 1 week of intense treatment. After this, the person may receive a 5-day treatment session every 4 weeks, with the cycle repeating three or four times. Doctors usually recommend a combination of chemotherapy medications rather than a single one.
What is maintenance therapy after chemotherapy?
Maintenance therapy is the ongoing treatment of cancer with medication after the cancer has responded to the first recommended treatment. Maintenance therapy, sometimes called continuous therapy, is used for the following reasons: To prevent the cancer's return.
How long is maintenance for ALL?
Maintenance treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is given to maintain remission. It is usually given over a long period of time and often lasts for 2–3 years.
How long is interim maintenance 2?
Interim Maintenance and Delayed Intensification Interim maintenance lasts about eight weeks and can require periodic hospitalization for chemotherapy. The next phase, delayed intensification, includes a shortened version of the induction and consolidation cycles to prevent resistant cells from appearing and growing.
How many phases is the usual treatment for AML?
The usual treatment of AML is divided into two phases: induction of remission and post-remission therapy.
Why is AML so hard to treat?
“Acute myeloid leukemia progresses rapidly with high intensity, and because it is a disease of the bone marrow, it interferes with the production of normal blood cells that are essential for various normal functions,” explains Jalaja Potluri, M.D., medical director, oncology development, AbbVie.
Can AML be cured completely?
Although AML is a serious disease, it is treatable and often curable with chemotherapy with or without a bone marrow/stem cell transplant (see the Types of Treatment section). It is important to remember that statistics on the survival rates for people with AML are an estimate.
How often do you get maintenance chemo?
Depending on the drug or combination of drugs, each treatment can last a few hours or a few days. You may have treatments every week or every 2, 3 or 4 weeks.
What are the side effects of maintenance chemo?
Other side effects of chemotherapy treatment might include: constipation. jaw pain. numbness and tingling in the fingers or toes.
Does maintenance chemo cause hair loss?
Most people think that chemotherapy drugs always cause hair loss. But some don't cause any hair loss at all or only slight thinning. Other types of chemotherapy may cause complete hair loss. It might include your eyelashes, eyebrows, underarm, leg and sometimes pubic hair.
Stopping maintenance chemotherapy | Cancer Chat
Hi. Update on my decision. I spoke with all my family at length about this. Everyone of them agreed that I should stop the chemotherapy. Although they obviously don't want me to die anytime soon, they don't want to see me constantly suffering from the side effects of the chemo.
Maintenance therapy in AML: The past, the present and the future
Curative treatment in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) depends on successful induction therapy to achieve a complete remission (CR), and subsequent post-remission therapy to prevent relapse. High relapse rates after consolidation therapy and after allogeneic stem cell transplant contribute to suboptimal …
If Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Doesn’t Respond or Comes Back After ...
Whether you or someone you love has cancer, knowing what to expect can help you cope. Here you'll find in-depth information on specific cancer types – including risk factors, early detection, diagnosis, and treatment options.
List of 25 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Medications Compared - Drugs.com
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is cancer that starts inside bone marrow, the soft tissue inside bones that helps form blood cells. The cancer grows from cells that would normally turn into white blood cells.
Oral Azacitidine (CC-486) Maintenance for AML in First Remission
Extended Description. The title of the Visual Abstract is Oral Azacitidine (CC-486) Maintenance for AML in First Remission. In a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial, 472 patients who were ...
What is APL post remission?
Consolidation (post-remission therapy) The acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) subtype of AML is treated differently. Treatment for AML usually needs to start as quickly as possible after it is diagnosed because it can progress very quickly. Sometimes another type of treatment needs to be started even before the chemo has had a chance to work.
How long does it take for leukemia to go down?
This is called leukostasis. Chemo can take a few days to lower the number of leukemia cells in the blood.
What happens when blood cells recover from leukemia?
When the blood cell counts recover, the doctor will again check cells in a bone marrow sample to see if the leukemia is in remission. Remission induction usually does not destroy all the leukemia cells, and a small number often remain.
How many IV lines are needed for pheresis?
Two intravenous (IV) lines are required – the blood is removed through one IV, goes through the machine, and then is returned to the patient through the other IV. Sometimes, a single large catheter is placed in a vein in the neck or under the collar bone for the pheresis, instead of using IV lines in both arms.
Can you take midostaurin with chemo?
For patients whose leukemia cells have an FLT3 gene mutation, the targeted therapy drug midostaurin (Rydapt) might be given along with chemo. This drug is taken twice daily as a pill. For patients whose leukemia cells have the CD33 protein, the targeted drug gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg) might be added to chemo.
Should stem cells be given for leukemia?
Still others feel that stem cell transplants should be given if the leukemia is likely to come back based on certain gene or chromosome changes. Research in this area continues to study which AML patients get the most benefit from stem cell transplant and which type of transplant is best in each situation.
Can older people tolerate intensive consolidation?
Older patients or those in poor health may not be able to tolerate intensive consolidation treatment. Often, giving them more intensive therapy raises the risk of serious side effects (including treatment-related death) without providing much more of a benefit. These patients may be treated with:
How long does it take to cure lymphoblastic leukaemia?
Treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is divided into 3 phases. These are: Treatment for ALL usually takes between 2 and 3 years. The maintenance phase of treatment takes up most of this time.
What is the aim of consolidation therapy?
Your doctor might also call it the intensification phase. The aim is to get rid of any leukaemia cells that might still be there and to stop it from coming back. This phase of treatment might take a few months.
What is the aim of the induction phase?
Aim of the induction phase. The aim of the induction phase is to destroy the leukaemia cells. If there is no sign of leukaemia in your blood and bone marrow after treatment it is called a complete remission (CR).
How long do you have to stay in hospital after chemo?
Chemotherapy kills off many of your healthy bone marrow cells as well as the leukaemia cells. So you need to stay in hospital for about a month until you have recovered. There are different combinations of drugs your doctors might use.
What happens if you are not in remission?
You move on to the next phase of treatment if you are in remission (consolidation). If you’re not in remission you usually have more chemotherapy.
Where do leukaemia cells travel?
Leukaemia cells can sometimes travel to the brain and spinal cord (the central nervous system, CNS). So as part of your induction treatment you have chemotherapy and possibly a steroid into the fluid that circulates around the spinal cord and brain. This is called intrathecal chemotherapy.
How many people die from AML?
According to the National Cancer Institute, AML strikes about 20,000 people per year in the United States, and kills more than 11,000. It mainly affects middle-aged and older adults.
What is AML in blood smear?
Blood smear under microscopy showing adult acute myeloid leukemia. Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the most common form of acute leukemia in adults, that has gone into remission following initial chemotherapy remain in remission longer and have improved overall survival when they are given a pill form of the cancer drug azacitidine as ...
Treating Leukostasis
- Some people with AML have very high numbers of leukemia cells in their blood when they are first diagnosed, which can cause problems with normal blood circulation. This is called leukostasis. Chemo can take a few days to lower the number of leukemia cells in the blood. In the meantime, leukapheresis (sometimes just called pheresis) might be used before chemo. In leukapheresis, t…
Induction
- This first phase of treatment is aimed at quickly getting rid of as many leukemia cells as possible. How intense the treatment is can depend on a person’s age and health. Doctors often give the most intensive chemo to people under the age of 60, but some older patients in good health may benefit from similar or slightly less intensive treatment. People who are much older or are in poo…
Consolidation
- Induction is considered successful if remission is achieved. Further treatment (called consolidation) is then given to try to destroy any remaining leukemia cells and help prevent a relapse.
Treating Frail Or Older Adults
- Treatment of AML in people under 60 is fairly standard. It involves cycles of intensive chemo, sometimes along with a stem cell transplant (as discussed above). Many patients older than 60 are healthy enough to be treated in the same way, although sometimes the chemo may be less intense. People who are much older or are in poor health may not be ab...