Medication
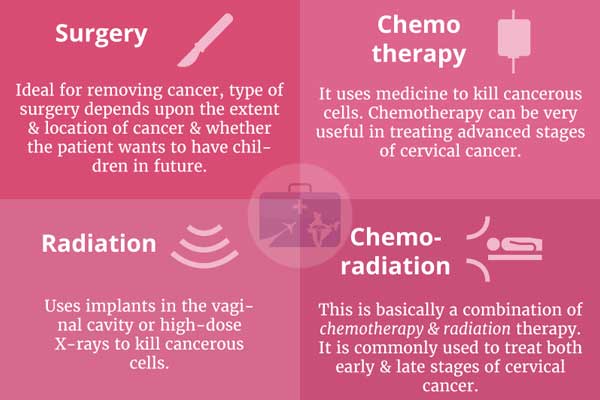
- For surgery to remove precancerous growths, a portion of the cervix is generally enough. ...
- For more locally advanced cervical tumors where surgery can not achieve cure alone, radiation therapy is preferred. ...
- Chemotherapy is a cancer-fighting medication that not only sensitizes the cervical cancer cells to radiation and makes radiation work better. ...
Procedures
“This study provides a proof of concept of immunotherapeutic checkpoint inhibition in cervical cancer. If cemiplimab is approved, it will provide a second-line treatment option for women with recurrent cervical cancer,” Tewari said.
Therapy
Gynecologists use several tests to diagnose cervical cancer, including:
- Pelvic exam: a visual and physical assessment of the external and internal female pelvic organs
- Pap smear: a screening that collects cells from the cervix
- HPV test: an STI test involving a sample of cervical cells
- Endocervical curettage: collection and examination of cervical tissue
- Colposcopy: examination of the cervix with a magnifying instrument
Nutrition
There has been a known correlation between the treatment of severe prodromal cervical cancer (CIN3, or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3, high-grade dysplasia) and higher risk pregnancies later in life, including preterm and very preterm birth, neonatal sepsis and early infant death.
What is the best treatment for cervical cancer?
How do you cure cervical cancer?
How is cervical cancer diagnosed and treated?
Is there a cure for cervical cancer?
How is pre cervical cancer treated?
Treatment for cervical pre-cancer In serious cases, it can mean surgery to remove abnormal cells, cryosurgery to freeze the cells, or laser therapy to burn away the cells. But more often the recommended treatment is monitoring the situation with more frequent Pap tests every six to 12 months.
What happens if you have pre cervical cancer?
Early-stage cervical cancer generally produces no signs or symptoms. Signs and symptoms of more-advanced cervical cancer include: Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, between periods or after menopause. Watery, bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and have a foul odor.
How long does it take for precancerous cervical cells to become cancer?
In fact, once cells in the cervix begin to undergo abnormal changes, it can take several years for the cells to grow into invasive cervical cancer. Many women experience precancerous changes in the cervix in their 20s and 30s, though the average woman with cervical cancer is diagnosed in her 50s.
Can pre cervical cancer go away?
For most women, pre-cancerous cells will go away without any treatment. But, in some women pre-cancers turn into true (invasive) cancers. Treating cervical pre-cancers can prevent almost all cervical cancers.
How often does pre cancer become cancer?
Cancers that begin in epithelial cells (roughly 85% of cancers) may have a precancerous state before they turn into cancer. These cells are found in the skin and the lining tissue of many organs. Some precancerous conditions include: Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN): A precancerous state of cervical cancer2.
How serious are precancerous cells?
Often, precancerous lesions are not invasive and a person will not develop cancer. In some cases these precancerous cells, if left alone, may go on to become “invasive” cancer cells. Sometimes, it may take these cells a few years, or even decades to progress.
Will getting a hysterectomy get rid of HPV?
A hysterectomy will not cure the HPV which has caused the CIN, as there is no cure for HPV, but the CIN cannot have spread anywhere else in your body and will only be in your cervix area-it doesn't travel through the bloodstream, and remains where the HPV infection is.
What happens if colposcopy is positive?
Colposcopy results A normal result means your cervix appears healthy and you have a low risk of developing cervical cancer before your next screening test. Depending on your age, you'll be invited for a cervical screening appointment in 3 or 5 years.
What causes precancerous cells in cervix?
It is also called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Strongly associated with sexually transmitted human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, cervical dysplasia is most common in women under age 30 but can develop at any age.
What does it mean to have pre cancer?
The takeaway is that a pre-cancerous condition does not mean you have cancer. It simply means you have an increased risk of cancer, which should serve as a reminder to stay current with medical visits and screening tests and communicate concerns or changes to your doctor.
Is CGIN worse than CIN?
CGIN is usually classified as low grade (mild) or high grade (severe). High grade CGIN is the equivalent of CIN3. CGIN can be multi-focal – this means that more than one area is affected at one time, with normal tissue lying between them.
What are the symptoms of pre cancer?
But to be safe, talk to your doctor about these five signs and symptoms.Unexplained Weight Loss. When you lose weight for no reason, call your doctor. ... Fatigue. This isn't fatigue similar to how you feel after a long day of work or play. ... Fever. ... Pain. ... Skin Changes.
How to treat cervical cancer?
Stage IVB cervical cancer is not usually considered curable. Treatment options include radiation therapy with or without chemo to try to slow the growth of the cancer or help relieve symptoms . Most standard chemo regimens include a platinum drug (cisplatin or carboplatin) along with another drug such as paclitaxel (Taxol), gemcitabine (Gemzar), or topotecan. The targeted drug bevacizumab (Avastin) may be added to chemo or immunotherapy alone with pembrolizumab (Keytruda) may also be an option.
What is the best treatment for pelvic cancer?
If the cancer has recurred in the center of the pelvis only, extensive surgery (s uch as pelvic exenteration) may be an option for some patients, and offers the best chance for possibly curing the cancer (although it can have major side effects). Radiation therapy (sometimes along with chemo) might be another option.
What is the treatment for a tumor that has grown into blood vessels?
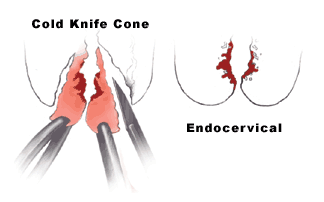
If the cancer has grown into blood or lymph vessels, one treatment option is a cone biopsy (with negative margins) with removal of pelvic lymph nodes. Another option is a radical trachelectomy along with removal of the pelvic lymph nodes.
What is the best treatment for cancer after birth?
Surgery options after birth for early-stage cancers include a hysterectomy, radical trachelectomy, or a cone biopsy. If the cancer is stage IB or higher, then you and your doctor must decide whether to continue the pregnancy. If not, treatment would be radical hysterectomy and/or radiation. Sometimes chemotherapy can be given during ...
What is the goal of cancer treatment?
No matter which type of treatment your doctor recommends, it's important that you understand the goal of treatment (to try to cure the cancer, control its growth, or relieve symptoms ), as well as its possible side effects and limitations.
What is the procedure for a woman who wants to have children after cancer?
A cone biopsy is the preferred procedure for women who want to have children after the cancer is treated. If the edges of the cone don’t contain cancer cells (called negative margins), the woman can be watched closely without further treatment as long as the cancer doesn’t come back. If the edges of the cone biopsy have cancer cells (called ...
What is the most important factor in choosing a cancer treatment?
The stage of a cervical cancer is the most important factor in choosing treatment. But other factors can also affect your treatment options, including the exact location of the cancer within the cervix, the type of cancer (squamous cell or adenocarcinoma), your age and overall health, and whether you want to have children.
What are the treatments for cervical cancer?
Common types of treatments for cervical cancer include: Surgery for Cervical Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Cervical Cancer. Chemotherapy for Cervical Cancer. Targeted Therapy for Cervical Cancer. Immunotherapy for Cervical Cancer.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What are the best doctors for cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team may include: 1 A gynecologist: a doctor who treats diseases of the female reproductive system 2 A gynecologic oncologist: a doctor who specializes in cancers of the female reproductive system who can perform surgery and prescribe chemotherapy and other medicines 3 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer 4 A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancer
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary methods refer to treatments that are used along with your regular medical care. Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment.
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team may include: A gynecologist: a doctor who treats diseases of the female reproductive system. A gynecologic on cologist: a doctor who specializes in cancers of the female reproductive system who can perform surgery and prescribe chemotherapy and other medicines. A radiation on cologist: a doctor who uses radiation ...
Why is it important to discuss treatment options with your doctor?
Making treatment decisions. It's important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisions that best fit your needs. It’s also very important to ask questions if there’s anything you’re not sure about.
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
How to treat cervical cancer during pregnancy?
Treatment of cervical cancer during pregnancy depends on the stage of the cancer and how long the patient has been pregnant. A biopsy and imaging tests may be done to determine the stage of the disease. To avoid exposing the fetus to radiation, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is used.
What is the risk factor for cervical cancer?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the major risk factor for cervical cancer. Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn't mean that you will not get cancer.
How big is stage 2 cervical cancer?
Stage II cervical cancer. In stages IIA1 and IIA2, cancer has spread from the cervix to the upper two-thirds of the vagina but has not spread to the tissue around the uterus. In stage IIA1, the cancer is 4 centimeters or smaller. In stage IIA2, the cancer is larger than 4 centimeters.
What is the purpose of DNA and RNA in a cervical Pap test?
Cells are collected from the cervix and DNA or RNA from the cells is checked to find out if an infection is caused by a type of HPV that is linked to cervical cancer. This test may be done using the sample of cells removed during a Pap test.
Where does cervical cancer form?
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where a fetus grows). The cervix leads from the uterus to the vagina (birth canal). Anatomy of the female reproductive system.
What is the procedure to remove abnormal cells from a Pap test?
Biopsy: If abnormal cells are found in a Pap test, the doctor may do a biopsy. A sample of tissue is cut from the cervix and viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. A biopsy that removes only a small amount of tissue is usually done in the doctor’s office.
How does chemo work?
When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle , the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body ( systemic chemotherapy ). When chemotherapy is placed directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas ( regional chemotherapy ). The way the chemotherapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated.
What tests are done to determine if you have cervical cancer?
Your cancer's stage is a key factor in deciding on your treatment. Staging exams include: Imaging tests.
What is the test for cervical cancer?
A Pap test can detect abnormal cells in the cervix, including cancer cells and cells that show changes that increase the risk of cervical cancer. HPV DNA test.
What is palliative care?
Palliative care is specialized medical care that focuses on providing relief from pain and other symptoms of a serious illness. Palliative care specialists work with you, your family and your other doctors to provide an extra layer of support that complements your ongoing care.
What tests can be done to check if you have cancer?
Tests such as X-ray, CT, MRI and positron emission tomography (PET) help your doctor determine whether your cancer has spread beyond your cervix. Visual examination of your bladder and rectum. Your doctor may use special scopes to see inside your bladder and rectum.
Can you get pregnant with cervical cancer?
A hysterectomy can cure early-stage cervical cancer and prevent recurrence. But removing the uterus makes it impossible to become pregnant.
Can you remove cancer from a small cervix?
Surgery to cut away the cancer only. For a very small cervical cancer, it might be possible to remove the cancer entirely with a cone biopsy. This procedure involves cutting away a cone-shaped piece of cervical tissue, but leaving the rest of the cervix intact.
Can you use chemotherapy for cervical cancer?
Sometimes both methods are used. For locally advanced cervical cancer, low doses of chemotherapy are often combined with radiation therapy, since chemotherapy may enhance the effects of the radiation . Higher doses of chemotherapy might be recommended to help control symptoms of very advanced cancer.
What causes cervical cancer?
CIN and cervical cancer are caused by the sexually transmitted Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). The initial infection usually occurs during adolescence, and up to 80% of women are infected with HPV at some point during their lifetime.
How many visits to check for cervical cancer?
Current screening methods using cervical cytology, HPV testing, and colposcopy require up to three visits with communication of results between each visit.
How long does it take for HPV to clear?
HPV infection is necessary but not sufficient to develop CIN. More than 90% of infections are spontaneously cleared by the immune system within one year without treatment. Approximately 60% of CIN 1 lesions regress without treatment and less than 1% progress to cancer.
How much does it cost to treat cervical dysplasia?
The cost associated with the diagnosis and treatment of cervical dysplasia and genital warts in the United States is estimated to be 3 billion dollars per year. The risk factors for CIN are the same as the risk factors for HPV infection and cervical cancer. They include:
What is the most common high risk subtype of cervical cancer?
HPV 16 and 18 are the most common high-risk subtypes and account for 70% of cervical cancer cases. Prophylactic vaccines are currently available to protect against HPV (see the chapter on prophylatic vaccinations). HPV infection is necessary but not sufficient to develop CIN.
What is the best way to treat ectocervix?
Cryotherapy. Cryotherapy cools the ectocervix with a metal cryoprobe using a refrigerant gas – either carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide. The ectocervix is cooled to -20ºC, causing crystallization of intracellular water that destroys the lesion.
How many cervical cancer deaths are there in the world?
There are approximately 12,710 new cases and 4,290 cervical cancer related deaths per year. However, 85% of cervical cancer cases in the world occur in developing countries due to a lack of screening programs.