What is the latest treatment for HIV?
A treatment that is accepted as best for the initial treatment of a condition or disease. The recommended first-line HIV treatment regimens include antiretroviral (ARV) drugs that are safe, effective, and convenient for most people with HIV who have never taken ARVs before.
What is the best medicine for HIV?
2 rows · Guidelines from the British HIV Association (BHIVA) list a range of options for people taking ...
What is the newest HIV drug?
What is HIV treatment? HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months.
What is first line HIV therapy?
First-line treatment for children is based on a combination of at least 3 antiretroviral drugs. Zidovudine and lamivudine remain the first-choice nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. The lopinavir + ritonavir combination is the first-choice HIV protease inhibitor, but the oral solution is poorly accepted by children because of its unpleasant taste and the high ethanol content of the …

What is second-line treatment for HIV?
A boosted protease inhibitor (bPI) plus two nucleoside analogues (NRTIs) are recommended for second-line ART. ATV/r and LPV/r are the preferred bPIs for second-line ART. Simplification of second NRTI options is recommended.
What is first line and second-line treatment for HIV?
First-line ART regimens consisted of two nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs; zidovudine or stavudine and lamivudine) and one non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI; nevirapine or efavirenz), while second-line consisted of ritonavir-boosted lopinavir with 2 NRTIs.Aug 22, 2017
What is HIV 1 and treatment?
There's currently no cure or vaccine for HIV-1. However, it can be managed through the use of antiretroviral drugs. When these medications are taken daily as prescribed, viral load can become undetectable. This helps prevent the virus from causing further damage to the immune system.Mar 24, 2021
What is first line ART treatment?
Preferred first Line regimens drugs are TDF + 3TC + EFV (FDC) while Alternative regimen are AZT + 3TC + EFV,AZT + 3TC + NVP and TDF + 3TC + NVP [4, 5]. The first ART regimen offers the best opportunity for effective virological suppression and immune recovery [5, 6].Dec 3, 2019
What is the first line regimen in SA?
The preferred first-line ART regimen is tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-lamivudine-dolutegravir (TLD) for those clients ini a ng ART, experiencing side-effects to EFV, or for those who prefer to use DTG after being given all the necessary informa on.Oct 12, 2019
What is first line drug?
a drug that is the first choice for treating a particular condition because it is considered a very effective treatment for that condition with the least likelihood of causing side effects. A first-line medication may be a class of drugs (e.g., SSRIs for depression) as well as a single drug.
Which are the 5 antiretroviral drugs?
These drugs block a protein that infected cells need to put together new HIV virus particles.Atazanavir or ATV (Reyataz)Darunavir or DRV (Prezista)Fosamprenavir or FPV (Lexiva)Indinavir or IDV (Crixivan)Lopinavir + ritonavir, or LPV/r (Kaletra)Nelfinavir or NFV (Viracept)Ritonavir or RTV (Norvir)More items...•Jul 28, 2020
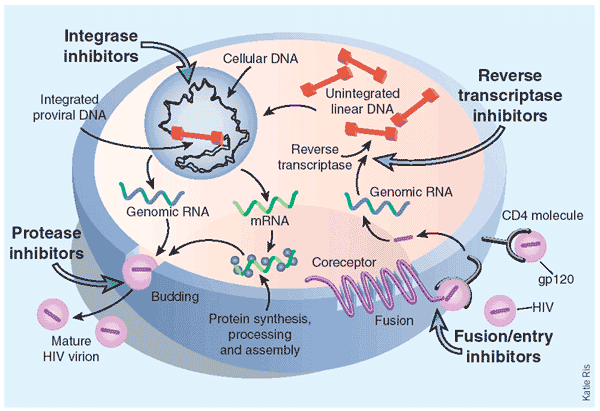
What are the 6 classes of antiretroviral drugs?
These drugs are distributed into six distinct classes based on their molecular mechanism and resistance profiles: (1) nucleoside-analog reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), (2) non–nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), (3) integrase inhibitors, (4) protease inhibitors (PIs), (5) fusion inhibitors, ...
What treatment is given for low CD4 count?
Antiretroviral drugs interrupt this process. The aim of treatment is to reduce levels of HIV in your body (often called your 'viral load'), so your CD4 count increases and your body's ability to fight infections improves.Jan 29, 2021
WHO recommended PEP regimen?
Wherever PEP is indicated and source is ART naive or unknown: recommended regimen is Tenofovir 300 mg + Lamivudine 300 mg + Efavirenz 600 mg once daily for 28 days. Wherever available, single pill containing these formulations should be used. Dual drug regimen should not be used any longer in any situation for PEP.
