What are the treatment options for squamous cell carcinoma in situ?
Abstract. Background: Squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCCIS) is thought to be a precursor to squamous cell carcinoma. It should be treated before invasive cancer develops, especially in transplant recipients, who may develop more aggressive skin cancers. Treatment can involve surgical and nonsurgical methods.
What is squamous cell carcinoma in situ (sccis)?
Jan 25, 2022 · Any combination of radiation therapy and invasive procedures are used to treat Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ. The prognosis depends upon early diagnosis and treatment that is administered How Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity Be Prevented A few methods to prevent Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity include:
How to diagnose and treat squamous cell carcinoma of the skin?
Apr 03, 2022 · Several effective treatment modalities exist for precancerous skin lesions, including squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCCIS) and actinic keratosis. Most of these treatments are easily performed in...
When is radiation therapy used to treat squamous cell carcinoma?
Excision: Cutting out the tumor, along with a small margin of normal skin, is often used to treat squamous cell cancers. Curettage and electrodesiccation: This approach is sometimes useful in treating small (less than 1 cm across), thin squamous cell cancers, but …
How serious is squamous cell carcinoma in situ?
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is usually not life-threatening, though it can be aggressive. Untreated, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin can grow large or spread to other parts of your body, causing serious complications.May 13, 2021
How fast does squamous cell carcinoma in situ spread?
Squamous cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes (spreads to other areas of the body), and when spreading does occur, it typically happens slowly.
What is the most common treatment for squamous cell carcinoma?
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer TreatmentMohs Surgery. Mohs surgery has the highest cure rate of all therapies for squamous cell carcinomas. ... Curettage and Electrodessication. This very common treatment for squamous cell carcinoma is most effective for low-risk tumors. ... Cryosurgery. ... Laser Surgery.
Is squamous cell carcinoma in situ considered malignant?
Carcinoma in situ refers to cancer in which abnormal cells have not spread beyond where they first formed. The words “in situ” mean “in its original place.” These in situ cells are not malignant, or cancerous. However, they can sometime become cancerous and spread to other nearby locations.Aug 22, 2019
How do I know if squamous cell carcinoma has spread?
How to Tell If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has SpreadThe tumor is thicker than 2 millimeters.The tumor has grown into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin.The tumor has grown into the nerves in the skin.The tumor is present on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip.Oct 4, 2021
What percentage of squamous cell skin cancers metastasize?
The risk of metastasis from a high risk SCC runs from 10 to 30%. The treatment for an SCC depends on its type, location and risk.
What is considered early treatment for squamous cell carcinoma?
Cryotherapy. Cryotherapy (cryosurgery) is used for some early squamous cell cancers, especially in people who can't have surgery, but is not recommended for larger invasive tumors or those on certain parts of the nose, ears, eyelids, scalp, or legs.Jun 24, 2020
What is squamous cell carcinoma in situ?
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ, also called Bowen disease, is the earliest form of squamous cell skin cancer. “In situ” means that the cells of these cancers are still only in the epidermis (the upper layer of the skin) and have not invaded into deeper layers.Jul 26, 2019
What kills squamous cell carcinoma?
Cryotherapy (cryosurgery) Cryotherapy is used most often for pre-cancerous conditions such as actinic keratosis and for small basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For this treatment, the doctor applies liquid nitrogen to the tumor to freeze and kill the cells.Feb 22, 2021
What stage is squamous cell carcinoma in situ?
Stage 0. Cancer is found only in the original tumor in the skin. It is only in the epidermis and has not spread to the dermis. Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ.
How is carcinoma in situ treated?
The standard treatment is breast-preserving surgery (a lumpectomy) with radiation therapy, which results in successful outcomes for most patients. Cancers can be larger than expected, so about 20% of the time, patients need a re-excision lumpectomy — another surgery — to remove all of the cancer.
What does at least squamous cell carcinoma in situ mean?
Listen to pronunciation. (KAR-sih-NOH-muh in SY-too) A group of abnormal cells that remain in the place where they first formed. They have not spread.
What is the best treatment for squamous cell cancer?
Surgery. Different types of surgery can be used to treat squamous cell skin cancers. Excision: Cutting out the tumor, along with a small margin of normal skin, is often used to treat squamous cell cancers.
Is radiation therapy good for cancer?
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is often a good option for patients with large cancers, especially in areas where surgery would be hard to do (such as the eyelids, ears, or nose), or for patients who can’t have surgery.
Can you have cryotherapy for squamous cell cancer?
Cryotherapy (cryosurgery) is used for some early squamous cell cancers, especially in people who can’t have surgery, but is not recommended for larger invasive tumors or those on certain parts of the nose, ears, eyelids, scalp, or legs.
Can lymph nodes be dissected?
Lymph node dissection: Removing regional (nearby) lymph nodes might be recommended for some squamous cell cancers that are very large or have grown deeply into the skin, as well as if the lymph nodes feel enlarged and/or hard. The removed lymph nodes are looked at under a microscope to see if they contain cancer cells.
Can you get radiation after surgery?
Sometimes, radiation therapy might be recommended after surgery. Immunotherapy: For advanced squamous cell cancers that can’t be cured with surgery or radiation therapy, one option might be using an immunotherapy drug such as cemiplimab (Libtayo) or pembrolizumab (Keytruda).
Can squamous cell skin cancer be cured?
Most squamous cell skin cancers are found and treated at an early stage, when they can be removed or destroyed with local treatment methods. Small squamous cell cancers can usually be cured with these treatments. Larger squamous cell cancers are harder to treat, and fast-growing cancers have a higher risk of coming back.
What is the difference between imiquimod and 5-fluorouracil?
5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and imiquimod are creams or gels that can be applied directly to affected areas of the skin to treat superficial SCCs with minimal risk of scarring. Imiquimod activates the immune system to attack cancerous cells, while 5-FU is a topical therapy that targets cancerous and precancerous cells.
How does scalpel surgery work?
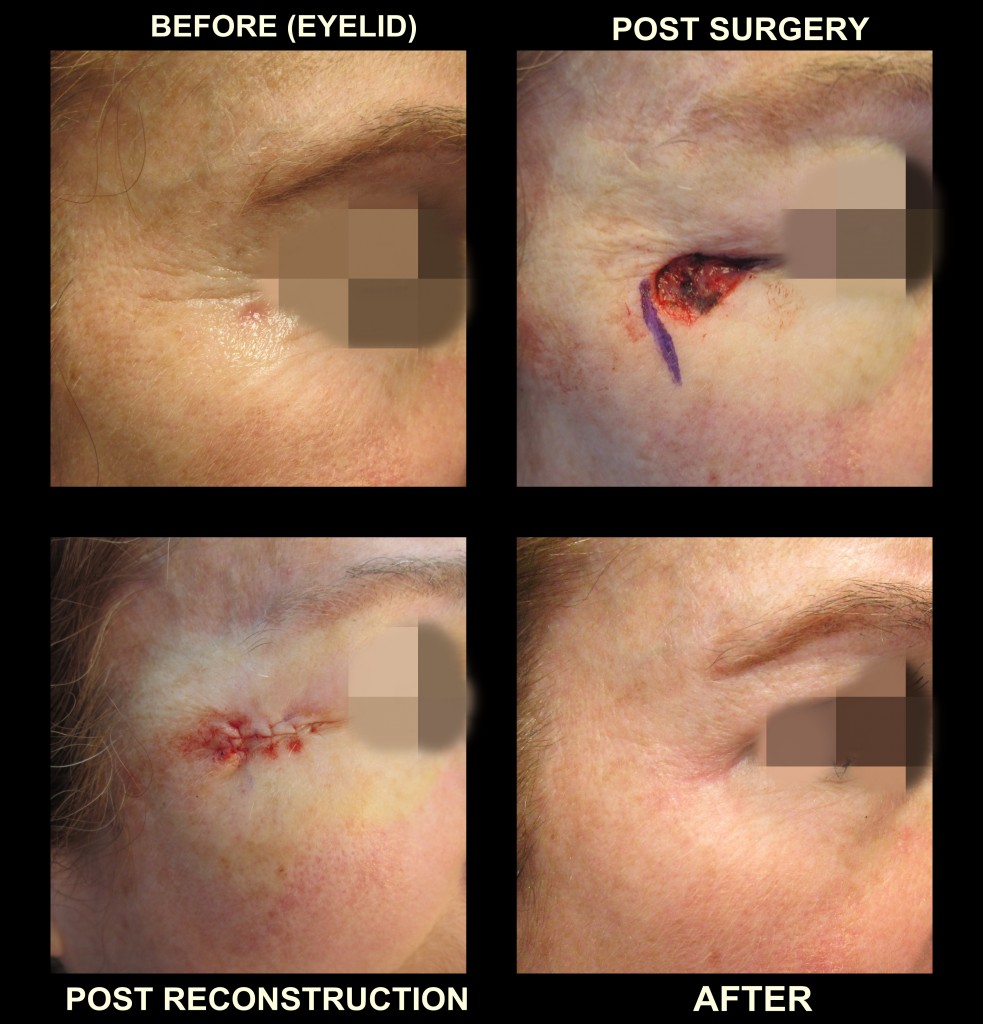
Using a scalpel, the surgeon removes the entire tumor along with a “safety margin” of surrounding normal tissue. The margin of normal skin removed depends on the thickness and location of the tumor. Typically, the patient goes home after the surgery, and the excised tumor goes to the lab. If the lab finds cancer cells ...
Can a cancer wound heal on its own?
The doctor repeats this process until there is no evidence of cancer. Then the wound may be closed or, in some cases, allowed to heal on its own.
How does a curette work?
How it works. The physician scrapes or shaves off the SCC with a curette (a sharp instrument with a ring-shaped tip), then uses heat or a chemical agent to stop the bleeding and destroy remaining cancer cells. The procedure may be repeated a few times during the same session until no cancer cells remain.
Can radiation therapy be used for SCC?
Radiation therapy is primarily used for SCCs that are hard to treat surgically, and in elderly patients or people in poor health for whom surgery is not advised. For some cases of advanced SCC, especially those with perineural involvement, radiation may be used after surgery, or in combination with other treatments.
How does laser therapy work?
How it works. The physician directs a beam of intense light at the tumor to target the cancerous cells. Some lasers vaporize (ablate) the skin cancer, while others (nonablative lasers) convert the beam of light to heat, which destroys the tumor.
Can SCC be cured?
Effective Options for Early Stage SCC. Most squam ous cell carcinomas (SCCs) of the skin can be cured when found and treated early. Treatment should happen as soon as possible after diagnosis, since more advanced SCCs of the skin are more difficult to treat and can become dangerous, spreading to local lymph nodes, distant tissues and organs.
What is squamous cell carcinoma in situ?
This simply means that the cancer cells haven’t yet spread beyond the epidermis.
What is the term for a cancer cell that has spread beyond the epidermis?
Early forms of squamous cell carcinoma, also known as Bowen disease, are classified as in situ, which means “in place” in Latin. This simply means that the cancer cells haven’t yet spread beyond the epidermis. When the carcinoma spreads deeper into the skin, into the lymph nodes or organs, it is considered to be metastasized.
Can squamous cell carcinoma spread to lymph nodes?
This cancer usually develops slowly but can spread to the lymph nodes and other organs if left untreated. If caught early though, it is highly treatable. Skin cancer symptoms: what to look out for. A doctor will diagnose squamous cell carcinoma with a biopsy.
What is the treatment for squamous cell carcinoma?
When squamous cell carcinoma spreads to other parts of the body, drug treatments might be recommended, including: Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells. If squamous cell carcinoma spreads to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body, chemotherapy can be used alone or in combination with other treatments, ...
What is the treatment for cancer cells?
During photodynamic therapy, a liquid drug that makes the cancer cells sensitive to light is applied to the skin. Later, a light that destroys the skin cancer cells is shined on the area.
How does immunotherapy work?
Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process. For squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, immunotherapy might be considered when the cancer is advanced and other treatments aren't an option. There is a problem with information submitted for this request.
Is skin cancer treatable?
Although skin cancer is usually highly treatable, just hearing the word "cancer" can make it difficult to focus on what the doctor says next. Take someone along who can help you remember the information. Below are some basic questions to ask your doctor about squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
What is laser treatment?
Laser therapy. An intense beam of light vaporizes growths, usually with little damage to surrounding tissue and with a reduced risk of bleeding, swelling and scarring. Laser treatment may be an option for very superficial skin lesions. Freezing.
How to treat superficial skin cancer?
Photodynamic therapy. Photodynamic therapy combines photosensitizing drugs and light to treat superficial skin cancers.
Can you get skin cancer if you have already had it?
If you've already had skin cancer, you have an increased risk of a second cancer. Talk with your dermatologist about how often you should have a skin examination to look for signs of another skin cancer. Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment, and what to expect from your doctor.
How to remove squamous cell?
Surgery is often recommended to remove squamous cell lesions, particularly those classified as high risk. Surgical removal involves injecting a local anesthetic and removing the tumor from the skin along with a “safety margin” to ensure that all of the cancer cells have been removed.
What is the best treatment for a tumor?
Radiation Therapy. Radiation therapy with x-rays or high-energy particles can be useful for treating tumors in areas that are difficult to treat with surgery, or in older people and others at a higher risk for complications with surgery.
What is the term for a pink spot on the skin?
While most skin cancer arises as a brand new spot, some squamous cell carcinoma develops from a precancer called actinic keratosis, or solar keratosis (usually a rough, flat, pink spot on the skin, which may become firm and raised above the normal skin surface if it becomes cancerous).
Can you delay skin cancer treatment?
Our skin cancer experts are experienced in helping people make a treatment decision they are comfortable with. It’s important not to delay treatment for too long, since this can make the cancer more difficult to cure. Waiting to treat squamous cell skin cancer also increases the risk of hurting your appearance and leading to difficulties ...
What is the procedure to remove precancerous cells?
Another option for small, low-risk lesions is topical chemotherapy.
Do you have to wear a mask at MSK?
Masks Are Still Required at MSK. Patients and visitors must continue to wear masks while at MSK, including people who are fully vaccinated. MSK is offering COVID-19 vaccines to all patients age 12 and over. To schedule or learn more, read this. For Adult Patients /.
What is the advantage of surgery?
An advantage of surgery is that the tissue can be sent to a laboratory for microscopic evaluation by a pathologist, who will verify whether the entire tumor has been removed along with enough space between the cancerous and noncancerous tissue. Any form of surgery can leave a scar, some more noticeable than others.