Which is worse non-small or small cell lung cancer?
Non-small cell lung cancers include adenocarcinoma, squamous cell, and large cell carcinoma. Small cell cancers vary , depending on the expression of specific genes. Some types are more aggressive than others, but generally, small cell cancer is more aggressive than non-small cell lung cancer.
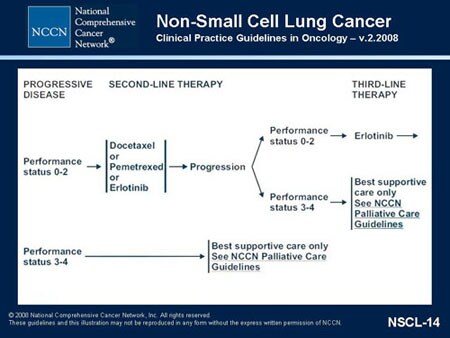
What is the best treatment for NSCLC?
If you have stage I NSCLC, surgery may be the only treatment you need. This may be done either by taking out the lobe of the lung that has the tumor (lobectomy) or by taking out a smaller piece of the lung (sleeve resection, segmentectomy, or wedge resection).
What is the most successful treatment for lung cancer?
People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments. People with small cell lung cancer are usually treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Surgery. An operation where doctors cut out cancer tissue.
Is non-small cell lung cancer the same as lung cancer?
NSCLC is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small cell lung cancer (SCLC). The most common types of NSCLC are squamous cell carcinoma, large cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma, but there are several other types that occur less frequently, and all types can occur in unusual histologic variants.
Can non-small cell carcinoma be cured?
Yes. Non-small cell lung cancer is curable, especially with early detection and treatment. Certain factors can affect your overall prognosis, such as: The stage of the cancer (the size of the tumor and whether it is only in your lung or has spread to other places in your body).
What is advanced NSCLC?
Advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer, with a poor prognosis and no known cure. Survival time is often short because of limited treatment options. Recent advances in targeted therapy and immunotherapy have changed the landscape for the treatment of advanced NSCLC.
What is the newest treatment for lung cancer?
Atezolizumab is approved to treat some people with non-small cell lung cancer after surgery. An immune checkpoint inhibitor is a drug that blocks proteins on immune system cells which then allows them to fight cancer.
What is the new pill for lung cancer?
Tagrisso (osimertinib) is now approved for patients whose tumors have a specific epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation (T790M) and whose disease has gotten worse after treatment with other EGFR-blocking therapy.
Can you survive non-small cell lung cancer?
For people with localized NSCLC, which means the cancer has not spread outside the lung, the overall 5-year survival rate is 63%. For regional NSCLC, which means the cancer has spread outside of the lung to nearby lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate is about 35%.
Which type of lung cancer is most likely to metastasis?
Lung carcinomas have some preferential sites for metastasis, such as the brain, bones, and adrenal glands. Other organs are involved usually in late stage of the disease.
Which is worse right or left lung cancer?
Results. There was no significant distinction in overall survival (OS) between right (n = 53 496) and left (n = 36 911) side tumors (hazard ratio [HR] 0.993, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.9756–1.011; P = 0.432).
How aggressive is non-small cell carcinoma?
NSCLC grows and spreads less aggressively than small cell lung cancer. This means that it often can be treated more successfully with surgery, chemotherapy, and other medical treatments. Prognosis varies, but the earlier a diagnosis is made, the better the outlook.