
- Rest your body. It needs time to heal.
- Ice your shin to ease pain and swelling. Do it for 20-30 minutes every 3 to 4 hours for 2 to 3 days, or until the pain is gone.
- Use insoles or orthotics for your shoes. ...
- Take anti-inflammatory painkillers, if you need them.
How to heal shin splints fast?
· Musculoskeletal causes of shin pain. Shin pain may be caused by inflammation or damage to your muscles and bones including: Anterior compartment syndrome of the lower leg. Bone fracture. Shin splints. Stress fracture of the tibia (shin bone) Tendonitis (inflammation of one or more leg muscle tendons)
What causes shin pain when walking or running?
· In most cases, you can treat shin splints with simple self-care steps: Rest. Avoid activities that cause pain, swelling or discomfort — but don't give up all physical activity. While you're... Ice. Apply ice packs to the affected shin for 15 to 20 minutes at a …
What causes shin pain?
The best course of treatment for shin splints is to stop any activity that's causing the pain until the injury is healed. Other treatment may include: Stretching exercises Strengthening exercises Cold packs Medicine, such as ibuprofen Running shoes with a stiff heel and special arch support Can shin splints be prevented?
Are there medications to treat shin splints?
· Place ice packs wrapped in towels on the affected area for 15 minutes every few hours until symptoms subside. Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and naproxen sodium can...
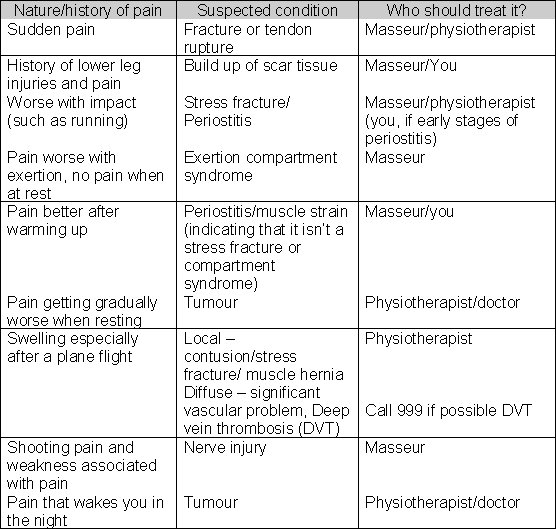
What is the best way to get rid of shin pain?
Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE) methodRest. Rest from all activities that cause you pain, swelling, or discomfort. ... Ice. Place ice packs on your shins for 15 to 20 minutes at a time. ... Compression. Try wearing a calf compression sleeve to help reduce inflammation around your shins.Elevation.
Which medicine is best for shin pain?
You can try an over-the-counter (OTC) pain reliever like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB), naproxen sodium (Aleve), or acetaminophen (Tylenol) to reduce shin splint discomfort.
How do you stop shin bone pain?
8 Tips to Prevent Shin SplintsStretch your calves and hamstrings. ... Avoid sudden increases in physical activity. ... Exercise on softer surfaces when possible. ... Strengthen your foot and the arch of your foot. ... Strengthen your hip muscles. ... Buy new athletic shoes that are right for you. ... Stay at a healthy body weight.More items...
What is the most common treatment for shin splints?
Most cases of shin splints can be treated with rest, ice and other self-care measures. Wearing proper footwear and modifying your exercise routine can help prevent shin splints from recurring.
What deficiency causes shin pain?
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with tibial bone pain and tenderness.
How do you get rid of leg pain fast?
If you have leg pain from cramps or overuse, take these steps first:Rest as much as possible.Elevate your leg.Apply ice for up to 15 minutes. ... Gently stretch and massage cramping muscles.Take over-the-counter pain medicines such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Is a hot bath good for shin splints?
An easier version of this would be to visit a hot tub (find one at your gym) and bring a big bag of ice with you. First, throw the ice bag on your shins for 7-8 min., then sit at the edge of the hot tub for 8-10 soaking your legs, and repeat.
How long do shin splints take to heal?
This phase lasts approximately 2 to 4 weeks. If you add up all the time it takes to heal injured tissue in your body, then it would take approximately 7 to 9 weeks. Most cases of shin splints last about that long as well.
Does massage help shin splints?
If you're suffering from shin splint pain, massage therapy can help with pain relief. The deep tissue strokes release built-up tension, resulting in pain release and the prevention of scar tissue accumulation.
How do you strengthen your shins?
0:322:58Fight Shin Splints and Build Strong Shins! - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd now you're gonna pull your toes up pull them towards your knees keep your quads squeeze flexMoreAnd now you're gonna pull your toes up pull them towards your knees keep your quads squeeze flex those muscles in front of your shins. Lower all the way down.
How do you get rid of shin splints overnight?
Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE) methodRest. Rest from all activities that cause you pain, swelling, or discomfort. ... Ice. Place ice packs on your shins for 15 to 20 minutes at a time. ... Compression. Try wearing a calf compression sleeve to help reduce inflammation around your shins.Elevation.
Can arthritis cause shin pain?
"The condition slowly wears away joint cartilage so the surfaces of the shin bone, thighbone, and kneecap rub together, which can lead to pain, swelling, and inflammation and make movement difficult," says Dr.
How long do shin splints take to heal?
Shin splints often go away once the legs have had time to heal, usually in three to four weeks. Most people can resume an exercise program after their legs have healed. It takes longer to recover from a stress fracture, so it is best to have shin splints treated early.
Is Voltaren good for shin splints?
Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory drugs (like Nurofen or Voltaren) can assist in speeding up recovery and may be recommended by your physio.
Is a hot bath good for shin splints?
An easier version of this would be to visit a hot tub (find one at your gym) and bring a big bag of ice with you. First, throw the ice bag on your shins for 7-8 min., then sit at the edge of the hot tub for 8-10 soaking your legs, and repeat.
What causes pain in shins at night?
If you're experiencing cramps at night, this could be from restlessness and turning over in bed. This triggers the muscle causing it to cramp. Interestingly, they can also be caused by a lack of movement, specifically if you hold a position for a long period of time.
What is shin pain?
Shin pain is pain that occurs along the shin bone (tibia) in the front part of the lower leg. The shin extends all the way from the knee to the ankle. One common cause of shin pain is shin splints, a term to describe pain that results from overuse or participation in sports involving running or other impact on the foot.
What are the symptoms of shin pain?
Shin pain may accompany symptoms related to other body systems including: Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing. Fever. Numbness or tingling in other areas of the body.
What causes a tingling sensation in the back of the spine?
Examples include: Arthritis affecting the spine. Degenerative joint disease. Herniated disc.
What is the pain of a claudication?
The pain of peripheral artery disease (PAD, also called peripheral vascular disease, or PVD, which is a narrowing or blockage of arteries due to a buildup of fat and cholesterol on the artery walls, which limits blood flow to the extremities), known as intermittent claudication, occurs in the legs while walking.
Why does my shin hurt?
Another common cause of shin pain is a stress fracture of the tibia. Peripheral neuropathy (disorder that causes dysfunction of nerves that lie outside your brain and spinal cord) may cause a painful, burning or prickling sensation of the skin of the lower legs.
Can shin pain be a sign of a serious condition?
In some cases, shin pain may occur with other symptoms that might indicate a serious condition that should be immediately evaluated in an emergency setting. Seek immediate medical care if you, or someone you are with, have shin pain along with other serious symptoms including:
How to prevent shin pain?
Protection – Prevent the shin from suffering from further damage. Stop training or playing immediately and apply cold therapy and a compression wrap.
What causes shin pain?
The following conditions are very rarely seen as a cause of shin pain, however, a doctor or professional practitioner should be aware of them, particularly if shin pain is persistent or not responding to conventional treatments. Syphilis. Sickle-cell anemia. Hyperparathyroidism.
What is the pain in the top of the shin?
Osgood Schlatter disease is a painful injury of the knee affecting children between the ages of 8 and 15 years old. Pain is felt on the bumpy bit at the top of the shin but may radiate down. Pes anserine bursitis is inflammation of a bursa or sack of fluid on the inside of the knee.
What is referred pain in the shin?
Referred pain – where a problem or injury elsewhere causes pain in the shin. It can occur from the spine, from the ankle joint, from a cyst on the knee cartilage or from a Baker’s cyst. A Bakers cyst is a swelling behind the knee and, although this can cause pain down into the shin, it is not particularly common.
Where is the pain on the outside of the calf?
However, pain may be felt on the outside of the shin in the anterior compartment or the big muscle on the outside of the shin.
Why does my shin hurt so bad?
Symptoms include constant pain and tenderness at a point deep in the muscle.
What happens when you exercise and your shins hurt?
When you exercise, the muscle fills with blood and expands causing pain. With rest, your pain eases, only to return again when normal training resumes. Treatment may involve long-term rest, biomechanical analysis, shin taping, or in some cases, surgery is required to release the sheath allowing the muscle to expand.
How to heal a shin splint?
In most cases, you can treat shin splints with simple self-care steps: 1 Rest. Avoid activities that cause pain, swelling or discomfort — but don't give up all physical activity. While you're healing, try low-impact exercises, such as swimming, bicycling or water running. 2 Ice. Apply ice packs to the affected shin for 15 to 20 minutes at a time, four to eight times a day for several days. To protect your skin, wrap the ice packs in a thin towel. 3 Take an over-the-counter pain reliever. Try ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), naproxen sodium (Aleve) or acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) to reduce pain.
How to diagnose shin splints?
Shin splints are usually diagnosed based on your medical history and a physical exam. In some cases, an X-ray or other imaging studies can help identify other possible causes for your pain, such as a stress fracture.
How to prevent shin splints?
You may be able to prevent shin splints by wearing good fitting athletic shoes. Also, gradually increase the intensity, duration, and frequency of a new exercise routine. It may also help to switch between high impact activities and low impact activities such as swimming or cycling.
What is a shin splint?
Shin splints refer to the pain and tenderness along or just behind the large bone in the lower leg. They develop after hard exercise, sports, or repetitive activity. Shin splints cause pain on the front or outside of the shins or on the inside of the lower leg above the ankle.
What happens if you get a shin splint?
As the shin splint progresses, the pain will increase. The symptoms of shin splints may look like other conditions or medical problems. Always talk with your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How does a shin splint feel?
In time, pain becomes constant and the shin is painful to the touch. Pain that starts on the inside of the lower leg above the ankle. Pain gets worse when standing on the toes or rolling the ankle inward. As the shin splint progresses, the pain will increase. The symptoms of shin splints may look like other conditions or medical problems.
How do you know if you have a shin splint?
What are the symptoms of shin splints? These are the most common symptoms of shin splints: Pain felt on the front and outside of the shin. It's first felt when the heel touches the ground during running. In time, pain becomes constant and the shin is painful to the touch.
How to treat a swollen thigh?
Treatment includes stopping the activity that causes pain. Stretching and strengthening exercises may also help . You can also apply cold packs, take medicines, such as ibuprofen, and wear good fitting athletic shoes.
What is a shin splint?
Shin splints are pains that occur along the front of your lower leg or tibia bone. They are a common occurrence in people who indulge in activities that involve high impact stresses on the feet and legs. Shin splints affect a range of people, including military personnel, dancers, and runners; they often occur when training routines are changed, ...
Where does a shin splint hurt?
Shin splints are characterized by pain in the lower leg, on the front, outside, or inside of the leg. Often, the pain starts as the exercise begins, gradually gets better as the session continues, then gets worse again after exercising is complete.
How to treat a swollen thigh?
Rest and recuperation: switch to lower impact activities such as swimming while the condition heals. Place ice packs wrapped in towels on the affected area for 15 minutes every few hours until symptoms subside. Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and naproxen sodium can help ease the pain.
Does pain stop when you exercise?
Initially, the pain will stop when exercise stops, but if the condition worsens, the pain can become constant. It is important to have the pain checked by a doctor because other conditions have similar symptoms (see section on diagnosis).
What is the pain of a tibia?
Pain and tenderness along the tibia. Potential swelling of the lower legs. In chronic cases, there may be lumps or bumps felt along the bones. In severe cases, there may be red patches on the skin around painful areas.
What are the symptoms of a shin splint?
Medical conditions that have similar symptoms to shin splints include: Reduced blood flow in the lower leg (more common in smokers). Leg muscle bulging out of place (muscle hernia ). Swelling of muscles causing nerve compression (compartment syndrome). Nerve problems in the lower back (radiculopathy).
What causes shin splints?
Other factors that increase the risk of shin splints include: Share on Pinterest. A sudden increase in exercise intensity increase s the risk of shin splints. Smoking and general lack of fitness.
What is a shin splint?
Shin splints are injuries to the front of the outer leg. While the exact injury is not known, shin splints seem to result from inflammation due to injury of the soft tissues in the front of the outer leg. Shin splints are a member of a group of injuries called overuse injuries. Shin splints occur most commonly in runners or aggressive walkers.
What causes shin splints?
Similarly, a tight Achilles tendon or weak ankle muscles are also often implicated in the development of shin splints.
What is the best test for a fractured tibia?
Radiology tests, such as X-rays, bone scan, or MRI scan, can be helpful in this setting to detect stress fracture of the tibia bone.
What are the symptoms of chronic injuries?
Symptoms of chronic injuries include soreness, dull aching pain, and pain during participation in physical activity. Find out about treating shin splints ».
How long is a shin splint?
An area of discomfort measuring 4-6 inches (10 -15 cm) in length is frequently present. Pain is often noted at the early portion of the workout, then lessens, only to reappear near the end of the training session. Shin splint discomfort is often described as dull at first.
What are the risk factors for shin splints?
Risk factors for shin splints include running and over-training on hills, inadequate footwear for athletic activity, and poor biomechanics of the design of the legs and feet.
Where is the shin splint located?
The pain is characteristic and located on the outer edge of the mid region of the leg next to the shinbone (tibia). It can be extreme and halt workouts. The diagnosis requires a careful focused examination. A multifaceted approach of "relative rest" can restore a pain -free level ...
What muscle is responsible for shin pain?
The tibialis anterior muscle of the shin usually contains significant myofascial trigger points (muscle knots) — an under-diagnosed & under-treated factor in many cases of shin pain.
What is a shin splint?
Shin splints is an extremely common repetitive strain injury in runners and running athletes. It can be impressively stubborn, because there are several possible overlapping types/causes, some more subtle and less “mechanical” ...
Is 14 Shin splints a physical injury?
But it’s definitely not just that. First of all, not all loading is physical or simple. 14 Shin splints is routinely defined as an overload, overuse, or exercise-induced problem, and this is correct — but it’s also not the whole story. Not every case involves tissue overloading, but most probably do. And not every case only involves tissue overload.
Can a rehab plan cause shin pain?
Often the only problem with a rehab plan is that it was started too aggressively. Muscle pain is probably a significant factor in many cases of shin pain, but this is almost always missed or underestimated — health care has a huge blind spot for muscle, and often just ignores the role of muscle in injuries. 10.
Do feet have shins?
Feet have entire professions devoted to them, but not shins! For most professionals, shin pain is just one of a list of hundreds of common pain problems they deal with, and they are more or less completely unaware of the finer points of the subject, particularly recent scientific research.
Is a shin splint the only kind of shin pain?
But it is definitely not the only kind.
Why are shin splints stubborn?
It can be impressively stubborn, because there are several possible overlapping types/causes, some more subtle and less “mechanical” than most people ever suspect . Shin splints treatment depends on what type you have. “Many people are afraid of running because between 30 to 70 percent (depending on how you measure it) of runners get injured every ...
What is a shin splint?
Medial tibial stress syndrome (MTSS), commonly known as “shin splints,” is a frequent injury of the lower extremity and one of the most common causes of exertional leg pain in athletes (Willems T, Med Sci Sports Exerc 39(2):330–339, 2007; Korkola M, Amendola A, Phys Sportsmed 29(6):35–50, 2001; Hreljac A, Med Sci Sports Exerc 36(5):845–849, 2004). Although often not serious, it can be quite disabling and progress to more serious complications if not treated properly. Often, the cause of MTSS is multi-factorial and involves training errors and various biomechanical abnormalities. Few advances have been made in the treatment of MTSS over the last few decades. Current treatment options are mostly based on expert opinion and clinical experience. The purpose of this article is to review published literature regarding conservative treatment options for MTSS and provide recommendations for sports medicine clinicians for improved treatment and patient outcomes.
What is MTSS in shin?
Medial tibial stress syndrome (MTSS) is an overuse injury or repetitive-stress injury of the shin area. Various stress reactions of the tibia and surrounding musculature occur when the body is unable to heal properly in response to repetitive muscle contractions and tibial strain.
What muscles are affected by MTSS?
Muscle imbalance and inflexibility, especially tightness of the triceps surae (gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles), is commonly associated with MTSS [1, 7, 8]. Athletes with muscle weakness of the triceps surae are more prone to muscle fatigue, leading to altered running mechanics, and strain on the tibia [1]. Clinicians should also examine for inflexibility and imbalance of the hamstring and quadriceps muscles.
Does MTSS cause pain?
The most common complaint of patients with MTSS is vague, diffuse pain of the lower extremity, along the middle-distal tibia associated with exertion [1, 6]. In the early course of MTSS, pain is worse at the beginning of exercise and gradually subsides during training and within minutes of cessation of exercise. As the injury progresses, however, pain presents with less activity and may occur at rest.
Is there a systematic review of literature on MTSS?
Many studies focused on the etiology and risk factors for MTSS, rather than treatment. However, a recent systematic review of literature demonstrated serious methodological flaws in four RCTs [5]. It is apparent that few interventions and conservative treatment options for MTSS have undergone rigorous examination [5].
Is a X-ray necessary for MTSS?
Imaging is usually not necessary for the diagnosis of MTSS. However, if the patient fails to improve with conservative management, plain film radiography may be considered. X-rays are usually negative within the first 2–3 weeks after the onset of injury [28]. Long-term radiographic changes of those with chronic MTSS with periosteal involvement may show periosteal exostoses. Those that progress from MTSS to stress fracture may develop a dreaded black line on radiograph, which indicates a more ominous sign [13].
How to relieve shin pain?
Get enough rest to relieve the pain in the shins before the next exercise or workout session. Wear the right size of shoes. Wear shock-absorbing insoles to reduce the impact of shin splints. Use KT tapes to relieve the pressure and strain on the shin muscles.
What is the best treatment for shin splints?
Apple cider vinegar is touted to have anti-inflammatory properties. This may help in treating shin splints.
How long does it take for a shin splint to heal?
The pain that accompanies shin splints usually vanishes in 3 to 4 weeks. Nevertheless, shin splints may take 3 to 6 months to heal completely.
How to get rid of shin splints while pregnant?
However, pregnant women may also follow the tips mentioned below to get relief: Elevate your legs as often as you can. Sleep on your side. Consume plenty of fluids.
Why does my shin hurt?
Common Causes Of Shin Splints. The pain in the shin may be due to the following reasons: Stress Fracture: Repeated stress to the shin bone may result in a small fracture. This fracture, which is an overuse injury, is referred to as stress fracture.
What are some good foods to eat to help with shin splints?
Bananas are a rich source of potassium. Potassium has anti-inflammatory properties ( 19 ). This may help in treating muscle inflammation that occurs due to shin splints.
Does pickle juice help with shin splints?
A study showed that pickle juice could inhibit muscle cramps ( 10 ). This may make pickle juice one of the best cost-effective treatments for shin splints.

Symptoms
Society and culture
- Shin splints is a common term used to describe shin pain. However, this is a general term to describe pain on the inside of the shin, of which there can be a number of causes.
Treatment
- Initial treatment involves rest and applying cold therapy to reduce pain and inflammation. A simple shin taping technique can help protect the area and relieve shin pain. Identifying and correcting training errors, footwear or biomechanical problems are important. Once pain allows, a gradual return to full fitness with a progressive rehabilitation ...
Causes
- Compartment syndrome occurs when the muscle swells up within its surrounding sheath, causing increased pressure and pain. Acute compartment syndrome can develop from direct trauma or impact to the shin. Bleeding of the muscle within the sheath surrounding it occurs, causing increased pressure and pain which can be severe. If pain becomes progressively worse and acut…
Clinical significance
- Tibia fractures and fibula fractures can occur after an acute trauma or impact. The lower leg is a common area for fractures and can often be broken in contact sports like rugby. A broken leg can take a while to heal, depending on where the fracture is and how clean the break is. DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) is a blood clot in a vein that is commonly seen in the calf muscle, particularly f…
Epidemiology
- Tumors of bone and soft tissue are rare, but most likely occur in athletes in their 20s and 30s. Osteosarcomata can occur at the ends of the long bones, particularly of the lower leg causing joint pain.
Signs and symptoms
- Infections such as osteomyelitis or cellulitis may cause pain. The condition can be classed as acute, sub-acute, or chronic depending on the time frame between the initial infection or injury and the bone infection developing. This can be two months or more in chronic cases.