- surgery to remove the cancer, which may include a Whipple procedure.
- stent placement or percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage as palliative therapy, to relieve jaundice and other symptoms and improve the quality of life.
Medication
You could try:
- yoghurts or fromage frais
- other soft puddings such as trifle or chocolate mousse
- dried fruit
- stewed or fresh fruit (bananas are high in calories)
- nuts
- cheese
- instant soups (make up with milk to boost calories)
- cereal
- milky drinks
- flapjacks
Procedures
The statistics are also split into 2 types of bile duct cancer: 25 out of 100 people (25%) survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis. Almost 10 out of 100 people (almost 10%) survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
Therapy
Those who have bile duct cancer outside the liver have slightly better chances. A stage 1 patient has a five-year-survival rate of thirty percent. This drops to twenty-four percent for stage 2 and stage 3. At stage four, the survival rate is only two percent. Early detection is essential.
Nutrition
When you wake up after the operation you may have the following:
- An IV line to give you fluids.
- A Foley ® catheter in your bladder to monitor the amount of urine you are making. ...
- Compression boots on your lower legs. ...
- A pain pump called a patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) device. ...
- A nasogastric (NG) tube that’ placed through your nose into your stomach. ...
- A biliary drainage tube to drain bile. ...
What to do if you have bile duct cancer?
What is the survival rate of bile duct cancer?
What is the prognosis for Stage 4 bile duct cancer?
What is the recovery time for bile duct surgery?
See more
What is the life expectancy for someone with bile duct cancer?
If the cancer is diagnosed in an early stage, the 5-year survival rate is 17%. If the cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate is 16%. If the cancer has spread to a distant part of the body, the 5-year survival rate is 2%. The 5-year survival rate for intrahepatic bile duct cancer is 9%.
Is cancer of the bile duct treatable?
Bile duct cancer is often treatable. But it can be difficult to treat. The treatment you have will depend on: the size and type of bile duct cancer you have.
Does chemo cure bile duct cancer?
Chemo does not cure these cancers, but it might help people live longer. As palliative therapy: Chemo can help shrink tumors or slow their growth for a time.
Where does bile duct cancer usually spread to?
If a tumor grows through the bile duct wall, it can invade (grow into) nearby blood vessels, organs, and other structures. It might also grow into nearby lymphatic or blood vessels, and from there spread to nearby lymph nodes or to other parts of the body.
Can bile duct cancer go into remission?
So far, several cases have been reported, in which advanced cholangiocarcinoma was completely treated with gemcitabine chemotherapy in Japan,17-20 although only one of them has shown complete remission histopathologically.
How aggressive is bile duct cancer?
Bile duct cancer, also known as cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare but aggressive form of cancer. Only about 8,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with bile duct cancer each year.
Are there any new treatments for cholangiocarcinoma?
FDA Approves First Targeted Treatment for Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma, a Cancer of Bile Ducts. Today, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted accelerated approval to Pemazyre (pemigatinib), the first treatment approved for adults with certain types of previously treated, advanced cholangiocarcinoma.
What is the best hospital for bile duct cancer?
Expertise and rankings Mayo Clinic is one of the major referral centers in the United States for primary sclerosing cholangitis, which is the major risk factor for bile duct cancer. Mayo Clinic surgeons pioneered the use of liver transplant to treat hilar cholangiocarcinoma.
What are the final stages of bile duct cancer?
In most cases, the condition is at an advanced stage by this time. The blockage will cause bile to move back into the blood and body tissue, resulting in symptoms such as: jaundice – yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, itchy skin, pale stools and dark-coloured urine. unintentional weight loss.
Is bile duct cancer slow growing?
Cholangiocarcinomas are usually slow-growing tumors that spread locally via the lymphatic system. Treatment and long-term prognosis are dependent upon the location of the mass.
How painful is bile duct cancer?
Early bile duct cancers seldom cause pain, but bigger tumors may cause belly pain, especially below the ribs on the right side.
How long can you live with Stage 4 cholangiocarcinoma?
Many studies report a dismal median survival of approximately 6 months. In this case, we have a patient diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma who has remarkably exceeded life expectancy to greater than 4 years with a fourth line agent Sorafenib.
What tests can be done to detect bile duct cancer?
Techniques used to diagnose bile duct cancer include computerized tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) combined with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP).
How to test bile ducts?
A test to examine your bile duct with a small camera. During endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), a thin, flexible tube equipped with a tiny camera is passed down your throat and through your digestive tract to your small intestine . The camera is used to examine the area where your bile ducts connect to your small intestine. Your doctor may also use this procedure to inject dye into the bile ducts to help them show up better on imaging tests.
How to treat cholangiocarcinoma?
The results of your imaging tests will help guide your treatment. Treatments for cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer) may include: Surgery. When possible, doctors try to remove as much of the cancer as they can. For very small bile duct cancers, this involves removing part of the bile duct and joining the cut ends.
How does chemotherapy help with cancer?
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be used before a liver transplant. It may also be an option for people with advanced cholangiocarcinoma to help slow the disease and relieve signs and symptoms. Chemotherapy drugs can be infused into a vein so that they travel throughout the body. Or the drugs can be administered in a way so that they are delivered directly to the cancer cells.
How to get a tissue sample from a liver biopsy?
If the suspicious area is within or near the liver, your doctor may obtain a tissue sample by inserting a long needle through your skin to the affected area (fine-needle aspiration). He or she may use an imaging test, such as an endoscopic ultrasound or CT scan, to guide the needle to the precise area.
What tests are done for cholangiocarcinoma?
If your doctor suspects cholangiocarcinoma, he or she may have you undergo one or more of the following tests: Liver function tests. Blood tests to measure your liver function can give your doctor clues about what's causing your signs and symptoms. Tumor marker test.
Can clinical trials be used to cure cancer?
Clinical trials can't guarantee a cure, and they might have serious or unexpected side effects. On the other hand, cancer clinical trials are closely monitored to ensure they're conducted as safely as possible. They offer access to treatments that wouldn't otherwise be available to you.
Who treats bile duct cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your cancer care team. These might include:
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your cancer care team. These might include: 1 A surgeon or a surgical oncologist: a surgeon who specializes in cancer treatment 2 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer 3 A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancer 4 A gastroenterologist (GI doctor): a doctor who treats diseases of the digestive system 5 A hepatologist: a doctor who treats disease of the liver and bile ducts
Why do we do clinical trials?
Clinical trials are carefully controlled research studies that are done to get a closer look at promising new treatments or procedures . Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone.
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary methods refer to treatments that are used along with your regular medical care. Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment.
Why is it important to discuss all treatment options with your doctor?
It’s important to discuss all treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs. You may feel that you need to make a decision quickly, but it’s important to give yourself time to absorb the information you have learned.
How to learn more about clinical trials?
If you would like to learn more about clinical trials that might be right for you, start by asking your doctor if your clinic or hospital conducts clinical trials.
How to contact bile duct cancer?
Bile Duct Cancer. We're here for you. Call us at 1-877-632-6789 1-877-632-6789 or. request an appointment online. Let's get started. Request an appointment online. Diagnosis & Treatment. Cancer Types.
How long does bile duct cancer last?
Since most bile duct cancers are diagnosed in more advanced stages, the current five-year survival rate is only 10% to 30%, depending upon the type of cancer. Bile duct cancer can be divided into two main categories: Intrahepatic and extrahepatic.
Why choose MD Anderson for biliary cancer treatment?
MD Anderson's Gastrointestinal Center treats biliary cancer patients as individuals, not statistics.
What is the disease that starts in the bile ducts that passes through the pancreas and connect?
Distal bile duct cancer: This disease starts in the part of the bile ducts that passes through the pancreas and connects with the small intestine. It makes up 20 to 40% of bile duct cancer cases.
What is a hilar tumor?
This disease is sometimes called hilar cancer or Klatskin tumors. Distal bile duct cancer: This disease arises in the common bile duct, the portion of the bile ducts that passes through the pancreas and connects with the small intestine. It accounts for 20-30% of all bile duct cancer cases.
What is the most common type of extrahepatic bile duct cancer?
There are two types of extrahepatic bile duct cancers: Perihilar bile duct cancer (perihilar cholangiocarcinoma): Perihilar bile duct cancer is the most common type of extrahepatic bile duct cancer, accounting for 40-60% of all bile duct cancer cases. It occurs at the junction where the bile ducts exit the liver.
What is the fluid that the bile ducts carry?
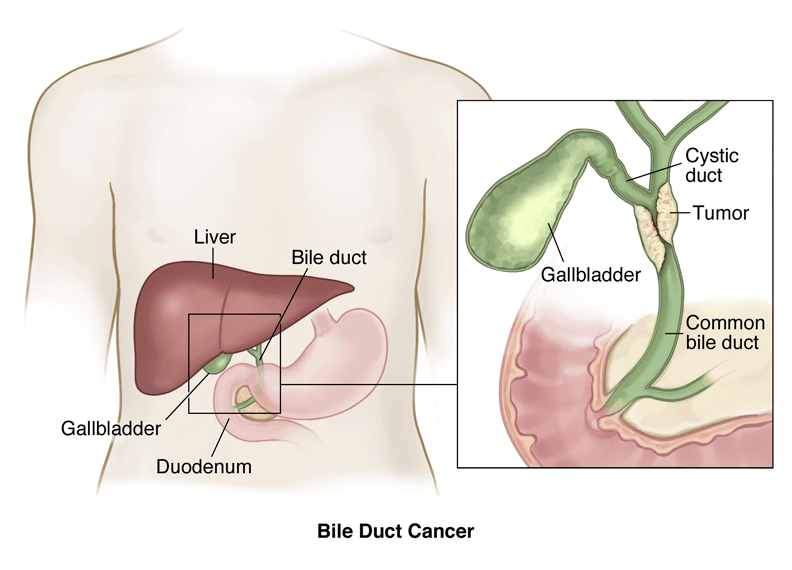
They carry a thick fluid called bile, from the liver to the upper part of the small intestine (duodenum) to aid in digesting food. The bile ducts are a tree-like structure of vessels within and around the liver and gallbladder. They carry a thick fluid called bile, from the liver to the upper part of the small intestine (duodenum) ...
Why is it so difficult to resect a bile duct tumor?
Because of its proximity to major blood vessels and diffuse extension within the liver, a bile duct tumor can be difficult to resect. Total resection is possible in 25% to 30% of lesions that originate in the distal bile duct; the resectability rate is lower for lesions that occur in more proximal sites. [ 3]
What is the staging system for bile duct cancer?
Bile duct cancer is classified as resectable (localized) or unresectable, with obvious prognostic importance. The TNM (tumor, node, metastasis) staging system is used for staging bile duct cancer, commonly after surgery and pathologic examination of the resected specimen.
What is the most common type of perihilar bile duct tumor?
Adenocarcinomas are the most common type of perihilar bile duct tumor. The histologic types of perihilar bile duct cancer include the following: [ 2]
What are the bile ducts outside the liver called?
The bile ducts located outside of the liver are called extrahepatic bile ducts. They include part of the right and left hepatic ducts that are outside the liver, the common hepatic duct, and the common bile duct. The extrahepatic bile ducts can be further divided into the perihilar (hilum) region and distal region.
What is the classification of bile duct tumors?
The classification of bile duct tumors has changed to include intrahepatic tumors of the bile ducts and extrahepatic tumors (perihilar and distal) of the bile ducts. Approximately 50% of cholangiocarcinomas arise in the bile ducts of the perihilar region; 40% arise in the distal region; and 10% arise in the intrahepatic region.
Where are the bile ducts located?
The bile ducts located within the liver are called intrahepatic bile ducts. Tumors of the intrahepatic bile ducts originate in small intrahepatic ductules or large intrahepatic ducts that are proximal to the bifurcation of the right and left hepatic ducts. These tumors are also known as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas.
Where do the right and left hepatic ducts exit the liver?
The hilum is the region where the right and left hepatic ducts exit the liver and join to form the common hepatic duct that is proximal to the origin of the cystic duct. Tumors of this region are also known as perihilar cholangiocarcinomas or Klatskin tumors. Distal region.
How does the doctor know I have bile duct cancer?
Because the bile ducts are deep inside the body, the doctor can’t see or feel them during a physical exam. Most of the time, these cancers aren't found until they cause problems that make a person go to a doctor.
Where does intrahepatic bile duct cancer start?
Intrahepatic bile duct cancers start in the bile ducts that are inside the liver.
What is it called when cancer cells travel to the lungs?
Cancer cells in the bile ducts can sometimes travel to the lungs and grow there. When cancer cells do this, it’s called metastasis . To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the bile ducts. Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when bile duct cancer spreads to the lungs (or any other place), ...
How does chemo work?
Chemo (chemotherapy), the use of drugs to fight cancer. These drugs go into the blood and spread through the body. Chemo is given in cycles or rounds. Each round of treatment is followed by a break to allow your body to get better from the side effects. Your doctor can pick from more than one chemo drug. Chemo might be used before or after surgery. It also can be used to help shrink tumors and ease problems they're causing.
What is a CAT scan for cancer?
The probe can be pointed at the bile ducts. It can also be used to take out a little bit of tissue that can be checked for cancer. CT or CAT scan: Uses x-rays to make pictures of your insides. This can show clear pictures of the bile ducts and the area around it to see if the cancer has spread.
Why is radiation used in cancer treatment?
Radiation uses high energy x-rays to kill cancer cells. Radiation (along with chemotherapy) can be used when the cancer is too far along to be taken out by surgery. It can also be used before surgery to try to shrink a tumor so it can be taken out. It might be used after surgery, also, to kill any cancer cells that may have been missed. Radiation is often used to help make symptoms better – such as to ease pain or blockages caused by large tumors.
Can you have surgery on a cancer patient?
Surgery is used to try to take out all of the cancer. If the cancer has spread, surgery may not be possible. There's more than one way to do surgery. Ask your doctor what kind of surgery you will have, the goal of the surgery, and what you can expect.
What is the treatment for bile duct cancer?
You may receive chemotherapy before surgery to shrink a bile duct tumor. This is called neoadjuvant therapy . If you receive chemotherapy after surgery to destroy and cancer cells that may remain, it is called adjuvant therapy.
Why is chemotherapy given for bile duct cancer?
Chemotherapy is also occasionally given to relieve symptoms due to bile duct cancer, such as a tumor that is pressing on a nerve and causing pain.
Can you get bile duct cancer removed?
Research has suggested that the combination of gemcitabine and cisplatin can lengthen the lives of people with bile duct cancer that cannot be removed by surgery. Chemotherapy is also occasionally given to relieve symptoms ...
What is bile duct cancer?
Bile Duct Cancer (Cholangiocarcinoma) Liver Gallbladder and Pancreas. Cholangiocarcinoma, or bile duct cancer, occurs when a malignant (cancerous) tumor grows in one of the ducts that transport bile from the liver to the small intestine.
What tests are done to diagnose bile duct cancer?
Other tests your doctor may perform include: Laboratory Tests. Imaging Scans. Endoscopic Diagnosis.
What is the procedure to remove bile duct tissue?
During an ERCP, your doctor can perform a biopsy and remove bile duct tissue for analysis. Cholangioscopy . A cholangioscope is a special type of endoscope that your doctor inserts inside the bile duct. The cholangioscope is used to see and biopsy the tumor directly. You may have a cholangioscopy done during an ERCP.
What type of scan is used to determine if you have bile duct cancer?
Each type of scan utilizes a different kind of technology to obtain the images. Scans include: Transabdominal ultrasound. This is usually the first test you will undergo if bile duct cancer is suspected. During an ultrasound, sound waves bounce off your internal organs and tissue to create an image.
What is the name of the tube that is used to view the upper GI tract?
Endoscopic Diagnosis. An endoscope is a thin, flexible, lighted tube used to view your upper gastrointestinal tract. Your upper GI tract includes the esophagus, stomach and duodenum (the first part of your small intestine). An enteroscope, a specialized endoscope , allows your doctor to view an even larger part of your small intestine.
What tests can be done to check for liver cancer?
Laboratory Tests. Blood tests will check your liver function and look for markers that may indicate a tumor. Tests include: Liver function tests. CEA and CA19-9, blood tests that check for underlying gastrointestinal malignancies.
Is a bile duct CT scan better than an MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) . An MRI is slightly superior to a CT scan for visualizing bile duct tumors. An MRI uses magnetic waves to create a detailed image. The latest MRI technology, magnetic resonance cholangiography (MRCP), is a specific type of MRI used to help diagnose bile duct cancer.
What is the treatment for cholangiocarcinoma?
Mayo Clinic offers all standard treatments for cholangiocarcinoma, including surgery, radiation therapy, radiofrequency ablation, photodynamic therapy, and chemotherapy and other drug treatments.
Which is the best hospital for digestive disorders?
Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., ranks No. 1 for digestive disorders in the U.S. News & World Report Best Hospitals rankings. Mayo Clinic in Phoenix/Scottsdale, Ariz., and Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., are ranked among the Best Hospitals for digestive disorders by U.S. News & World Report. Mayo Clinic Children's Center in Rochester is ranked the No. 1 hospital in Minnesota, and the five-state region of Iowa, Minnesota, North Dakota, South Dakota and Wisconsin, according to U.S. News & World Report's 2021-2022 "Best Children's Hospitals" rankings.
What is cholangiocarcinoma specialist?
Specialists have extensive experience caring for people with bile duct cancers and they perform a high volume of operations and procedures on the liver and bile ducts. Mayo Clinic specialists are among the most experienced procedural experts (endoscopists, interventional radiologists, cancer surgeons and transplant surgeons) in the world.
What is palliative care at Mayo Clinic?
Mayo Clinic also offers palliative care, which is specialized medical care that focuses on providing relief from pain and other symptoms of a serious illness. At Mayo Clinic, palliative care specialists work with you, your family and your other doctors to provide an extra layer of support that complements your ongoing care.
What is Mayo Clinic?
At Mayo Clinic, experts work together to provide you with exactly the care you need. Your care team is made up of experts in cholangiocarcinoma, including specialists in gastroenterology and hepatology, radiology, medical oncology, radiation oncology, pathology, surgery, transplant, and other areas if needed.
Does Mayo Clinic have liver transplants?
Mayo Clinic pioneered the use of liver transplant for some types of bile duct cancer. It is still one of the few medical centers in the United States to offer liver transplant as a treatment option for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Mayo Clinic also offers palliative care, which is specialized medical care that focuses on providing relief from pain ...
Does Mayo Clinic offer radiation therapy?
Mayo Clinic offers all standard treatments for cholangiocarcinoma, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, photodynamic therapy and biliary drainage. Mayo Clinic also offers proton therapy — a newer form of high-energy radiation therapy — at its campuses in Arizona and Minnesota.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment