Radiation is the most preferred treatment because it has the greatest chance of curing the disease. It involves projecting high-energy beams on the cancerous lymph nodes. Stages II to IV follicular lymphoma Monoclonal antibodies: These drugs, given intravenously (IV), act like the body's disease-fighting cells (antibodies).
What is the treatment for limited low grade lymphoma?
Treatment for limited low grade NHL. The most common type of low grade NHL is follicular lymphoma. For limited disease, you are most likely to have radiotherapy to the affected lymph nodes. This can help control the lymphoma for a long time, and may cure it.
What are the treatment options for Stage 4 lymphoma?
The treatment for stage 4 lymphoma will be dependent on the type of lymphoma that a person has, their medical history, and which organs it affects. Treatment for stage 4 Hodgkin lymphoma typically involves multiple cycles of chemotherapy drugs.
What are the treatment options for primary central nervous system lymphoma?
Primary central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma. Doctors limit the dose of radiation to try to lessen this problem. If CNS lymphoma keeps growing or comes back after treatment, further options may include chemo (using different drugs), radiation therapy, or a stem cell transplant if the person is healthy enough.
Which medications are used in the treatment of malignant lymphoma?
Jones SE, Grozea PN, Miller TP, et al: Chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone alone or with levamisole or with levamisole plus BCG for malignant lymphoma: A Southwest Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 3 (10):1318-1324, 1985.

How do they treat low grade lymphoma?
Treatment for limited low grade NHL The most common type of low grade NHL is follicular lymphoma. For limited disease, you are most likely to have radiotherapy to the affected lymph nodes. This can help control the lymphoma for a long time, and may cure it.
What is stage IV lymphoma?
Stage 4 is the most advanced stage of lymphoma. Lymphoma that has started in the lymph nodes and spread to at least one body organ outside the lymphatic system (for example, the lungs, liver, bone marrow or solid bones) is advanced lymphoma.
What is the prognosis for low grade lymphoma?
Purpose: Despite modern therapy, patients with low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (NHLs) have a median survival of only 7 to 10 years.
Can you recover from low grade lymphoma?
Younger people tend to do better than older people. For those younger than 60: around 60 out of 100 (around 60%) will survive their lymphoma for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
What type of lymphoma is not curable?
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma or Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. It's found mainly in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen. This type of lymphoma can't be cured.
Which type of lymphoma is worse?
The type of chemotherapy you receive will depend on how aggressive the cancer is. “T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas tend to be more aggressive,” Strati says. “Whereas B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas may be more slow-growing.”
Can you live 20 years or low-grade lymphoma?
People with low-grade NHL often live with their lymphoma for many years and can have a normal life expectancy.
Should low-grade lymphoma be treated?
Low-grade lymphomas generally respond well to treatment but they are hard to get rid of completely. They are usually treated with the aim of controlling the lymphoma rather than curing it. Low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphomas can often be controlled for many years.
Which is worse non Hodgkin's lymphoma or Hodgkin's lymphoma?
The prognosis of Hodgkin's lymphoma is also better than that of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma since non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is often diagnosed at a more advanced stage. Both forms of blood cancer are treatable when caught early, however.
Is low grade lymphoma hereditary?
Some people inherit DNA mutations from a parent that increase their risk for some types of cancer. Having a family history of lymphoma (Hodgkin Lymphoma, Non Hodgkin Lymphoma, CLL) does seem to increase your risk of lymphoma. Gene changes related to NHL are usually acquired during life, rather than being inherited.
Can you live a normal life after lymphoma?
It takes time but most people adjust well to life after a diagnosis of lymphoma and find a 'new normal'. This might involve making some changes to your everyday life.
Can you treat lymphoma without chemo?
Other options for DLBCL that is no longer responding to chemo might include some type of immunotherapy (such as CAR T-cell therapy or a monoclonal antibody) or a targeted therapy drug such as selinexor (Xpovio). Clinical trials of new treatments may be another good option for some people.
How long do you live with stage 4 lymphoma?
the type of lymphoma. the organs affected. your age and overall health. According to the ACS, the five-year survival rate for stage 4 Hodgkin’s lymphoma is about 65 percent. The five-year survival rate for people with stage 4 NHL varies depending on the subtype of NHL and other factors.
How long does it take to treat follicular lymphoma?
