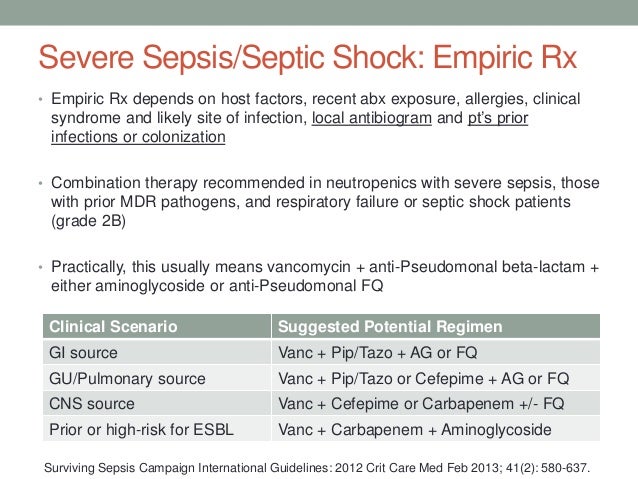
Are empiric antibiotics appropriate for severe sepsis and septic shock?
Conclusion: Empiric antibiotic therapy was acceptable for severe sepsis and septic shock patients treated in the ICU. The appropriate selection of empiric antibiotics was related to a greater rate of de-escalation and better survival.
What is the best treatment for sepsis?
They include: Antibiotics. Treatment with antibiotics should begin immediately. Intravenous fluids. People who have sepsis often receive intravenous fluids right away, usually within three hours. Vasopressors.
How important is timeliness of antibiotic administration in sepsis?
The totality of data indicates that timeliness of antibiotic administration is an important aspect of management for patients with septic shock but not invariably for septic patients without shock. For some patients with sepsis but no shock, prompt antibiotic therapy is important to optimize prognosis (eg, bacterial meningitis, purpura fulminans).
How can we improve time to infusion for antibiotics in septic patients?
There are many strategies that can improve time to infusion for the first dose of antibiotics in septic patients including improving access to antibiotics in EDs, floors, and ICUs and creating interdisciplinary teams that rapidly respond to patients with suspected sepsis.

What is the best antibiotic to treat sepsis?
The majority of broad-spectrum agents administered for sepsis have activity against Gram-positive organisms such as methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, or MSSA, and Streptococcal species. This includes the antibiotics piperacillin/tazobactam, ceftriaxone, cefepime, meropenem, and imipenem/cilastatin.
What is the first line treatment for sepsis?
The recommended first-line agent for septic shock is norepinephrine, preferably administered through a central catheter. Norepinephrine has predominant alpha-receptor agonist effects and results in potent peripheral arterial vasoconstriction without significantly increasing heart rate or cardiac output.
What is the treatment protocol for sepsis?
TreatmentAntibiotics. Treatment with antibiotics begins as soon as possible. ... Intravenous fluids. The use of intravenous fluids begins as soon as possible.Vasopressors. If your blood pressure remains too low even after receiving intravenous fluids, you may be given a vasopressor medication.
What are examples of empiric antibiotic therapy?
The most commonly used antibiotic for both empirical and adjusted therapy was amoxicillin/clavulanate (Table 2). Broad-spectrum antibiotics (cefepime, imipenem, meropenem, piperacillin/tazobactam) or vancomycin were initially administered to 95 patients (17.6%).
What is the gold standard for sepsis?
There is no 'gold standard' against which the diagnostic criteria can be calibrated.” In 2004 the Surviving Sepsis Campaign released its initial guidelines for sepsis management in the journals of Critical Care Medicine and Intensive Care Medicine.
Why is vancomycin used for sepsis?
It stands to reason that use of the maximum nontoxic dose of a concentration-dependent killing agent hastens clearance of infecting microorganisms and contributes to reduced mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock. Vancomycin is another antimicrobial that relies upon concentration-dependent killing effects.
How long is antibiotic treatment for sepsis?
The current Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC) guideline makes a general recommendation that 7 to 10 days of antibiotic coverage is likely sufficient for most serious infections associated with sepsis and septic shock, although this course may be lengthened in some scenarios (eg, undrained foci of infection, ...
What 6 interventions are delivered if sepsis is suspected?
Take blood cultures and consider source control. Administer empiric intravenous antibiotics. Measure serial serum lactates. Start intravenous fluid resuscitation.
When should antibiotics be given for patients with sepsis?
Treatment for sepsis You should get antibiotics within 1 hour of arriving at hospital. If sepsis is not treated early, it can turn into septic shock and cause your organs to fail. This is life threatening.
What is meant by empiric therapy?
Empirical Therapy, Empirical Treatment. Treatment given based on experience, without precise knowledge of the cause or nature of a disorder.
What is empiric antibiotic selection?
The empiric method of antibiotic selection makes use of this philosophy by using our observations of the patient (history, physical examination and laboratory test results) along with our past clinical experiences and the medical literature to scientifically select antibiotics.
What is empiric broad spectrum antibiotics?
Empiric antibiotic therapy refers to the use of antibiotics to treat a suspected bacterial infection despite lack of a specific bacterial diagnosis. Definitive diagnosis of the species of bacteria often occurs through culture of blood, sputum, or urine, and can be delayed by 24 to 72 hours.
How much does the risk of progression from severe sepsis to septic shock increase?
The risk of progression from severe sepsis to septic shock increases 8% for each hour before antibiotics are started. Selection of antimicrobial agents is based on a combination of patient factors, predicted infecting organism (s), and local microbial resistance patterns.
Is anaerobic coverage necessary for intra-abdominal infections?
Anaerobic coverage should be provided for intra-abdominal infections or others where anaerobes are significant pathogens. Empiric antifungal or antiviral therapy may be warranted. For patients with healthcare-associated infections, resistant micro-organisms will further complicate the choice of empiric antimicrobials.
Is broad spectrum antimicrobial therapy important?
Conclusion: Early administration of broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs is one of the most important, if not the most important, treatment for patients with sepsis or septic shock. Drugs should be initiated as soon as possible, and the choice of should take into account patient factors, common local pathogens, hospital antibiograms ...
What is the best treatment for sepsis?
Supportive care. People who have sepsis often receive supportive care that includes oxygen. Depending on your condition, you may need to have a machine help you breathe. If your kidneys have been affected, you may need to have dialysis.
How to treat septic shock?
A number of medications are used in treating sepsis and septic shock. They include: 1 Antibiotics. Treatment with antibiotics begins as soon as possible. Broad-spectrum antibiotics, which are effective against a variety of bacteria, are usually used first. After learning the results of blood tests, your doctor may switch to a different antibiotic that's targeted to fight the particular bacteria causing the infection. 2 Intravenous fluids. The use of intravenous fluids begins as soon as possible. 3 Vasopressors. If your blood pressure remains too low even after receiving intravenous fluids, you may be given a vasopressor medication. This drug constricts blood vessels and helps increase blood pressure.
What antibiotics are effective against a variety of bacteria?
Broad-spectrum antibiotics, which are effective against a variety of bacteria, are usually used first. After learning the results of blood tests, your doctor may switch to a different antibiotic that's targeted to fight the particular bacteria causing the infection. Intravenous fluids.
What tests can be done to determine if you have an infection in your lungs?
If the site of infection is not readily found, your doctor may order one or more of the following imaging tests: X-ray. X-rays can identify infections in your lungs. Ultrasound. This technology uses sound waves to produce real-time images on a video monitor.
What should a prescriber do after empiric antibiotics?
After the initiation of empiric antibiotics, prescribers should review the appropriateness of the antibiotic regimen chosen for opportunities to de-escalate or potentially even stop therapy . If the totality of diagnostic work suggests that the patient did not have sepsis and infection was unlikely, antibiotics should be discontinued. Antimicrobial stewardship program guidelines recommend a prescriber-led review of the antibiotic regimen that requires persuasive and enforced prompting of prescribers to achieve meaningful impact [ 85 ]. Examples of tools to aid prescribers to consider de-escalation include checklists, which when used in the ICU setting have resulted in reduced duration of antibiotic therapy, 72-hour antibiotics time-outs prompted by the HER, which have been shown to increase the rate of de-escalation, and antibiotic stop orders, which have been particularly helpful in stopping empiric vancomycin utilization [ 86, –, 88 ]. In addition, de-escalation of antibiotics in patient who are determined to have culture-negative sepsis has been shown to be safe, including a study of critically ill surgical patients [ 89 ].
What should hospitals implement to aid in the rapid and accurate diagnosis of septic patients?
Hospitals should implement quality improvement measures to aid in the rapid and accurate diagnosis of septic patients and to ensure antibiotics are given to patients in an expedited fashion after antibiotic order. empiric antibiotics, sepsis, septic shock, antimicrobial resistance. Topic:
What is an essential education pearl for nursing staff?
An essential education pearl for nursing staff is the order of administration of antibiotics in patients with sepsis or septic shock. Often patients are being started on broad-spectrum empiric therapy that provides coverage of MRSA and Pseudomonas species.
Is Candida an empiric disease?
Candida is often a consideration in patients who need empiric treatment, especially when the patients are neutropenic or have some other relevant immunodeficiency. Other yeasts, including Histoplasma, Coccidioides, Blastomyces, and Cryptococcus, can present with life- threatening syndromes that merit empiric therapy. Molds can cause severe morbidity and significant mortality especially in immunosuppressed patients, but molds rarely cause septic shock and usually present subacutely.
Is Sepsis a life threatening condition?
Sepsis is a syndrome that includes infection-related organ dysfunction that is not immediately life threaten ing, and infection-related organ dysfunction including shock that is immediately life threatening. For patients in whom the likelihood of infection is low, and the urgency of treatment is minimal, there are major advantages to avoiding a rush to judgment and obtaining serial observations and additional testing before initiating antibiotic therapy. Antibiotic therapy, even for a few doses, can lead to unnecessary cost, major toxicity, clinically important changes in microbial flora, and enhancement of drug resistance. For patients where the likelihood of infection is high but acuity is low, there may be ample time to collect data so that the initial antimicrobial regimen is targeted rather than broad. For patients where the acuity is high, or the outcome is likely to be affected adversely by delayed therapy, it is appropriate and prudent for hospitals to develop systems in which patients are expeditiously recognized and promptly treated with an antimicrobial regimen that is broad enough to cover all plausibly likely pathogens.
Is antibiotic therapy targeted or empiric?
Antibiotic therapy for sepsis can be empiric or targeted, depending on the information available at the time of initial decision. Empiric therapy is generally defined as the initial antibiotic regimen selected in the absence of definitive microbiological pathogen identification and susceptibility testing.
Abstract
Sepsis is a common consequence of infection, associated with a mortality rate > 25%. Although community-acquired sepsis is more common, hospital-acquired infection is more lethal. The most common site of infection is the lung, followed by abdominal infection, catheter-associated blood steam infection and urinary tract infection.
Background
Sepsis is a common and life-threatening illness in the ICU, requiring timely and effective antimicrobial therapy. The aims of this review are to identify the most common sites of sepsis, the likely pathogens, and the optimal approach to antimicrobial therapy.
Sepsis epidemiology, infection site and pathogens
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction syndrome caused by a dysregulated host response to infection, associated with a mortality rate over 25%, that has been designated a global health priority [ 1 – 3 ]. The majority of sepsis is community-acquired, and progression can be insidious, making diagnosis difficult [ 3, 4 ].
The importance of early appropriate and timely therapy
Timely administration of appropriate antibiotic therapy (i.e., with activity in vitro against the causative pathogens) is the cornerstone of the management of serious ICU infections [ 1 ]. Observational, prospective and retrospective studies support the use of appropriate empiric antibiotic therapy in sepsis and septic shock [ 16 – 19 ].
Biomarkers to guide sepsis therapy
Clinical and biological signs of sepsis are neither sensitive nor specific, particularly in older patients and the immunocompromised, making decisions about starting and stopping antibiotics challenging in ICU patients [ 5 ].
Antibiotic therapy: principles of use and new agents
While appropriate therapy refers to the use of an antimicrobial agent to which the etiologic pathogen is sensitive, it is also necessary to administer the right dose, at the optimal time, that penetrates into the site of infection.
Pneumonia: initial empiric therapy for CAP, HAP, VAP
Severe community acquired pneumonia (CAP) [ 56 – 59 ].
When did sepsis become a global health priority?
On May 2017, the World Health Assembly (WHA) and World Health Organization (WHO) made sepsis a global health priority and adopted a resolution that urged the 194 United Nations Member States to improve the prevention, diagnosis, and management of sepsis5.
What is the World Health Assembly's resolution on sepsis?
To improve sepsis management and reduce its burden, in 2017, the World Health Assembly and World Health Organization adopted a resolution that urged governments and healthcare workers to implement appropriate measures to address sepsis.
Is sepsis a global health problem?
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition caused by infection and represents a substantial global health burden. Recent epidemiological studies showed that sepsis mortality rates have decreased, but that the incidence has continued to increase.
Is lactate retained in sepsis?
First, lactate was not retained in the sepsis definition. Hence, by the Sepsis-3 definitions, patients with an increased lactate level but no hypotension (or compensated septic shock) can be missed.
Is lactate level a component of the definitions of septic shock?
That is, the lactate level is not a component of the definitions until the patient becomes hypotensive.
Does sepsis increase survival?
However, early detection of sepsis with timely, appropriate interventions increases the likelihood of survival for patients with sepsis. Also, performance improvement programs have been associated with a significant increase in compliance with the sepsis bundles and a reduction in mortality.
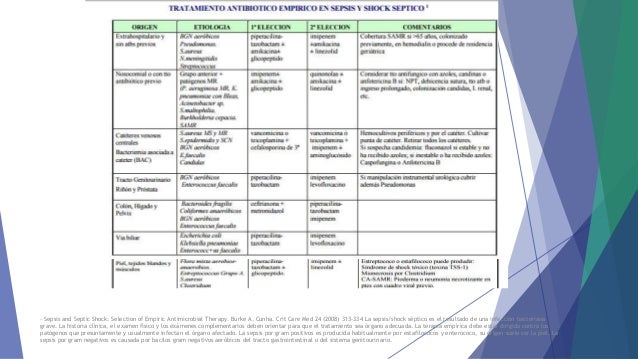
Definitions
Etiology and Risk Factors
- Male gender and increased age are associated with a greater risk of acquiring sepsis.1,2,7 The rate of infection rises with increasing length of ICU stay and worsening degree of organ failure.3TABLE 1 lists predictors of mortality in sepsis patients.1-3
Supportive Therapy
- The Surviving Sepsis Campaign provides strong recommendationsregarding hemodynamic support and adjunctive therapy in sepsis. SeeTABLE 2 for current recommendations.
The Pharmacist’S Role
- Pharmacists are optimally placed to interact with many differenthealth care professionals, affording them many opportunities to improvepatient care via the optimization of sepsis management. Among theseopportunities are appropriate antibiotic selection, de-escalation ofantibiotic therapy, and sepsis bundle (protocol) implementation. Selection of Appropriate Anti…
Conclusion
- Sepsis infections, which can be difficult to manage, are common inhospitalized patients, particularly ICU patients. Proper management isvital to reducing the morbidity, mortality, and costs associated withthese infections. Since pharmacists are in a position to interact with avariety of health care professionals, they have the opportunity toimprove patient care through t…