
not present
| SEDIMENTATION (for conventional systems) ... | Turbidity Goal | Criteria |
| Settled water | < 2.0 NTU, 95% of the time. | If average annual raw water turbidity is ... |
| Settled water | < 1.0 NTU, 95% of the time. | If average annual raw water turbidity is ... |
| FILTRATION (conventional and direct syst ... | Turbidity Goal | Criteria |
What are the steps in a water treatment plant?
- Remove specific contaminants
- Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system
- Improve the taste of drinking water
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
Water Treatment Process: Follow Water Through a Surface Water Treatment Plant
- Coagulation. ...
- Flocculation. ...
- Sedimentation (or Clarification) The water continues on to the sedimentation basin, or clarifier, after the flocs have been formed. ...
- Filtration. ...
- Disinfection. ...
- Chlorination Operations. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What are the components of a water treatment plant?
What are the components of a water treatment plant?
- Raw water source ( River, lake, impounding reservoir, canal)
- Intake well
- Jackwell
- Raw water pumping system
- Raw water conveyance system to Water treatment plant
- Cascade areator
- Parshel flume
- Alum mixer
- Intake channels
- Carifier
What is the largest water treatment plant in the US?
“The Northeast Water Purification Plant Expansion is currently the largest water treatment project on the planet — not just in the State of Texas, not just in the United States, but on the planet,” said Houston Mayor Sylvester Turner, according to the Houston Chronicle. “Can you imagine this plant just a couple of weeks ago was ...
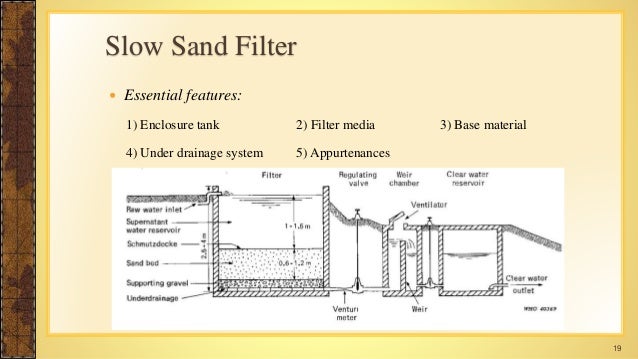
What is the purpose of a water treatment plant?
The purpose of a public or private water treatment facility is to make water potable (safe to drink) and palatable (pleasant to taste) while also ensuring that there is a sufficient supply of water to meet the community's needs.
What are the objectives achieved through water treatment?
The objective of municipal and industrial waste water treatment is to extract pollutants, remove toxicants, neutralise coarse particles, kill pathogens so that quality of discharged water is improved to reach the permissible level of water to be discharged into water bodies or for agricultural land.
What are the main objectives of treating water and aeration process in water treatment?
3.1 Purpose of Aeration 1. To remove taste and odour by gases due to organic decomposition. 2. To increase the dissolved oxygen.
What is the objective of the primary treatment system?
The objective of primary treatment is the removal of settleable organic and inorganic solids by sedimentation, and the removal of materials that will float (scum) by skimming.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
The wastewater treatment plant is the common form of treating and removing impurities from wastewater from households and industries. On the other hand, desalination refers to the treatment of saline water which includes processes like distillation and reverses osmosis. Distillation is basically a process of treating the saline water ...
Why is water treatment important?
Water treatment is important to earth because the availability of fresh water is limited in the earth and the demand is high.
Why is desalination important?
It is important as it converts the saline water (which is actually of no use and is available in abundance on the earth) to potable water. This can help in solving the problem of water scarcity in the world. Most Recommended Read For You: Ways To Save Natural Resources & Its Conservation.
What is distillation in water?
Distillation is basically a process of treating the saline water of oceans and seas to make it fit for human consumption. “Globally, only 20 Percent of wastewater produced receive proper treatment”. (UNESCO 2012).
How does water purification help the water cycle?
It helps to balance the water cycle by maintaining groundwater and surface water. The water purified at the treatment plants can be used for various purposes like drinking, households use, industrial application, agriculture, and irrigation purposes, etc.
What is the last process that involves the addition of disinfectant to destroy the harmful bacteria, parasites, viruses,
Disinfection – It is the last process which involves the addition of disinfectant to destroy the harmful bacteria, parasites, viruses, and other micro-organisms. If you want to know more about the way to save mother earth, then head over to this article where we have discussed more earth saving tips.
Why is it important to have a regular supply of drinking water?
Those who have a regular supply of drinking water it is their duty to understand the value of clean water and therefore should not be taken for granted. They can also help in improving the efficiency of water treatment by reducing water pollution. importance of water treatment.
When was the first potable water treatment plant?
Already in 2001, the first potable water treatment plant using a MIEX® -DOC process was launched in Australia. In this plant, the MIEX ® -DOC step was introduced prior to conventional treatment, and a significant improvement in water quality was observed.
What is centralized water treatment?
Centralized water treatment plants are based on coagulation, flocculation and disinfection processes and found to be most cost-effective in treating large quantities of water.
What is the water district in Orange County?
Orange County Water District (OCWD). OCWD located between Los Angeles and San Diego counties in southern California manages the groundwater basin that supplies about 3.0 × 10 8 m 3 per year potable water to a population of more than 2 million.
What is the water used in CMF-S?
Raw (surface) water is pre-screened, and dosed with lime and carbon dioxide in a contact reactor to control alkalinity and corrosion. Next, water is dosed with a coagulant, liquid aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to entering the CMF-S plant to remove colour, some organic content, and dissolved metals.
What is the Bendigo water treatment plant?
I. Bendigo water treatment plant (BWTP). The 12.54 × 10 4 m 3/day (33 MGD) BWTP has been producing drinking water for nearly 1 million people in central Victoria, Australia since 2002. It is one of the largest if not the largest MF plant in the world. The plant combines submerged microfiltration (CMF-S), ozonation and biological activated carbon (BAC) to treat a variable and difficult raw water. Raw (surface) water is pre-screened, and dosed with lime and carbon dioxide in a contact reactor to control alkalinity and corrosion. Next, water is dosed with a coagulant, liquid aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to entering the CMF-S plant to remove colour, some organic content, and dissolved metals. The coagulant dosage is typically 5–6 mg/l. The coagulant precipitate is removed by MF. The coagulant/CMF-S process removes up to 15% of the dissolved organic carbon.64
What is water treatment automation?
Automation of water treatment plant involves the control system opening and closing valves and starting and stopping equipment in predefined sequences to complete specific tasks or to provide the desired process plant output. To achieve these results the automation system relies on signals from correctly selected and placed instruments, devices such as actuators and motor control circuits and reliable control logic. The degree of automation to be used is fundamental to developing an automation system.
What is make up water treatment?
Make up water treatment. Treated raw water is mixed with potable water and pumped to the boiler feedwater treatment system. The system is designed to remove 99% of the dissolved minerals and provide high-purity water to the boiler.
Why do people use water treatment units?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: Remove specific contaminants. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system. Improve the taste of drinking water.
How does a water treatment unit work?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1 Remove specific contaminants 2 Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3 Improve the taste of drinking water
What is the process of boiled water?
Distillation is a process in which impure water is boiled and the steam is collected and condensed in a separate container, leaving many of the solid contaminants behind. Disinfection. Disinfection is a physical or chemical process in which pathogenic microorganisms are deactivated or killed.
What are the steps of water treatment?
Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water.
Why is surface water more contaminated than ground water?
Typically, surface water requires more treatment and filtration than ground water because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more sediment and pollutants and are more likely to be contaminated than ground water. Some water supplies may also contain disinfections by-products, inorganic chemicals, organic chemicals, and radionuclides.
What is a water softener?
Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water. A water softener typically uses sodium or potassium ions to replace calcium and magnesium ions, the ions that create “hardness.”. Distillation Systems.
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
The most common types of household water treatment systems consist of: Filtration Systems. A water filter is a device which removes impurities from water by means of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or biological process. Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water.
What is water treatment?
The water treatment process to deliver safe and wholesome water to customers includes many steps. Coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection are the water treatment processes that make up a conventional surface water treatment plant. These water treatment processes ensure that the water consumers receive is safe ...
What is the purpose of the Surface Water Treatment Rule?
The goal of the SWTR is to reduce illnesses related to pathogens in drinking water. These pathogens include coliform, Giardia, and Cryptosporidium .
What is coagulation in water treatment?
History of Coagulation in Drinking Water Treatment. Coagulation has been an important process in high-rate filtration plants in the United States since the 1880s. Aluminum and iron salts have been used in the coagulation process since the beginning. These salts are still the most commonly used coagulants today.
What is turbidity in water?
This cloudiness is known as turbidity . Visual turbidity is unpleasant to consumers. Visual turbidity is also an indicator to operators and regulators that the water may still contain pathogens. The Surface Water Treatment Rule therefore requires that turbidity be removed to very low levels.
What are the common coagulants used today?
Common coagulants used today include aluminum sulphate (alum), ferric sulphate, ferric chloride, and sodium aluminate. Synthetic organic polymers were introduced in the 1960s. Depending on your system’s water quality, it may be necessary to employ a combination of two or more coagulants.
How does contact time work in water treatment?
In order for systems to be sure that they are properly disinfecting the filtered water, the Surface Water Treatment Rule requires systems to provide enough contact time. Contact time (CT) is a function of the known disinfection concentration and the amount of time that the disinfectant is in contact with the water. Contact time is expressed in terms of mg/L-min. The EPA has published tables that show how much CT credit water systems will receive. In order to use these tables you use the concentration of chlorine, time, water temperature and pH.
How does surface water treatment work?
In order to meet the requirements of the Surface Water Treatment Rule, a water system must both remove and inactivate the pathogens in the water. This process begins with coagulation, which destabilizes the particles in the water. Then, during flocculation, the destabilized particles bump into each other and form larger and larger flocs. These large flocs are given adequate time to settle out of solution via gravity during sedimentation. Any remaining particles and pathogens will be removed during the filtration treatment process. Finally, the water is disinfected to inactivate any remaining pathogens prior to entering the water system’s distribution system.
Why are water treatment plants important?
Drinking water treatment plants are used to remove particles and organisms that lead to diseases and protect the public’s welfare and supply pure drinkable water to the environment, people and living organisms.
What is water treatment?
Water treatment, as a word originally means the act or process of making water more potable or useful, as by purifying, clarifying, softening or deodorizing it. To provide drinking water to the public is one of the most important tasks of communities and the design of water supply systems has to follow the rules of engineering sciences ...
What is sedimentation in water?
Sedimentation : The heavy particles (floc) settle to the bottom and the clear water moves to filtration. Filtration : The water passes through filters, some made of layers of sand, gravel and charcoal that help remove even smaller particles.
What is the process of removing dirt and other particles suspended in water?
Coagulation: removes dirt and other particles suspended in water. Alum and other chemicals are added to water to form tiny sticky particles called “floc” which attract the dirt particles. The combined weight of the dirt and the alum (floc) become heavy enough to sink to the bottom during sedimentation.
How is water treated differently?
Water is treated differently in different communities depending on the quality of the water which enters the plant. For example; groundwater requires less treatment than water from lakes, rivers and streams. In order to analyse all these technical aspects in the drinking water treatment systems and for the supplement of a training guide on drinking ...
How many people do not have access to clean water?
783 million people do not have access to clean and safe water, 1 in 9 people worldwide do not have access to safe and clean drinking water. Diarrhea caused by inadequate drinking water, sanitation, and hand hygiene kills an estimated 842,000 people every year globally, or approximately 2,300 people per day.
What is wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment (WWT) is a process to remove harmful contaminants from wastewater or sewage produced by households and industrial facilities. Wastewater is full of contaminants including bacteria, chemicals, and other toxins and nutrients.
How does wastewater reduce the amount of waste?
Waste Reduction: Through the treatment of wastewater, the amount of harmful waste that is usually released into the environment is reduced. By doing so, companies can reduce the health risks associated with environmental pollution, as well as reduce the water loss induced through water pollution.
What temperature is sludge treated?
It is treated with anaerobic bacteria in special fully-enclosed digesters that are heated to 35 degrees Celsius.
What is the purpose of Sewage Treatment Plants?
Sewage is made up of wastewater from homes and businesses, as well as perhaps pre-treated industrial waste. There are numerous sewage treatment processes from which to choose.
Advantages & Disadvantage of a Sewage Treatment Plant
A sewage treatment plant has numerous advantages. Let’s have a look at a few of them:
Effects of wastewater pollutants
If wastewater is not adequately treated, it can have a severe influence on the environment and human health. Fish and wildlife populations may be harmed, oxygen levels may be depleted, beach closures and other limits on recreational water usage, restrictions on fish and shellfish harvesting, and drinking water contamination may occur.
How does the Sewage Treatment Plant protect our environment?
Untreated sewage water pollutes our ecosystem and rivers in the thousands of gallons range. A liter of wastewater pollutes 8 liters of clean water, according to researchers and scientists. You can see how dangerous it is for the river now.
