
Procedures
"I didn't know what to do ... and hypothermia," the NWS website says.Lessons learned and a happy endingFortunately for Dawn O'Hair, what she lacked in winter preparation she made up for in a good decision, good luck and good connections with people ...
Therapy
What is Hypothermia and How to Treat It. Hypothermia occurs when body temperature falls below 35.0 ºC (95 ºF). The normal range of body temperature is variable, but is generally accepted to be between 36 ºC and 37.2ºC (97 ºF and 99 ºF). It depends largely on a person's age, weight, level of physical activity and even the menstrual cycle ...
Nutrition
Symptoms of malignant hyperthermia usually occur within the first hour after exposure to the trigger medication. However, the symptoms can be delayed for up to 12 hours. Most cases occur in children and adults younger than 30.
What does hypothermia do to a person?
The following can also cause a lack of feeling in your body:
- a stroke
- spinal cord injuries
- burns
- malnutrition
What is hypothermia and how to treat it?
How long does it take to die from hypothermia?
What are the dangers of hypothermia?
What to do for hypothermia?
How to help someone with hypothermia?
How to raise body temperature?
How to warm blood?
What is the best way to warm up the body?
How to protect yourself from cold weather?
What causes the body temperature to drop?
See more
About this website
What is the goal temperature for therapeutic hypothermia?
Treatment goal In most centers, the patient is actively cooled by using an induced hypothermia protocol for 24 hours to a goal temperature of 32ºC-36ºC. The goal is to achieve the target temperature as quickly as possible.
What is the overarching goal of performing controlled hypothermia?
Targeted temperature management (TTM) previously known as therapeutic hypothermia or protective hypothermia is an active treatment that tries to achieve and maintain a specific body temperature in a person for a specific duration of time in an effort to improve health outcomes during recovery after a period of stopped ...
How is therapeutic hypothermia beneficial?
Hypothermia improves neurologic outcome and decreases mortality in patients with global cerebral ischemia, such as cardiac arrest patients and infants with hypoxicischemic encephalopathy. To provide effective treatment, optimal induction and safe rewarming methods need to be determined.
How does hypothermia treatment work?
How does therapeutic hypothermia help? Hypothermia counteracts neuroexcitation in brain cells by stabilizing calcium and glutamate release, reducing the degree of cell death. It also stabilizes the blood-brain barrier and suppresses the inflammatory process, reducing cerebral edema.
What is the goal of targeted temperature management?
Targeted temperature management aims to reduce mortality and improve neurological outcomes in unresponsive patients who achieve ROSC after cardiac arrest.
How do you monitor therapeutic hypothermia?
Monitor and document vital signs every 15 minutes X4, every 30 minutes X2, then every 1 hour with the exception of patient temperature, which will continue every 15 minutes until reaching target temperature of 33°C. Continually monitor cardiac rhythm documentation at least every 6 hours and with any rhythm changes.
Why do we induce hypothermia?
Induced hypothermia aims to avoid the complications associated with hypothermia. It is principally used in comatose cardiac arrest survivors, head injury, and neonatal encephalopathy. The mechanism of action is thought to be mediated by prevention of cerebral reperfusion injury.
Why is it important to keep patients at rest when they are hypothermic?
Why is it important to keep patients at rest when they are hypothermic? Since the blood is warmest in the extremities, exercise or unnecessary movement could quickly circulate the warm blood and raises the core body temperature. Which of the following does NOT make infants and children more prone to hypothermia?
Does hypothermia increase heart rate?
At temperatures below 95 F (35 C), shivering is seen. Heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure increase. As the temperature drops further, pulse, breathing rate, and blood pressure all decrease.
When do you initiate targeted temperature management?
The task force recommends targeted temperature management for adults with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with an initial shockable rhythm at a constant temperature between 32°C and 36°C for at least 24 hours.
What Is Therapeutic Hypothermia?
Therapeutic hypothermia is a procedure used to cool a person's body to a temperature that is lower than normal. The procedure is done after a cardi...
Why Is Therapeutic Hypothermia done?
Therapeutic hypothermia is done to reduce the risk of brain swelling, blood clots, and seizures after cardiac arrest. The procedure may help the pe...
How Is Therapeutic Hypothermia done?
The therapeutic hypothermia process often begins with an IV of cold liquid to cool the person's body quickly. The person's body is slowly warmed 12...
What Happens During Therapeutic Hypothermia?
1. Healthcare providers will check the person's blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing rate throughout the process. Monitors in the person's eso...
What Are The Risks of Therapeutic Hypothermia?
1. Effects of medicines given to prevent shivering may last longer than expected. Therapeutic hypothermia may cool the person too fast or to a temp...
Hypothermia: Signs, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Hypothermia, when body temperature drops below normal levels, is a life-threatening emergency and should be treated immediately. Learn about the signs, symptoms, treatment, and causes of ...
NCBI Bookshelf
NCBI Bookshelf
Hypothermia - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic
When your body temperature drops, your heart, nervous system and other organs can't work normally. Left untreated, hypothermia can lead to complete failure of your heart and respiratory system and eventually to death.
What is the treatment for hypothermia?
This treatment is known as hypothermia therapy, but it has many other names, such as “therapeutic hypothermia,” “cooling therapy,” and “neonatal cooling.”. Hypothermia therapy involves cooling the baby down to a temperature below homeostasis to allow the brain to recover from a hypoxic-ischemic injury. Typically, the target temperature is about ...
When should my baby get hypothermia therapy?
If your baby was diagnosed with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), doctors have to begin hypothermia therapy very shortly after the oxygen deprivation occurred. According to the Academic Medical Center Patient Safety Organization (AMC PSO), hypothermia therapy should ideally be commenced within six hours of birth (under certain circumstances, this may be done within 12 hours) (2).
How much temperature should a newborn be after hypothermia?
The AMC PSO suggests that the baby’s temperature should be increased by 0.2 – 0.5 degrees Celsius, until it reaches 36.5 degrees Celsius.
How soon after birth can you give hypothermia?
However, it must be given very shortly after birth/the oxygen-depriving incident in order to be effective (ideally within six hours). This treatment is known as hypothermia therapy, but it has many other names, ...
How long does it take for a baby to get hypothermia?
According to the Academic Medical Center Patient Safety Organization (AMC PSO), hypothermia therapy should ideally be commenced within six hours of birth (under certain circumstances, this may be done within 12 hours) (2). The sooner hypothermia therapy begins, the greater the chance that the baby’s potential disabilities will be minimized.
Can a hospital provide hypothermia?
Not all hospitals will be equipped to provide therapeutic hypothermia because not all NICUs are the same. Community hospitals, for example, may not have brain cooling equipment, but they should have the ability to transfer the baby to a bigger or more specialized hospital that can provide cooling. It is a good idea to inquire about what kind of care a neonatal care unit can provide when researching hospitals.
Who is the HIE Help Center?
The HIE Help Center is run by ABC Law Centers (Reiter & Walsh, P.C.), a medical malpractice firm exclusively handling cases involving HIE and other birth injuries. Our lawyers have over 100 years of combined experience with this type of law, and have been advocating for children with HIE and related disabilities since the firm’s inception in 1997.
What is therapeutic hypothermia?
Therapeutic hypothermia is a type of treatment. It’s sometimes used for people who have a cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest happens when the heart suddenly stops beating. Once the heart starts beating again, healthcare providers use cooling devices to lower your body temperature for a short time. It’s lowered to around 89°F to 93°F (32°C to 34°C).
How long does hypothermia last?
That’s when chilled fluids are given through an IV (intravenous) line into your bloodstream. The therapeutic hypothermia will likely last around 24 hours. The medical team will slowly rewarm you over several hours. They may set cooling blankets at gradually higher temperatures.