Treatment usually lasts about six months. To treat slow-growing follicular lymphoma, your doctor may start by prescribing rituximab and chemotherapy drugs.
What is the most aggressive type of lymphoma?
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common aggressive subtype. It affects about 30 percent of people with NHL in the United States. Indolent NHL is slow growing. It accounts for about 30 percent of NHL cases in the United States, reports the LLS. Follicular lymphoma is the most common type of indolent NHL.
What is the stage of lymphoma?
Hodgkin’s lymphoma. non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) If you’re diagnosed with lymphoma, your doctor will perform tests to learn what stage of the disease you have. Stage 4 is the most advanced stage of lymphoma. The characteristics of stage 4 lymphoma vary, depending on the subtype of lymphoma you have.
What stage is Hodgkin's lymphoma?
If you have Hodgkin’s lymphoma that’s spread through one or more organs outside of your lymphatic system, you’ll be diagnosed with stage 4 of the condition. For example, the cancer might have spread to your liver, lungs, or bone marrow.
Is stage 4 lymphoma curable?
A diagnosis of “stage 4 lymphoma” might be difficult to accept. But it’s important to know that some types of stage 4 lymphoma may be curable. Your outlook depends, in part, on the type of stage 4 lymphoma that you have.
What is the best treatment for follicular lymphoma?
For follicular lymphoma, you are most likely to have a combination of chemotherapy and a type of targeted immunotherapy called a monoclonal antibody (MAB). For example, R-CVP includes the following: 1 the chemotherapy drugs cyclophosphamide and vincristine 2 the steroid prednisolone 3 a MAB called rituximab
What type of immunotherapy is used for follicular lymphoma?
For follicular lymphoma, you are most likely to have a combination of chemotherapy and a type of targeted immunotherapy called a monoclonal antibody (MAB). For example, R-CVP includes the following: You might have chlorambucil chemotherapy tablets if you are not fit enough to have combination chemotherapy.
What is limited grade NHL?
Limited disease generally means you have stage 1 or stage 2 NHL. Find out about the stages of NHL. The most common type of low grade NHL is follicular lymphoma. For limited disease, you are most likely to have radiotherapy to the affected lymph nodes. This can help control the lymphoma for a long time, ...
How long does stage 2 lymphoma last?
Some people with stage 2 bulky lymphoma might have advanced disease, depending on their circumstances. The treatment for advanced low grade NHL aims to control it for as long as possible, rather than cure it. Treatment can often control the disease for several years.
How to cure low grade NHL?
This treatment includes intensive chemotherapy and radiotherapy followed by a stem cell or bone marrow transplant.
Can you have chemotherapy with rituximab?
You might have a combination of chemotherapy drugs and a drug like rituximab. Or you might have a drug on its own, such as the chemotherapy drug bendamustine. If it is difficult for you to make trips to the hospital, your doctor may choose a treatment that means you don't have to go so often.
Does lymphoma come back after a period of time?
Some types of low grade lymphoma tend to come back after a period of time. You need more treatment if this happens. The next lot of treatment you have is called second line treatment. Your doctor considers a number of things before deciding what is likely to be the best treatment for you.
What is stage 4 lymphoma?
Summary. Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system. Stage 4 lymphoma means that cancer has spread to an organ external to the lymphatic system. The survival rates vary widely depending on an individual’s risk factors and type of cancer.
How long can you live with stage 4 Hodgkin lymphoma?
It is important to note that everyone is different, and many people can live much longer than these estimates suggest. Overall, the 5-year survival rate for stage 4 Hodgkin lymphoma is 65 percent. The following risk factors affect a person’s prognosis and can make lymphoma more severe: presence of B symptoms.
What is the term for cancer that develops in the lymphatic system?
Lymphoma is the term that people use to describe cancer that develops in the lymphatic system. There are two main types of lymphoma : Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma .
What is the hallmark of Hodgkin lymphoma?
The hallmark of Hodgkin lymphoma is the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, which are mature B-type immune cells that have become cancerous. An estimated 95 percent of Hodgkin lymphomas are classic Hodgkin lymphoma, of which there are four subtypes: nodular sclerosis. mixed cellularity.
How many types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma are there?
There are more than 90 types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and it is possible to classify them in different ways. For example, doctors may classify non-Hodgkin lymphoma as either T-cell or B-cell, according to the type of lymphocyte that it affects.
How old do you have to be to get lymphoma?
