
Medication
Jun 06, 2018 · Administered as a slow infusion at 10 mg/kg IV (max dose 17 mg/kg or 100 mg/min depending on guidelines used) Discontinue at conversion to sinus rhythm conversion or at the onset of hypotension. The current literature and guidelines both support Procainamide as a …
Procedures
Sep 02, 2021 · Ventricular tachycardia, also called VT or V-tach, is a type of abnormal heart rhythm that occurs when the heart beats too fast. It is a potentially life-threatening condition that can result in heart attack, stroke, or sudden cardiac arrest.Depending on the severity of the condition, the best treatment aims to:
Self-care
The vasopressor that is used for the treatment of VF/Pulseless VT is epinephrine. Epinephrine is primarily used for its vasoconstrictive effects. Which medication therapy is first line treatment for stable supraventricular tachycardia SVT )? Adenosine is the first-line medical treatment for the termination of paroxysmal SVT.
Nutrition
Oct 20, 2021 · What is the first line treatment for ventricular tachycardia? Anti-arrhythmic medications are the first-line therapy in emergency departments and CCUs, as discussed earlier. Amiodarone is most commonly used, along with lidocaine, and in some cases procainamide.
Which medications are used in the treatment of ventricular tachycardia (VT)?
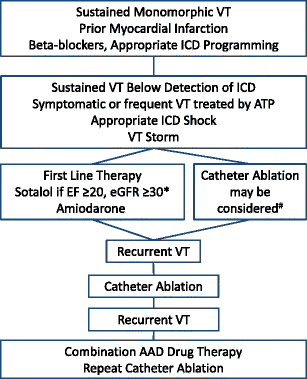
Dec 05, 2017 · In stable patients with monomorphic VT and normal LV function, restoration of sinus rhythm is typically achieved with intravenous (IV) procainamide, amiodarone, or sotalol. Lidocaine may also be...
What is the long term treatment for monomorphic ventricular tachycardia?
2 days ago · Researchers reported that ablation after first ICD shock for ventricular tachycardia was associated with lower risk for the primary endpoint compared with standard care (HR = 0.11; 95% CI, 0.01-0 ...
How do you treat tachycardia in a stable patient?
Mar 03, 2022 · What Is The First Line Treatment For Ventricular Tachycardia? Emergency departments and treatment centers use anti-arrhythmic medication as the main therapy. Lidorasal, along with animadarone, and procainamide may also be taken.
What are the goals of ventricular tachycardia treatment?

What is the drug of choice for ventricular tachycardia?
Amiodarone is the drug of choice for the treatment of hemodynamically unstable VT that is refractory to other antiarrhythmic agents. Prehospital studies currently suggest that amiodarone is safe and efficacious for use in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.Dec 5, 2017
What is the first thing to do for ventricular tachycardia?
If you have ventricular tachycardia, you may be given medications called anti-arrhythmics by mouth or IV to slow the fast heart rate. Other heart medications, such as calcium channel blockers and beta blockers, may be prescribed with anti-arrhythmic drugs.Feb 2, 2022
Does VT always require immediate cardioversion?
Individuals suffering from pulseless VT or unstable VT are hemodynamically compromised and require immediate electric cardioversion to shock them out of the VT rhythm.
When do you use adenosine vs amiodarone?
If QRS is wider than 0.12 seconds, establish IV access and obtain a 12 lead ECG. Consider adenosine only if the rhythm is regular and monomorphic. Consider antiarrhythmic infusions such as procainamide, amiodarone, or sotalol IV. Consider an expert consultation.Jul 2, 2021
How is Vtach ACLS treated?
Apply defibrillator pads (or paddles) and shock the patient with 120-200 Joules on a biphasic defibrillator or 360 Joules using a monophasic. Continue High Quality CPR for 2 minutes (while others are attempting to establish IV or IO access).
Which medication therapy is first line treatment for stable supraventricular tachycardia SVT )?
Adenosine (Adenocard) Adenosine is the first-line medical treatment for the termination of paroxysmal SVT.Apr 5, 2017
How is asystole treated?
Asystole is treated by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) combined with an intravenous vasopressor such as epinephrine (a.k.a. adrenaline). Sometimes an underlying reversible cause can be detected and treated (the so-called "Hs and Ts", an example of which is hypokalaemia).
How is pulseless VT treated?
Medical treatment of pulseless VT usually is carried out along with defibrillation and includes intravenous vasopressors and antiarrhythmic drugs. 1 mg of epinephrine IV should be given every 3 to 5 minutes. Epinephrine can be replaced by vasopressin given 40 units IV once.Aug 9, 2021
How do you treat stable VT?
In stable patients with monomorphic VT and normal LV function, restoration of sinus rhythm is typically achieved with intravenous (IV) procainamide, amiodarone, or sotalol. Lidocaine may also be used, but this agent may have common and limiting side effects and, consequently, increase the overall mortality risk.
What is the difference between adenosine and atropine?