Why might I need therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest?
Therapeutic hypothermia can help only some people who have had cardiac arrest. Some people regain consciousness right after cardiac arrest. These people often do not need this procedure. It is helpful only for people whose heartbeat returns after a sudden cardiac arrest. If the heartbeat doesn’t restart soon, it won't help.
What kind of care do you need for a cardiac arrest?
You will need follow-up care . Medical care will depend on the reason for the cardiac arrest and the degree of damage. Other health problems you have will also determine the care you need. You may need medicine, procedures, and physical therapy. Some people might need surgery for heart disease.
What is the best way to check your temperature?
Your heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs will be closely watched. Healthcare providers use special thermometers to check your internal temperature. The provider may use cooling blankets, ice packs, or cooling pads to bring the body temperature down. The goal is to cool as quickly as possible.
Is hypothermia dangerous?
Therapeutic hypothermia is very helpful for some people. But it has some rare risks. Some of these risks include: Another abnormal heart rhythm, especially slow heart rates. Severe blood infection (sepsis) Blood is less able to clot. This can cause bleeding. Electrolyte and metabolic problems.
Does lowering temperature reduce brain damage?
Experts are not sure why lowering the body’s temperature reduces brain damage. The chemical reactions of the body slow down. The lowered temperature may also lessen inflammation in the brain. Both of these factors may help reduce injury.
How is therapeutic hypothermia done?
The therapeutic hypothermia process often begins with an IV of cold liquid to cool the person's body quickly. The person's body is slowly warmed 12 to 24 hours later. Several methods may be used to keep body temperature at a cooled level:
What is used to cool a person's body?
Ice packs, icy cold wet towels, or fans may be used. The ice packs are placed on the person's neck, armpits, torso, and groin. A cooling blanket may be laid over the person's body. Cool water runs through the cooling blanket. During endovascular cooling, a catheter is placed into a big vein in a person's groin.
What is an epidural heat exchanger?
An epidural heat exchanger is a machine attached to a cooling catheter that is in the epidural space. The epidural space contains cerebrospinal fluid. The machine sends cool water into and out of the cooling catheter. The fluid stays cooled and keeps the spinal cord from swelling.
What happens when you cool down?
Cooling may cause the person's blood pressure to become too high or too low. This can cause the heart to beat slowly or out of rhythm. Fluid loss from cooling can lead to dehydration or electrolyte (body chemical) levels that are out of balance.
Does shivering help with hypothermia?
Shivering increases body temperature and decreases the benefits of therapeutic hypothermia. Healthcare providers will use medicines to stop the person from shivering. Healthcare providers may also use warm air in the room to help control shivering.
How to prevent cardiac dysrhythmia with hypothermia?
To prevent cardiac dysrhythmia with continued hypothermia, rescuers or paramedics should attempt rewarming in the field. (A notable exception would be isolated frostbite injury in which limb rewarming would preclude self-rescue because of pain.) Gently place patients in an environment most favorable to reducing further heat loss from evaporation, radiation, conduction, or convection. Remove wet clothing, and replace it with dry blankets or sleeping bags. Initiate active external rewarming with heat packs (eg, hot water bottles, chemical packs) placed in the axillae, on the groin, and on the abdomen. Be aware of the risk of causing body surface burns from exuberant active external rewarming. In dire circumstances, rescuers may provide skin-to-skin contact with patients when heat packs are unavailable and such therapy would not delay evacuation.
When to initiate resuscitation for hypothermia?
A reasonable approach is to initiate resuscitation on all hypothermic patients unless a patient presents with a frozen chest or other obvious nonsurvivable injuries. A patient can be warmed aggressively and resuscitated until the core temperature rises above 32°C. At that juncture, if no signs of life are present and the patient is not responding to advanced cardiac life support measures, termination of resuscitation may be indicated.
What is prehospital management?
This should be the preeminent concern. Conscious patients can develop ventricular fibrillation suddenly; prehospital workers, particularly those operating in remote search-and-rescue operations, should avoid inadvertent jerky movement of severely hypothermic patients. Patients who develop hypothermia-induced dysrhythmia in the field may be beyond resuscitation. How the hypothermic heart deteriorates into the rhythm of ventricular fibrillation remains under debate.
What temperature should a patient be warming to?
An optimal warming strategy is elusive. Some have postulated that rapidly warming a patient to 33°C and maintaining him or her at that temperature, using hypothermia therapeutically as though he or she was a cardiac arrest patient might be beneficial.
Why should you avoid alcohol in cold weather?
Persons should avoid alcohol if anticipating exposure to cold because alcohol can disrupt temperature homeostasis by causing vasodilation.
Is hypothermia a real emergency?
Profound hypothermia is a true emergency, warranting the same resource-intensive resuscitation as myocardial infarction. Direct treatment at maintaining or restoring cardiac perfusion; maximizing oxygenation is indicated for a prolonged period until the core temperature is at least 32°C.
Can you heat up intravenous fluids?
Although many texts suggest that intravenous fluids be heated to 45°C, this temperature choice is based on convenience of previous study designs rather than any hard evidence. A trial using fluids heated to 65°C demonstrated more efficacy in treating severe hypothermia. Emergency departments that routinely treat hypothermia can keep blankets and intravenous fluid bags in a shared heater. In urgent situations, intravenous fluids that contain no dextrose or blood can be heated in a microwave oven. Once these simple measures have been applied, consider more difficult rewarming therapies.
What are the therapeutic interventions for hypothermia?
Nursing Interventions. The following are the therapeutic nursing interventions for Hypothermia: Interventions. Rationales. Regulate the environment temperature or relocate the patient to a warmer setting. Keep the patient and linens dry. These methods provide for a more gradual warming of the body.
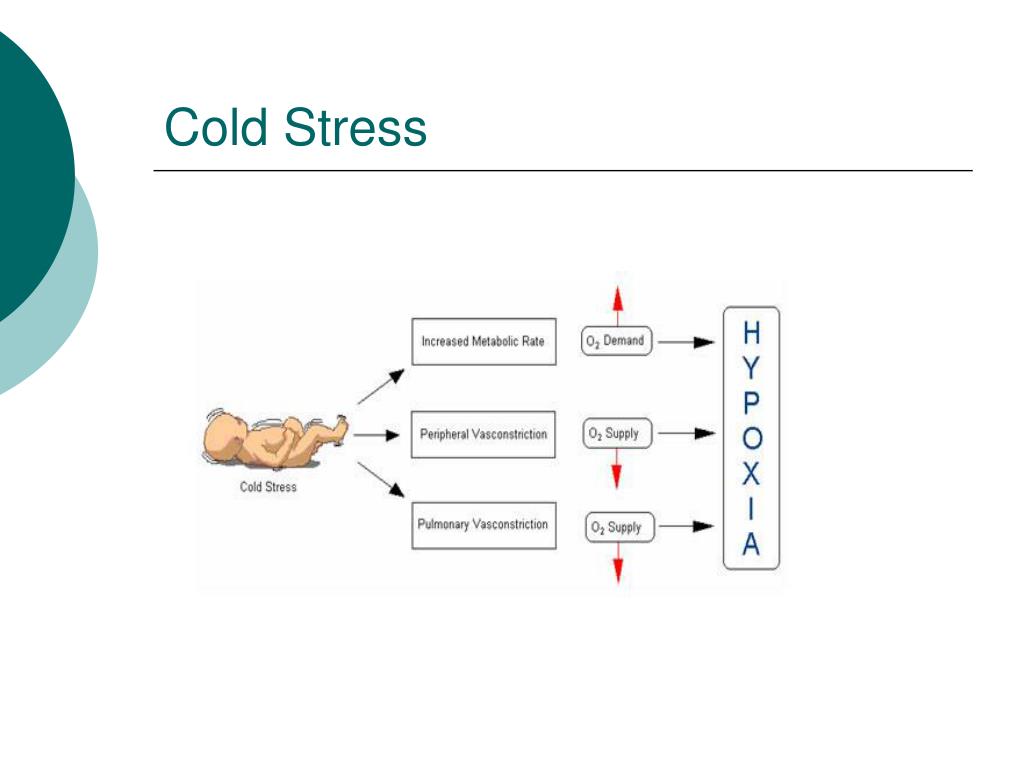
How does hypothermia occur?
Hypothermia occurs when the body fails to produce heat during metabolic processes, in cells that support vital body functions. Most heat is lost from the skin’s surface through convection, conduction, radiation, and evaporation. When the body temperature drops, the heart, nervous system, and other organs can’t work normally leading ...
What is the normal temperature for hypothermia?
ADVERTISEMENTS. Use this guide to create a nursing care plan and nursing interventions for hypothermia. Normal body temperature is around 37 °C (98.6 °F). Hypothermia occurs as the body temperature falls lower than normal; usually below 35 °C (95 °F). Hypothermia occurs when the body fails to produce heat during metabolic processes, ...
What happens when the body temperature drops?
When the body temperature drops, the heart, nervous system, and other organs can’t work normally leading to complete failure of the heart and respiratory system and eventually to death. Contents. Nursing Assessment. Nursing Interventions. See Also.
What are the risks of hypothermia?
Moderate to severe hypothermia increases the risk for ventricular fibrillation, along with other dysrhythmias. Evaluate the patient for drug abuse use, including antipsychotics, opioids, and alcohol. These groups of drugs contribute to vasodilation and heat loss. Evaluate the patient’s nutrition and weight.
How does moisture affect evaporative heat loss?
Moisture promotes evaporative heat loss. Control the heat source according to the patient’s physical response. Body temperature should be raised no more than a few degrees per hour. Vasodilation occurs as the patient’s core temperature increases leading to a decrease in BP.
What are the complications of rewarming?
Hypotension, metabolic acidosis, and dysrhythmias are complications of rewarming. Give extra covering (passive warming), such as clothing and blankets; cover postoperative patients with heat-retaining blankets. Warm blankets provide a passive method for rewarming. Give heated oral fluids for alert patients.
What is the implementation of hypothermia?
Implementation of hypothermia does require planning, education, and integration of multiple services within an institution. The basic framework for clinical protocols are well established, and institutions interested in establishing protocols may find a substantial amount of prior art in the literature (see hypothermia protocols ).
Where should hypothermia therapy be initiated?
When possible, hypothermia therapy for patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest should be initiated in the emergency department. Treatment can be continued while in the percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) laboratory and in the intensive care unit (ICU).
What temperature should be maintained in a lab?
The temperature should be maintained between 32ºC and 36ºC (class I, level of evidence: B-R)
How long does it take to rewarm after hypothermia?
In most cases, this can be achieved within 3-4 hours of initiating cooling. Rewarming is begun 24 hours after the time of initiation of cooling (ie, not from the time the target temperature is achieved). More evidence is needed to define the optimal duration of hypothermia treatment in humans.
When was hypothermia first used?
[ 8] The concept has experienced periodic reemergence in the medical literature, and recent studies of the modality date back mostly to the 1950s. In 1954 , Hegnauer and D'Amato demonstrated decreased oxygen consumption in hypothermic dogs, [ 9] and the study by Benson et al of hypothermia after cardiac arrest in humans [ 10] demonstrated decreased mortality.
Is hypothermia a DNR?
In addition, hypothermia is inappropriate in patients with a valid do not resuscitate order (DNR).
Does hypothermia impair clotting?
Known bleeding diathesis or with active ongoing bleeding - Hypothermia may impair the clotting system (however, patients may receive chemical thrombolysis, antiplatelet agents, or anticoagulants if deemed necessary in the treatment of the primary cardiac condition)
How long does hypothermia last?
More evidence is needed to define the optimal duration of hypothermia treatment in humans. In animal models, effective hypothermia treatment can be less than 24 hours if initiated rapidly after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). In other animal models with long duration of cardiac arrest and delayed initiation of hypothermia, ...
How long does it take to rewarm a patient after hypothermia?
In most cases, this can be achieved within 3-4 hours of initiating cooling. Rewarming is begun 24 hours after the time of initiation of cooling (ie, not from the time the target temperature is achieved). More evidence is needed to define the optimal duration of hypothermia treatment in humans. In animal models, effective hypothermia treatment can be less than 24 hours if initiated rapidly after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). In other animal models with long duration of cardiac arrest and delayed initiation of hypothermia, treatment for 48 hours is needed to achieve good neurological outcomes.
How long does it take to rewarm after cooling?
In most cases, this can be achieved within 3-4 hours of initiating cooling. Rewarming is begun 24 hours after the time of initiation of cooling (ie, not from the time the target temperature is achieved). More evidence is needed to define the optimal duration of hypothermia treatment in humans. In animal models, effective hypothermia treatment can ...
What is the diagnosis of hypothermia related to surgery?
Nursing Diagnosis: Hypothermia related to surgery as evidence reduction of body temperature of 94.4 degrees, mental confusion, drowsiness, and decreased pulse and respirations.
What are the conditions that are considered to be a nursing intervention?
This nursing care plan and diagnosis with nursing interventions is for the following conditions: Hypothermia, Low Body Temperature, Inablility to Regulate Body Temperature.
What to do for hypothermia?
Passive rewarming. For someone with mild hypothermia, it is enough to cover them with heated blankets and offer warm fluids to drink.
How to help someone with hypothermia?
Be gentle. When you're helping a person with hypothermia, handle him or her gently. Limit movements to only those that are necessary. Don't massage or rub the person. Excessive, vigorous or jarring movements may trigger cardiac arrest.
How to raise body temperature?
Depending on the severity of hypothermia, emergency medical care for hypothermia may include one of the following interventions to raise the body temperature: 1 Passive rewarming. For someone with mild hypothermia, it is enough to cover them with heated blankets and offer warm fluids to drink. 2 Blood rewarming. Blood may be drawn, warmed and recirculated in the body. A common method of warming blood is the use of a hemodialysis machine, which is normally used to filter blood in people with poor kidney function. Heart bypass machines also may need to be used. 3 Warm intravenous fluids. A warmed intravenous solution of salt water may be put into a vein to help warm the blood. 4 Airway rewarming. The use of humidified oxygen administered with a mask or nasal tube can warm the airways and help raise the temperature of the body. 5 Irrigation. A warm saltwater solution may be used to warm certain areas of the body, such as the area around the lungs (pleura) or the abdominal cavity (peritoneal cavity). The warm liquid is introduced into the affected area with catheters.
How to warm blood?
Heart bypass machines also may need to be used. Warm intravenous fluids. A warmed intravenous solution of salt water may be put into a vein to help warm the blood.
What is the best way to warm up the body?
Irrigation . A warm saltwater solution may be used to warm certain areas of the body, such as the area around the lungs (pleura) or the abdominal cavity (peritoneal cavity). The warm liquid is introduced into the affected area with catheters.
How to protect yourself from cold weather?
Cut away clothing if necessary to avoid excessive movement. Cover the person with blankets. Use layers of dry blankets or coats to warm the person. Cover the person's head, leaving only the face exposed. Insulate the person's body from the cold ground.
What causes the body temperature to drop?
Heat applied to the arms and legs forces cold blood back toward the heart, lungs and brain, causing the core body temperature to drop. This can be fatal. Don't apply direct heat. Don't use hot water, a heating pad or a heating lamp to warm the person.