Being male and more than 45 years of age may affect the prognosis for lymphoma. Survival rates provide people with a better understanding of how likely it is that treatment will be successful for their type and stage of cancer. Survival rates are estimates that vary depending on the stage of cancer.
Can stage 4 lymphoma be treated?
The continual improvement of available treatment options means that doctors may sometimes be able to cure stage 4 lymphoma, depending on the type and a person’s risk factors. If a cure is not possible, treatment aims to manage a person’s symptoms and maintain their quality of life.
What is the goal of lymphoma treatment?
The goal of treatment is to destroy as many cancer cells as possible and bring the disease into remission.
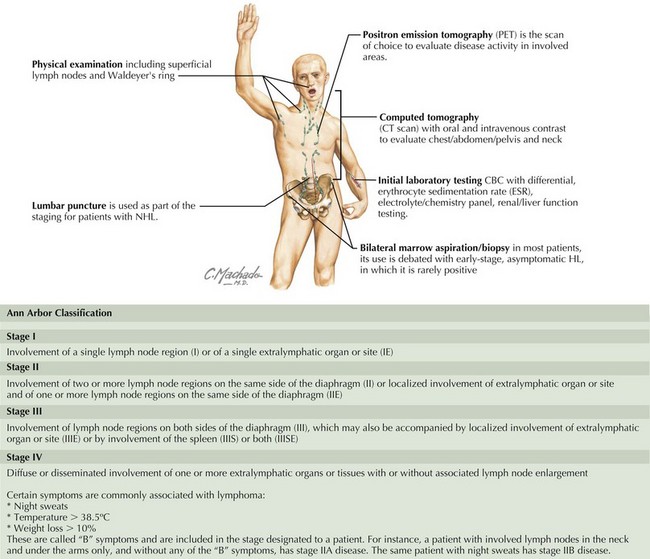
What tests can be done to determine if you have lymphoma?
Physical exam. Your doctor checks for swollen lymph nodes, including in your neck, underarm and groin, as well as a swollen spleen or liver. Removing a lymph node for testing. Your doctor may recommend a lymph node biopsy procedure to remove all or part of a lymph node for laboratory testing. Advanced tests can determine if lymphoma cells are ...
How to determine if lymphoma is present?
Advanced tests can determine if lymphoma cells are present and what types of cells are involved. Blood tests. Blood tests to count the number of cells in a sample of your blood can give your doctor clues about your diagnosis. Removing a sample of bone marrow for testing. A bone marrow aspiration and biopsy procedure involves inserting a needle ...
What is the treatment for cancer?
Radiation therapy . Radiation therapy uses high-powered beams of energy, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. Bone marrow transplant. A bone marrow transplant, also known as a stem cell transplant, involves using high doses of chemotherapy and radiation to suppress your bone marrow.
Can lymphoma be treated with supplements?
No supplements have been found to treat lymphoma. But integrative medicine may help you cope with the stress of a cancer diagnosis and the side effects of cancer treatment. Talk to your doctor about your options, such as: Physical activity. Art therapy. Meditation. Music therapy. Relaxation exercises. Acupuncture.
What is immunotherapy for lymphoma?
Types of Immunotherapy for Lymphoma. Your doctor may talk to you about using immunotherapy to help treat your lymphoma. It’s a newer type of cancer treatment that works with your natural immune system to find and kill cancer cells in your body. These are the different kinds of immunotherapy you may get for lymphoma:
What is the drug used to treat lymphoma?
This leads to the death of the cancer cells, with little to no effect on your normal cells that don’t have the antigen. Rituximab ( Rituxan) is the monoclonal antibody that doctors most often use to treat lymphoma. This drug targets the CD20 antigen, which many types of lymphoma make too much of.
What antigens do lymphoma cells carry?
For instance, you may get alemtuzumab ( Campath) if your cells have the CD52 antigen. There are also monoclonal antibodies that carry cancer-killing substances to lymphoma cells. Your lymphoma cells might have the CD30 antigen, in which case brentuximab vedotin ( Adcetris ), a monoclonal antibody attached to chemo, ...
What antibodies target CD20?
Doctors can also use other monoclonal antibodies that target CD20. Examples are ibritumomab tiuxetan ( Zevalin ), obinutuzumab ( Gazyva ), and ofatumumab ( Arzerra ). You might get a monoclonal antibody that targets a different antigen that’s found on your lymphoma cells.
