
When does bradycardia need treatment?
Jun 13, 2020 · What is the initial treatment for bradycardia in ACLS? Prepare for transcutaneous pacing. Consider administering atropine 0.5 mg IV if IV access is available. If the atropine is ineffective, begin pacing. Consider epinephrine or dopamine while waiting for the pacer or if pacing is ineffective.
How much atropine do you give for bradycardia?
ACLS Drugs for Bradycardia (2020) There are three medications used in the bradycardia algorithm: atropine, epinephrine, and dopamine. Read about each drug and its use within the bradycardia algorithm below. When symptomatic bradycardia occurs, the primary objective is to identify and treat the cause of the problem.
What is the most common bradycardia treatment?
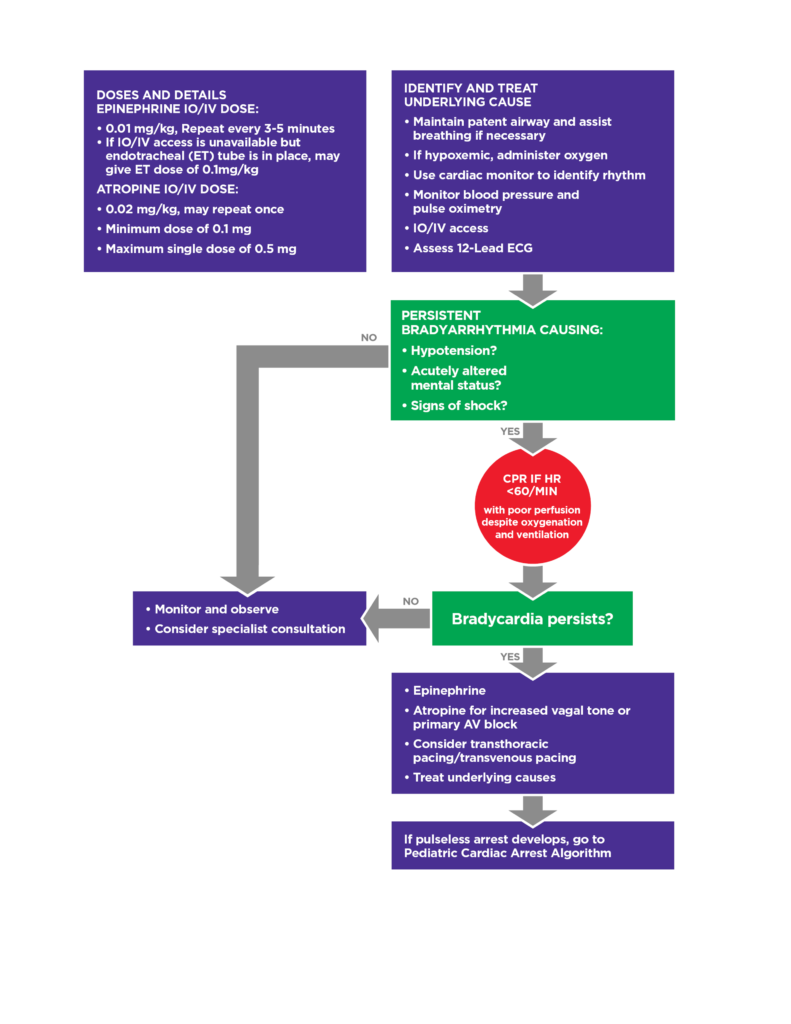
Jul 01, 2021 · Symptomatic bradycardia, heart rate typically <50 beats per minute with presence of symptoms, is identified and treated directed at the underlying cause. Maintain a patent airway with assisted breathing as necessary. Administer supplemental oxygen if hypoxic. Place the patient on continuous cardiac monitoring to identify rhythm along with frequent monitoring of …
When to give atropine ACLS?
There are 3 medications that are used in the Bradycardia ACLS Algorithm. They are atropine, dopamine (infusion), and epinephrine (infusion). Atropine: The first drug of choice for symptomatic bradycardia. The dose in the Bradycardia ACLS algorithm is 0.5mg IV push and may repeat up to a total dose of 3mg.
What can you do for ACLS bradycardia?
If the patient is symptomatic, administer atropine 1.0 mg IV or IO bolus and repeat the atropine every 3 to 5 minutes to a total dose of 3 mg: If atropine does not relieve the bradycardia, continue evaluating the patient to determine the underlying cause and consider transcutaneous pacing.
What is the initial treatment for bradycardia?
Atropine. In the absence of reversible causes, atropine remains the first-line drug for acute symptomatic bradycardia (Class IIa).Nov 28, 2005
When do you treat bradycardia ACLS?
Regardless of the patient's rhythm, if their heart rate is too slow and the patient has symptoms from that slow heart rate, the bradycardia should be treated to increase the heart rate and improve perfusion, following the steps of the bradycardia algorithm below.
What is the best treatment for bradycardia?
The standard treatment for a slow heart rate is to implant a pacemaker. For people with bradycardia, this small device can help restore a normal heartbeat.
How does atropine treat bradycardia?
Abstract. The use of atropine in cardiovascular disorders is mainly in the management of patients with bradycardia. Atropine increases the heart rate and improves the atrioventricular conduction by blocking the parasympathetic influences on the heart.
What is Isoprenaline used for?
Isoprenaline is indicated to treat mild or transient episodes of heart block not requiring electric shock or pacemakers, serious episodes of heart block and Adams-Stokes attacks not caused by ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, and bronchospasm during anesthesia.
What medication is usually the first given for symptomatic bradycardia?
Atropine. Atropine is the first line medication for the treatment of bradycardia. The administration of atropine typically causes an increase in heart rate. This increase in the heart rate occurs when atropine blocks the effects of the vagus nerve on the heart.
When is atropine given in ACLS?
If the patient is presenting with hypotension, acute altered mental status, signs of shock, ischemic chest discomfort or signs of acute heart failure administer Atropine IV at the dose of 1 mg every 3 to 5 minutes. Do not administer more than 3 mg total.Jul 1, 2021
What is the correct treatment protocol for asystole?
When treating asystole, epinephrine can be given as soon as possible but its administration should not delay initiation or continuation of CPR. After the initial dose, epinephrine is given every 3-5 minutes. Rhythm checks should be performed after 2 minutes (5 cycles) of CPR.
What is the initial drug of choice for SVT treatment?
Adenosine (Adenocard) Adenosine is the first-line medical treatment for the termination of paroxysmal SVT.Apr 5, 2017
What medication is used to speed up heart rate?
Atropine IV/IM. Used to increase heart rate through vagolytic effects, causing increase in cardiac output.Dec 27, 2017
What is the decision point for ACLS intervention in the bradycardia algorithm?
The decision point for ACLS intervention in the bradycardia algorithm is determination of adequate perfusion. For the patient with adequate perfusion, observe and monitor the patient. If the patient has poor perfusion, preparation for transcutaneous pacing should be initiated, and an assessment of contributing causes (H’s and T’s) should be carried out.
What is relative bradycardia?
Relative bradycardia occurs when a patient may have a heart rate within normal sinus range, but the heart rate is insufficient for the patient’s condition. An example would be a patient with a heart rate of 80 bpm when they are experiencing septic shock.
What is the difference between bradycardia and bradycardia?
Symptomatic Bradycardia. Bradycardia is defined as any rhythm disorder with a heart rate less than 60 beats per minute. (Usually less than 60) Symptomatic bradycardia, however, is defined as a heart rate less than 60/min that elicits signs and symptoms, but the heart rate is typically less than 50/min.
Is bradycardia a physiologic condition?
A: Bradycardia may be physiologic in the hypothermic patient. This type of bradycardia is an appropriate response to the decreased metabolic rate that normally occurs with hypothermia. Also the hypothermic ventricle is more prone to fibrillation with any sort of irritation. Thus the irritation of TCP could induce VF.
What is TCP in medical terms?
Transcutaneous pacing (TCP) Preparation for TCP takes place as atropine is being given. If atropine fails to alleviate symptomatic bradycardia, TCP is initiated. Ideally, the patient receives sedation prior to pacing, but if the patient is deteriorating rapidly, it may be necessary to start TCP prior to sedation.
Does atropine cause bradycardia?
First, atropine may be used for any type of block but may negatively affect outcomes if the bradycardia is being caused by myocardial infarction. This negative effect may occur because atropine increases the heart rate and myocardial oxygen demand.
What are the symptoms of bradycardia?
ACLS providers should also look for adverse signs and symptoms of the bradycardia which include: 1 Chest discomfort 2 Shortness of breath 3 Decreased level of consciousness 4 Weakness 5 Fatigue 6 Light-headedness or dizziness 7 Hypotension 8 Congestive heart failure 9 Ventricular arrhythmias related to the bradycardia 10 Acutely altered mental status 11 Signs of shock
What is absolute bradycardia?
Absolute bradycardia is defined as a pulse rate less than 60 beats per minute. During the initial patient assessment, ACLS providers must determine whether any life-threatening signs and symptoms are present that have been caused by that bradycardia.
What is the heart rate of a person with bradycardia?
Bradycardia is defined as a heart rate less than 60 beats per minute. It’s vital to remember that if the bradycardia, regardless of the underlying reason, is causing the patient to display symptoms related to the bradycardia, it should be treated.
Can bradycardia cause shock?
Signs of shock. Sometimes the symptom is not due to the bradycardia. For example, hypotension associated with bradycardia may be due to myocardial dysfunction rather than the bradycardia. Healthcare providers should keep this in mind when they reassess the patient’s response to treatment.
What are the symptoms of bradycardia?
5. Common bradycardia symptoms include: syncope. presyncope. transient dizziness or lightheadedness. fatigue. dyspnea on exertion. heart failure symptoms.
What is bradycardia heart rate?
What is bradycardia? The National Institutes of Health defines bradycardia* as a heart rate <60 bpm in adults other than well-trained athletes. 9 The determination on whether or not treatment is necessary for bradycardic events is generally based on the presence of bradycardia symptoms. The clinical manifestations of bradycardia can vary widely from insidious symptoms to episodes of frank syncope. 5
When a patient is evaluated for symptomatic bradycardia, an in-depth history and physical is
When a patient is evaluated for symptomatic bradycardia, an in-depth history and physical is important, along with the identification of possible reversible causes. The following is a list of conditions associated with bradycardia and conduction disorders: 11
What percentage of patients with sleep apnea have sinus bradycardia?
The prevalence of sinus bradycardia in patients with sleep apnea can be as high as 40%, with episodes of second- or third-degree AV block in up to 13% of patients. 8
How much atropine is given?
Atropine 0.5 mg intravenous (IV) is given up to a total of 3 mg. 1 Atropine sulfate acts by reversing the cholinergic-mediated decreases in the heart rate and AV node conduction. 1. If atropine is ineffective, two treatment pathways are available.
Can exercise be used for ischemia?
Although not routinely recommended for assessment of ischemia, exercise testing can be considered in patients with symptoms temporally related to exercise, asymptomatic second-degree AV block, or for suspected chronotropic incompetence. 11
