Medication
Combination of vancomycin and beta-lactam therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureusbacteremia: a pilot multicenter randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62:173–180.
Procedures
Vancomycin remains the initial antibiotic of choice for the treatment of patients with MRSA bacteremia and endocarditis due to isolates with vancomycin MIC≤2 μg/mL. Daptomycin is an effective, although more costly alternative, and ceftaroline appears promising.
Nutrition
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a bacterium that is resistant to (unaffected by) many commonly used antibiotics.
What are the treatment options for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureusbacteremia?
The best defense against MRSA is to maintain good hygiene, including frequent and thorough hand washing, and to avoid the sharing of personal care items. HA-MRSA and CA-MRSA differ at the genetic level and have distinct biologic properties.
What is the initial antibiotic of choice for the treatment of MRSA?
What is MRSA (Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus)?
What is the best defense against MRSA?

What is the latest treatment for MRSA?
Recent findings: Linezolid, daptomycin and tigecycline have been approved during the last decade to treat infections due to MRSA.
What is the best antibiotic to treat MRSA?
Vancomycin is generally considered the drug of choice for severe CA-MRSA infections. Although MRSA is usually sensitive to vancomycin, strains with intermediate susceptibility, or, more rarely, resistant strains have been reported.
Which is the newest antibiotic in the MRSA treatment arsenal?
Tigecycline (a glycylcycline antibiotic) was developed in response to the growing prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and Acinetobacter baumannii.
What is the first line treatment for MRSA?
Some antibiotics available in oral formulations are treatment options for MRSA: First-line therapy: trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX; Bactrim DS, Septra DS. Sulfamethoprim-DS). This agent has been shown to be 95% effective.
Which antibiotic is most effective against Staphylococcus aureus?
The antibiotics most effective against all S aureus cultures for outpatients were linezolid (100%), trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole (95%) and tetracyclines (94%). Linezolid (100%), trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole (100%) were most effective against MRSA isolates.
Which antibiotic is most effective for treating hospital acquired methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus MRSA infection?
Although MRSA cannot be effectively treated with antibiotics such as methicillin, nafcillin, cephalosporin or penicillin, it can usually be treated with an antibiotic called vancomycin. Recently, however, a few strains of Staphylococcus aureus have even developed some degree of resistance to vancomycin.
What major class of antibiotics is effective in the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus?
Vancomycin continues to be the drug of choice for treating most MRSA infections caused by multi-drug resistant strains. Clindamycin, co-trimoxazole, fluoroquinolones or minocycline may be useful when patients do not have life-threatening infections caused by strains susceptible to these agents.
Is methicillin still used?
Methicillin. Methicillin was the first semisynthetic penicillinase-resistant penicillin. It has been withdrawn from the market in the United States because of the high incidence of interstitial nephritis associated with its use.
Have they found a cure for MRSA?
Scientists in Germany have discovered a new drug to combat one of the most dangerous antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the world, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and it's buried inside human noses.
How is MRSA treated in hospitals?
If you get an MRSA infection, you'll usually be treated with antibiotics that work against MRSA. These may be taken as tablets or given as injections. Treatment can last a few days to a few weeks.
What are methicillin antibiotics?
methicillin, also called meticillin, antibiotic formerly used in the treatment of bacterial infections caused by organisms of the genus Staphylococcus. Methicillin is a semisynthetic derivative of penicillin.
What oral antibiotics treat MRSA?
At home — Treatment of MRSA at home usually includes a 7- to 10-day course of an antibiotic (by mouth) such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (brand name: Bactrim), clindamycin, minocycline, linezolid, or doxycycline.
What causes MRSA flare ups?
MRSA is spread by touching an infected person or exposed item when you have an open cut or scrape. It can also be spread by a cough or a sneeze. Poor hygiene -- sharing razors, towels, or athletic gear can also be to blame.
What internal organ is most affected by MRSA?
MRSA most commonly causes relatively mild skin infections that are easily treated. However, if MRSA gets into your bloodstream, it can cause infections in other organs like your heart, which is called endocarditis. It can also cause sepsis, which is the body's overwhelming response to infection.
Is there an over the counter treatment for MRSA?
National report - An over-the-counter compound with essential oils is not only superior in completely killing community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus organisms, it also acts faster than two other OTC products for the prevention of skin and soft-tissue infections, researchers say.
What is the best treatment for MRSA?
Vancomycin or daptomycin are the agents of choice for treatment of invasive MRSA infections [1]. Alternative agents that may be used for second-line or salvage therapy include telavancin, ceftaroline, and linezolid. Recent studies of treatment of MRSA bacteremia are reviewed. Vancomycin.