What antibody is used to test lymphoma cells?
Monoclonal Antibodies. Your doctor will get your lymphoma cells tested to see if they have certain markers -- proteins called antigens. You’ll get a monoclonal antibody drug that aims at the antigens found on your lymphoma cells. Monoclonal antibodies are made in a lab.
What is the treatment for follicular lymphoma?
Follicular lymphoma: If you have a large stage I or II, or a certain kind of stage III or IV follicular lymphoma, your first treatment will likely be rituximab and chemo. You might get radiation, too. Then, if the lymphoma shrinks or goes away, you may get rituximab alone as maintenance therapy.
What antibodies can be used instead of rituximab?
Ibritumomab ( Zevalin) or obinutuzumab ( Gazyva) are other monoclonal antibodies you might get instead of rituximab. Tazemetosta t may be an option for patients that have failed or are resistant to treatments & can be used for FL with specific types of mutations.
What is the treatment for non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Many people treated for non-Hodgkin lymphoma will receive some form of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, biologic therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these. Bone marrow, stem cell transplantation, or CAR T-cell therapy may sometimes be used.
How long does non-Hodgkin lymphoma last?
Although “indolent” or slow growing forms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma are not currently curable, the prognosis is still very good. Patients may live for 20 years or more following an initial diagnosis. In certain patients with an indolent form of the disease, treatment may not be necessary until there are signs of progression.
Is lymphoma a heterogeneous disease?
Blood cancers, including lymphoma, are extremely heterogeneous, and can involve a variety of treatment options, often in combination. Some form of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination is typically used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma. Bone marrow or stem cell transplantation may also sometimes be done under special ...
What are the symptoms of lymphoma B?
Nonspecific lymphoma symptoms, commonly referred to as B symptoms, include fatigue, fever, weight loss, and drenching night sweats.
Is radiation therapy curative?
Radiation therapy has been shown to produce significant, possibly curative results in a subgroup of patients with early-stage (I or II) localized low-grade lymphoma. [27] . Except for palliative reduction of bulky disease, radiation therapy is not commonly used in the management of advanced disease.
Is low grade lymphoma a risk factor?
Low-grade lymphoma patients may be at high risk for the negative implications of uncertainty, and may benefit from research evaluating the impact of uncertainty in illness, as well the value of implementing interventions designed to help patients cope with uncertainty and fear of recurrence or progression.
Is non-Hodgkin's lymphoma incurable?
Low-grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) is an indolent form of the disease with a generally slow course of progression. Although still usually incurable, low-grade disease has shown responsiveness to some of the newer
What is the treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma?
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) tends to grow quickly. Most often, the treatment is chemotherapy (chemo), usually with a regimen of 4 drugs known as CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), plus the monoclonal antibody rituximab (Rituxan). This regimen, known as R-CHOP, is most often given in cycles 3 weeks apart.
What is the best treatment for mantle cell lymphoma?
For mantle cell lymphomas that don’t respond or that come back after initial treatment, chemo with drugs such as bendamustine, bortezomib (Velcade), cladribine, fludarabine, or lenalidomide (Revlimid) may be used, sometimes along with other chemo drugs or with rituximab.
What is the treatment for follicular lymphoma?
If treatment is needed for follicular lymphoma that is only in 1 lymph node group or in 2 nearby groups that are both above or below the diaphrag m (the thin muscle separating the chest from the abdomen), the preferred treatment is radiation therapy to the lymph node areas affected by lymphoma (called involved site radiation ). Other choices include treatment with chemo plus a monoclonal antibody (rituximab [Rituxan] or obinutuzumab [Gazyva]), or rituximab alone, which might be followed by radiation therapy.
How to treat malt lymphoma?
Early-stage gastric MALT lymphomas are treated with antibiotics combined with drugs that block acid secretion by the stomach (called proton pump inhibitors ). Usually the drugs are given for 10 to 14 days. This may be repeated after a couple of weeks. Examination of the stomach lining using upper endoscopy (where a flexible tube with a viewing lens is passed down the throat and into the stomach) is then repeated at certain intervals to see if the H. pylori is gone and if the lymphoma has shrunk. About 2 out of 3 of these lymphomas go away completely with antibiotic treatment, but it can sometimes take several months to be effective. In cases where symptoms need to be relieved before the antibiotics take effect or where antibiotics don’t shrink the lymphoma, radiation therapy to the area is often the preferred treatment. The monoclonal antibody rituximab may be another option.
