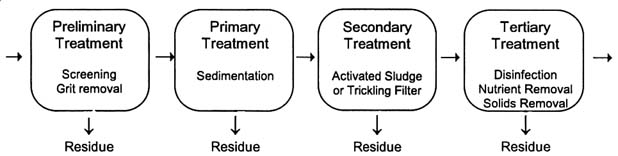
- Primary Treatment: Primary treatment consists of removing floating and suspended solids by mechanical means. ...
- Secondary Treatment: Secondary treatment of waste involves the biological degradation of organic material by micro-organisms under controlled conditions. ...
- Tertiary Treatment:
What does tertiary treatment remove?
What are the 4 stages of sewage treatment?
- Screening and Pumping.
- Grit Removal.
- Primary Settling.
- Aeration / Activated Sludge.
- Secondary Settling.
- Filtration.
- Disinfection.
- Oxygen Uptake.
Why is the primary secondary and tertiary sector declining?
These are the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors. The primary sector and the secondary sectors are declining due to a number of reasons such as cheaper imports and the increasing use of technology, taking over jobs which used to be done by hand, e.g. milking cows.
What is an example of tertiary care?
What are the 3 levels of health care in Australia?
- medical services.
- public hospitals.
- medicines.
What is tertiary wastewater treatment, and how does it work?
- Bag filters: Bag filters are ideal for wastewater treatment plants that need to reduce contaminants to a specific micron rating. ...
- Drum filters: A drum filter consists of a drum with a woven cloth filter around it. ...
- Disc filters: A disc filter consists of a central drum attached to multiple discs with cloth filters. ...

What is the difference between primary and secondary treatment?
The initial and primary water treatment process removes large matter from wastewater while the secondary treatment will remove smaller particles already dissolved or suspended.
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
How is the primary treatment stage different from secondary treatment stage?
In the primary stage, solids are allowed to settle and removed from wastewater. The secondary stage uses biological processes to further purify wastewater. Sometimes, these stages are combined into one operation.
What is an example of tertiary treatment?
Solid–Liquid Filtration – Examples of Processes The main tertiary treatment process is then filtration, using either a sand bed or a membrane process, usually microfiltration, possibly followed by ultrafiltration.
What is primary treatment?
Listen to pronunciation. (PRY-mayr-ee TREET-ment) The first treatment given for a disease. It is often part of a standard set of treatments, such as surgery followed by chemotherapy and radiation.
What is secondary treatment of sewage?
Secondary treatment is the removal of biodegradable organic matter (in solution or suspension) from sewage or similar kinds of wastewater. The aim is to achieve a certain degree of effluent quality in a sewage treatment plant suitable for the intended disposal or reuse option.
What happens tertiary treatment?
Tertiary water treatment is the final stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process. This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Removing these harmful substances makes the treated water safe to reuse, recycle, or release into the environment.
How does tertiary treatment work?
Tertiary wastewater treatment often works by using a combination of physical and chemical processes to remove harmful microbiological contaminants from wastewater. The process usually involves filtration followed by additional disinfecting treatment.
What is meant by secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment is the second step in most waste treatment systems during which bacteria consume the organic parts of the wastes. This is accomplished by bringing the sewage, bacteria and oxygen together in trickling filters or within an activated sludge process.
What is removed in secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment removes the soluble organic matter that escapes primary treatment. It also removes more of the suspended solids. Removal is usually accomplished by biological processes in which microbes consume the organic impurities as food, converting them into carbon dioxide, water, and energy…
What does primary treatment remove?
The purpose of primary treatment is to settle material by gravity, removing floatable objects,and reducing the pollution to ease secondary treatment. Primary Treatment aims to reduce the Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Total Suspended Solids (TSS) in the wastewater.
Why is tertiary treatment important?
Tertiary treatment eliminates matter from wastewater that could be harmful to the environment. The process involves removing materials such as heavy metals, toxic chemicals, and other pollutants.
What are the stages of sewage treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 6: Filtration. ... Step 7: Disinfection. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
What are the various stages of sewage treatment?
Wastewater is treated in 3 phases: primary (solid removal), secondary (bacterial decomposition), and tertiary (extra filtration).
What are the four stages of sewage treatment?
4-Step Wastewater Sludge Treatment ProcessStep 1 – Sludge Thickening. The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. ... Step 2 – Sludge Digestion. After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. ... Step 3 – Dewatering. ... Step 4 – Disposal.
What are the stages of STP?
The 3 Main Stages of Sewage Treatment DesignThe Primary Stage. The first stage in the sewage treatment is the primary sedimentation stage. ... The Secondary Stage. ... The Tertiary Stage.
What is secondary care in healthcare?
Secondary Care. Medical specialists and other health professionals, who typically don’t have initial contact with patients, provide secondary care.
What is primary care?
Primary Care. The primary care level is the “gatekeeper”, the first point of medical consultation. As a patient you are usually seen by a primary care physician, also called a general practitioner or family physician. Primary care is provided at a doctor’s office, health center or Urgent Care center. The Emergency Room is also often ...
What is the fourth level of care?
A fourth level of care, quarternary care , is a more complex level of tertiary care. Uncommon, highly specialized and experimental treatments and procedures are considered to be at the quarternary care level. For more information about health care, find additional articles in the Einsurance online journal. « Teach Your Teen to Be A Safe Driver.
Do you need a referral for secondary care?
Some secondary care physicians do not require a patient to have a referral from a primary care practitioner. Another category of secondary care is hospital care, or acute care. The term covers care as an admitted patient in a hospital, a visit to a hospital ER, attendance in childbirth, medical imaging ...
Is the emergency room a primary care facility?
The Emergency Room is also often a source of primary care for the un- or under-insured. According to the New England Healthcare Institute, demand for primary care continues to grow as patients become older and sicker. At the same time, there’s an increasing shortage of general practitioners.
What is considered preliminary treatment?
Preliminary Treatment: Physical. When wastewater arrives at the treatment plant, it contains many solids that cannot be removed by the wastewater treatment process. This can include rags, paper, wood, food particles, egg shells, plastic, and even toys and money.
What happens when wastewater enters the secondary clarifier?
When the wastewater enters the two Secondary Clarifiers, it still contains lots of microorganisms from the Aeration Basins and looks brown and murky. The Secondary Clarifiers are identical to the Primary Clarifiers; materials in the wastewater sink and float and rotating arms remove this material from the water.
How much water does a secondary clarifier hold?
The Secondary Clarifiers each hold 800,000 gallons of water.
What is secondary care?
Secondary care is where most people end up when they have a medical condition to deal with that can't be handled at the primary care level. Your insurance company may require that you receive a referral from your PCP rather than going directly to a specialist. There are times when problems with specialty care develop.
Why do you need a PCP in tertiary care?
That's because your PCP can help you establish and maintain a management plan for the long term. 2
What are the different levels of care?
Medical professionals frequently talk about levels of care. They're divided into the categories of primary care, secondary care, tertiary care, and quaternary care. Each level is related to the complexity of the medical cases being treated as well as the skills and specialties of the providers. Since you sometimes hear these words as ...
What is level of care?
Levels of care refer to the complexity of medical cases, the types of conditions a physician treats, and their specialties.
What are the primary care doctors?
There are some primary care specialties as well. For instance, OB-GYNs, geriatricians, and pediatricians are all primary care doctors; they just happen to specialize in caring for a particular group of people.
How do primary care providers benefit the healthcare system?
Studies have shown that primary care providers benefit the healthcare system as a whole by offering enhanced access to healthcare services, better health outcomes, and a decrease in hospitalization and use of emergency department visits. 1 .
What are the primary medical problems that you may seek?
Injury: You may also seek primary care for a broken bone, a sore muscle, a skin rash, or any other acute medical problem.
What are the three main stages of sewage treatment?
The three standard sewage-treatment stages include primary, secondary, and tertiary steps . Primary treatment is almost always applied.
What is sewage treatment?
Sewage-treatment plants use a series of steps to remove any biological and chemical contaminants that are a risk to human health or the environment. Such plants eliminate final traces of suspended solids; halt the undesirable growth of algae; reduce nutrient content; and remove undesirable taste, color, and odor.
What is biological oxidation?
The process—called biological oxidation—involves trickling filters, activated sludge, and stabilization ponds. Unless tertiary treatment will be used, the wastewater is disinfected with chlorine and then discharged. Sludge remaining from the primary- and secondary-treatment processes is sent to a sludge digester for further processing.
Is tertiary treatment always used?
Although secondary treatment is recommended for most sewage, many plants are not equipped to perform it. Tertiary treatment, a relatively expensive cleansing step, is used even less frequently, usually only when water of drinking quality is desired. Primary treatment.
What is the difference between primary and secondary treatment?
The principal difference in primary and secondary treatment is the process that breaks down the sewage in wastewater. In the primary method, the waste processes through a physical procedure with equipment and filtration. While secondary treatment may use similar items, this method uses biological treatment through microbes.
How is primary treatment different from secondary treatment?
Another difference between these processes is how much time they take to complete. The primary treatment takes a shorter period to finish, but the secondary takes much longer as organic microbes consume the waste.
What is the Primary Treatment of Wastewater?
Through the primary treatment, it is possible to remove materials that float and settle on top of water. Through primary treatment, it is possible to implement screening water treatment, reduce particles to fragments, remove grit and initiate sedimentation.
How is wastewater treated?
The primary treatment of wastewater occurs through sedimentation with filtering out large contaminant particles within the liquid. The contaminants separate as they are passed through several tanks and other filters. Leftover sludge filters through a digester to suspend solids from the wastewater.
What is primary wastewater treatment?
The primary wastewater process utilizes equipment to break up larger particles and then uses sedimentation or a floating process for extraction. Many treatments that use the primary method then proceed to the secondary treatment process.
What is the process of removing impurities from water?
The removal in the secondary wastewater treatment process generally occurs through a biological process with consumption of impurities in water by microbes, converting the matter into energy, carbon dioxide gases, and water. AOS can help with municipal wastewater treatment services in both primary and secondary processes.
What is the process of removing large particles from wastewater?
The initial and primary water treatment process removes large matter from wastewater while the secondary treatment will remove smaller particles already dissolved or suspended. Sedimentation and filtration are the processes involved in the primary treatment method while biological breakdown occurs through aerobic or anaerobic units in secondary processes.
What is the difference between primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention?
The Difference Between Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Prevention. Prevention is divided into three categories: primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. “ Primary prevention targets individuals who may be at risk to develop a medical condition and intervenes to prevent the onset of that condition . Examples include childhood vaccination ...
What is tertiary prevention?
Tertiary prevention targets individuals with a known disease, with the goal of limiting or preventing future complications. Examples include screening patients with diabetes for microalbuminuria, rigorous treatment of diabetes mellitus, and post-myocardial infarction prophylaxis with b-blockers and aspirin.” ABFM question critique
What are some examples of secondary prevention?
Examples include childhood vaccination programs, water fluoridation, anti-smoking programs, and education about safe sex. Secondary prevention targets individuals who have developed an asymptomatic disease and institutes treatment to prevent complications.
