
Medication
The main treatment for acute bacterial prostatitis is the use of antibiotics (such as ampicillin, levofloxacin or clindamycin) to kill the bacteria. Depending on the antibiotic and the type of bacteria, this treatment can last anywhere from several weeks to a few months.
Self-care
Dec 21, 2017 · Hot baths or over-the-counter pain relievers can help when chronic prostatitis causes muscle tenderness or spasms. For some men, the best choice is a pain medication that also reduces inflammation, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or another NSAID. Anticholinergic drugs. These medications, which include tolterodine (Detrol) and oxybutynin (Ditropan), reduce the …
Nutrition
May 15, 2000 · An antibiotic is used to treat prostatitis that is caused by an infection. Some antibiotics that might be used are trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and...
Can prostatitis be cured by itself?
Men with acute bacterial prostatitis may need 14 to 30 days of antibiotics, starting with IV antibiotics in the hospital. Rarely, men need surgery to drain an abscess on the prostate. Treating chronic bacterial prostatitis is challenging. You may need up to three months of antibiotics to sterilize the prostate.
How I cured my prostatitis at home?
Apr 12, 2022 · Drugs that best fit these criteria are the fluoroquinolones, doxycycline, minocycline (particularly effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [MRSA]), trimethoprim (available in...
How long does it take for Cipro to help prostatitis?
Feb 23, 2022 · Alpha blockers work by relaxing the prostate bladder muscles to encourage urine flow. Five-alpha reductase inhibitors partially shrink the prostate by reducing levels of dihydrotestosterone.
How do you cure prostatitis?
Dec 15, 2021 · This allowed the prostate tissue to be removed through the urethra. Bipolar enucleation of the prostate. Transurethrally enucleation can be performed with two different of energy sources. It can be completed with a holmium laser. This is called holmium laser enucleation of prostate, or HoLEP. Another option is with bipolar energy, called BipoLEP.
What is the fastest way to get rid of prostatitis?
The following remedies might ease some symptoms of prostatitis:Soak in a warm bath (sitz bath) or use a heating pad.Limit or avoid alcohol, caffeine, and spicy or acidic foods, which can irritate your bladder.Drink plenty of water. This will cause you to urinate more and help flush bacteria from your bladder.Feb 19, 2022
What triggers prostatitis?
Causes vary depending on the type of prostatitis. Acute bacterial prostatitis is usually caused by common strains of bacteria. The infection may have spread from other parts of the urinary or reproductive systems. Chronic bacterial prostatitis generally has the same cause as acute bacterial infection.Feb 19, 2022
What is the best antibiotic to treat prostatitis?
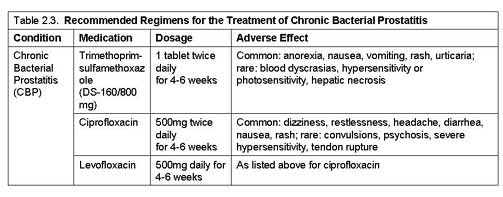
Oral antimicrobial agents are the mainstay of treatment for chronic bacterial prostatitis (CBP), with the most effective medications being fluoroquinolones and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX).May 25, 2021
What is the safest antibiotic for prostatitis?
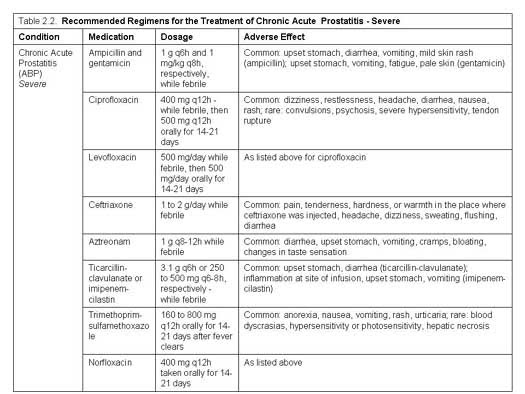
Common Antibiotic Regimens for Acute Bacterial ProstatitisMedicationStandard dosageTrimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra)1 DS tablet (160/800 mg) twice a dayDoxycycline (Vibramycin)100 mg twice a dayCiprofloxacin (Cipro)500 mg twice a dayNorfloxacin (Noroxin)400 mg twice a day1 more row•May 15, 2000
Can prostatitis be cured naturally?
Most cases of acute prostatitis will clear up with antibiotic treatment. Some severe cases of infection may require a hospital stay. There is the chance that acute prostatitis can become chronic. Symptoms of chronic prostatitis may be reduced with diet and lifestyle changes.
Is prostatitis serious?
Symptoms of prostatitis also can signal more serious conditions, including prostate cancer. Men with symptoms of prostatitis should see a health care provider. Men with the following symptoms should seek immediate medical care: complete inability to urinate.
How long should I take ciprofloxacin 500mg for prostatitis?
For outpatients, oral fluoroquinolones (the most common regimen is ciprofloxacin 500 mg orally twice daily) may be initiated for 2 to 4 weeks. According to one source, the optimal treatment duration is 6 weeks.Apr 18, 2014
Which is better doxycycline or ciprofloxacin?
Although more expensive than doxycycline, ciprofloxacin is a bactericidal compound which is better tolerated and has a lower risk of toxicity and of development of resistance. It can be considered, together with doxycycline, as an antibiotic of first choice in the treatment of Mediterranean spotted fever.
What is the best medication for enlarged prostate?
Alpha blockers — which include alfuzosin (Uroxatral), doxazosin (Cardura), tamsulosin (Flomax) and silodosin (Rapaflo) — usually work quickly in men with relatively small prostates.
Which is better levofloxacin or ciprofloxacin?
Both levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin were well tolerated, with similar rates of adverse events. Conclusions: Levofloxacin 500 mg once daily for 28 days is as effective as ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice daily for 28 days for the treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Can prostatitis be cured?
Most cases of acute bacterial prostatitis are cured with treatment. Sometimes prostatitis can come back even after you've been cured. Your health care provider may use more than one treatment at a time. Some men have to manage living with the symptoms until the inflammation goes away.
What is the best painkiller for prostatitis?
Depending on how long you have had symptoms, your doctor may suggest: painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen. a medicine called an alpha-blocker if you have problems peeing; alpha blockers can help relax the muscles in the prostate gland and the base of the bladder.
How to treat prostatitis?
Even though no bacteria are implicated in this kind of prostatitis, a physician will sometimes prescribe antibiotics in case there is a hidden infection. Most often, however, therapy involves treating the symptoms. Options include: 1 Over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve) 2 Soaking in a hot bath 3 Medications such as phenazopyridine (Pyridium), oxybutynin, or tolterodine to help with frequent, urgent, or painful urination 4 Psychological counseling to help with the ongoing pain
What is the procedure to remove bacterial prostatitis?
When such a surgery is deemed necessary, a laparoscopic prostatectomy (partial or radical) may be performed.
How long does it take for antibiotics to kill prostatitis?
Depending on the antibiotic and the type of bacteria, this treatment can last anywhere from several weeks to a few months . Escherichia coli infections are one of the most common causes, with this species of bacteria found in 65 to 80 percent of cases.
What is the name of the gland that sits below the urinary bladder?
Prostatitis Treatments. Prostatitis is the inflammation or infection of the male prostate, a walnut-shaped gland that sits just below the urinary bladder. Because there are several distinct kinds of prostatitis, treatment varies by the type and severity of the symptoms.
Why is it important to treat a prostate infection?
Such blockages are especially important to treat so as to prevent urine from backing up in the urinary tract and damaging the kidneys.
How long does it take for PSA to return to normal after antibiotics?
PSA levels should return to normal four to six weeks after treatment with antibiotics.
What is the best medicine for urination?
Medications such as phenazopyridine (Pyridium), oxybutynin, or tolterodine to help with frequent, urgent, or painful urination. Psychological counseling to help with the ongoing pain.
What is the best treatment for prostatitis?
For some men, the best choice is a pain medication that also reduces inflammation, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or another NSAID. Anticholinergic drugs.
What is the term for a group of problems characterized by burning or painful urination, urgency, and
The term prostatitis, which means inflammation of the prostate, refers to a group of syndromes characterized by urinary problems such as burning or painful urination, urgency, and trouble voiding; difficult or painful ejaculation; and pain in the perineum or lower back.
Which alpha blocker is less likely to lower blood pressure?
Selective alpha blockers such as alfuzosin (Uroxatral) or tamsulosin (Flomax) are less likely to lower blood pressure. Complementary therapies.
Can antibiotics help with prostatitis?
Antibiotics. The traditional view has been that unless there is evidence of bacterial infection, antibiotics are unlikely to be effective at treating chronic prostatitis. However, antibiotics sometimes work in men whose prostatitis had been preceded by a urinary tract infection.
Can you take an antibiotic with an alpha blocker?
An antibiotic might be combined with an al pha blocker to get better relief from discomfort and voiding difficulties. But if a first course of antibiotics does not improve symptoms, then a second one is unlikely to work, so it's wise to explore other options.
Does alpha blocker work for prostatitis?
These drugs relax the muscles at the neck of the bladder, easing the flow of urine. These drugs are most likely to work when the main symptom of chronic prostatitis is difficulty urinating. Choice of what alpha blocker to use may depend on side effects.
What is prostatitis treatment?
The term prostatitis describes a wide spectrum of conditions with variable etiologies, prognoses and treatments. Unfortunately, these conditions have not been well studied, and most recommendations for treatment, including those given here, are based primarily on case series and anecdotal experience.
How long do antibiotics last for prostatitis?
If the patient responds to therapy, antibiotics are continued for at least three to four weeks, although some men require treatment for several months.
How many subtypes of prostatitis are there?
These subtypes are acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic nonbacterial prostatitis and prostadynia. 5 Although this classification system has been widely used, it has never been validated for diagnostic or therapeutic utility.
What is CBP in men?
Chronic bacterial prostatitis (CBP) is a common cause of recurrent urinary tract infections in men. Patients typically have recurrent urinary tract infections with persistence of the same strain of pathogenic bacteria in prostatic fluid or urine. Symptoms can be quite variable, but many men experience irritative voiding symptoms, possibly with pain in the back, testes, epididymis or penis, low-grade fever, arthralgias and myalgias. Many patients are asymptomatic between episodes of acute cystitis. Signs may include urethral discharge, hemospermia and evidence of secondary epididymoorchitis. 13 Often the prostate is normal on digital rectal examination. No single clinical finding is diagnostic, although urine or prostatic secretion cultures can aid in the evaluation.
Why is prostatitis considered a wastebasket of clinical ignorance?
One author has described prostatitis as “a wastebasket of clinical ignorance” 1 because so many poorly characterized syndromes are diagnosed as prostatitis. The spectrum of prostatitis ranges from straightforward acute bacterial prostatitis to complex conditions that may not even involve prostatic inflammation.
What is the term for a chronic pain syndrome in which the prostate gland is inflamed?
The term prostatitis is applied to a series of disorders, ranging from acute bacterial infection to chronic pain syndromes, in which the prostate gland is inflamed. Patients present with a variety of symptoms, including urinary obstruction, fever, myalgias, decreased libido or impotence, painful ejaculation and low-back and perineal pain.
How long does it take for PSA to return to normal?
It does appear that PSA levels return to normal four to six weeks after a 14-day course of antibiotics. 23 Treatment is routinely recommended only in patients with chronic asymptomatic prostatitis known to elevate the PSA level. In these patients, it may be prudent to treat before drawing subsequent PSA samples.
What are the symptoms of prostatitis?
Symptoms of acute prostatitis may include: Pain around the penis, testicles, anus, lower abdomen or lower back. May be severe. Pain when defecating (passing poo) Pain when urinating (peeing), frequent urination (especially at night, urgent urination, problems starting or "stop-start" peeing, or blood in the urine.
How long does prostatitis last?
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis generally last for at least 3 months and may include: Pain around the penis, testicles, anus, lower abdomen or lower back. May be severe. Erectile dysfunction, pain when ejaculating or pelvic pain after sex.
What is the swelling of the prostate gland?
Prostatitis is a swelling and inflammation of the prostate gland. The prostate gland is a small walnut-shaped gland that sits just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra in men. It secretes prostate fluid, one of the main components of semen. Prostatitis can develop in men of all ages, but more commonly affects men between the ages ...
What age do men get prostatitis?
Prostatitis can develop in men of all ages, but more commonly affects men between the ages of 30 and 50. There are 2 main types: 1 chronic prostatitis: most common, not usually infection-related, symptoms come and go over several months 2 acute prostatitis: rare, symptoms come on suddenly and require immediate treatment, usually caused by an infection
How old do you have to be to get prostatitis?
Prostatitis can develop in men of all ages, but more commonly affects men between the ages of 30 and 50. There are 2 main types: chronic prostatitis: most common, not usually infection-related, symptoms come and go over several months.
What to do if you can't pass urine?
Hospital treatment may be necessary if you are unable to pass urine. If you have symptoms of chronic prostatitis, you may be referred to a urologist who specializes in genitourinary problems and management. Treatment may include: Painkillers.
How long do you have to take antibiotics for prostatitis?
You might have to take antibiotics for several weeks or even a few months. If prostatitis is severe, you might have to go to a hospital for treatment with fluids and antibiotics.
What causes prostatitis?
Two kinds of prostatitis, acute prostatitis and chronic bacterial prostatitis, are caused by infection of the prostate. Some kinds of prostatitis might be caused when the muscles of the pelvis or the bladder don't work right.
Why is my prostate red?
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland. When part of your body is inflamed, it is red, hot and sore. Prostatitis can cause many symptoms. It can make it difficult or painful to urinate. It can make you have to urinate more often.
What can I do to help a hidden infection?
Your doctor might try an antibiotic to treat a hidden infection. Other treatments are aimed at making you feel better. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, and hot soaking baths may help you feel better.
Where is the prostate located?
The prostate is a gland that lies just below a man's urinary bladder. It surrounds the urethra like a donut and is in front of the rectum. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the bladder, through the penis and out of the body.
Does prostatitis cause cancer?
Although prostatitis can cause you trouble, it does not cause cancer. There is a blood test some doctors use for prostate cancer called the prostate-specific antigen test (called the PSA, for short). If you have prostatitis, your PSA level might go up. This does not mean you have cancer.
Can prostatitis be passed on to a partner?
However, most cases are caused by infections that are not sexually transmitted. These infections can't be passed on to sexual partners.
What is the most common type of prostatitis?
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome, or CPPS (category 3): CPPS is the most common prostatitis type. Prostate gland inflammation occurs in approximately 1 out of 3 men.
What is a prostatic infection?
Prostatitis is a group of conditions that includes acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS). It can cause infection, inflammation and pain in the prostate gland. Men with asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis don’t have symptoms. Acute (sudden) prostatitis is a medical emergency. Urology 216.444.5600.
What is the name of the condition that causes pain in the genitals and pelvis?
Prostate gland inflammation occurs in approximately 1 out of 3 men. As the name implies, this type causes chronic pain in the pelvis, perineum (the area between the scrotum and rectum) and genitals. Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis (category 4): This condition causes prostate gland inflammation but no symptoms.
How common is prostatitis in men?
Half of all men have symptoms of prostatitis at some point in their lives. It’s the most common urinary tract issue in men younger than 50. In men over 50, it’s the third most common. More than two million men see a healthcare provider every year for prostatitis symptoms.
How long does it take to sterilize a prostate?
Treating chronic bacterial prostatitis is challenging. You may need up to three months of antibiotics to sterilize the prostate. If the prostate can’t be sterilized, low-dose antibiotics can be used long term to prevent recurrences. Some men need surgery to remove prostate stones or scar tissue in the urethra.
How long does it take for antibiotics to kill prostatitis?
Antibiotics can kill bacteria that cause bacterial types of prostatitis. Men with acute bacterial prostatitis may need 14 to 30 days of antibiotics, starting with IV antibiotics in the hospital. Rarely, men need surgery to drain an abscess on the prostate. Treating chronic bacterial prostatitis is challenging.
What is the blood test for prostate cancer?
This exam may include prostate massage to collect a sample of seminal fluid. Urinalysis: A urinalysis and urine culture check for bacteria and UTIs. Blood test: A blood test measures PSA, a protein made by the prostate gland. High levels may indicate prostatitis, BPH or prostate cancer.
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that occurs when the prostate and surrounding tissues expand. Typically, a male’s prostate is roughly the size of a walnut or golf ball, however, it has the potential to grow up to the size of an orange as the gland grows.
Treating BPH With Rezūm Water Therapy
Rezūm water therapy is a great option to provide lasting relief for those who do not want to treat BPH with medication or invasive surgery. This is a non-surgical treatment that uses the power of water, vapor, or steam, to remove excess prostate tissue that is pressing against the urethra, causing lower urinary tract symptoms.
Benefits of Using Rezūm Water Therapy
Having BPH can mean frequent trips to the bathroom and even interrupted sleep. The greatest benefit of Rezūm water therapy is how it works to relieve frustrating BPH symptoms that otherwise may still be present. Rezūm water therapy does not require painful surgery or medication, and is minimally invasive.
Treating BPH with UroLift
Similar to Rezūm, UroLift is a one time, in-office procedure that provides rapid relief and recovery for men living with symptoms of an enlarged prostate. The UroLift system is a relatively straightforward procedure that utilizes tiny implants to lift the enlarged prostate tissue away from the urethra so that urine is no longer blocked.
Benefits of Using UroLift
As you know, benign prostatic hyperplasia can have a negative impact on a man’s quality of life. An advantage of UroLift is that it doesn’t just treat BPH symptoms, but it completely removes the blockage to the urethra so that lower urinary tract symptoms do not worsen or reoccur.
Which Treatment is Right for Me?
Ultimately, the decision of which treatment would be best for your enlarged prostate should be decided between you and your healthcare provider. It’s important to discuss the process for each procedure with your doctor to determine the best treatment for enlarged prostate.
Other Available BPH Treatments
Although Rezūm and UroLift are the best treatment for enlarged prostate, they aren’t the only methods available to you. The severity of BPH varies from person to person, so not every treatment will be effective for every patient.
Signs and symptoms
Diagnosis
Classification
Causes
Specialist to consult
Treatment
- The symptoms associated with prostatitis can be caused by a number of conditions. You may be referred to a specialist in urinary and reproductive system disorders (urologist). Your health care provider will conduct a physical exam, review your symptoms and medical history, and order tes…
Research
Prognosis
Epidemiology
Adverse effects
Selected publications