What is a chemo drug?
The chemo can be a single drug (such as bendamustine) or a combination of drugs, such as the CHOP ( cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vin cristine, prednisone) or CVP ( cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone) regimens. If some lymph nodes are very large from the lymphoma, radiation may be used to reduce symptoms.
How long does it take for lymphoma to come back?
It often comes back after treatment, although it can take many years to do so. It’s not always clear if the lymphoma needs to be treated right away, especially if the lymphoma isn’t causing problems other than mildly swollen lymph nodes. Some people may never need treatment at all. For those who do, sometimes it might be years before treatment is needed.
Where does lymphoma start?
This lymphoma begins in the brain or spinal cord. It often develops in older people or those with immune system problems caused by AIDS or drugs given to keep transplanted organs from being rejected.
What does it mean when a non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is in remission
After treatment, your doctor may tell you that your non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is in "remission," which means your cancer isn't active anymore . It's natural to feel a swirl of emotions, but you'll also have a bunch of questions about what comes next. You'll probably need regular checkups and tests to look for signs the disease may have returned.
What tests are done to determine if you have non-Hodgkin's lymphoma?
Your doctor may recommend other tests, depending on your chance of getting other cancers and where your non-Hodgkin's lymphoma was located. Some of these are: Pulmonary function tests to measure how well your lungs are working. Colonoscopy. Skin exams.
Can you get a scan for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma?
But if lab tests or your symptoms show signs that your non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is coming back, you'll probably get a scan.

Causes
Pathophysiology
- The disease can develop in any part of the body. Most commonly the initial site is the lymph nodes, which are crucial parts of the lymphatic and immune system. There are numerous sub-types of lymphomas which are classified according to characteristics, location, or extent.
Prognosis
- Low grade lymphoma, also known as indolent lymphoma, is usually very slow growing and most often incurable, though many patients respond positively to treatment. Low grade lymphomas can be localized in the initial stages, or in severe cases it can spread to different sites. The patients treatment choices and quality of life are largely determined by the disease growth and spread.
Types
- Types of low grade lymphoma include: follicular lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, extranodal marginal zone lymphoma, nodal marginal zone lymphoma, splenic marginal zone lymphoma, small lymphocytic lymphoma, lymphoplasmacytic lymphomas, and skin lymphomas.
Epidemiology
- About 40% of non-Hodgkin lymphoma are classified as low grade. It is more common among older patients and affects men and women almost equally.
Signs and symptoms
- Patients with low grade lymphoma usually experience little to no symptoms. The first signs of the disease include swollen but painless lymph nodes. Fever, night sweats, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, bone, abdominal or chest pain, loss of appetite, itching and nausea occur in time.
Diagnosis
- Because many symptoms can be explained by other illnesses, an early diagnosis can be difficult. Diagnosis begins when the physician performs a complete physical examination and requests a personal medical and family history. A biopsy to analyze the damaged tissue is usually the next stop. Other tests can include chest, abdomen and pelvis or other computed tomographic (CT) i…
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Which lymphoma treatments are right for you depends on the type and stage of your disease, your overall health, and your preferences. The goal of treatment is to destroy as many cancer cells as possible and bring the disease into remission. Lymphoma treatments include: 1. Active surveillance.Some forms of lymphoma are very slow growing. You and your doctor may decide t…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Alternative Medicine
- No supplements have been found to treat lymphoma. But integrative medicine may help you cope with the stress of a cancer diagnosis and the side effects of cancer treatment. Talk to your doctor about your options, such as: 1. Physical activity 2. Art therapy 3. Meditation 4. Music therapy 5. Relaxation exercises 6. Acupuncture 7. Massage
Coping and Support
- A lymphoma diagnosis can be overwhelming. With time you'll find ways to cope with the stress and uncertainty of cancer. Until then, you may find it helps to: 1. Learn about lymphoma.If you'd like to know more about your lymphoma, ask your doctor for the details of your cancer — the type, the stage and your prognosis. Ask for good sources of up-to-date information on your treatment …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Make an appointment with your primary care doctor if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you. If your doctor suspects you have lymphoma, he or she may refer you to a doctor who specializes in diseases that affect the blood cells (hematologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of ground to cover, it's a good idea to be well prepared. Her…