Quinolones and cotrimoxazole are found to reach the renal tissue and urine in adequate concentrations; hence are widely used as treatment options for UTI
Urinary Tract Infection
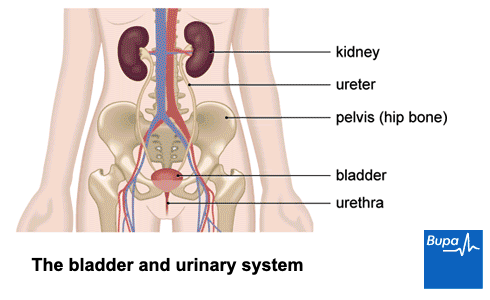
Infection of any part of the urinary system, including kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
What are the safest antibiotics for UTI?
Your healthcare provider may consider several factors, like:
- The severity of your UTI symptoms
- Your medical history, including allergies
- Your medication history and any antibiotics you’ve taken recently
- A urine culture to find out exactly what type of bacteria are causing your UTI
What is the best OTC for UTI?
- TREAT YOUR URINARY TRACT INFECTION EARLY. Early treatment is the key to fast UTI relief and preventing more serious problems. ...
- TRUST THE SAME TYPE OF UTI TESTS MANY DOCTORS USE. AZO Test Strips offer you the most reliable, over-the-counter UTI home test available. ...
- 2 TESTS IN 1. ...
- ACCURATE Trust AZO to give you accurate results. ...
- FAST. ...
How long before antibiotics work with UTI?
Within the first 1 to 2 days of starting your antibiotics, you’ll probably notice your UTI symptoms start to fade away. If your UTI is more severe or you’ve had symptoms for a while before starting antibiotics, it might take a few more days for you to notice improvement.
How many days should you take Bactrim for UTI?
How many days should you take Bactrim for UTI? Adults: The usual adult dosage in the treatment of urinary tract infections is 1 BACTRIM DS (double strength) tablet or 2 BACTRIM tablets every 12 hours for 10 to 14 days. An identical daily dosage is used for 5 days in the treatment of shigellosis. Click to read full answer.

What is the best antibiotic for UTI with kidney disease?
Quinolones and cotrimoxazole are found to reach the renal tissue and urine in adequate concentrations; hence are widely used as treatment options for UTI in CKD.
What is the first line medication therapy for a patient with chronic kidney failure?
The use of ACE inhibitors and ARBs has been found to slow progression of CKD and is considered first-line treatment in patients with albuminuria.
What antibiotics can CKD patients take?
Penicillins are generally well tolerated in patients with kidney disease. Hypersensitivity reactions are commonly reported, and an association between penicillins and interstitial nephritis exists, but patients with kidney disease are not considered to be at higher risk (10).
Is ciprofloxacin safe for CKD patients?
**Ciprofloxacin is not usually an appropriate empiric choice for UTI due to the significantly increased risk of Clostridium difficile infection in renal impairment. However due to the limited options available when managing UTI in patients with CKD 4 and 5 (also 3b in men) it may be used with caution.
Why are ACE inhibitors used in CKD?
Abstract. ACE inhibitors effectively reduce systemic vascular resistance in patients with hypertension, heart failure or chronic renal disease. This antihypertensive efficacy probably accounts for an important part of their long term renoprotective effects in patients with diabetic and non-diabetic renal disease.
Which of the following medications is the most appropriate initial treatment for a patient with chronic kidney disease and hypertension?
Both dihydropyridine and non-dihydropyridine CCBs are useful in the management of hypertension in CKD. Dihydropyridine CCBs (such as amlodipine) can be used as first-line therapy in non-proteinuric CKD, either alone or in combination.
Is nitrofurantoin safe in CKD?
Use of nitrofurantoin can be problematic for patients with renal dysfunction. Reduced renal function may lead to toxicity due to an increase in nitrofurantoin serum levels. Impaired renal function also decreases the efficacy of nitrofurantoin as an antibacterial medicine in the urinary tract.
Is levofloxacin safe in CKD?
Since levofloxacin is excreted mainly by the kidneys, the dose of Levofloxacin Tablets should be adjusted in patients with renal impairment....Levofloxacin 500 mg Film-coated Tablets.IndicationDaily dose regimen (according to severity)Duration of treatment (according to severity)Uncomplicated cystitis250 mg once daily3 days8 more rows
Does ciprofloxacin need renal adjustment?
In patients with severe infections and severe renal impairment, a unit dose of 750 mg may be administered at the intervals noted above....Dosage Modifications in Patients with Renal Impairment.Creatinine Clearance (mL/min)Dose5–29250–500 mg every 18 hours3 more rows•Apr 25, 2022
Is bactrim safe in CKD?
The double-strength tablet of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra), which is commonly prescribed, should be avoided unless the patient's creatinine clearance is known to exceed 50 mL per minute; the single-strength tablet of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is preferable.
Is Augmentin safe for kidney patients?
Kidney disease. If you have severe kidney disease, you should not take Augmentin XR. However, you may be able to take Augmentin, but your doctor may prescribe it at a lower dosage.
Is ofloxacin safe for kidneys?
The good absorption of ofloxacin after oral administration is not influenced by renal failure. Total plasma clearance (CL) is largely dependent on renal elimination of the drug, and renal clearance (CLR) and urinary recovery are reduced in parallel with reductions in renal function.
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Symptoms, Diagnosis, Medication
Bladder infections can be painful and often require medical treatment. Get the latest information on urinary tract infections...
Bladder Infections: UTI Causes, Symptoms, Treatments
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI's) can happen to anyone. Learn about symptoms, causes and home remedy treatments for bladder and...
Urinary Tract Infection Quiz
How would you know if you had urinary tract infection (UTI)? Take the Urinary Tract Infection in Adult Quiz to learn the causes,...
How long should you take antibiotics for a recurrent UTI?
For recurrent UTIs, there are several antibiotic options for prevention: A shorter course (3 days) of antibiotics at the first sign of UTI symptoms; a prescription may be given to you to keep at home, but testing should be done at least once to confirm you have a UTI and not another problem.
What is the first line of antibiotics?
First-line options are usually selected from nitrofurantoin, fosfomycin and sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim. Amoxicillin/clavulanate ( Augmentin) and certain cephalosporins, for example cefpodoxime, cefdinir, or cefaclor may be appropriate options when first-line options cannot be used.
What causes most UTIs in women?
Most UTIs in women (roughly 85%) are caused by a bacteria known as Escherichia coli (E. coli). Other types of bacteria, such as Staphylococcus saprophyticus may infrequently be present. UTI symptoms in women and men are similar. However, urinary tract infections occur more frequently in women than in men.
How much does a UTI cost?
Roughly 40% of women experience a UTI at some time, and in women, it is the most common infection. Healthcare costs related to UTIs exceed $1.6 billion per year. A urinary tract infection (UTI) can happen anywhere along your urinary tract, which includes the kidneys (the organ that filters the blood to make urine), ...
What is it called when bacteria get into the bladder?
A lower urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria gets into the urethra and is deposited up into the bladder -- this is called cystitis . Infections that get past the bladder and up into the kidneys are called pyelonephritis.
Why do women get UTIs?
Women are also more likely to get an infection after sexual activity or when using a diaphragm and spermicide for birth control. Other risk factors for the development of UTIs include catheter use, urinary tract structural abnormalities, diabetes, and a suppressed immune system.
How long does it take to get rid of cystitis?
Length of treatment for cystitis can range from a single, one-time dose, to a course of medication over 5 to 7 days. Kidney infections may require injectable treatment, hospitalization, as well as a longer course of antibiotic, depending upon severity of the infection.
What is the first line of treatment for urinary tract infections?
Antibiotics usually are the first line treatment for urinary tract infections. Which drugs are prescribed and for how long depend on your health condition and the type of bacteria found in your urine.
How long should I take antibiotics for a UTI?
For an uncomplicated UTI that occurs when you're otherwise healthy, your doctor may recommend a shorter course of treatment, such as taking an antibiotic for one to three days. But whether this short course of treatment is enough to treat your infection depends on your particular symptoms and medical history.
What kind of imaging is used to detect urinary tract infections?
If you are having frequent infections that your doctor thinks may be caused by an abnormality in your urinary tract, you may have an ultrasound, a computerized tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Your doctor may also use a contrast dye to highlight structures in your urinary tract.
How long does it take for a UTI to clear up?
Often, UTI symptoms clear up within a few days of starting treatment. But you may need to continue antibiotics for a week or more.
How to get rid of a urinary infection?
Avoid drinks that may irritate your bladder. Avoid coffee, alcohol, and soft drinks containing citrus juices or caffeine until your infection has cleared. They can irritate your bladder and tend to aggravate your frequent or urgent need to urinate.
Why do doctors ask for urine samples?
Your doctor may ask for a urine sample for lab analysis to look for white blood cells, red blood cells or bacteria. To avoid potential contamination of the sample, you may be instructed to first wipe your genital area with an antiseptic pad and to collect the urine midstream. Growing urinary tract bacteria in a lab.
How to prepare for a UTI appointment?
To prepare for your appointment: Ask if there's anything you need to do in advance, such as collect a urine specimen. Take note of your symptoms, even if you're not sure they're related to a UTI. Make a list of all the medications, vitamins or other supplements that you take. Write down questions to ask your doctor.
How Common Are UTIs?
According to the National Kidney Foundation, 20% of women will experience a UTI at some point in their life. Of those, one in five will have a second UTI, and 30% of that narrowed group will have a third. Additionally, 80% of women who have three UTIs will have repeat infections after that.
What Are the Most Common UTI Symptoms?
Frequent and painful urination are two of the most well-known symptoms of a UTI, but they aren’t the only ones. (It’s also possible, but uncommon, to experience no symptoms at all.) In general, the symptoms of a UTI vary according to what part of your urinary tract is affected.
How Are Most UTIs Diagnosed?
There are several ways that your physician can diagnose a UTI. To provide the best antibiotic treatment for UTI, he or she needs to determine the location of the infection and whether your UTI is complicated. He or she also needs to rule out other conditions that present similarly to UTI, such as vaginitis or certain sexually transmitted diseases.
Can Doctors Treat UTIs Via Telemedicine?
Telemedicine is an increasingly popular method of treating UTIs. In addition to being convenient, it’s also discreet and frequently more affordable than an in-office visit.
What Antibiotics Are Used To Treat Bacterial UTIs?
Once your physician has determined the location of your UTI and whether it’s complicated, he or she will likely suggest an antibiotic for treatment. Infections in the lower urinary tract are typically treated with oral medication (capsules, tablets, powders), while upper-tract UTIs usually merit intravenous (IV) antibiotics.
Do Cranberries Cure UTIs?
No home remedies for UTIs exist. Drinking water can help to flush the infection from your body faster, and keep you hydrated (thus better equipped to fight the infection) for example, but it’s not a “cure.”
Is There Any Other Way To Prevent a UTI?
While there’s no foolproof way to ensure you never have a UTI, there are strategies and behaviors that may lower your risk:
What is the MIC of 90% of UTI?
The MIC for 90% of the bacteria that commonly cause UTI is usually <16 μg/ml. Hence, there is a large safety range as long as the kidney can concentrate urine to some degree. Even though it is unlikely that cystitis would require parenteral therapy, it is pertinent to comment on the data in Table 1.
Is empiric carbapenem a good antibiotic for septic shock?
In the bacteremic patient with septic shock, an empiric carbapenem (imipenem or meropenem) is reasonable because of the high level of predictive efficacy versus E. coli, other Enterobacteriaceae, many enterococci, and P. aeruginosa.
Can you use nitrofurantoin alone?
In summary, antimicrobials with anticipated effectiveness in patients with urethritis/cystitis and chronic renal insufficiency are selected fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin) and trimethoprim alone. Nitrofurantoin should not be used because of low urine drug concentrations.
Can trimethoprim be used in cyst fluid?
Published reports indicate that effective concentrations of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin, and chloramphenicol can be achieved in the cyst fluid ( 3, 4 ). In contrast, penicillins, cephalosporins, and aminoglycosides do not achieve adequate cyst concentrations ( 19 ).
Can renal insufficiency cause UTI?
After adjustment for age, the frequency of UTI in patients with chronic renal insufficiency is not known to be different from that in the general population. On the one hand, the chronic disease that causes the renal insufficiency could reduce the risk for UTI as a result of reduction of risk factors such as sexual activity. Alternatively, the risk might be increased by disease factors ( e.g., papillary necrosis, nephrolithiasis, neurogenic bladder) and the management of comorbidities with Foley catheters and intravenous lines. No literature that addressed this question was found.
Is bacteriuria more common in women with diabetes than in women without diabetes?
Asymptomatic bacteriuria in women with diabetes is roughly three-fold greater than in women without diabetes, regardless of the degree of control of the hyperglycemia ( 9 ). Women with diabetes are more prone to severe cystitis, ascending pyelonephritis, and severe forms of pyelonephritis ( e.g., perinephric abscess, papillary necrosis) ( 9 ).
Is pyelonephritis a parenchymal infection?
A long-standing issue is whether UTI represent surface mucosal (uroepithelial) or parenchymal infections or both. Infections of the urethra are viewed as superficial, whereas pyelonephritis is considered a parenchymal infection. Cystitis ranges from mild (superficial) to invasion of the wall of the bladder.
What to take for a urinary infection?
For fever or discomfort, take a nonaspirin pain reliever such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or ibuprofen (Motrin IB, Advil, others). Stay hydrated. Drinking fluids will help flush bacteria from your urinary tract. Avoid coffee and alcohol until your infection has cleared.
How long does it take for a kidney infection to clear up?
Usually, the signs and symptoms of a kidney infection begin to clear up within a few days of treatment. But you might need to continue antibiotics for a week or longer. Take the entire course of antibiotics recommended by your doctor even after you feel better. Your doctor might recommend a repeat urine culture to ensure the infection has cleared.
What tests do you take to check for bacteria?
Your doctor might also take a blood sample for a culture — a lab test that checks for bacteria or other organisms in your blood. Other tests might include an ultrasound, CT scan or a type of X-ray called a voiding cystourethrogram.
How do antibiotics treat a UTI?
UTIs can be caused by many different types of germs including bacteria or fungi — and in rare cases, even viruses. But bacterial UTIs are the most common.
What antibiotics can treat a UTI?
Not all antibiotics work for treating UTIs, but several do. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, and fosfomycin are the most preferred antibiotics for treating a UTI. Here are a few important facts about those three.
What are potential side effects of antibiotics for UTI?
In addition to the notable side effects we’ve already covered, there are a few more potential antibiotic side effects you’ll want to know about.
How long do I need to take antibiotics to treat a UTI?
How long you take antibiotics for a UTI depends on how severe your UTI is and which antibiotic you’re prescribed. Some medications like fosfomycin only require one dose, while a more severe UTI might require 14 days — or more — of treatment. Most require 3 to 7 days of treatment.
Do I really need to take antibiotics for a UTI?
In most cases, it makes sense to start antibiotics if you know you have a bacterial UTI since this is the only way to treat it.
Can UTI symptoms linger after I take antibiotics?
Since UTI symptoms usually improve just a few days after starting antibiotics, you’ll want to talk to your healthcare provider if you notice that UTI symptoms are still hanging around after finishing your antibiotics.
Are there over-the-counter antibiotics for UTI treatment?
If you have a UTI and are noticing symptoms, chances are you’ll want to get rid of it as soon as possible. And since all antibiotics requires a prescription, you may wonder whether a quick trip to your local pharmacy for an over-the-counter UTI treatment might be worthwhile.

Overview
Causes
Clinical significance
Symptoms
Epidemiology
Treatment
Diagnosis
Results
Medical uses
Safety
Prognosis
Uses
Research
- Cranberry has been studied as a preventive maintenance agent for UTIs. According to one expert, the active ingredient in cranberries -- A-type proanthocyanidins (PACs) -- is effective against UTI-causing bacteria, but is only in highly concentrated cranberry capsules, not in cranberry juice. Cranberry seems to work by preventing bacteria from stick...
Risks
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
- Many people drink cranberry juice to prevent UTIs. There's some indication that cranberry products, in either juice or tablet form, may have infection-fighting properties. Researchers continue to study the ability of cranberry juice to prevent UTIs, but results are not conclusive. If you enjoy drinking cranberry juice and feel it helps you prevent ...
Preparing For Your Appointment