Medication
The standard of treatment for a GBM is surgery, followed by daily radiation and oral chemotherapy for six and a half weeks, then a six-month regimen of oral chemotherapy given five days a month. To start, the neurosurgeon will remove as much of the tumor as possible and may implant medicated wafers right into the brain.
Procedures
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common primary malignant brain tumor in adults. Regardless of ideal multidisciplinary treatment, including maximal surgical resection, followed by radiotherapy plus concomitant and maintenance temozolomide (TMZ), almost all patients experience tumor progression with nearly universal mortality and a median survival of less than 15 months.
Therapy
Aug 26, 2016 · Although radiation and chemotherapy prolong life, they greatly reduce quality of life—so much so, in fact, that some patients opt out of treatment. The purpose of Glioblastoma Foundation is to transform the standard of care for glioblastoma by supporting the development of drug therapies for glioblastoma.
Nutrition
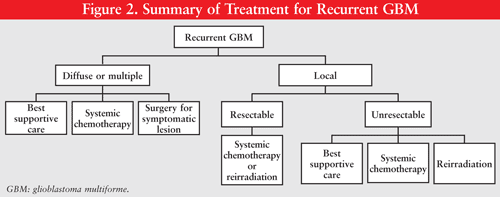
The best treatment for glioblastoma currently is surgery to remove as much of the tumour as possible, followed by a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Surgery for glioblastomas The first treatment for glioblastomas is usually neurosurgery .
See more
Oct 01, 2016 · Background. Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and aggressive malignant brain tumor in adults. Current treatment options at diagnosis are multimodal and include surgical resection, radiation, and chemotherapy. Significant advances in the understanding of the molecular pathology of GBM and associated cell signaling pathways have opened …
How would an expert treat his own glioblastoma?
Is there any natural treatment for glioblastoma multiforme?
Can Avastin cure glioblastoma?
What is the best treatment for gist cancer?
Are there any new treatments for glioblastoma?
A clinical trial has found that selinexor, the first of a new class of anti-cancer drugs, was able to shrink tumors in almost a third of patients with recurrent glioblastoma, an aggressive brain cancer. “Glioblastoma is an incurable brain cancer that needs new therapeutic approaches.Feb 4, 2022
Is there any hope for glioblastoma?
The hope is that the average life expectancy for patients with glioblastoma — around 14 months — will significantly expand due to therapies like CAR-T. Fortunately for patients, that sort of progress is possible at the Penn Brain Tumor Center and Abramson Cancer Center, according to Donald M. O'Rourke, MD, and Arati S.Sep 18, 2018
Can glioblastoma go into remission?
In remission, symptoms may let up or disappear for a time. Glioblastomas often regrow. If that happens, doctors may be able to treat it with surgery and a different form of radiation and chemotherapy.6 days ago
Where is the best treatment for glioblastoma?
The standard of treatment for a GBM is surgery, followed by daily radiation and oral chemotherapy for six and a half weeks, then a six-month regimen of oral chemotherapy given five days a month.
What is the best hospital for glioblastoma?
As a top-ranked cancer hospital, MD Anderson also is home to one of the world's largest collections of glioblastoma clinical trials designed to improve outcomes for patients. These trials include studies of new chemotherapies, radiation therapies and immunotherapies, among other treatments.
What happens in the last days of glioblastoma?
Results: A total of 57 patients, who died due to glioblastoma in a hospital setting, were included. The most frequent signs and symptoms in the last 10 days before death were decrease in level of consciousness (95%), fever (88%), dysphagia (65%), seizures (65%), and headache (33%).
Has anyone been cured of glioblastoma?
Although there is no cure for glioblastoma, patients with this malignancy have many treatment options available to them.
Is a glioblastoma always fatal?
Glioblastoma incidence is very low among all cancer types, i.e., 1 per 10 000 cases. However, with an incidence of 16% of all primary brain tumors it is the most common brain malignancy and is almost always lethal [5,6].
Why is glioblastoma incurable?
To date GBM remains incurable due to its heterogeneity and complex pathogenesis. Continued research efforts will help to provide better treatment options to combat the disease in future.
What is the life expectancy of someone with glioblastoma?
The median survival time with glioblastoma is 15 to 16 months in people who get surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation treatment. Median means half of all patients with this tumor survive to this length of time. Everyone with glioblastoma is different. Some people don't survive as long.
Can you survive inoperable glioblastoma?
Sometimes called “The Terminator” due to its fast and deadly nature, glioblastoma has a median survival time of nine months without treatment and an additional seven months with standard therapies, researchers have noted.Dec 12, 2019
How fast does glioblastoma grow back?
Glioblastoma gets the highest grade in its family — grade IV — in part because of its high growth rate. These cancers can grow 1.4 percent in a single day. The growth is happening on a microscopic level, but a glioblastoma tumor can double in size within seven weeks (median time).Jul 20, 2017
How to treat glioblastoma?
The best treatment for glioblastoma currently is surgery to remove as much of the tumour as possible, followed by a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Why are glioblastoma cells resistant to treatment?
Unfortunately glioblastomas are aggressive tumours and often appear resistant to treatment. This is probably due to the fact that the cells within the tumour are not all of the same type. This is known as ' heterogeneity '. This means that treatments will kill off some types of cell within the glioblastoma, but leave others, which can then continue to grow.
What is the treatment for a tumor that cannot be removed by surgery?
Chemoradiation comprises radiotherapy over a period of weeks along with rounds of the chemotherapy drug temozolomide (TMZ). It is used to slow the growth of any tumour cells that cannot be removed by surgery.
Why is it so hard to remove glioblastoma?
With glioblastomas it can be difficult to remove the whole tumour because: they are diffuse, this means they have threadlike elements that spread out into the brain. it can be hard to tell the difference between the edges of the main part of the tumour and normal brain tissue. This means that parts of the tumour may get left behind after surgery.
Can you use Avastin with glioblastoma?
You may have heard that the use of another drug, called bevacizumab (Avastin®), may be helpful in the treatment of glioblastomas. However, in Europe it is felt that there is insufficient evidence for its effect on brain tumours and for this reason it is not licensed for use with brain tumours in the UK.
Can glioblastoma wafers be used in the UK?
This means the treatment gets round the blood-brain barrier that prevents many chemotherapy drugs from entering the brain. The wafers are only licensed in the UK for use in recurrent gliobla stomas (glioblastomas that have come back) and when the surgeon is confident that at least 90% of the tumour has been removed.
Why is it so difficult to resection a GBM?
Extensive and complete surgical resection of GBM is difficult because these tumors are frequently invasive and are often in eloquent areas of the brain, including areas that control speech, motor function, and the senses.
What is the most aggressive brain tumor?
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and aggressive malignant brain tumor in adults. Current treatment options at diagnosis are multimodal and include surgical resection, radiation, and chemotherapy. Significant advances in the understanding of the molecular pathology of GBM and associated cell signaling pathways have opened opportunities ...
Where do GBMs occur?
Although GBMs occur almost exclusively in the brain, they can also appear in the brain stem, cerebellum, and spinal cord. Sixty-one percent of all primary gliomas occur in the four lobes of the brain: frontal (25%), temporal (20%), parietal (13%), and occipital (3%) (American Association of Neuroscience Nurses [AANN], 2014).
Is radical resection curative?
Because of the high degree of invasiveness, radical resection of the primary tumor mass is not curative, and infiltrating tumor cells invariably remain within the surrounding brain, leading to later disease progression or recurrence (Wilson et al., 2014).
Is glioma a hereditary disease?
An increased risk of glioma development is seen in some specific genetic diseases, such as neurofibromatosis 1 and 2, tuberous sclerosis, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, retinoblastoma, and Turcot syndrome; however, less than 1% of patients with a glioma have a known hereditary disease ( Ellor et al., 2014). Clinical Presentation.
