
Symptoms
- Ill-fitting dentures 1
- Sharp or jagged teeth scraping the tongue’s surface
- Vitamin A or B deficiency
- Oral candidiasis—a short-term fungal infection of the mouth
- Oral lichen planus—a rash that can occur inside the mouth
Causes
How often does leukoplakia turn to cancer? Your doctor takes a sample of the cells (biopsy) to find out what the patches are. Only about 5 out of every 100 people (5%) diagnosed with leukoplakia have cancerous or precancerous changes. But about 50 out of 100 (50%) erythroplakia lesions can become cancerous. ...
Complications
Treatment of leukoplakia is most effective after early diagnosis. Regular follow-up visits to the healthcare provider are vital, as is learning to thoroughly and regularly perform self-inspections of the mouth. Usually, removing the source of the irritation (smoking, chewing tobacco, or excessive alcohol use) will be enough to cure the condition.
How do I choose the best leukoplakia treatment?
You can prevent leukoplakia in the following ways:
- Completely quit the use of both chewable and smoked tobacco, as it is the major cause of leukoplakia in people.
- Reduce your alcohol consumption to prevent leukoplakia.
- Brush your teeth regularly to keep the bad bacteria away from your mouth. ...
How often does leukoplakia turn to cancer?
Can leukoplakia be cured?
What to do for leukoplakia?
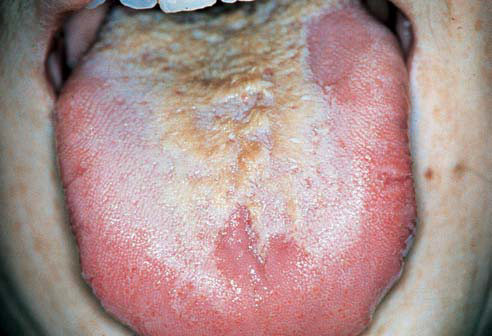
How successful is leukoplakia treatment?
Leukoplakia treatment is most successful when a lesion is found and treated early, when it's small. Regular checkups are important, as is routinely inspecting your mouth for areas that don't look normal.
How to diagnose leukoplakia?
Diagnosis. Most often, your doctor diagnoses leukoplakia by: Examining the patches in your mouth. Attempting to wipe off the white patches. Discussing your medical history and risk factors. Ruling out other possible causes.
What is the procedure to remove leukoplakia?
Oral brush biopsy. This involves removing cells from the surface of the lesion with a small, spinning brush. This is a non-invasive procedure, but does not always result in a definitive diagnosis. Excisional biopsy. This involves surgically removing tissue from the leukoplakia patch or removing the entire patch if it's small.
What to do to get ready for dental appointment?
To get ready for your appointment, make a list of: Key medical and dental information, such as prior instances of symptoms and treatment, if any. All medications, vitamins, herbal remedies and other supplements that you regularly take.
Can hairy leukoplakia cause mouth cancer?
Treating hairy leukoplakia. Usually, you don't need treatment for hairy leukoplakia. The condition often causes no symptoms and isn't likely to lead to mouth cancer. If your doctor recommends treatment, it may include: Medication.
Can leukoplakia return after stopping treatment?
Your doctor may recommend regular follow-up visits to monitor changes to your mouth or ongoing therapy to prevent leukoplakia patches from returning.
Where does leukoplakia occur?
Leukoplakia usually occurs on your gums, the insides of your cheeks, the bottom of your mouth — beneath the tongue — and, sometimes, your tongue. It isn't usually painful and may go unnoticed for a while. Leukoplakia may appear: White or grayish in patches that can't be wiped away. Irregular or flat-textured.
What is the color of leukoplakia?
Leukoplakia may appear: White or grayish in patches that can't be wiped away. Irregular or flat-textured. Thickened or hardened in areas. Along with raised, red lesions (speckled leukoplakia or erythroplakia), which are more likely to show precancerous changes.
What is the white stuff on the side of your tongue?
Hairy leukoplakia. Hairy leukoplakia causes fuzzy, white patches that resemble folds or ridges, usually on the sides of your tongue. It's often mistaken for oral thrush, an infection marked by creamy white patches that can be wiped away, which is also common in people with a weakened immune system.
How long does it take for leukoplakia to heal?
See your dentist or primary care professional if you have any of the following: White plaques or sores in your mouth that don't heal on their own within two weeks.
What does it mean when your mouth is white?
Overview. Leukoplakia. Open pop-up dialog box. Close. Leukoplakia. Leukoplakia. Leukoplakia appears as thick, white patches on the inside surfaces of your mouth. It has a number of possible causes, including repeated injury or irritation. It can also be a sign of precancerous changes in the mouth or mouth cancer.
What is it called when you have a change in your mouth?
So it's best to see your dentist or primary care professional if you have unusual, persistent changes in your mouth. A type of leukoplakia called hairy leukoplakia, sometimes called oral hairy leukoplakia, primarily affects people whose immune systems have been weakened by disease, especially HIV/AIDS.
Does hairy leukoplakia affect HIV?
Although the use of antiretroviral drugs has reduced the number of cases, hairy leukoplakia still affects a number of HIV-positive people, and it may be one of the first signs of HIV infection.
What is a leukoplakia?
What is leukoplakia? Leukoplakia is a condition in which thick, white or grayish patches form usually inside your mouth. Smoking is the most common cause. But other irritants can cause this condition as well. Mild leukoplakia is usually harmless and often goes away on its own.
What causes hairy leukoplakia?
Hairy leukoplakia. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is the main cause of hairy leukoplakia. Once you get this virus, it remains in your body permanently. EBV is usually dormant. However, it can cause hairy leukoplakia patches to develop at any time. Outbreaks are more common in people with HIV or other immune problems.
What are the symptoms of a swollen mouth?
The condition is marked by unusual-looking patches inside your mouth. These patches can vary in appearance and may have the following features: 1 white or gray color 2 thick, hard, raised surface 3 hairy/fuzzy (hairy leukoplakia only) 4 red spots (rare)
How long does it take for a leukoplakia to develop?
Leukoplakia can occur on your gums, the inside of your cheeks, under or on your tongue, and even on your lips. The patches may take several weeks to develop. They’re rarely painful.
What is the redness in the mouth?
These patches can vary in appearance and may have the following features: Redness may be a sign of cancer.
Does hairy leukoplakia cause mouth cancer?
Hairy leukoplakia is not likely to result in mouth cancer and usually does not require removal. Your healthcare provider might prescribe antiviral medications to help stop the patches from growing. Topical ointments containing retinoic acid can also be used to reduce patch size.
Can you remove a leukoplakia patch?
If a biopsy comes back positive for oral cancer, the patch must be removed immediately. This can help prevent cancer cells from spreading. Patches can be removed by using laser therapy, a scalpel, or a freezing procedure. Hairy leukoplakia is not likely to result in mouth cancer and usually does not require removal.
How to prevent leukopolakia?
Preventing oral conditions such as leukoplakia involves dietary and lifestyle changes such as quitting tobacco and alcohol consumption. A diet rich in essential nutrients and antioxidants can help keep such conditions at a bay. Leukoplakia at any stage should be treated with care.
What are the two types of leukoplakia?
Based on the exact location, they are of two types-. Leukoplakia buccalis: Affects buccal mucosa. Leukoplakia lingualis: Affects the lingual mucosa. Based on the nature of the lesions, oral leukoplakia has the following subtypes-. Homogeneous leukoplakia: Here the plaque is generally uniform, thick and extends over a wider area.
What are the white spots on the oesophagus?
Oesophageal leukoplakia: Plaques appear on the oesophageal lining and may progress to oesophageal cancer. The lesions appear as small, opaque and white bumps which may appear similar to early oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Leukoplakia of the bladder: White patches appear along with squamous metaplasia.
What is sublingual keratosis?
Sublingual keratosis: This refers to the leukoplakia of the floor of the mouth or below the tongue. Candidal leukoplakia: It results from infections caused by Candida albicans. Oral hairy leukoplakia: Rough and hairy lesions form on the sides of the tongues due to infections caused by the Epstein Barr virus.
What is the radiation that causes lesions in the lower lip?
Ultraviolet radiation: It gives rise to lesions in the lower lip and is often associated with cheilosis. Pathogens: Certain varieties of microbial pathogens like Candida, Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) can attack and damage the squamous epithelium in the mouth.
What causes plaque on the buccal mucosa?
Overuse of mouthwash contain ing more than 25% alcohol leads to the formation of greyish plaques on the buccal mucosa. Sanguinaria: This is a variety of herbal extract found in different kinds of toothpaste. It causes “sanguinaria associated keratosis”. It is often accompanied by dysplasia.
What is oral disease?
Oral diseases are very common in all age groups and genders and arise from infections in the mucosal lining in most cases. These infections can occur in other parts of the body as well. Acute mucosal inflammation and plaque formation may result in such cases. This condition is termed as leukoplakia. It may progress to cancerous conditions in some ...
What causes leukoplakia?
Other conditions mentioned as potential causes of oral leukoplakia are : 1 Habits such as chewing pens, biting your lip or tooth grinding 2 Sun exposure on the lips 3 Using dental products that contain sanguinarine 4 Human papilloma virus infection
How to diagnose leukoplakia?
Oral Leukoplakia is normally diagnosed by examining the white patches in the mouth or the fuzzy manifestation of hairy leukoplakia on the tongue, after excluding other diseases that could cause similar symptoms, such as oral thrush.
What is oral leukoplakia?
Oral leukoplakia describes a white plaque that does not rub off and cannot be characterized as any other condition. [1] [2] Though it may occur in any part of the mouth, it generally affects the tongue, gums, and inner cheek. [2] Physicians will usually biopsy oral leukoplakia lesions as 20-40% of cases are precancerous or cancerous at the time of biopsy and another 8-15% become cancerous over time. [2] The exact cause of oral leukoplakia is not known. Factors that may increase the risk of developing oral leukoplakia include smoking, alcohol use, vitamin deficiencies, malocclusion, and a weakened immune system. [1] [2] Treatment depends on the biopsy results and the size, appearance, and location of the oral leukoplakia. Removal or ablation of the lesion by surgery, laser, or cryotherapy (use of low temperature) may be recommended. [1] [2]
What are the factors that increase the risk of oral leukoplakia?
Factors that may increase the risk of developing oral leukoplakia include smoking, alcohol use, vitamin deficiencies, malocclusion, and a weakened immune system. [1] [2] Treatment depends on the biopsy results and the size, appearance, and location of the oral leukoplakia. Removal or ablation of the lesion by surgery, laser, ...
Is leukoplakia precancerous?
Physicians will usually biopsy oral leukoplakia lesions as 20-40% of cases are precancerous or cancerous at the time of biopsy and another 8-15% become cancerous over time. [2] . The exact cause of oral leukoplakia is not known. Factors that may increase the risk of developing oral leukoplakia include smoking, alcohol use, vitamin deficiencies, ...
How to diagnose leukoplakia?
Your doctor or dentist can diagnose leukoplakia during an oral exam. If the patches appear suspicious, you may be referred for further testing, like a biopsy. It’s important to see your dentist as soon as possible if you notice white patches that are painful or exhibit any of these symptoms:
Is leukoplakia more common in men than women?
The exact cause of leukoplakia is unclear, but there are several factors associated with the condition. It’s more common in men than women, and rarely occurs in people under the age of 30.
Can leukoplakia be wiped away?
While thrush also appears as whitish patches it’s usually softer and can bleed more easily. Unlike thrush, leukoplakia patches cannot be wiped away.
Can leukoplakia cause cancer?
Usually, individuals don’t experience permanent damage from leukoplakia, however it can increase your risk of developing cancer. The patches can also signal the presence of cancer or an underlying health condition.

Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
Prevention
- Leukoplakia treatment is most successful when a lesion is found and treated early, when it's small. Regular checkups are important, as is routinely inspecting your mouth for areas that don't look normal. For most people, removing the source of irritation ― such as stopping tobacco or alcohol ― clears the condition. When this isn't effective or if t...