
Medication
Your healthcare provider may consider several factors, like:
- The severity of your UTI symptoms
- Your medical history, including allergies
- Your medication history and any antibiotics you’ve taken recently
- A urine culture to find out exactly what type of bacteria are causing your UTI
Self-care
Here are a few supplements that have been studied:
- D-Mannose. D-Mannose is a type of sugar that is found in cranberries. ...
- Bearberry leaf. Bearberry leaf is also known as uva ursi. ...
- Cranberry extract. Like cranberry juice, cranberry extract works by preventing bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract.
- Garlic extract. ...
What are the safest antibiotics for UTI?
Other ways to help manage a UTI:
- Drinking plenty of water may help to dilute your urine and help flush out bacteria that causes UTIs.
- Avoid coffee, alcohol and soft drinks that contain citrus juices and caffeine. ...
- Place a heating pad over your abdomen to help ease pressure and discomfort.
What is the best treatment for UTI?
Temporary relief for UTI includes mixing half teaspoon of baking soda with 8 ounces of water in a glass. This provides relief for the first warning signs of UTI. Increase consumption of water to further cleanse the body by flushing out harmful substances in the body. Cranberry juice is also a good remedy to fight UTI.
What is the over the counter medication for UTI?
Is there a temporary relief for UTI?
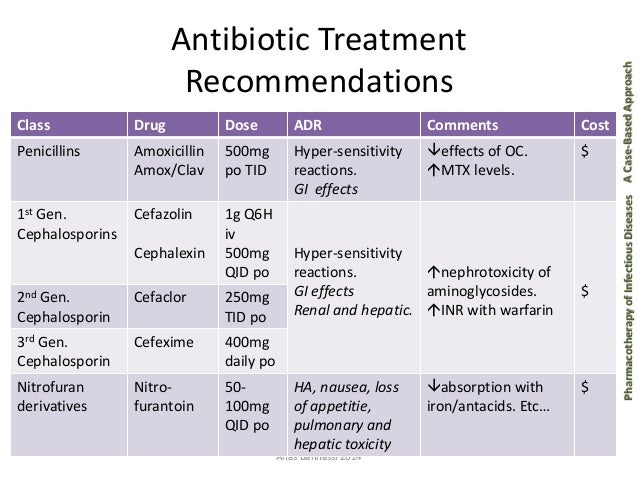
What is the best antibiotic for urinary tract infection?
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, and fosfomycin are the most preferred antibiotics for treating a UTI....Common doses:Amoxicillin/clavulanate: 500 twice a day for 5 to 7 days.Cefdinir: 300 mg twice a day for 5 to 7 days.Cephalexin: 250 mg to 500 mg every 6 hours for 7 days.
What is a first line medication treatment option for an uncomplicated UTI?
First-line treatment options for acute uncomplicated cystitis include nitrofurantoin (macrocrystals; 100 mg twice per day for five days), trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra; 160/800 mg twice per day for three days in regions where the uropathogen resistance is less than 20 percent), and fosfomycin (Monurol; ...
What is the gold standard for UTI treatment?
Urine culture is the gold standard for detection of urinary tract infection. However, asymptomatic bacteriuria is common, particularly in older women, and should not be treated with antibiotics. Conversely, in symptomatic women, even growth as low as 102 colony-forming unit/mL could reflect infection.
Is ciprofloxacin best for UTI?
Ciprofloxacin is considered to be the standard treatment for patients with complicated urinary tract infections (UTI).
Which is better for UTI cefuroxime or ciprofloxacin?
Bacteriologic eradication at end of therapy was similar between the two groups (97% ciprofloxacin, 95% cefuroxime axetil). Both treatments were equally well tolerated.
Will amoxicillin treat a UTI?
UTIs can cause infection and inflammation. Doctors commonly prescribe antibiotics such as amoxicillin to treat urinary tract infections and help you feel better. Taking amoxicillin to treat a urinary tract infection (UTI) should start helping you feel better within a few days.
How long should I take ciprofloxacin 500mg for UTI?
For urinary tract or serious kidney infections: Adults—250 to 500 milligrams (mg) 2 times a day, taken every 12 hours for 7 to 14 days. Children—Dose is based on body weight and must be determined by your doctor.
Is Augmentin good for UTI?
Augmentin is FDA-approved for treating UTI. According to the Infectious Diseases Society of America, Augmentin is not a first-choice antibiotic for UTI. It should be used when other medications such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole cannot be used.
What antibiotics are used for UTI?
Other antibiotics used to treat UTI include: 1 Beta-lactams, including penicillins and cephalosporins ( amoxicillin, Augmentin, Keflex, Duricef, Ceftin, Lorabid, Rocephin, Cephalexin, Suprax and others). Many organisms have shown resistance to some of these drugs. 2 Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole combination antibiotic (Bactrim DS and Septra DS). Many organisms have shown resistance to some of these drugs. 3 Fluoroquinolones ( Cipro, Levaquin and Floxin). The risk of antibiotic resistance to this is developing. These should not be given to pregnant women or children. 4 Tetracyclines (Sumycin, Vibramycin or Minocin) are used for Mycoplasma or Chlamydia infections. These should not be given to pregnant women or children. 5 Aminoglycosides (gentamicin, amikacin and tobramycin) are usually used in combination with other antibiotics to treat severe UTIs. 6 Macrolides ( clarithromycin, azithromycin and erythromycin) are often used to treat urinary problems caused by sexually transmitted diseases. 7 Fosfomycin ( Monurol) is a synthetic phosphonic acid derivative and used for acute cystitis but not for more complicated UTIs.
What is the UTI in the urinary tract?
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection of the bladder, kidneys, ureters, or urethra. E. coli, a type of bacteria that lives in the bowel and near the anus, causes most UTIs. UTI symptoms include pain, abdominal pain, mild fever, urinary urgency and frequency.
What are the symptoms of a UTI in a child?
Urinary Tract Infections in Children. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are very common in children. Symptoms and signs include fever and abdominal pain. Associated symptoms and signs include flank pain, vomiting , and blood in the urine. Treatment for a UTI involves antibiotic therapy.
How many tubes are there in the urinary system?
Urinary Tract Infection or Urinary Infection. The urinary system of your body includes two kidneys, two tubes (ureters), a urine sac (bladder) and an opening to expel the urine from the body (urethra).
What to do if you have a recurring urinary infection?
Treatment may include longer doses of antibiotics or more potent doses of antibiotics delivered intravenously.
How to prevent urinary tract infection?
To prevent urinary tract infection, some research suggests that the following may be helpful: Increasing fluid intake: The doctor may recommend increased fluid intake to help flush bacteria out of the urinary system. Drinking cranberry juice: Drinking 8 ounces of cranberry juice a day may help prevent recurrent UTIs.
What is the most common urological condition?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a bacterial infection that occurs anywhere in the urinary tract -- including the urethra ( urethritis ), bladder ( cystitis ), and kidney ( pyelonephritis ). These infections are among the most common urological conditions, with cystitis occurring most frequently, and both women and me n are susceptible.
How long should I take phenazopyridine for UTI?
This medication should not be taken for more than two days and has side effects that include headache, nausea, and changes in urine color (orange).
Is trimethoprim good for UTI?
Trimethoprim: Trimethoprim is the standard treatment for urinary tract infections in otherwise-healthy adults. It is one of the more potent UTI antibiotics, so most patients only require a three-day course. Trimethoprim is generally well-tolerated with few side effects, which generally include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea/constipation or stomach pain.
What to do if you have a UTI while taking antibiotics?
Call your doctor if you develop any side effects while taking your antibiotic. Sometimes other illnesses, such as sexually transmitted diseases, have symptoms similar to UTIs. Your doctor can determine if a UTI or different illness is causing your symptoms and determine the best treatment.
What is a UTI?
What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)? UTIs are common infections that happen when bacteria, often from the skin or rectum, enter the urethra, and infect the urinary tract. The infections can affect several parts of the urinary tract, but the most common type is a bladder infection (cystitis).
Why are UTIs more common in women?
UTIs are more common in women and girls because their urethras are shorter and closer to the rectum, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
What age group is most likely to get UTIs?
Age (older adults and young children are more likely to get UTIs) Structural problems in the urinary tract, such as prostate enlargement. Poor hygiene, particularly in children who are potty-training.
What are the factors that increase the risk of UTI?
Other factors that can increase the risk of UTIs: A previous UTI. Sexual activity, and especially a new sexual partner. Changes in the bacteria that live inside the vagina (vaginal flora), for example caused by menopause or use of spermicides. Pregnancy.
Can a UTI cause vomiting?
Fever. Chills. Lower back pain or pain in the side of your back. Nausea or vomiting that your child may have a UTI. Younger children may not be able to tell you about UTI symptoms they are having. While fever is the most common sign of UTI in infants and toddlers, most children with fever do not have a UTI.
Can antibiotics cause diarrhea?
However, any time you take antibiotics, they can cause side effects. Side effects can range from minor reactions, such as a rash, to very serious health problems, such as antibiotic-resistant infections or C. diff infection, which causes diarrhea that can lead to severe colon damage and death. Call your doctor if you develop any side effects ...