How much daptomycin should I take for MRSA?
This is reflected in the Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines for treatment of MRSA infections, where daptomycin dosing is recommended at 8 to 10 mg/kg for complicated bacteremia and in combination with other agents if there has been prior vancomycin treatment failure [1].
What is the fifth generation of cephalosporin?
Ceftaroline. Ceftaroline is a fifth-generation cephalosporin with bactericidal activity against MRSA and VISA as well as Gram-negative pathogens [14]. Ceftaroline fosamil, the pro-drug of ceftaroline, received approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2010.
When was telavancin approved?
Telavancin was approved in November 2009 in the United States for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI), and in June 2013 in US for hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) caused by gram-positive pathogens including MRSA where alternative treatments are not suitable.
Is daptomycin a good substitute for vancomycin?
Daptomycin is an acceptable alternative to vancomycin for treatment of MRSA bacteremia. Historically, daptomycin has been used as salvage therapy in patients failing vancomycin therapy, particularly with high vancomycin MIC infections, but increasingly it is being used as initial therapy in high inoculum MRSA infections.
Is telavancin effective for MRSA?
Telavancin may prove effective for treatment of MRSA bacteremia. In a phase 2 trial of telavancin for treatment of bacteremia including 17 patients, cure rates were comparable for telavancin and standard therapy (88 vs 89%) [8].
Is vancomycin bactericidal?
aureus. Furthermore, vancomycin is slowly bactericidal, which may be partly responsible for reported clinical failures in treatment of bacteremia and endocarditis.
What are the two principles of treating Staph Aureus?
The two principles of treating Staph aureus infections, including MRSA infections, are source control and antibiotic therapy: Source control : This refers to reducing the numbers of bacteria at the site of infection. In the case of skin infections, your provider may drain boils or abscesses.
Where does MRSA colonize?
The bacterium remains within the skin or mucosa where it has established colonization. Problems arise when MRSA on the skin surface in a colonized person enters the skin through a wound or other opening and invades deeper structures.
What is the MRSA superbug?
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) You may have heard MRSA called a superbug. These bacteria cause potentially deadly staph infections that are resistant to common antibiotics. Stronger antibiotics may be needed to treat MRSA. Prevention tactics include keeping all wounds covered and practicing good handwashing techniques.
What is a HA MRSA?
Two categories of MRSA are: Hospital-associated (HA): HA-MRSA refers to MRSA infections that are associated with healthcare settings, such as hospitals and nursing homes.
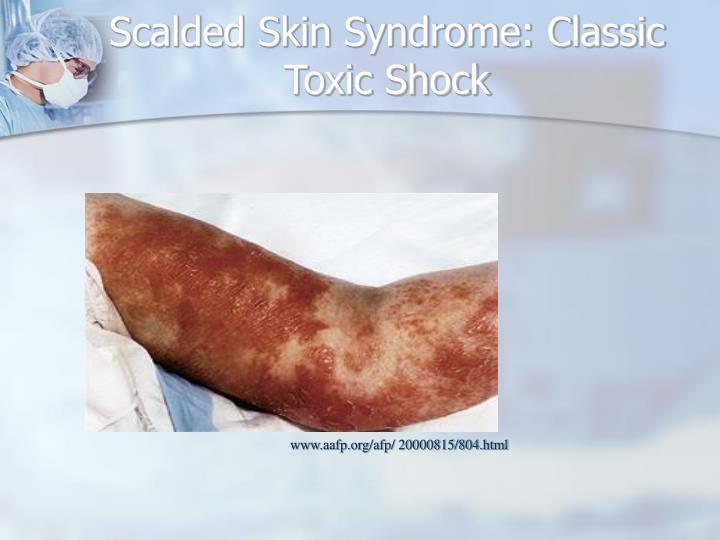
What does MRSA look like?
MRSA can cause a skin rash or infection that looks like a spider bite or pimples. The red, swollen bumps may feel warm and be tender to touch. The rash may ooze. MRSA can also cause deeper infections in different parts of the body.
How many Americans have staph?
Approximately 1 in 3 Americans are carriers of staph bacteria at any time. Up to half of these could be MRSA. It's important to emphasize that Staph aureus or MRSA carriage is not a disease.
Where does staph live?
Staphylococcus aureus (staph) bacteria live in the nose or on skin. You can harbor staph bacteria, including MRSA, and not know it. A healthcare expert might refer to this as bacterial colonization. Colonized people (carriers) may one day develop an MRSA infection, or they might stay healthy.
How to prevent MRSA infection?
The pus from infected sores may contain MRSA, and keeping wounds covered can help prevent the spread of the bacteria. Keep personal items personal. Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, sheets, razors, clothing and athletic equipment. MRSA spreads on infected objects as well as through direct contact.
Why is MRSA a drug resistant disease?
For years, antibiotics have been prescribed for colds, flu and other viral infections that don't respond to these drugs. Even when antibiotics are used appropriately , they contribute to the rise of drug-resistant bacteria because they don't destroy every germ they target. Bacteria live on an evolutionary fast track, so germs that survive treatment with one antibiotic soon learn to resist others.
What does MRSA look like?
Staph skin infections, including MRSA, generally start as swollen, painful red bumps that might look like pimples or spider bites.
What is the MRSA infection?
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection is caused by a type of staph bacteria that's become resistant to many of the antibiotics used to treat ordinary staph infections. Most MRSA infections occur in people who've been in hospitals or other health care settings, such as nursing homes and dialysis centers.
Where is staph found?
Different varieties of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, commonly called "staph," exist. Staph bacteria are normally found on the skin or in the nose of about one-third of the population. The bacteria are generally harmless unless they enter the body through a cut or other wound, and even then they usually cause only minor skin problems in healthy people.
What are the risks of developing MRSA?
Men who have sex with men have a higher risk of developing MRSA infections. Having HIV infection. People with HIV have a higher risk of developing MRSA infections. Using illicit injected drugs. People who use illicit injected drugs have a higher risk of MRSA infections.
What are the risk factors for CA-MRSA?
Risk factors for CA-MRSA. Participating in contact sports. MRSA can spread easily through cuts and scrapes and skin-to-skin contact. Living in crowded or unsanitary conditions. MRSA outbreaks have occurred in military training camps, child care centers and jails. Men having sex with men.
How to prevent MRSA infection in hospital?
The following guidelines can help patients, healthcare workers, and visitors prevent MRSA infections from spreading in the hospital: using soap and water or an alcohol-based hand rub.
What is MRSA in hospitals?
Healthcare-associated MRSA. MRSA frequently causes illness in people with a compromised immune system who spend time in the hospital and other healthcare facilities. This type is called healthcare-associated MRSA or hospital-acquired MRSA. MRSA is more likely to happen in a hospital because:
How does MRSA spread?
MRSA can spread from person to person through direct skin-to-skin contact or when a person with MRSA bacteria on their hands touches an object that another person then touches . MRSA bacteria can survive for a long time on surfaces and objects, including fabrics and door handles. In 2000, scientists. Trusted Source.
How to prevent MRSA from spreading?
Actions such as regular hand washing can reduce the risk of MRSA spreading. MRSA is a common and potentially serious infection that has developed resistance. Trusted Source. to several types of antibiotics. These include methicillin and related antibiotics, such as penicillin, vancomycin, and oxacillin.
Why is MRSA called a superbug?
Prevention. Outlook. Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, commonly known as MRSA, is a form of contagious bacterial infection. People sometimes call it a superbug because it is resistant to numerous antibiotics. This resistance makes it challenging to treat.
Why is MRSA more likely to happen in a hospital?
MRSA is more likely to happen in a hospital because: Infections can easily spread when there are many people in a limited space. People in the hospital may have a higher risk of contracting the infection. When people are older or have certain health conditions, they may be less able to resist infection.
What are the factors that increase the risk of developing community-associated MRSA?
Factors that increase the risk of developing community-associated MRSA include: living with a lot of people, such as on a military base, in jail, or on a campus. having regular skin-to-skin interaction with other people, for example, in contact or collision sports, such as soccer.
When was MRSA first recognized?
MRSA is categorized by the setting in which it is acquired. The first type, healthcare-acquired MRSA (HA-MRSA), has been recognized since the 1960s. Strains of staph were identified in patients in hospital and healthcare facilities that were resistant to methicillin (resistance to penicillin had occurred even earlier).
How many MRSA cases are associated with healthcare facilities?
The majority of MRSA cases, 85 percent, were associated with healthcare facilities, while approximately 14 percent occurred in individuals with no known exposure to healthcare. The staph bacterium continues to evolve and is beginning to show resistance to additional antibiotics. In 2002 the first staph strains were found ...
Why is it important to track staph?
As strains of staph continue to adapt and change over time, it is critical for healthcare workers to track these changes. They need to know which strains are present within a community at any point in time, to which antibiotics the strains are resistant, and the severity of disease caused by the circulating strains.
What is the name of the drug that is resistant to beta-lactams?
This form is known as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and is usually referred to by the acronym MRSA. What sets MRSA apart is that it is resistant to an entire class of antibiotics called beta-lactams. This group of antibiotics includes methicillin, and the more commonly prescribed penicillin, amoxicillin, and oxacillin among others. ...
What is CA MRSA?
Of greater concern is a second type of MRSA which appeared in the 1990s and is known as community-acquired MRSA (CA-MRSA). CA-MRSA occurs outside of hospital settings and usually manifests itself as a skin infection in an otherwise healthy individual. CA-MRSA can develop into a more serious, life-threatening illness.
How many students died from MRSA in 2007?
Highly publicized accounts of the deaths of at least three students from CA-MRSA in late 2007 prompted concern among students, parents, and school officials. The best defense against MRSA is to maintain good hygiene, including frequent and thorough hand washing, and to avoid the sharing of personal care items.
Which strain of MRSA causes the most cases of CA-MRSA?
They chose the USA300 strain, one of two strains that cause the majority of CA-MRSA cases, because it has emerged as the predominant strain causing skin infections, as well as more serious infections, in both pediatric and adult patients in many states.
What is the MRSA staph?
This topic review discusses the signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, treatment, and prevention of a particularly dangerous form of Staph aureus called methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA; pronounced "Mursa").
How long does it take to get rid of MRSA?
At home — Treatment of MRSA at home usually includes a 7- to 10-day course of an antibiotic (by mouth) such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (brand name: Bactrim), clindamycin, minocycline, linezolid, or doxycycline.
How long do you need antibiotics after discharge?
This may be needed for a short period of time or for as long as six to eight weeks. Intravenous antibiotics can be given at home, by a visiting nurse, or in a rehabilitation facility.
How long does it take to get results from a skin test for MRSA?
People with skin infections can be tested for MRSA with a culture. Results of the test are usually available in 24 to 72 hours. People with infections of the lung, bone, joint, or other internal areas usually require blood tests as well as imaging studies (eg, x-ray, computed tomography [CT] scan, echocardiogram).
How does MRSA spread?
In hospitals and other long-term health care facilities, MRSA can be spread from one patient to another on the hands of health care workers. Hands may become contaminated with MRSA when health care workers touch a patient's skin, wounds, wound dressings, or devices, such as IV tubing.
What is the bacterium that is found on the skin?
Staphylococcus aureus ( Staph aureus or " Staph ") is a bacterium that is carried on the skin or nasal lining of up to 30 percent of healthy individuals. In this setting, the bacteria usually cause no symptoms.
Where does MRSA occur?
Community-associated MRSA infections may occur more commonly in certain populations, such as daycare centers, prisons, in the military, or in athletes who play on a team. Spread of MRSA within households is common.
How can healthcare facilities make prevention of MRSA infections a priority?
Healthcare facilities can make prevention of MRSA infections a priority, assess their relevant data, implement prevention actions and evaluate progress.
What is the CDC's MRSA surveillance?
CDC is engaged in several short- and long-term MRSA surveillance (infection tracking) projects that involve collaboration with health departments, individual hospitals, and academic medical centers, among others. Understanding the burden of MRSA infections—how much is occurring, where it is happening, and how it is being spread – is essential ...
How does MRSA spread?
MRSA is usually spread by direct contact with an infected wound or from contaminated hands, usually those of healthcare providers. Also, people who carry MRSA but do not have signs of infection can spread the bacteria to others (i.e., people who are colonized).
How to know if MRSA is a bacterial infection?
The only way to know if MRSA is the cause of an infection is to perform a culture (a laboratory test) of the bacteria. Obtaining bacteria to culture is a procedure done by a healthcare provider. Top of Page.
Can staph be resistant to antibiotics?
Yes. Staphylococcus aureus (staph) have become resistant to several antibiotics, making MRSA and other types of resistant staph major antibiotic-resistance problems. In CDC’s landmark report, Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013.
Can MRSA be prevented?
Yes. Numerous studies, including a 2019 publication about Veterans Affairs Medical Centers, demonstrate that MRSA prevention efforts can reduce infections. Successful MRSA prevention requires action both at the healthcare facility level, among healthcare providers and healthcare leadership. See the Strategies to Prevent Hospital-onset ...
Can you get MRSA from your nose?
Although many people carry MRSA bacteria in their nose, most do not develop serious MRSA infections. Significant progress was made to reduce MRSA bloodstream infections in healthcare from 2005-2012, when the rates of MRSA bloodstream infections decreased by 17.1% each year.