Atropine is the first-line treatment for symptomatic bradycardia, except for patients with a heart transplant. The first-line treatment for stable patients with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a vagal maneuver. Adenosine is used for narrow complex, regular SVT if vagal maneuvers do not work.Nov 1, 2019
Are adenosine and amiodarone the same?
Adenosine and amiodarone are antiarrhythmic agents that slow conduction, suppress premature heart beats, are used for the emergency treatment of supraventricular tachycardia [1–3], and are used for long-term treatment of atrioventricular tachycardia [4].Jun 14, 2017
Can you use adenosine for ventricular tachycardia?
Adenosine is safe and effective for differentiating wide-complex supraventricular tachycardia from ventricular tachycardia.Oct 9, 2009
What causes ventricular tachycardia?
Your heart rate is regulated by electrical signals sent to your heart muscle. Certain conditions can interfere with normal electrical signals and cause ventricular tachycardia:
What are the signs and symptoms of ventricular tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia goes away on its own in 30 seconds. However, sustained ventricular tachycardia can last more than 30 seconds and requires emergency treatment.
How is ventricular tachycardia diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms and take a complete medical history. They may order tests that include:
What can you do to prevent ventricular tachycardia?
Following your doctor’s treatment recommendations can help you prevent or manage episodes of the disease. In some cases, the causative factor (cardiovascular disorder, tumor, drugs, electrolyte imbalance, etc.) may need to be addressed and treated. It is also advised to adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes:
Top Best Treatment of Ventricular Tachycardia Related Articles
This procedure is used to treat abnormal heart rhythms. Depending on the type of arrhythmia and the presence of other heart disease, a nonsurgical ablation or a surgical ablation, may be performed. During a catheter ablation, catheters are advanced to the heart via blood vessels in the groin, neck, and arm.
What is the first line treatment for ventricular tachycardia?
Anti-arrhythmic medications are the first-line therapy in emergency departments and CCUs, as discussed earlier. Amiodarone is most commonly used, along with lidocaine, and in some cases procainamide.
What do you give someone in V tach?
Medication: A number of antiarrhythmic medications are used to prevent ventricular tachycardia. These include: Sotolol. Flecainide.
Can you live with ventricular tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia may last for only a few seconds, or it can last for much longer. You may feel dizzy or short of breath, or have chest pain. Sometimes, ventricular tachycardia can cause your heart to stop (sudden cardiac arrest), which is a life-threatening medical emergency.
What is the first treatment for tachycardia?
Pacemaker. Some types of tachycardias may be treated with a pacemaker. A pacemaker is a small device that’s surgically implanted under your skin. When the device senses an abnormal heartbeat, it sends an electrical pulse that helps the heart resume a normal beat.
Do you defibrillate v tach?
Ventricular tachycardia (v-tach) typically responds well to defibrillation. This rhythm usually appears on the monitor as a wide, regular, and very rapid rhythm.
What do you do in V tach?
Sustained ventricular tachycardia often requires urgent medical treatment, as this condition may sometimes lead to sudden cardiac death. Treatment involves restoring a normal heart rate by delivering a jolt of electricity to the heart. This may be done using a defibrillator or with a treatment called cardioversion.
What is a run of V tach?
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a fast, abnormal heart rate. It starts in your heart’s lower chambers, called the ventricles. VT is defined as 3 or more heartbeats in a row, at a rate of more than 100 beats a minute. If VT lasts for more than a few seconds at a time, it can become life-threatening.
What are the symptoms of tachycardia?
Unstable patients have signs or symptoms of insufficient oxygen delivery to vital organs as a result of the tachycardia. Such manifestations may include the following: 1 Dyspnea 2 Hypotension 3 Altered level of consciousness
Why do you need to have a catheter ablation?
In these patients, ablation is used to treat symptoms rather than to reduce the risk of sudden death. In patients with structurally normal hearts, catheter ablation can eliminate symptomatic VT arising from the right or left ventricle. Catheter ablation may also be used in patients with cardiomyopathy.
Can tachycardia cause cardiomyopathy?
Prolonged exposure to this (or any other) tachycardia may cause a tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy, which typically improves with medical or ablative treatment of the VT. [ 19] Pulseless VT. Pulseless VT, in contrast to other unstable VT rhythms, is treated with immediate defibrillation.
Can antiarrhythmics be used for VT?
Combinations of these therapies are often used when structural heart disease is present. Antiarrhythmic drugs have traditionally been the mainstays of treatment for clinically stable patients with VT. However, some patients experience unacceptable side effects or frequent recurrence of VT with drug therapy.
Does polymorphic VT recur?
Polymorphic VT in stable patients typically terminates on its own. However, it tends to recur. After sinus rhythm returns, the ECG should be analyzed to determine whether the QT interval is normal or prolonged. Polymorphic VT in patients with a normal QT interval is treated in the same manner as monomorphic VT.
Can VT cause hemodynamic collapse?
Sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) may lead to hemodynamic collapse. Consequently, these patients require urgent conversion to sinus rhythm. The strategy for conversion depends on whether the patient is hemodynamically stable or unstable.
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment