
Medication
Such treatments may include: Medications to manage blood pressure, cholesterol, triglycerides, diabetes, and problems with blood clotting. Lifestyle modifications, such as following a healthy diet, getting physical activity, quitting smoking, and …
Therapy
12 rows · Antihypertensive properties of Ca 2+ channel blockade could further mitigate nerve cell damage in ...
Self-care
Nov 01, 2021 · Because many different disease processes can result in different forms of vascular dementia, there may not be one treatment for all. However, vascular dementia is often managed with medications to prevent strokes and reduce the risk of additional brain damage.
Nutrition
What is the best treatment for vascular dementia? Vascular dementia clinical trialsMemantine. Memantine belongs to the aminoadamantane chemical class and is structurally similar to amantadine, an antiparkinson and antiviral drug. ...
What is the best medication for vascular dementia?
Aug 11, 2021 · Experimental Treatments. Also, some experimental medications are being studied for treatment of VCI. Most of these seek to reduce vascular disease or increase blood flow to the brain’s arteries. Several cardiac medications are being researched, including some calcium channel blockers. So far, though, the most promising evidence supports prevention.
What is the life expectancy of vascular dementia?
Aug 10, 2018 · 30 Best Natural Treatments For Vascular Dementia 1. Turmeric This is the first out of the best treatments for vascular dementia that we want to reveal in this article... 3. Ginseng It has been used in China to help us prevent aging and disease for centuries. Some researchers reported a... 4. ...
Is there a cure for vascular dementia?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved any drugs specifically to treat symptoms of vascular dementia, but there is evidence from clinical trials that drugs approved to treat Alzheimer’s symptoms may also offer a modest benefit in people with vascular dementia. Treatment primarily works to prevent the worsening of vascular dementia by treating the …
What drugs are used for vascular dementia?
Aug 11, 2021 · As far as vascular dementia treatment goes, you may help them regulate their blood pressure or diabetes with diet, exercise, medication, and the prevention of other drug and alcohol use. Leaving sticky notes with routine instructions, to-do lists, and other helpful cues allows for a greater sense of independence despite the change in their cognition.
See more
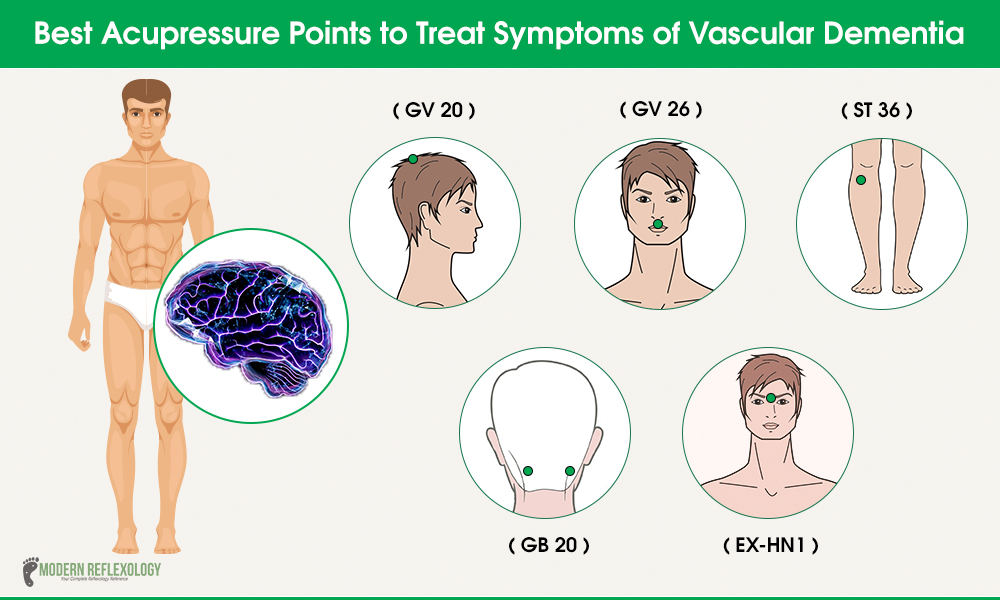
What is the best medication for vascular dementia?
medicines such as low-dose aspirin or clopidogrel to reduce the risk of blood clots and further strokes. anticoagulant medicines, such as warfarin, which can also reduce the risk of blood clots and further strokes.
How do you slow down vascular dementia?
But treatment can sometimes help slow down vascular dementia....This will often involve:eating a healthy, balanced diet.losing weight if you're overweight.stopping smoking.getting fit.cutting down on alcohol.taking medicines, such as those used to treat high blood pressure, lower cholesterol or prevent blood clots.
