Medication
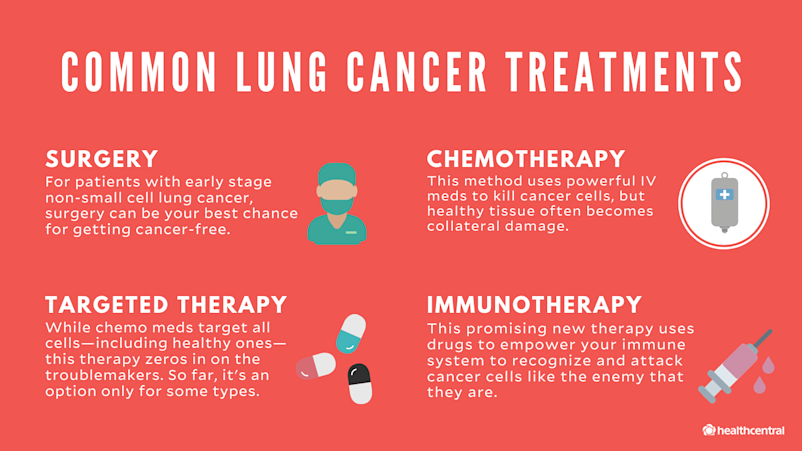
People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments. People with small cell lung cancer are usually treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Procedures
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved three new drugs to treat lung cancer and expanded the use of eight therapeutics in 2020. Of the newest drugs, Capmatinib (Tabrecta) and Pralsetinib (Gavreto) are used to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and Lurbinectedin (Zepzelca) is used to treat small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Therapy
Fortunately, an important development in treating advanced lung cancer was announced last year. In a large study, people taking a drug called Avastin, together with chemotherapy, lived an average of two months longer than those taking chemo alone -- a big improvement for people with a disease that can kill so quickly.
Nutrition
Immunotherapy is a major focus in lung cancer treatment research today. Clinical trials are ongoing to look at new combinations of immunotherapies with or without chemotherapy to treat lung cancer.
What are the treatments for non-small cell lung cancer?
What's new in lung cancer treatment in 2020?
Is there a cure for advanced lung cancer?
What is immunotherapy for lung cancer?
What is the most successful treatment for lung cancer?
People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments. People with small cell lung cancer are usually treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Surgery. An operation where doctors cut out cancer tissue.
Is lung cancer curable now?
As with many other cancers, a key to surviving lung cancer is catching it in its earliest stages, when it is most treatable. For patients who have small, early-stage lung cancer, the cure rate can be as high as 80% to 90%.
What are the three new treatments for lung cancer?
Anti-angiogenesis therapy. The following anti-angiogenic drugs may be options for lung cancer: Bevacizumab (Avastin, Mvasi), in combination with chemotherapy and atezolizumab (Tecentriq), an immunotherapy drug (see below) Ramucirumab (Cyramza), in combination with the chemotherapy drug docetaxel.
Is there any hope for lung cancer patients?
Yes, you CAN survive a lung cancer diagnosis. Exciting new treatments for lung cancer are being discovered that may be used alone, before or after, or in combination with traditional chemotherapy, radiation and surgery.
Can you live 20 years after lung cancer?
Each year, tens of thousands of people are cured of NSCLC in the United States. And, some patients with advanced lung cancer can live many years after diagnosis. Sometimes patients who are told that their lung cancer is incurable live longer than many who are told that their lung cancer is curable.
What is the life expectancy with lung cancer?
Survival for all stages of lung cancer around 40 out of every 100 people (around 40%) survive their cancer for 1 year or more after diagnosis. around 15 out of every 100 people (around 15%) will survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
Is lung cancer always terminal?
Life expectancy Doctors classify lung cancer as a terminal illness. Approximately 16% of people with this type of cancer survive more than 5 years after their initial diagnosis. Various factors influence a person's life expectancy estimate following a diagnosis of lung cancer.
Can lung cancer Stage 4 Be Cured?
Stage 4 NSCLC is not curable but it is treatable. Nearly 40% of people who learn they have lung cancer are already at stage 4 of the disease when they're newly diagnosed. 1 Thankfully, in recent years, several advances in treatments have significantly improved survival.
What are the last stages of lung cancer before death?
What are the signs of end-of-life lung cancer?Persistent cough and shortness of breath.Fluid build-up around lungs.Severe fatigue.Loss of appetite and nausea.
Can you live a long life after lung cancer?
This means that about 1 out of 5 people with lung cancer will live for 5 years or longer after diagnosis. The outlook improves when a doctor diagnoses and treats lung cancer early. The NCI add that over half of people who receive a diagnosis of localized lung cancer will live for 5 years or longer following diagnosis.
Where does lung cancer usually spread to first?
Most lung cancers first spread to lymph nodes within the lung or around the major airways.
Can you live a normal life with lung cancer?
Being diagnosed with lung cancer is a terrifying place to be. However, with advances in treatment, more people are living longer and living well with lung cancer. If you have been diagnosed with lung cancer, you can make positive lifestyle choices and changes to improve your quality of life.
What is the FDA approved drug for lung cancer?
Topic Guide. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved three new drugs to treat lung cancer and expanded the use of eight therapeutics in 2020. Of the newest drugs, Capmatinib (Tabrecta) and Pralsetinib (Gavreto) are used to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and Lurbinectedin (Zepzelca) is used to treat small cell lung cancer ...
How old do you have to be to get a lung cancer screening?
The American Cancer Society recommends people who are 55 to 74 years old, are in fairly good health, are current smokers or who have quit in the past 15 years, and have smoked a certain number of cigarettes per day should receive regular lung cancer screenings.
What is PD-1 inhibitor?
PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab (Keytruda) was approved to treat patients with unresectable or metastatic tumor mutational burden-high (TMB-high) solid tumors, whose cancer has progressed following prior treatment and who have no satisfactory alternative treatment options.
What is the most common cause of lung cancer?
Smokers exposed to radon and asbestos are at higher risk. The most common causes of lung cancer in non-smokers include: Air pollution. Secondhand smoke.
How many new drugs will be approved for lung cancer in 2020?
In 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved three new drugs to treat lung cancer, along with expanded use of eight previously approved therapeutics. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for most cases (80% to 85%) of lung cancer. There are a number of different mutations that can accelerate the spread (metastases) ...
What is the FDA approved treatment for tumors?
The FDA also approved the expanded use of eight previously approved therapeutics: PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab (Keytruda) was approved to treat patients with unresectable or metastatic tumor mutational burden-high (TMB-high) solid tumors, whose cancer has progressed following prior treatment and who have no satisfactory alternative treatment ...
What is the treatment for lung cancer?
Lung cancer treatment options may include: Surgery. Removal of the tumor (stage 0) Removal of the lobe of the lung that has the tumor (lobectomy) or removal of a smaller piece of the lung (sleeve resection, segmentectomy, or wedge resection) (Stage 1)
What is tabrecta used for?
Tabrecta (capmatinib) is a medication used for the treatment of adults with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have a mutation that leads to mesenchymal-epithelial transition exon 14 (METex14) skipping as detected by an FDA-approved test.
What is a zepzelca?
Zepzelca (lurbinectedin) is a type of chemotherapy indicated to treat adult patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) that is metastatic, i.e. cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, and that does not respond (any more) to treatment with chemotherapy that contains platinum. Zepzelca (lurbinectedin) was approved by The Food ...
What is Tepmetko used for?
Tepmetko (tepotinib) is a MET inhibitor indicated for the treatment of advanced or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in adults with MET exon 14 (METex14) skipping mutations.
What is the treatment for nonsmall cell lung cancer?
People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments. People with small cell lung cancer are usually treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Surgery.
What are the two types of lung cancer?
Lung cancers usually are grouped into two main types:small cell and non-small cell. These types of lung cancer grow differently and are treated differently. Non-small cell lung cancer is more common than small cell lung cancer. Cancer from other organs also may spread to the lungs. When cancer cells spread from one organ to another, ...
What is the term for an operation where doctors cut out cancer tissue?
An operation where doctors cut out cancer tissue. Chemotherapy. Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer. Radiation therapy. Using high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to kill the cancer. Targeted therapy. Using drugs to block the growth and spread of cancer cells.
What is the FDA's priority review for Retevmo?
