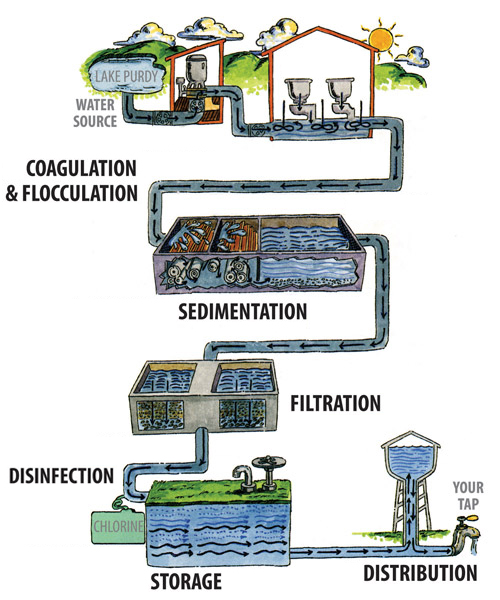
What is the first step in water treatment?
Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water. The positive charge of these chemicals neutralizes the negative charge of dirt and other dissolved particles in the water.
What are the processes of a raw water treatment facility?
Specific treatment processes vary, but a typical raw water treatment facility process will usually include the following steps: Raw water (untreated water found naturally in the environment) can come from many sources, including rivers, lakes, oceans, or groundwater.
What are the general steps in purification of drinking water?
General steps in purification of drinking water includes. 1. Aeration: Raw water is first collected in large aeration tank and the water is aerated by bubbling compressed air through perforated pipes. 2. Storage or settling: 3. Coagulation: 4. Filtration: 5. Disinfection:
What are the different methods of water treatment?
Public drinking water systems use various methods of water treatment to provide safe drinking water for their communities. Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment.
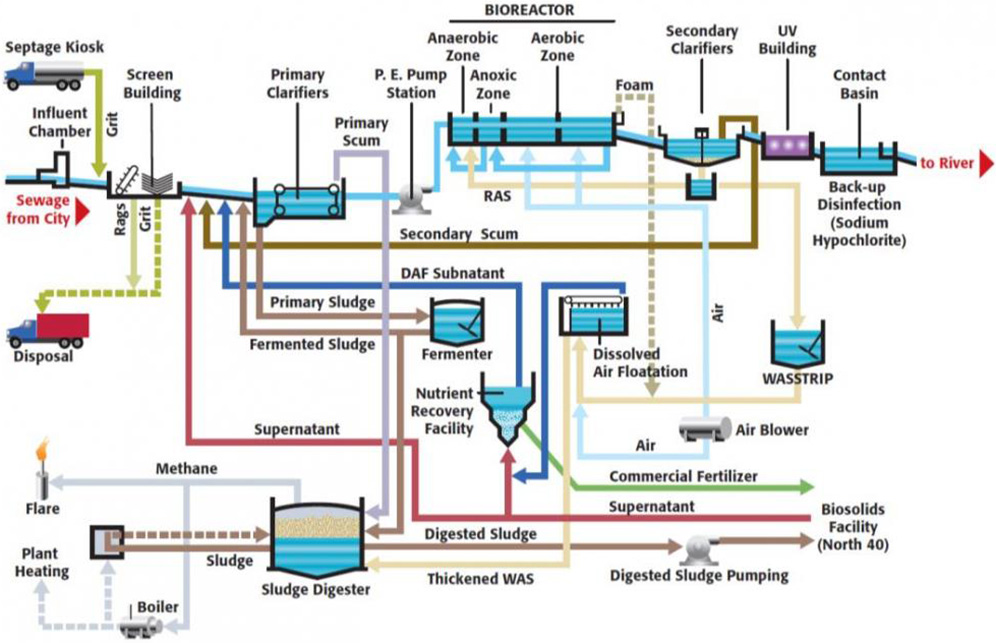
What is the step of raw water treatment?
