
If the cancer is contained in your prostate, surgery or a second attempt at radiation is suggested. If you've had a radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy is a good option. If you had radiation, radical prostatectomy might be the best approach. Cryosurgery might also be an option.
What is the best treatment for early stage prostate cancer?
Feb 19, 2017 · More aggressive tumours are better managed by active treatment (such as radiotherapy, brachytherapy or surgery) because of their greater tendency to spread outside the prostate and to grow faster. Key point: aggressive cancers need active treatment (radiotherapy, brachytherapy or surgery) to target the cancer directly.
How is the initial treatment of prostate cancer determined?
Radiation and surgery are the main treatments for early-stage prostate cancer. But other options include: Cryosurgery. This treatment uses very cold gas to freeze and kill cancer cells. Side ...
What is the Prostate Cancer Care Guide?
Covers the treatment options for early-stage prostate cancer, such as active surveillance, surgery, and radiation therapy, and helps men decide which treatment is the best for them. Treatment Choices for Men With Early-Stage Prostate Cancer - NCI
Is prostate cancer curable at an early stage?
Mar 11, 2009 · The treatment options for early-stage prostate cancer fall into three broad categories: surgery, radiation therapy, and active surveillance. Your doctor will make a treatment recommendation based on your “numbers” as well as a mathematical tool known as a nomogram, which can help you and your doctor better assess how extensive your cancer is likely to be and …
Can early stages of prostate cancer be cured?
What is the best treatment for stage 1 prostate cancer?
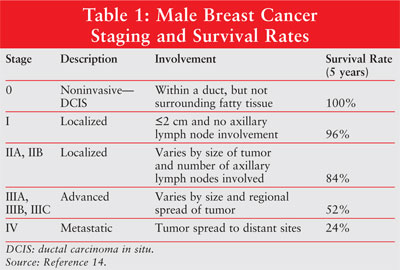
What is the survival rate of stage 1 prostate cancer?
It's characterized by a PSA of less than 10 ng/mL, a grade group score of 1, and a Gleason score of 6. Stage 1 prostate cancer has a 5-year survival rate of nearly 100 percent .Feb 9, 2021
What is the best treatment for slow growing prostate cancer?
What is the safest treatment for prostate cancer?
Is it better to have prostate removed or radiation?
What are the symptoms of stage 1 prostate cancer?
- Burning or pain during urination.
- Difficulty urinating, or trouble starting and stopping while urinating.
- More frequent urges to urinate at night.
- Loss of bladder control.
- Decreased flow or velocity of urine stream.
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Blood in semen.
- Erectile dysfunction.
What are the 5 warning signs of prostate cancer?
- A painful or burning sensation during urination or ejaculation.
- Frequent urination, particularly at night.
- Difficulty stopping or starting urination.
- Sudden erectile dysfunction.
- Blood in urine or semen.
How do I know what stage my prostate cancer is?
- Digital rectal exam (DRE)
- PSA (prostate-specific antigen) test.
- Transrectal ultrasound.
- MRI of the prostate.
- CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis to see if the cancer has spread.
What is the newest treatment for prostate cancer?
How is prostate cancer staged?
Prostate cancer is staged based on the extent (how much the cancer has spread) of the cancer (using T, N, and M categories) and the PSA level and Gleason score (Grade Group) when it is first diagnosed. For prostate cancers that haven't spread (stages I to III), doctors also use risk groups (based on how far the prostate tumor has grown, PSA level, ...
Can stage IV prostate cancer be cured?
Most stage IV cancers can’t be cured, but are treatable. The goals of treatment are to keep the cancer under control for as long as possible and to improve a man’s quality of life. Treatment of stage IV prostate cancer may also include treatments to help prevent or relieve symptoms such as pain.
How to treat a swollen intestine?
Initial treatment options may include: 1 Hormone therapy 2 Hormone therapy with chemotherapy 3 Hormone therapy with external beam radiation 4 Chemotherapy 5 Surgery (TURP) to relieve symptoms such as bleeding or urinary obstruction 6 Treatments aimed at bone metastases, such as denosumab (Xgeva), a bisphosphonate like zoledronic acid (Zometa), external radiation aimed at bones, or a radiopharmaceutical such as strontium-89, samarium-153 or radium-223 7 Observation (for those who are older or have other serious health issues and do not have major symptoms from the cancer) 8 Taking part in a clinical trial of newer treatments
Can prostate cancer be treated with radiation?
For men without any prostate cancer symptoms who are elder ly and/or have other serious health problems that may limit their lifespan, observation or active surveillance is often recommended. For men who wish to start treatment, radiation therapy (external beam or brachytherapy) or radical prostatectomy may be options.
Does stage 2 prostate cancer grow outside the prostate?
Stage II cancers have not yet grown outside of the prostate, but are larger, have higher Gleason scores, and/or have higher PSA levels than stage I cancers. Stage II cancers that are not treated with surgery or radiation are more likely than stage I cancers to eventually spread beyond the prostate and cause symptoms.
What is stage 3 prostate cancer?
Stage III. Stage III cancers have grown outside the prostate and may have reached the bladder or rectum (T4). They have not spread to lymph nodes or distant organs. These cancers are more likely to come back after treatment than earlier stage tumors. Treatment options at this stage may include:
Can stage 3 prostate cancer spread to lymph nodes?
Stage III cancers have grown outside the prostate and may have reached the bladder or rectum (T4). They have not spread to lymph nodes or distant organs. These cancers are more likely to come back after treatment than earlier stage tumors. Treatment options at this stage may include:
What are the best treatments for prostate cancer?
Doctors usually recommend three main types of treatment for prostate cancer in its early stages: 1 Watchful waiting or active surveillance 2 Surgery 3 Radiation therapy
How to stop prostate cancer from growing?
Hormone therapy. Male hormones like testosterone can make prostate cancer cells grow. If your doctor thinks your disease could come back after surgery, you might get therapy to stop your body from making those substances. Another type of hormone therapy prevents cancer cells from receiving testosterone.
What does it mean when you have prostate cancer?
When you’re diagnosed with prostate cancer at an early stage, usually stage I or II, it means the disease hasn't spread outside your prostate gland. That means you have a few good treatment options to choose from. It’s important to pick one that’s right for your condition and one that will give you the best quality of life.
Can you treat prostate cancer right away?
Prostate cancer often grows very slowly. You might not need to treat it right away -- or at all -- especially if you're older or have other health issues. For some men, the treatments themselves have risks that are greater than the benefit of getting rid of the cancer. Watchful waiting may be an option in this case.
What is the procedure to remove prostate cancer?
The main operation doctors do is called a radical prostatectomy. The surgeon will remove the whole organ, plus some of the tissue around it. Retropubic prostatectomy.
How does radiation kill prostate cancer?
Radiation. Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays to kill cancer cells. You can get it in one of two ways: External beam radiation therapy focuses X-rays on your prostate from a machine outside your body. The doctor will direct the radiation right to the gland and adjust the dose to target the cancer.
Can testosterone cause prostate cancer?
Male hormones like testosterone can make prostate cancer cells grow. If your doctor thinks your disease could come back after surgery, you might get therapy to stop your body from making those substances. Another type of hormone therapy prevents cancer cells from receiving testosterone.
What is the treatment for prostate cancer?
The treatment options for early-stage prostate cancer fall into three broad categories: surgery, radiation therapy, and active surveillance. Your doctor will make a treatment recommendation based on your “numbers” as well as a mathematical tool known as a nomogram, which can help you and your doctor better assess how extensive your cancer is likely to be and whether it is likely to become active in the future.
Is there a one size fits all treatment for prostate cancer?
There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for early-stage prostate cancer. Even the experts do not agree about which men with such cancers should be treated, which treatment method is best — or whether, for some tumors, any treatment is even necessary.
How long did T1C prostate cancer last?
Investigators followed 81 men diagnosed with stage T1c prostate cancer for at least one year (some for nearly five years). The men underwent semiannual PSA tests and digital rectal exams and had annual prostate biopsies to see if the cancer had become active. At time of repeat biopsy, cancer had progressed in 25 men.
Can prostate cancer be removed surgically?
But when treating prostate cancer, a comparable amount of tissue cannot be removed surgically or targeted. It takes a skilled surgeon and radiation oncologist to eradicate diseased tissue without harming portions of the rectum, bladder, and penis, thereby minimizing the likelihood of complications.
Is prostate cancer common?
Diagnostic tests are limited. We always knew that prostate cancer is common and that, until recently, it often went undiagnosed: Autopsies of men who died of other causes have shown that about one-third of men over age 50 have some cancerous cells in their prostate, while 90% of men over age 90 have such cells.
What is PCPT study?
The PCPT was a randomized controlled study — the type considered to be the gold standard in research (see “Randomized controlled trials,” below). The study, which involved almost 19,000 healthy men, was designed to evaluate whether the drug finasteride (Proscar) could prevent prostate cancer from developing.
How many men were in the PCPT study?
Of the 18,882 men enrolled in the study, 9,459 received a placebo.
What is stage 1 prostate cancer?
Stage I. The cancer is small, and it hasn't grown outside your prostate. Slow-growing cancers might never cause symptoms or other health problems. In this stage, your PSA levels and Gleason scores are low, and that's good. When they're higher, your cancer is more aggressive.
Is radiation therapy good for prostate cancer?
If you've had a radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy is a good option. If you had radiation, radical prostatectomy might be the best approach. Cryosurgery might also be an option. If the cancer has spread to other parts of your body, hormone therapy might be the most effective treatment.
Can stage IV cancer be cured?
This happens when your cancer has spread to the bladder, rectum, lymph nodes, organs, or bones. Cases of stage IV are rarely cured. Still, treatments can extend your life and ease your pain. In this stage, you should consider the following treatments:
What is the best treatment for bone cancer?
If the cancer has spread to other parts of your body, hormone therapy might be the most effective treatment. External or IV radiation therapy or bisphosphonate drugs can relieve your bone pain.
What does a PSA test show?
It’s also more likely to come back and require more intensive treatment. The PSA (prostate-specific antigen) test measure s levels of this protein in your blood. Your doctor then determines your Gleason score by looking at prostate tissue cells under a microscope.
How does the PSA test work?
It’s also more likely to come back and require more intensive treatment. The PSA (prostate-specific antigen) test measures levels of this protein in your blood. Your doctor then determines your Gleason score by looking at prostate tissue cells under a microscope.
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
There are three different doctors who might be involved in your care: 1 A medical oncologist, who treats cancer 2 A radiation oncologist, who also treats cancer 3 A urologist, who specializes in problems with the urinary tract and male reproductive organs
Getting help with treatment decisions
Making such a complex decision is often hard to do by yourself. You might find it helps to talk with your family and friends before making a decision. You might also find it helpful to speak with other men who have faced or are currently facing the same issues.
Some things to consider when choosing among treatments
Before deciding on treatment, here are some questions you may want to ask yourself:
Does ADT help with prostate cancer?
Past studies found that short-term ADT improves survival among patients with later stage tumors. The scientists looked at several outcomes, including lifespan, whether deaths occurred from prostate cancer or some other cause, and whether the cancer spread.
Does ADT cause hot flashes?
Prostate cancer-related deaths were reduced from 10% to 3%. The researchers note that a longer follow-up might also reveal some benefit from short-term ADT for men with low-risk disease. However, short-term ADT can cause hot flashes and higher rates of erectile dysfunction.
What is the best treatment for prostate cancer?
Active surveillance, surgery, and radiation therapy are the standard therapy choices for men with early-stage prostate cancer (see Types of Treatment, starting on page 8). Each has benefits (how treatments can help) and risks (problems treatment may cause). There is seldom just one right treatment choice.
What is the purpose of the prostate cancer booklet?
Its purpose is to help you learn about early-stage prostate cancer, different treatments, and the benefits and risks of each type of treatment. Most men will need more information than this booklet gives them to make a decision about treatment. For a list of groups that provide more information and support, please see the Ways to Learn More section on page 32. Also, see that section if you have prostate cancer that has spread beyond the prostate or that has returned after treatment.
How long does it take for a prostate cancer to grow?
Early-stage prostate cancer means that cancer cells are found only in your prostate. Compared with many other cancers, prostate cancer grows slowly. This means that it can take 10 to 30 years before a prostate tumor gets big enough to cause symptoms or for doctors to find it. Most men who have prostate cancer will die of something other than prostate cancer.
What is the best treatment for prostate cancer?
If your cancer has spread beyond your prostate to other areas of your body, your doctor may recommend: Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy can slow the growth of cancer cells, relieve signs and symptoms of cancer, and prolong the lives of men with advanced prostate cancer.
What to do if prostate cancer spreads?
If your cancer has spread beyond your prostate to other areas of your body, your doctor may recommend: Chemotherapy . Chemotherapy can slow the growth of cancer cells, relieve signs and symptoms of cancer, and prolong the lives of men with advanced prostate cancer. Training your immune system to recognize cancer cells.
How to confirm prostate cancer?
Biopsy. To confirm the diagnosis of prostate cancer, your doctor may recommend a biopsy procedure to remove a sample of suspicious cells for laboratory testing. In a lab, doctors can examine the cells and determine if they're cancerous.
How to stop prostate cancer from growing?
Hormone therapy. Hormone therapy is treatment to stop your body from producing the male hormone testosterone or to block the effects of testosterone on the cancer. Prostate cancer cells rely on testosterone to help them grow. Cutting off the supply of hormones may cause the cancer to shrink or to slow its growth.
How does radiation therapy work for prostate cancer?
Radiation therapy for stage 4 prostate cancer uses a large machine that moves around your body, directing energy beams to the area around the cancer (external beam radiation therapy). In men with very large prostate tumors or cancer that has spread to nearby lymph nodes (locally advanced prostate cancer), radiation therapy may be combined ...
Can prostate cancer be treated with surgery?
Surgery isn't often used to treat stage 4 prostate cancer, but it might be recommended in certain situations. In men with stage 4 prostate cancer, surgery is generally limited to men who are experiencing signs and symptoms that would be relieved by surgery, such as difficulty passing urine. Surgery may include:
Can you have prostate surgery for stage 4?
Surgery isn't often used to treat stage 4 prostate cancer, but it might be recommended in certain situations. In men with stage 4 prostate cancer, surgery is generally limited to men who are experiencing signs and symptoms that would be relieved by surgery, such as difficulty passing urine.
Very-Low-Risk Group
Low-Risk Group
Intermediate-Risk Group
- Radiation therapy (external beam or brachytherapy), often with ADT, is an option for men in this group. A radical prostatectomy with pelvic lymph node dissection (PLND)is also an option. Depending on the findings from surgery, treatments that might be discussed include: 1. External beam radiation therapy with or without ADT if the cancer is found in the lymph nodes or if it has …
High-Risk Group
- People with cancer in this group might be offered: 1. Radiation therapy (external beam with brachytherapy OR external beam radiation alone) along with ADTfor 1 to 3 years. 2. Radical prostatectomy with PLND. If cancer is found in the lymph nodes taken during surgery or if it has features that make it more likely to come back (recur), ADT with or without radiation might be re…
Very-High-Risk Group
- Treatment options for people in this group include: 1. External beam radiation therapy (with or without brachytherapy) along with ADT for 1 to 3 years. Sometimes, the chemotherapy drug docetaxel or the hormone drugabiraterone might be added to radiation plus ADT. 2. Radical prostatectomy with PLND(especially for younger men). If cancer is found in ...
Stage Iva
- Stage IVA cancers have spread to nearby lymph nodes but not to distant sites. For men who are healthy enough to get treatment or have symptoms from the cancer, options include: 1. External beam radiation treatment with ADT(with or without abiraterone) 2. ADT with or without abiraterone 3. Radical prostatectomy with PLND. If cancer is found in the lymph nodes taken dur…
Stage Ivb
- Stage IVBcancers have spread to distant organs such as the bones. Most stage IVB cancers can’t be cured, but are treatable. The goals of treatment are to keep the cancer under control for as long as possible and to improve a man’s quality of life. Initial treatment options may include: 1. ADT with abiraterone 2. ADT with apalutamide 3. ADT with chemotherapy,specifically docetaxel …