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is n...
When should I start treatment?
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the vir...
What if I delay treatment?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infecti...
What are the benefits of taking my HIV medicine every day as prescribed?
Treatment Reduces the Amount of HIV in the Blood The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load. Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will h...
Does HIV medicine cause side effects?
HIV medicine can cause side effects in some people. However, not everyone experiences side effects. The most common side effects are Nausea and vom...
Will HIV treatment interfere with my hormone therapy?
There are no known drug interactions between HIV medicine and hormone therapy. Talk to your health care provider if you are worried about taking HI...
What if my treatment is not working?
Your health care provider may change your prescription. A change is not unusual because the same treatment does not affect everyone in the same way.
Sticking to my treatment plan is hard. How can I deal with the challenges?
Tell your health care provider right away if you’re having trouble sticking to your plan. Together you can identify the reasons you’re skipping med...
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
Taking HIV medication consistently, as prescribed, helps prevent drug resistance. Drug resistance develops when people with HIV are inconsistent with taking their HIV medication as prescribed. The virus can change (mutate) and will no longer respond to certain HIV medication. If you develop drug resistance, it will limit your options ...
How long does it take to get rid of HIV?
There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission ...
Does HIV harm the immune system?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infections. This will put you at higher risk for transmitting HIV to your sexual and injection partners.
Can HIV be transmitted through sex?
If you have an undetectable viral load, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex. Having an undetectable viral load may also help prevent transmission from injection drug use.
Can I take pills at work?
A busy schedule. Work or travel away from home can make it easy to forget to take pills. It may be possible to keep extra medicine at work or in your car. But talk to your health care provider first. Some medications are affected by extreme temperatures and it is not always possible to keep medications at work.
Can you take a medicine if you missed it?
Missing a dose. In most cases, you can take your medicine as soon as you realize you missed a dose. Then take the next dose at your usual scheduled time (unless your pharmacist or health care provider has told you something different).
What is the HIV test?
Throughout your HIV disease, you will often use two test results: CD4 count, which is the number of an important type of immune cell, and HIV level ( viral load ), which is the amount of HIV found in a sample of your blood. Taken together with other blood tests, these results will give you a picture of the health of your immune system as it reacts to the HIV.
How should HIV treatment decisions be driven?
Project Inform believes that HIV treatment decisions should be driven by a combination of the best available medical data, a person's unique life situation, medical history, and personal preference. We also recognize that in most diseases earlier treatment usually leads to better treatment outcomes. There's no evidence to suggest this would not be true for HIV disease. Your doctor may have strong opinions about when to start therapy or which regimen is best for you. Your opinion and your concerns count too. Share your concerns with your doctor (s) so they can help you build the best strategy for you. Project Inform's publication, Building a Cooperative Doctor/Patient Relationship, offers tips.
Can you take HIV therapy?
Taking therapy can greatly slow the course of your HIV disease, extend your life and improve your quality of life. It may also cause side effects. You have time to get informed about your HIV disease as well as about when to start and what to start. This publication can help you do that.
Can HIV drugs lower CD4?
Being on effective HIV drugs should lower your HIV level as low as possible (preferably to undetectable) and increase your CD4 count. This should happen without causing debilitating side effects or harming your quality of life. The regimen should be easy enough to take so you can take each dose as prescribed (adhere well).
Do NNRTIs work with HIV?
NNRTIs work differently than NRTIs, but they act against HIV at the same place in its replication cycle. In first line therapy, NNRTIs are regularly used with two NRTIs. Regimens with Sustiva (efavirenz) have been compared to several other combinations and have consistently proven both potent and long-lasting. Sustiva is listed in the Guidelines as a preferred first line drug.
Is Fuzeon a first line drug?
The other two classes of HIV drugs are not recommended for first line use. The fusion inhibitor Fuzeon (enfuvirtide/T20) hasn't been studied in this way, and it's given as a shot twice a day. The CCR5 drug Selzentry (maraviroc) has been studied as part of first line therapy, but it failed to match up to Sustiva's potency. The integrase inhibitor Isentress (raltegravir) is now being studied, but very little data have been seen from it.
Is HIV medication easy to take?
If HIV drugs were easy to take, free from side effects and always worked in spite of resistance, then making decisions about when to start would be easy. While none are ideal, HIV medicines have improved over time, making them easier to take and generally more tolerable. The trick is to balance the benefits of reducing your HIV level and increasing your CD4 count along with the risks of side effects and treatment failure. These examples help make dealing with this struggle clearer. Each has its own possible benefits and disadvantages. These pros and cons are explained, but the only "right" answer for your situation comes from carefully considering both sides.
