Can Stage 2 melanoma be cured?
Several treatments for Stage IV melanoma are currently being tested in clinical trials for Stage II: Immunotherapy and immunotherapy combinations designed to boost the immune system to fight the return of melanoma. Targeted therapies and targeted therapy combinations that …
How long do you have to live with melanoma?
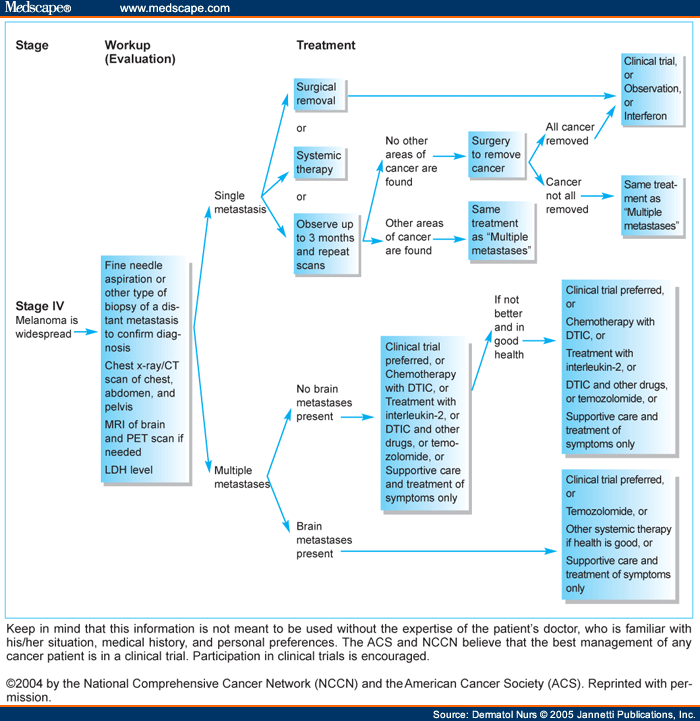
Treatment for Stage 2 Melanoma: Stage II melanoma is treated by removing the tumor surgically. Wide local excision, a minor surgery, usually cures local melanoma. Your doctor may suggest a sentinel lymph node biopsy to determine if the melanoma has spread to the nearest lymph node.
Is cancer of liver curable at Stage 2?
Surgery is the main treatment. To diagnose melanoma doctors remove the abnormal area and a small area of surrounding skin. You usually have a second operation to remove a larger area of healthy tissue around where the melanoma was. This is called a wide local excision. Find out more about a wide local excision.
How serious is Stage 2?
Mar 17, 2022 · Surgical removal is the usual treatment in stage II, but how much margin of normal tissue is removed will depend on the size of the cancer. If the melanoma is: 6. Between 1 mm and 2 mm thick, then 1 cm to 2 cm of healthy skin will be removed. Between 2 mm and 4 mm thick, then 2 cm of healthy skin will be removed.
Can Stage 2 melanoma be cured?
Treatment for Stage 2 Melanoma: Stage II melanoma is treated by removing the tumor surgically. Wide local excision, a minor surgery, usually cures local melanoma. Your doctor may suggest a sentinel lymph node biopsy to determine if the melanoma has spread to the nearest lymph node.
What happens if you have stage 2 melanoma?
Stage 2 melanoma means the tumor is more than 1 mm thick and may be larger or have grown deeper into the skin. It may be ulcerated or not ulcerated. The cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or to distant parts of the body. Surgery to remove the cancerous tumor is the usual treatment strategy.
What is the life expectancy of someone with stage 2 melanoma?
Five-Year Survival Rate by Melanoma Stage: Localized melanoma: Stage 0, Stage I, and Stage II: 98.4% Regional melanoma: Stage III: 63.6% Metastatic melanoma: Stage IV: 22.5%
How often does Stage 2 melanoma come back?
A diagnosis of stage 2 melanoma means it has been caught relatively early and most patients don't have further recurrence of their melanoma once treated.
What does melanoma Stage 2 look like?
Stage 2B means one of the following: the melanoma is between 2 and 4 mm thick and the outermost layer of skin covering the tumour looks broken under the microscope (it is ulcerated) the melanoma is thicker than 4 mm and is not ulcerated.
What is the most effective treatment for melanoma?
The main treatment for melanoma is surgical removal, or excision, of the primary melanoma on the skin. The extent of the surgery depends on the thickness of the melanoma. Most melanomas are found when they are less than 1.0 mm thick, and outpatient surgery is often the only treatment needed.
Can you live 20 years with melanoma?
Survival for all stages of melanoma almost all people (almost 100%) will survive their melanoma for 1 year or more after they are diagnosed. around 90 out of every 100 people (around 90%) will survive their melanoma for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
Which stage of melanoma has the best prognosis?
Melanoma can be treated most effectively in its early stages when it is still confined to the top layer of the skin (epidermis). The more deeply a melanoma grows into the lower layer of the skin (dermis), the greater the risk that it could spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
Is melanoma a death sentence?
Metastatic melanoma was once almost a death sentence, with a median survival of less than a year. Now, some patients are living for years, with a few out at more than 10 years. Clinicians are now talking about a 'functional cure' in the patients who respond to therapy.Oct 24, 2019
Can melanoma go into remission?
Herein, we report a case of metastatic melanoma successfully treated with combined therapy of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and nivolumab. Complete remission was achieved approximately 4 months after the initiation of treatment. The treatment was well tolerated and only grade 1 fatigue occurred.
How successful is immunotherapy for melanoma?
In a small study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, scientists reported a 3-year overall survival rate of 63 percent among 94 patients treated with this combination of drugs. All of the patients had stage 3 or stage 4 melanoma that couldn't be removed with surgery.Feb 25, 2020
What are the signs of melanoma coming back?
Symptoms of advanced melanomahard or swollen lymph nodes.hard lump on your skin.unexplained pain.feeling very tired or unwell.unexplained weight loss.yellowing of eyes and skin (jaundice)build up of fluid in your tummy (abdomen) - ascites.tummy pain.
Characteristics of Stage II Melanoma
Stage II melanomas are defined by two primary characteristics: tumor thickness and ulceration.
Stage IIA
The tumor is 1.01 – 2.0 mm thick, with ulceration, OR tumor is 2.01 – 4.0 mm thick, without ulceration.
Stage IIB
The tumor is 2.01 – 4.0 mm thick, with ulceration, OR tumor is greater than 4.0 mm thick, without ulceration. There is no evidence of spread to nearby lymph nodes. There is no evidence of metastasis to distant sites.
Treatment Options for Stage II Melanoma
Treatment of Stage II melanoma can include surgery, sentinel lymph node biopsy, immunotherapy, and clinical trials.
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SLNB)
SLNB is performed to determine whether any cancer cells have spread to the sentinel node, the first lymph node to receive drainage from the primary tumor, and the site where melanomas commonly spread to first. Sentinel lymph node biopsy is recommended for all Stage II tumors regardless of size.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are research studies to evaluate new therapies and improve cancer care. These studies are responsible for most of the advances in cancer prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. If you have melanoma, you may be eligible to participate in a clinical trial.
What to Ask Your Doctor about Stage II Melanoma
When your doctor tells you that you have Stage II melanoma, it can be overwhelming. But it is important to use the time with your doctor to learn as much about your cancer as you can. S/he will provide you important information about your diagnosis.
How to treat melanoma stage 2?
Treatment for Stage 2 Melanoma: Stage II melanoma is treated by removing the tumor surgically. Wide local excision, a minor surgery, usually cures local melanoma.
What is the treatment for melanoma?
Learn more about melanoma treatments here. Adjuvant Therapy: Some melanomas may have certain features that increase the chance of metastasis or recurrence. In these cases, your doctor may suggest the use of adjuvant therapy to help delay or prevent the melanoma from returning.
What is stage IIB?
Stage IIB: After achieving No Evidence of Disease (NED) following treatment for Stage IIB melanoma, you should conduct monthly self exams of your skin and lymph nodes and have an annual, full-body skin exam performed by a trained dermatologist for the rest of your life.
How thick is a stage 2 melanoma?
Stage II melanoma is divided into three subgroups: Stage IIA Melanoma: The melanoma tumor is more than 1.0 millimeter and less than 2.0 millimeters thick (up to the size of a new crayon point) with ulceration (broken skin) or more than 2.0 and less than 4.0 millimeters without broken skin.
What is considered high risk melanoma?
This is referred to as neoadjuvant therapy and is typically offered through clinical trials. High-risk melanoma usually is defined as melanoma that is deeper or thicker (more than 4.0 millimeters thick) at the primary site or involves nearby lymph nodes.
What is the staging system for melanomas?
The system assigns a stage based on tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) scores as well as additional prognostic factors. The goal is that melanomas of the same stage will have similar characteristics, treatment options, and outcomes.
Which stage of melanoma is thicker?
Stage II melanoma extends beyond the epidermis (very outer layer of skin) into the thicker dermis layer of the skin. It is thicker than Stage I melanoma and is slightly more likely to metastasize.
What is stage 2 melanoma?
Stage 2. Stage 2 is part of the number staging system. The melanoma is only in the skin and there is no sign that it has spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body. Stage 2 is divided into 2A, 2B and 2C.
How to diagnose melanoma?
To diagnose melanoma doctors remove the abnormal area and a small area of surrounding skin. You usually have a second operation to remove a larger area of healthy tissue around where the melanoma was. This is called a wide local excision. Find out more about a wide local excision. Your doctor usually offers you a test to see if ...
What does it mean when your lymph nodes are swollen?
Swollen lymph nodes. If after being diagnosed with melanoma your doctor can feel that the lymph nodes near to the melanoma are swollen (enlarged), you usually have an ultrasound scan and they take a sample of tissue from the lymph nodes (a biopsy).
What is it called when you have lymph nodes removed?
This is called a completion lymph node dissection. They may also suggest having treatment such as targeted cancer drugs or immunotherapy, to reduce the risk of the melanoma coming back.
What is a biopsy of lymph nodes called?
Your doctor usually offers you a test to see if the cancer has spread to the nearby lymph nodes. The test is called a sentinel lymph node biopsy. Your doctor removes the first lymph node or nodes that the melanoma could have spread to and they are checked for cancer cells.
What is stage 2C?
Stage 2C means the melanoma is thicker than 4 mm and under the microscope the outermost layer of skin covering the tumour looks broken (it is ulcerated). Call Cancer Research UK’s information nurses on freephone 0808 800 4040 from 9am to 5pm, Monday to Friday, for more information about staging for melanoma.
What is the TNM staging system?
TNM stages. Doctors also use another staging system for melanoma called the TNM staging system. It stands for Tumour, Node, Metastasis. T describes the size of the tumour. N describes whether there are any cancer cells in the lymph nodes. M describes whether the cancer has spread to a different part of the body.
How to treat early stage melanoma?
Treatment for early-stage melanomas usually includes surgery to remove the melanoma. A very thin melanoma may be removed entirely during the biopsy and require no further treatment. Otherwise, your surgeon will remove the cancer as well as a border of normal skin and a layer of tissue beneath the skin.
How to cope with melanoma?
Here are some ideas to help you cope: Learn enough about melanoma to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor about your cancer, including your treatment options and, if you like, your prognosis. As you learn more about cancer, you may become more confident in making treatment decisions. Keep friends and family close.
How to treat melanoma that has spread beyond the skin?
Treating melanomas that have spread beyond the skin. If melanoma has spread beyond the skin, treatment options may include: Surgery to remove affected lymph nodes. If melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes, your surgeon may remove the affected nodes.
What is the procedure to remove melanoma from lymph nodes?
If there's a risk that the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, your doctor may recommend a procedure known as a sentinel node biopsy. During a sentinel node biopsy, a dye is injected in the area where your melanoma was removed. The dye flows to the nearby lymph nodes.
What is the stage of melanoma?
Melanoma is staged using the Roman numerals 0 through IV. At stage 0 and stage I, a melanoma is small and has a very successful treatment rate. But the higher the numeral, the lower the chances of a full recovery. By stage IV, the cancer has spread beyond your skin to other organs, such as your lungs or liver.
How does thickness affect melanoma?
The thickness of a melanoma helps doctors decide on a treatment plan. In general, the thicker the tumor, the more serious the disease. Thinner melanomas may only require surgery to remove the cancer and some normal tissue around it.
What is used to close the site of a biopsy?
During an excisional biopsy, the doctor removes an entire lump or an entire area of abnormal skin, including a portion of normal skin. Stitches are generally used to close the biopsy site after this procedure.
How to treat stage 0 melanoma?
They are usually treated with surgical removal ("excision") of the melanoma and a minimal amount (about 0.5 cm) of normal skin (called the "margin"). Surgery at this stage usually cures the disease. For melanomas on the face, some doctors may instead prescribe a cream containing the drug Aldara (imiquimod). This is mainly used when surgery would create a cosmetic problem. The cream is applied anywhere from once a day to two times a week for around three months. 1
How does melanoma spread?
Melanomas spread by way of either the lymphatic system or the bloodstream. When they spread through the lymphatic system, they usually first spread to the lymph nodes that are closest to cancer, and once they spread to a first lymph node, spread down the line to others.
What is lymph node dissection?
Routine lymph node dissection (removal of lymph nodes near cancer) is an important staging tool in melanomas more than 1 mm thick, even though it has not been shown to improve survival in patients with stage I melanoma. 2 .
What does it mean when a biopsy came back positive for melanoma?
If your skin biopsy came back positive for melanoma, the most aggressive form of skin cancer, you might hear your melanoma described in stages. Early stage melanoma (0, I, or II) generally means your prognosis is good. ...
What happens if you find a sentinel node?
If the sentinel node (s) is found, it will then be biopsied along with removing the melanoma. If the sentinel node contains cancer, then your doctor will practice surveillance, closely watching the area for changes, rather than rushing to remove all the lymph nodes right away.
Can you take adjuvant therapy for stage 1 melanoma?
In stage I or II melanoma, your doctor may advise adjuvant therapy drugs or perhaps vaccines as part of a clinical trial to try to reduce the chance that the melanoma will come back. Current evidence for the effectiveness of adjuvant drug or radiation treatment for stage II patients, however, is limited. 3 .
How is melanoma treated?
Melanoma Stages: Explained. More. Melanoma is one of the most serious forms of skin cancer. In early stages, it may be treated through relatively simple surgery, but advanced stages can be lethal.
What is stage 1 and stage 2 melanoma?
Stage 1 and Stage 2 Melanoma. This is localized melanoma. Although cancer has grown to the next layer of skin, or the dermis, it has not reached the lymph nodes. Tumor thickness, or depth, and the presence of ulceration – skin breakage visible only under a microscope – further indicate how serious melanoma is.
What is the survival rate for melanoma?
Regional melanoma. For cancer that has spread to nearby lymph nodes or nearby areas of the body, the five-year survival rate is 64%. Distant melanoma. For cancer that has spread to remote parts of the body, such as distant skin areas, or the lungs or liver, the five-year survival rate is 23%.
How thick is a pencil point in stage 1 melanoma?
To give a sense of relative tumor sizes in stage 1 melanoma, the NCI website notes that a sharp pencil point is about 1 millimeter thick. A new crayon point is about 2 millimeter thick. In comparison, a new pencil eraser is about 5 millimeter thick. Stage 2A.
How does melanoma appear on the skin?
Melanoma can appear on the skin in several ways. It could be flat like a freckle or protrude like a mole. You could see changes in the size, color or shape of a birthmark or mole that you may have had for a long time.
Where is cancer spread?
Stage 4 melanoma is extremely advanced. Cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as remote lymph nodes or the lungs, liver, bone, soft tissue, spinal cord or brain.
What to do if you have abnormal skin?
Your doctor will do a thorough examination of the abnormal area. In addition to inspecting any moles, birthmarks or discolored areas, he or she may recommend a skin biopsy for a pathologist to examine the sample for possible cancerous cells.

Diagnosis
Treatment
- The best treatment for your melanoma depends on the size and stage of cancer, your overall health, and your personal preferences.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- A cancer diagnosis can change your life forever. Each person finds his or her own way of coping with the emotional and physical changes cancer brings. But when you're first diagnosed with cancer, sometimes it's difficult to know what to do next. Here are some ideas to help you cope: 1. Learn enough about melanoma to make decisions about your care.Ask your doctor about your c…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Start by seeing your family doctor if you notice any skin changes that concern you. Depending on your situation and the outcome of any tests, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in skin diseases (dermatologist) or to a doctor who specializes in cancer treatment (oncologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot to discuss, it's a good idea t…