What is the treatment for bladder infection?
In addition to antibiotics, there are some emerging treatment options, including d-mannose, a sugar that can be taken orally to stop the proliferation of bacteria in the bladder. This is a newer drug and has not yet been incorporated into routine clinical practice.
What is the name of the drug that is used in UTIs?
Nitrofurantoin (brand name Macro bid): This drug is used in 32% of UTIs in the United States. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim): This combination of two drugs is used in 26% of UTIs in the United States. Fosfomycin (Monurol): This newer drug only has to be taken one time, but it's expensive and rarely prescribed.
When is the next UTI?
June 11, 2020. June 18, 2020. Ladies, if you think you have a urinary tract infection, you are probably right. One study found that women who self-diagnose a UTI are right 84% of the time. You can apply this know-how to partner with your health care provider to pick the right treatment The go-to treatment of a UTI, which is caused by a bacteria, ...
What is the best way to treat urinary tract infections?
Drinking unsweetened cranberry juice is one of the most well-known natural remedies for urinary tract infections. Cranberries work by preventing bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract, thus preventing infection ( 13. Trusted Source. , 14.
How to prevent urinary tract infection?
Preventing urinary tract infections starts with practicing a few good bathroom and hygiene habits. First, it’s important not to hold urine for too long. This can lead to a buildup of bacteria, resulting in infection ( 26. Trusted Source.
What is the best way to prevent UTIs?
Cranberry extract: Like cranberry juice, cranberry extract works by preventing bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract. Garlic extract: Garlic has been shown to have antimicrobial properties and may be able to block the growth of bacteria to prevent UTIs ( 32. Trusted Source. , 33.
How to get rid of a bad gut bacteria?
Take a Probiotic . Probiotics are beneficial microorganisms that are consumed through food or supplements. They can promote a healthy balance of bacteria in your gut. Probiotics are available in supplement form or can be found in fermented foods, such as kefir, kimchi, kombucha and probiotic yogurt.
How to prevent a UTI infection?
Without further ado, here are the top 6 home remedies to fight UTI. 1. Drink Plenty of Fluids. Hydration status has been linked to the risk of urinary tract infection.
What are the most common causes of UTIs?
Bacteria from the bowel are the most common cause of UTIs, but fungi and viruses can also cause infection ( 1. Trusted Source. ). The two strains of bacteria Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus saprophyticus account for about 80% of cases ( 2. Trusted Source. ). Common symptoms of UTI include ( 1. Trusted Source.
Why are women more prone to infection?
This is because the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the bladder, is shorter in women than men. This makes it easier for bacteria to enter and reach the bladder ( 2. Trusted Source. ).
How long should you take antibiotics for a recurrent UTI?
For recurrent UTIs, there are several antibiotic options for prevention: A shorter course (3 days) of antibiotics at the first sign of UTI symptoms; a prescription may be given to you to keep at home, but testing should be done at least once to confirm you have a UTI and not another problem.
What is the first line of antibiotics?
First-line options are usually selected from nitrofurantoin, fosfomycin and sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim. Amoxicillin/clavulanate ( Augmentin) and certain cephalosporins, for example cefpodoxime, cefdinir, or cefaclor may be appropriate options when first-line options cannot be used.
What causes most UTIs in women?
Most UTIs in women (roughly 85%) are caused by a bacteria known as Escherichia coli (E. coli). Other types of bacteria, such as Staphylococcus saprophyticus may infrequently be present. UTI symptoms in women and men are similar. However, urinary tract infections occur more frequently in women than in men.
How much does a UTI cost?
Roughly 40% of women experience a UTI at some time, and in women, it is the most common infection. Healthcare costs related to UTIs exceed $1.6 billion per year. A urinary tract infection (UTI) can happen anywhere along your urinary tract, which includes the kidneys (the organ that filters the blood to make urine), ...
What is it called when bacteria get into the bladder?
A lower urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria gets into the urethra and is deposited up into the bladder -- this is called cystitis . Infections that get past the bladder and up into the kidneys are called pyelonephritis.
Why do women get UTIs?
Women are also more likely to get an infection after sexual activity or when using a diaphragm and spermicide for birth control. Other risk factors for the development of UTIs include catheter use, urinary tract structural abnormalities, diabetes, and a suppressed immune system.
How long does it take to get rid of cystitis?
Length of treatment for cystitis can range from a single, one-time dose, to a course of medication over 5 to 7 days. Kidney infections may require injectable treatment, hospitalization, as well as a longer course of antibiotic, depending upon severity of the infection.

Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment