How to prevent mud fever in horses?
The best way to prevent mud fever is to minimize exposure to wet, muddy conditions, which can be achieved through good paddock management or stabling the horse at night on clean, dry bedding so skin has a chance to dry out.
What is a mud fever?
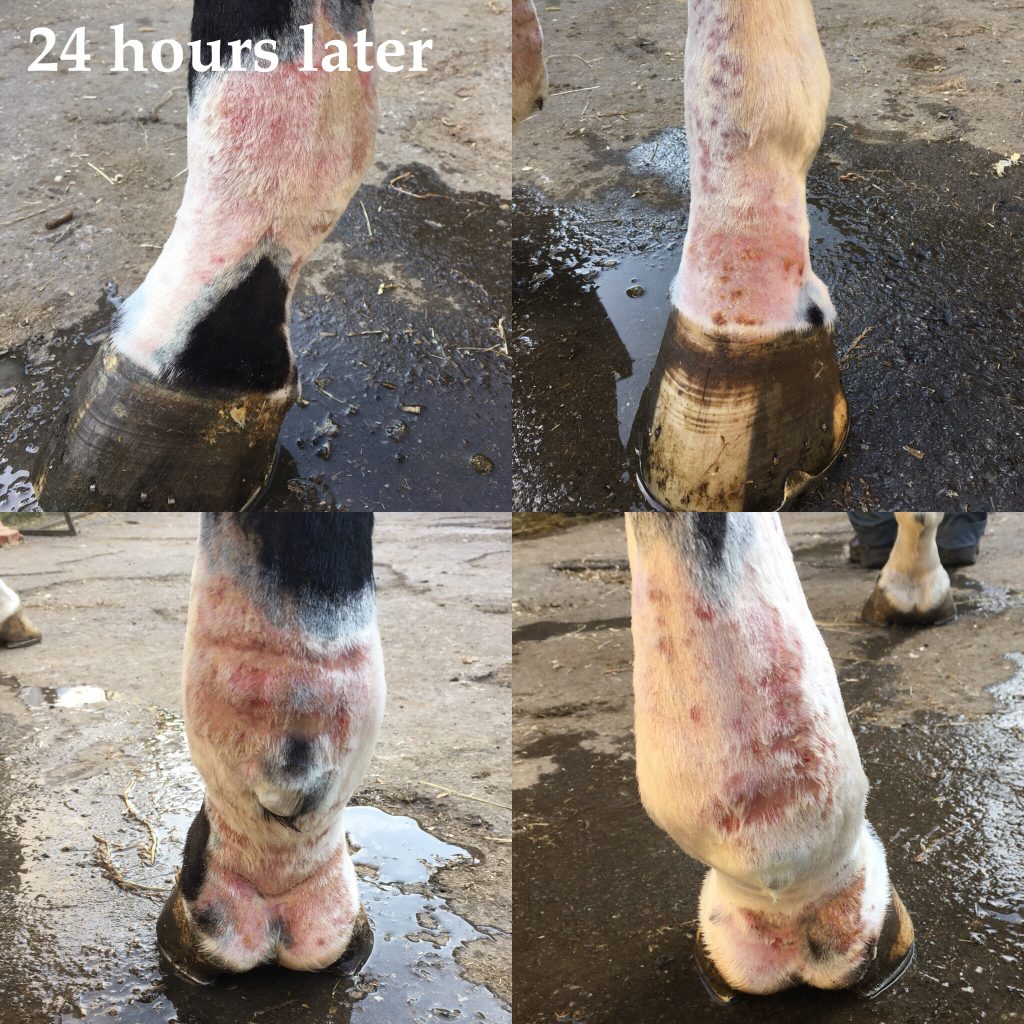
A- Mud fever, also known as scratches, pastern dermatitis, and greasy heel, is a common equine skin disease affecting the lower limbs, particularly the back of the pasterns and the bulbs of the heels.
How to get rid of a swollen ear?
2. Wash the area thoroughly but gently with warm water and an antibacterial cleanser. Avoid cold water and vigorous scrubbing, both of which will further irritate the skin.
How to get rid of scabs on face?
Avoid cold water and vigorous scrubbing, both of which will further irritate the skin. If the crusts are dried and hard, try to soak them off rather than picking at them. Tough scabs can also be softened prior to washing with a generous layer of antibacterial ointment or cream. 3.
What Causes Mud Fever?
Mud fever can occur from muddy fields or when riding in poor conditions – especially during winter.
How Can I Treat Mud Fever?
Try to remove your horse from situations that can make the condition worse. This may mean restricting their turnout, only letting them loose in an arena or even keeping them stabled. If your horse has a lot of hair then you may need to trim this off.
How Can I Prevent Mud Fever?
Your main aim should be to try and avoid your horse’s legs being wet regularly or for long periods. As mentioned previously, only wash your horse’s legs when really necessary. It is advised not to hose off your horse’s legs when they get dirty.
How often should I scrub my horse's legs for mud fever?
Mud fever is a stubborn foe. Even after you see no signs of the infection, continue to scrub your horse’s legs with antiseptic every few days. To keep the bacteria from striking again, follow the guidelines in our companion article, What Every Horse Owner Should Know about Mud Fever.
How to wash equine legs?
Follow these steps to wash your equine’s legs. Don’t just wash where you see mud fever; assume the bacteria is on all of his legs, at least from the knee down. Clean them all!
What is mud fever on horses?
Mud fever is the inflammation and irritation of the horse’s skin, usually on his pastern or heel area. Pastern dermatitis can sometimes be found on the horse’s belly, upper limbs or neck. Mud fever is also referred to as greasy heal, dew poisoning or cracked heel.
How long does it take for a horse to recover from mud fever?
Full recovery of mud fever in horses may take several weeks. The horse will need follow-up visits to monitor his progress. It is important to follow the veterinarian’s treatment plan. The veterinarian may want to have the complete blood count retaken to ensure there is no longer a bacterial infection.
What is the best treatment for mud fever?
Corticosteroid topical creams will help the lesions heal. Products such as Fiske’s Hoof and Hide Balm have been shown to be very effective in treating many skin conditions, including mud fever. In severe cases of mud fever, the horse must not be ridden or turned out until he has made a full recovery.
What does a veterinarian do for a horse?
The veterinarian will perform a physical exam that may include listening to your horse’s heart and lungs with a stethoscope, taking the patient’s temperature, palpation of the lymph nodes, limbs and skin . He may also take the patient’s blood pressure and pulse.
How to confirm a fungal infection?
To confirm the diagnoses he may suggest taking a culture or a skin scrape. The skin scrape is placed on a slide and observed under a microscope. The bacteria is visible under the microscope. A skin culture can help diagnose a fungal infection.
What does CBC mean in horse blood?
The veterinarian may suggest a complete blood count (CBC) to rule a secondary bacterial infection and to check the overall health of the horse. An elevated white cell count can confirm, if your horse has a bacterial infection. Top.
What is mud fever in horses?
Mud Fever in Horses: Cause, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment. Mud fever (subcutaneous streptothricosis) is an exudative dermatitis of animals , and very occasionally humans. It is most prevalent in ruminants and only occurs sporadically in horses. With the possible exception of sheep, animals in tropics are more often and more severely affected ...
Which horse is most susceptible to mud fever?
Foals and young horses are the most susceptible. Any part of the integument may be involved although the back, shoulders, and flanks are usually the most affected. Instances in which the patterns and coronets were the main areas affected have also been described as mud fever in horses.
How does D congolensis affect animals?
The organism may be present in a quiescent state in the epidermis until local climate conditions, precisely a period of warm, wet weather, promotes further multiplication of the mycelium and the formation of the zoospores. To establish infection in new areas of skin in an infected animal, or a previously uninfected animal, the motile zoospores, responding to carbon dioxide diffusing through the skin, must penetrate the sebaceous layer and enter the epidermis. They germinate in the dermis, producing a hypha and ultimately a mycelium.
Where does Dermatophilus congolensis live?
However, D congolensis lives only in the living tissue of the epidermis. It is a gram-positive organism which grows as branching filaments, the hyphal cylinders of which condense in two planes at right angles giving rise to coccoid bodies these coccoid bodies eventually become highly motile zoospores less than1 micrometer in diameter and are the essential means of dissemination of the pathogen. The filamentous mass- the mycelium- readily fragments.
What is the appearance of lesions in a clinically affected animal?
The appearance of the lesions in a clinically affected animal is highly suggestive of streptothricosis, which requires differentiation only from the injuries of the early stages of ringworm or pyoderma.
Does penicillin help with streptothricosis?
Since the lesions of streptothricosis usually heal spontaneously , therapy is required only for severe cases. Penicillin and streptomycin have a synergistic action on D congolensis in vitro, and a single parenteral injection of a combination of these drugs cures most cases. In severely affected horse in the tropics, an individual does of long-acting oxytetracycline is highly effective.
What is mud fever on horses?
‘Mud-fever’ as we will call it, goes by many different terms such as; rain scald (or rain rot), equine dermatitis, scratches or greasy heel. It is a collective term for what is essentially a bacterial, and in some cases fungal, infection that causes irritation and inflammation of the skin. It will often present itself in moist conditions and mostly affects the heels of a horse – however it can present itself anywhere on the body and will commonly also affect the face, shoulder, back and rump of a horse, where it may be referred to as rain scald.
How to tell if a horse has mud fever?
When it affects the lower limbs mud fever can be recognised with: 1 The cracking of skin, which will eventually worsen into a painful crust and scabbing. 2 Sometimes swelling may be present in the pastern or lower leg – the horse may present itself as lame. 3 The presence of small rough to touch scabs spreading up from the pastern and up through the cannon bone
How to keep horses dry in wet weather?
During long spells of wet weather, consider applying an oil based barrier cream to repel mud and moisture (great for protecting heels).
What does it mean when a horse is lame?
The cracking of skin, which will eventually worsen into a painful crust and scabbing. Sometimes swelling may be present in the pastern or lower leg – the horse may present itself as lame. The presence of small rough to touch scabs spreading up from the pastern and up through the cannon bone.
Can you use a rug on a horse?
Depending on the time of year – you may wish to use a lightweight rug though just be cautious as the infection can spread from horse to horse so ensure the rug is clean and only used for that horse. This solution is more practical if you horse has large areas of infection.
Why do horses get mud fever?
Mud fever is most often caused by bacteria and is common in the winter months when the horse is exposed to persistent wet, muddy conditions. This is because the wet conditions cause the skin to soften and mud rubs against this softened skin causing damage to the surface where bacteria can enter. There can be other causes of mud fever such as leg mites which break the skin and enable bacteria to enter. Horses with feathers are more at risk of leg mites and you will see them stamp their legs because they’re very itchy. If you suspect your horse has mites, speak to your vet for further advice.
How to treat a horse with scabs?
A general treatment plan should include: 1 Bringing your horse in out of the muddy and wet conditions to keep your horse’s skin clean and dry 2 Removing the scabs to help you gain easier access to the skin and to allow air to reach the skin to help the area heal. However, if you choose to do this proceed with care as it can be very uncomfortable for your horse and sedation may be necessary. Any loose scabs may be gently removed, but scabs should not be forcibly removed unless advised by your vet 3 Clean the affected area at least twice a day using a mild disinfectant, such as dilute Hibiscrub, then rinse with water and pat the leg dry with a clean towel 4 If your horse has thick feathers you may need to carefully clip the hair from the lower leg to expose the skin to the air and make it easier for you to clean and treat it 5 Applying stable bandages to dry legs can help keep them clean, provide support and reduce any potential swelling 6 Severe mud fever may require repeat treatments and cream applied to the skin. Your vet will be able to advise the course of action and treatment plan 7 If mites or a fungal infection have triggered the mud fever, individual treatment for these causes may be required.
How to prevent mud fever in horses?
Creating a barrier between the mud (and the bacteria within it) and your horse’s legs either by the use of a boot, a liquid coating or a powder is the most common technique for trying to prevent mud fever. If you are using a liquid or powder coating, look for products with anti-bacterial properties and take into consideration the natural levels ...
Why do horses have mud fever?
Wet and muddy conditions can cause the hooves and legs of your horse or pony to become vulnerable to bacteria and fungus, which are the most typical causes of mud fever . Here is a selection of products on the market designed to help prevent mud fever. Creating a barrier between the mud (and the bacteria within it) and your horse’s legs ...
What is magic mud?
Magic Mud is a soothing anti-fungal and anti-bacterial cream that can be applied regularly to the skin to help maintain healthy hooves and legs. This cream is great on itchy, flakey, scabby or cracked skin.#N#RRP: £15.99 for 400ml#N#Find out more: www.equine-america.co.uk#N#Buy now from Amazon >>
What are turnout boots for horses?
These turnout boots are well ventilated to keep your horse’s legs cool, and they have brush protection zones covered with leather to keep your horse as protected as possible from knocks in the field. Reaching down to the heel, these boots guard against mud fever as they are anatomically shaped around the coronet and pastern area. These boots are designed to help horses that will be standing for long periods in a muddy field as a prevention against mud fever.#N#RRP: £42.99 per pair#N#Find out more: www.premierequine.co.uk
What is Nettex Muddy Marvel?
Nettex Muddy Marvel barrier cream helps protect skin from mud, keeping it supple and in a healthy condition. This cream also has antibacterial properties to inhibit bacteria from infecting your horse’s legs.#N#RRP: £8.15 for 300ml#N#Find out more: www.nettexequine.com#N#Buy now from Amazon.co.uk >>
What is Cavalor Muddoc?
Cavalor MudDoc. This ointment is suitable for horses that suffer from mud fever. It is made of only natural ingredients and therefore can be used on horses with sensitive skin. It works by helping to stop bacteria from attaching to the foot and help fight active infections. RRP: £58 for 400ml.
What is Botanica cream?
Botanica Natural Herbal cream. A cream that helps to treat a wide range of skin conditions and infections such as mud fever. As it is made using natural materials, it can be used on even the most sensitive horses to help reduce inflammation. RRP: from £11.99 for 125ml. Find out more: www.botanica-international.co.uk.