The FDA also granted Retevmo Priority Review and Breakthrough Therapy designation, to promote development of drugs that fulfill an unmet medical need Additionally, Retevmo received Orphan Drug designation, which is intended to encourage the development of drugs for the treatment of rare diseases. Tabrecta (capmatinib)6.
How is lung cancer treated?
People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments. People with small cell lung cancer are usually treated with radiation therapy ...
What is targeted therapy?
Targeted therapy. Using drugs to block the growth and spread of cancer cells. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins. Doctors from different specialties often work together to treat lung cancer. Pulmonologists are doctors who are experts in diseases of the lungs.
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary and alternative medicine are medicines and health practices that are not standard cancer treatments. Complementary medicine is used in addition to standard treatments. Examples include acupuncture, dietary supplements, massage therapy, hypnosis, and meditation.
What are the two types of lung cancer?
The two main types of lung cancer are small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. These categories refer to what the cancer cells look like under a microscope. Non-small cell lung cancer is more common than small cell lung cancer. If you have lung cancer (especially non-small cell lung cancer), your doctor may run tests.
What is the process of finding out how far a lung cancer has spread?
Staging. If lung cancer is diagnosed, other tests are done to find out how far it has spread through the lungs, lymph nodes, and the rest of the body. This process is called staging . The type and stage of lung cancer tells doctors what kind of treatment you need.
How to shrink cancer?
Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins, or sometimes both. Radiation therapy. Using high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to kill the cancer. Targeted therapy. Using drugs to block the growth and spread of cancer cells.
What is alternative medicine?
Alternative medicine is used instead of standard treatments. Examples include special diets, megadose vitamins, herbal preparations, special teas, and magnet therapy. Many kinds of complementary and alternative medicine have not been tested scientifically and may not be safe.
What is it called when the cells in your lung grow?
When cells of the lung start growing rapidly in an uncontrolled manner, the condition is called lung cancer. Lung cancer can affect any part of the lung. Small-cell lung cancer is one of two major types of lung cancer, the other being non-small-cell lung cancer.
How can I prevent lung cancer?
You can also reduce your risk by avoiding exposure to radon, limiting or avoiding exposure to cancer-causing agents, and eating a healthy, balanced diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables.
What is the difference between lung cancer and asthma?
In lung cancer, lung cells exhibit abnormal and uncontrolled growth starting the lungs, while asthma is caused by inflammation and/or mucus that decreases or blocks the breathing passages (bronchioles) of the lungs . Asthma is usually an acute problem triggered by many different substances mainly affecting the lungs , while lung cancer is considered, once detected, an ongoing disease that can metastasize (spread) to other organs like the liver, bones or the brain.
How many stages of non-small cell lung cancer are there?
There are five stages with multiple substages of non-small cell lung cancer, the most common lung cancer type. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) occurs when lung cells become abnormal and keep dividing and forming more cells without order or control.
What are the symptoms of lung cancer?
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths. Symptoms and signs include coughing up blood, chest pain, wheezing, and chronic respiratory infections. Treatment depends upon the tumor stage, type of lung cancer, and the patient's overall physical condition.
Where do pancoast tumors spread?
Pancoast tumors are lung cancers that form at the top of the lung. They tend to spread to the chest wall rather than the lung tissue. These tumors usually respond well to treatment as long as they don't spread, or metastasize, to the lymph nodes or other systems.
Making Lung Cancer Treatment Decisions
Talking about lung cancer and its treatment options can be confusing. Make sure you understand your options and potential side effects before you make any decision.
Lung Cancer Treatment Options
Once your doctors have determined your lung cancer profile, they will present you with one or a combination of the following options:
Take Action
Voice your concerns to your doctor. He or she can discuss lung cancer treatment options with you and answer your questions. Download our Lung Cancer Treatment Organizer to keep track of your treatment plan.
What happens if cancer grows back?
If the cancer continues to grow during treatment or comes back, any further treatment will depend on the location and extent of the cancer, what treatments you’ve had, and on your health and desire for further treatment. It’s always important to understand the goal of any further treatment before it starts. You should understand if it’s to try to cure the cancer, to slow its growth, or to help relieve symptoms. It is also important to understand the benefits and risks.
What is the best treatment for cancer in the lungs?
If cancer growth in the lungs is causing symptoms such as shortness of breath or bleeding, radiation therapy or other types of treatment, such as laser surgery, can sometimes be helpful. Radiation therapy can also be used to relieve symptoms if the cancer has spread to the bones, brain, or spinal cord.
What is the first treatment for SCLC?
If you have extensive SCLC and are in fairly good health, chemotherapy (chemo), possibly along with an immunotherapy drug, is typically the first treatment. This can often shrink the cancer, treat your symptoms, and help you live longer.
What is the treatment for chest cancer?
If you are in good health, the standard treatment is chemo plus radiation to the chest given at the same time (called concurrent chemoradiation ). The chemo drugs used are usually etoposide plus either cisplatin or carboplatin.
What to do if you have only one small tumor in your lung?
If you only have one small tumor in your lung and there is no evidence of cancer in lymph nodes or elsewhere, your doctors might recommend surgery to remove the tumor and the nearby lymph nodes.
What to do if you smoke and have lung cancer?
If you smoke, one of the most important things you can do to be ready for treatment is to quit. Studies have shown that patients who stop smoking after a diagnosis of lung cancer tend to have better outcomes than those who don’t.
Why is it important to understand the goal of any further treatment before it starts?
You should understand if it’s to try to cure the cancer, to slow its growth, or to help relieve symptoms. It is also important to understand the benefits and risks.
Targeted Treatment for Lung Cancer
Nearly 60% of all people with lung cancer die within a year of their diagnosis and an estimated 164,000 Americans -- most of them smokers or ex-smokers -- are diagnosed each year.
Antibody Therapy for Lung Cancer
Your immune system does not see cancer cells as a threat, destroying them like it does viruses, bacteria, and foreign tissue. But the immune system can be trained to attack tumors, and researchers have taken the first steps toward creating lung cancer drugs that work this way.
What is the role of ROS1 in lung cancer?
A small percentage of non-small cell lung cancer patients have altered forms of the ROS1 gene. Crizotinib (Xalkori) and entrectinib (Rozlytrek) are approved as treatments for patients with these alterations.
What is an ALK inhibitor?
ALK inhibitors target the cancer-causing alteration in the ALK gene. These drugs continue to be refined for the five percent of lung cancer patients who have an ALK gene alteration. In addition to approved treatments such as ceritinib (Zykadia) and crizotinib (Xalkori), there have been recent approvals of:
What is Lorlatinib ALK inhibitor?
Lorlatinib (Lorbrena) These recently approved ALK inhibitors are improvements from previous ones in their enhanced ability to cross the blood–brain barrier. This progress is critical because, in non-small cell lung cancer patients with ALK alterations, disease progression tends to occur in the brain.
What is NCI trial?
NCI funds and oversees both early- and late-phase clinical trials to develop new treatments and improve patient care. Trials are available for both non-small cell lung cancer prevention, screening, and treatment, and small cell lung cancer prevention, screening, and treatment.
What is NCI funded research?
NCI-funded researchers are working to advance our understanding of how to prevent, detect, and treat lung cancer. There has been a great deal of progress made, for scientists are identifying many different genetic alterations that can drive lung cancer growth. This page highlights some of the latest research in lung cancer including clinical ...
What is the BRAF gene?
The BRAF gene makes the protein, B-Raf, which is involved in sending signals in cells and cell growth. This gene may be altered in some patients with non-small cell lung cancer, which can increase the growth and spread of cancer cells.
What are the treatments for lung cancer?
Treatment options for lung cancer are surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, targeted therapy , immunotherapy, and combinations of these approaches. While researchers continue to look for new treatment options for all stages of lung cancer, scientists currently have some promising results for advanced-stage disease, which are listed below.

Types of Lung Cancer
Staging
Types of Treatment
Clinical Trials
Specialist to consult
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- The two main types of lung cancer are small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. These categories refer to what the cancer cells look like under a microscope. Non-small cell lung cancer is more common than small cell lung cancer. If you have lung cancer (especially non-small cell lung cancer), your doctor may run testsexternal icon to find out if you have a change in your …
Which Treatment Is Right For Me?
- If lung cancer is diagnosed, other tests are done to find out how far it has spread through the lungs, lymph nodes, and the rest of the body. This process is called staging. The type and stage of lung cancer tells doctors what kind of treatment you need. For more information, visit Stages of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancerexternal icon and Stages of Small Cell Lung Cancer.external icon