The raw water is delivered to the headworks of the water treatment plant where the first of 5 major unit water treatment processes start the treatment to make the water safe to drink. The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below).
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
THE 5 STAGES OF WATER TREATMENTScreening. As water enters a water treatment plant, either from lakes, rivers, or the ground, it passes through a screening. ... Coagulation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What are the 3 steps of water treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
What is first step of raw water treatment Mcq?
Water Treatment MCQ Question 2 Detailed Solution The correct answer is Filtration. Filtration is a process used to separate solids from liquids or gases by using a filter medium that allows fluid to pass through but not solid.
What are the 4 main steps to water treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What is the fourth step of raw water treatment?
In the fourth step called ozonation, plant workers add a gas called ozone to destroy bacteria and other microorganisms as well as to improve taste. From there, the water is filtered using granular activated carbon to remove any fine particles.
What is the first stage in the treatment of wastewater?
Primary treatmentPrimary treatment (stage 1) Primary wastewater treatment involves sedimentation. This is when wastewater is temporarily held in large sedimentation tanks to remove settleable solids. With gravity, heavier solids sink to the bottom while lighter solids rise to the top.
What is the first step in primary treatment plant?
Wastewater Primary Treatment is the first step in the water treatment process meant for removing suspended solids (TSS), oil and grease, colour, and odour. The key components in this step are screens, grit chamber, flow equalization tank, and clarifier.
What is primary water treatment?
Primary Treatment As sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. After sewage has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.
What is the first step in primary sewage treatment plant Mcq?
1. What is the first step in primary sewage treatment plants? Explanation: Sewage treatment is one of the efficient ways to reduce the pollution load happening on marine waters. The primary treatment first undergoes for course screening which then proceeds to other steps like fine screening and all.
What is the next step after water abstraction in wastewater treatment Mcq?
5. What is the next step after water abstraction in wastewater treatment? Explanation: Initially, water is abstracted from the river, lake or water table and has a certain quality. Hence water is sent for treatment, where it undergoes transformation to be able to comply with intended uses.
What is the need of the water treatment process?
Water treatment removes contaminants and undesirable components, or reduces their concentration so that the water becomes fit for its desired end-use. This treatment is crucial to human health and allows humans to benefit from both drinking and irrigation use.
What are the steps of water treatment?
Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water.
How does a water treatment unit work?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1 Remove specific contaminants 2 Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3 Improve the taste of drinking water
What is the process of boiled water?
Distillation is a process in which impure water is boiled and the steam is collected and condensed in a separate container, leaving many of the solid contaminants behind. Disinfection. Disinfection is a physical or chemical process in which pathogenic microorganisms are deactivated or killed.
Why is surface water more contaminated than ground water?
Typically, surface water requires more treatment and filtration than ground water because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more sediment and pollutants and are more likely to be contaminated than ground water. Some water supplies may also contain disinfections by-products, inorganic chemicals, organic chemicals, and radionuclides.
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
The most common types of household water treatment systems consist of: Filtration Systems. A water filter is a device which removes impurities from water by means of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or biological process. Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water.
Why is chlorine added to water?
After the water has been filtered, a disinfectant (for example, chlorine, chloramine) may be added in order to kill any remaining parasites, bacteria, and viruses, and to protect the water from germs when it is piped to homes and businesses.
Why do people use water treatment units?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: Remove specific contaminants. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system. Improve the taste of drinking water.
How is drinking water purified?
1. Aeration: Raw water is first collected in large aeration tank and the water is aerated by bubbling compressed air through perforated pipes. Aeration removes bad odors and CO2.
How long does aerated water stay in a settling tank?
2. Storage or settling: Aerated water is then placed in settling tank and stored for 10-14 days. During storage about 90% of suspended solids settle down within 24 hrs and the water becomes clear.
How long does it take for a bacterial to die in water?
Similarly pathogenic bacteria gradually die and bacterial count decreases by 90% in first in first 5-7 days of storage. During storage organic matter present in water is oxidized by microorganisms.