How long can you live after being diagnosed with vascular dementia?
The average vascular dementia life expectancy after diagnosis is about five years. Some research suggests it may be shorter, at three years, in people who have the disease due to stroke.Aug 28, 2020
What are the first symptoms most likely to be seen in vascular dementia?
Vascular dementia signs and symptoms include:Confusion.Trouble paying attention and concentrating.Reduced ability to organize thoughts or actions.Decline in ability to analyze a situation, develop an effective plan and communicate that plan to others.Slowed thinking.Difficulty with organization.More items...•Jul 29, 2021
What are the 7 stages of vascular dementia?
The following are the seven stages of vascular dementia, from normal behavior to very severe decline.Normal Behavior. ... Mild Changes. ... Mild Decline. ... Moderate Decline. ... Moderately Severe Decline. ... Severe Decline. ... Very Severe Decline.Feb 28, 2022
Do blood thinners help vascular dementia?
New research published in the European Heart Journal suggests that blood-thinning drugs such as warfarin may protect not only against stroke, but also against dementia in people who have atrial fibrillation.Oct 25, 2017
What are the 5 stages of vascular dementia?
Preclinical. The first stage of dementia isn't really corrected described as such. ... Mild cognitive impairment. The impairments experienced at this stage tend to be minor and are not yet sufficient to substantially affect day-to-day life, work or relationships. ... Mild dementia. ... Moderate dementia. ... Severe dementia.
How do you know when vascular dementia is getting worse?
Over time a person with vascular dementia is likely to develop more severe confusion or disorientation, and further problems with reasoning and communication. Memory loss, for example for recent events or names, will also become worse.
What are the signs of end stage vascular dementia?
Signs of late-stage dementiaspeech limited to single words or phrases that may not make sense.having a limited understanding of what is being said to them.needing help with most everyday activities.eating less and having difficulties swallowing.bowel and bladder incontinence.More items...•Sep 3, 2021
What's the difference between vascular dementia and dementia?
The word dementia describes a set of symptoms that can include memory loss and difficulties with thinking, problem-solving or language. In vascular dementia, these symptoms occur when the brain is damaged because of problems with the supply of blood to the brain.
What is the most common cause of vascular dementia?
Vascular dementia is generally caused by conditions that occur most often in older people, such as atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), heart disease, and stroke. The number of people older than 65 years is increasing. People are living longer with chronic diseases, such as heart disease and diabetes.
Can you reverse vascular dementia?
There is currently no cure for vascular dementia: the brain damage that causes it cannot be reversed. However, there is a lot that can be done to enable someone to live well with the condition. This will involve drug and non-drug treatment, support and activities.
What is microarray analysis?
Microarray analysis allows simultaneous monitoring of the behavior of a very large number of genes, up to the whole genome. Studies using microarray analysis reveal a very complex picture associated with the regulation of nerve cell susceptibility to injury (or other diseases such as cancer).
Is rivastigmine used for dementia?
More studies are needed to understand if rivastigmine could be used for treatment of vascular dementia. Hydergine . Hydergine is a combination of four dihydro-derivatives of ergotoxine, also referred to as ergoloid mesylates, and has been in use in clinical medicine since 1949 for treatment of a variety of conditions.
Is vascular dementia the second most common type of dementia?
Epidemiologically, vascular dementia is considered the second most prevalent type of dementia after Alzheimer’s disease although this point of view maybe brought to doubt by our increasing understanding of Lewy body disease (Zesiewicz et al 2001; Henriksen et al 2006).
Is there a cure for vascular dementia?
Vascular dementia is a common condition for which there are no effective approved pharmacological treatments available. Absence of effective treatments creates a difficult situation for those suffering from the disease, their caregivers, and healthcare providers.
What is the second most common cause of dementia?
Now, v ascular c ognitive i mpairment (VCI), a term that includes the spectrum from mild cognitive changes to severe dementia, is considered the second most common cause of dementia, and we also have learned that many older adults develop both AD and vascular disease, a combination that results in worse cognitive decline and increased behavioral problems than those from either disease alone.
How long does it take for a stroke to develop VCI?
Another important feature of VCI is that it is more accurately considered a group of diseases than a single disease. In 15 to 30 percent of people who suffer a major stroke, VCI follows within three months. Another 20 to 25 percent of these people will develop a delayed dementia. Multiple smaller strokes, called lacunar infarcts, can also lead to VCI.
What is antidote application?
Antidote is a third-party application that allows you to search for clinical trials. It is not affiliated with, or endorsed by, the BrightFocus Foundation or our website. Please see our disclaimer related to third-party sites for more information. This content was last updated on: November 10, 2020.
Does vascular disease affect memory?
Researchers have been challenged to understand and classify the brain effects of vascular disease. In part, this is because our earlier definition of dementia, in use until 2015, called for the presence of a debilitating memory problem. However, VCI can affect other aspects of thinking and behavior earlier and more severely.
Does Zoloft help with depression?
Depression, agitation, and psychotic symptoms sometimes respond to off-label use of other medications. For example, a recent study reported improvement of depression using Zoloft® (sertraline) treatment in a group of patients with VCI.
Does blood pressure reduce cognitive decline?
So far, though, the most promising evidence supports prevention. Mid-life blood pressure reduction in people with elevated pressure has been shown to prevent stroke and cognitive decline, though the effect on cognition is a more modest one.
Did the MRI show a stroke?
There were mild abnormalities on her brain MRI: no actual strokes were seen , but there were many areas suggesting damage small blood vessels being a part to the part of the brain below the cerebral cortex (the outermost layer of the brain).
What is vascular dementia?
Vascular dementia is a brain disorder that affects the person’s memory and may cause difficulties in attention, language comprehension, remembering things, problem solving abilities, and communication skills. A person may develop vascular dementia due to severe head injuries, aging, a stroke, or Alzheimer’s disease.
What foods can help with vascular dementia?
Consume foods that are rich in folic acid including peas, papayas, strawberries, and oranges every day to get the essential nutrients as well as the folic acid in them in order to effectively prevent vascular dementia. 26.
What is the best supplement for dementia?
These fatty acids can help you prevent brain lesions, which are causative elements or precursors behind dementia, so you should take a fish oil supplement that is high in omega-3 fatty acids when you feel a bit fuzzy.
Is coconut oil good for dementia?
Coconut oil contains plenty of health benefits, and it is found to be useful to treating dementia because it is a powerful antioxidant and assists to keep the tissues and arteries healthy in our body. Add 1-2 tbsp. of virgin coconut oil everyday to prevent the symptoms of vascular dementia. Just ensure the coconut oil you use is organic, virgin coconut oil. Whereas, processed coconut oil has trans fatty acids and thus, it should not be eaten.
Do bananas help with dementia?
As a good source of potassium, bananas are a wonderful way to boost blood flow to our brain, thus enhancing memory, cognition as well as concentration. This is, in fact, one on the list of natural treatments for vascular dementia that all of my readers should learn and try to add some bananas to their diets for good.
Does green tea help with dementia?
In fact, this is also among the list of natural treatments for vascular dementia, so people should add more green tea or matcha tea into their diets to benefit them. Keep reading: 27 Health and Beauty Benefits of Drinking Green Tea. 8. Cinnamon Extract. Plaque buildup in your brain is a main cause of dementia.
Does Salvia cause neurocognitive impairment?
Salvia, however, contains microdilation properties that may increase the blood flow in some parts of the brain and simultaneously slow down the reduction that comes as a result of vascular dementia.
Vascular Dementia Timeline & Stages
When vascular dementia first sets in, you may notice difficulties with cognitive skills such as planning, decision making, problem solving, thinking, following directions, and concentrating. An individual’s memory, fluency, clarity, and depth perception can be negatively impacted in the early vascular dementia stages.
Symptoms of Vascular Dementia
If a stroke or series of strokes bring on vascular dementia, most people tend to see symptoms quickly. In this scenario, vascular dementia could affect your loved one’s level of cognition, thinking, and recall. This depends on what areas of the brain were impacted during the stroke and to what degree.
Vascular Dementia Timeline & Life Expectancy
Although vascular dementia affects everyone differently, the life expectancy or timeline for a person with the condition is around five years after the first appearance of symptoms. It’s generally caused by a stroke or heart attack. However, successful vascular dementia treatment can help promote a purpose-filled way of life during this time.
Who Has a High Risk of Developing Vascular Dementia
Those who are at high risk for vascular dementia | Factors that increase the probability of developing vascular dementia include high blood pressure, smoking, excessive drinking, diabetes, and heart disease. Although not controllable—men, African Americans, and those between the ages of 60 to 75 tend to be at an increased risk.
Vascular Dementia Treatment Options
Unfortunately, the damage vascular dementia causes with brain tissue cannot be undone. It’s still important to enroll in proper treatment to ensure your loved one lives their life to the fullest.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Doctors can nearly always determine that you have dementia, but there's no specific test that confirms you have vascular dementia. Your doctor will make a judgment about whether vascular dementia is the most likely cause of your symptoms based on the information you provide, your …