
- Surgery to remove the tumor. This is a highly effective treatment for acoustic neuromas. ...
- Stereotactic radiosurgery. This form of radiation therapy delivers precisely targeted radiation to the tumor while avoiding the surrounding healthy tissue. ...
- Observation.
Nutrition
Apr 08, 2021 · Treatment options may vary depending on the size and growth of the acoustic neuroma, your health, and if you’re experiencing symptoms. To treat acoustic neuroma, your doctor may suggest one or more of three potential treatment methods: wait and see, surgery, and radiation therapy. Wait and See
See more
Dec 30, 2021 · If the tumor becomes sufficiently large enough that it requires treatment then surgical intervention is a common mode of treatment for the removal of acoustic neuroma and is also a highly successful form of treatment.
Is there a real cure for acoustic neuroma?
Several treatment modalities are currently used for the treatment of acoustic neuromas. Until recently, surgical removal of the tumor was the standard form of therapy. Patients now also have the option of undergoing a noninvasive radiation treatment, called stereotactic radiosurgery (aka Novalis Shaped-Beam Surgery, Gamma Knife, Cyberknife, Protom Beam, etc.) to halt the growth …
What are three main courses of treatment for acoustic neuroma?
Dec 03, 2016 · The best hospitals for Acoustic neuroma treatment are: University Hospital Tuebingen, Charite University Hospital Berlin, University Hospital Freiburg 🏥 Top 5 cheapest hospitals for Acoustic neuroma treatment
How to treat acoustic neuroma with home remedies?
A vestibular schwannoma (also known as acoustic neuroma, acoustic neurinoma, or acoustic neurilemoma) is a benign, usually slow-growing tumor that develops from the balance and hearing nerves supplying the inner ear. The tumor comes from an overproduction of Schwann cells—the cells that normally wrap around nerve fibers like onion skin to ...
How long does it take to remove an acoustic neuroma?
Radiation. Radiation therapy is another treatment option for acoustic neuromas. Typically for acoustic neuromas, stereotactic radiation is used because this allows the radiation to be delivered with increased precision to the tumor while minimizing the radiation exposure to the normal, healthy tissues surrounding the acoustic neuroma such as the brainstem, cerebellum, …
Can you shrink an acoustic neuroma?
Rarely, an acoustic neuroma may shrink on its own. While the frequency varies, people with an acoustic neuroma may have an MRI scan at least once a year to determine whether the tumor has grown.
When should an acoustic neuroma be removed?
You may need surgery to remove an acoustic neuroma, especially if the tumor is: Continuing to grow. Very large. Causing symptoms.Jul 2, 2021
What is the treatment of choice for acoustic neuromas?
As discussed below, the therapeutic options for acoustic neuromas include observation, surgery and radiosurgery. The optimal treatment varies according to whether the tumor is large or small, whether it has caused neurologic damage prior to treatment and on patient factors.
What is the survival rate for acoustic neuroma?
Multivariate analyses revealed that postoperative mortality following acoustic neuroma excision was 0.5%, with adverse discharge disposition of 6.1%. The odds ratio for mortality in African Americans compared with Caucasians was 8.82 (95% confidence interval = 1.85–41.9, P = . 006).Aug 19, 2011
What kind of surgeon removes an acoustic neuroma?
A neurosurgeon or neuro-otologist can remove acoustic neuromas. The suboccipital approach is performed by a neurosurgeon.
Who is the best surgeon for acoustic neuroma?
Rick Friedman, MD, PhD, and Marc Schwartz, MD, are international authorities on the effective treatment of acoustic neuromas, brain tumors and inner ear disorders.Nov 15, 2017
What happens if acoustic neuroma goes untreated?
Left untreated, an acoustic neuroma can block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid and cause hydrocephalus, which can in turn lead to severe vision problems and difficulty breathing and swallowing. Fortunately, most patients seek treatment long before an acoustic neuroma reaches this stage.
At what size should an acoustic neuroma be removed?
11, 27 Observation alone may be the best option for tumors up to 1.5 cm in size. If they grow, they can undergo low-morbidity surgery providing this is done promptly, before the tumor reaches the critical size of 1.5 cm.
Can acoustic neuroma stop growing?
Most acoustic neuromas grow very slowly, although the growth rate is different for each person and may vary from year to year. Some acoustic neuromas stop growing, and a few even spontaneously get smaller. The tumor doesn't invade the brain but may push against it as it enlarges.Jan 10, 2017
Can you live a long life with acoustic neuroma?
The patient may choose to live with the acoustic neuroma as long as it is not a life-threatening condition rather than risk further hearing loss that can potentially occur from therapy. If an acoustic neuroma eventually causes symptoms, then radiation therapy or microsurgery may be necessary.
Do acoustic neuromas grow back?
You may get regular tests to watch its growth. Neuromas that cause problems may be treated with radiation or surgery. An acoustic neuroma that is removed does not usually grow back.
Is acoustic neuroma serious?
Large acoustic neuromas can be serious because they can sometimes cause a life-threatening build-up of fluid in the brain (hydrocephalus). But it's rare for them to reach this stage. Many grow very slowly or not at all, and those that grow more quickly can be treated before they become too big.
What is the treatment for acoustic neuromas?
The options for the treatment of the acoustic neuromas include surgery and radiosurgery. Our approach to surgery for acoustic neuromas is based on the Johns Hopkins experience of nearly 100 years of surgery of the brain. Experience with this type of surgery appears to be essential in minimizing the risk of complications as acoustic neuromas.
What are the issues in acoustic neuroma treatment?
For both surgery and radiotherapy approaches to acoustic neuroma treatment, the important issues in the treatment of the acoustic neuromas are preservation of the facial nerve, preservation of hearing and control of the tumor. "Control of the tumor" is a phrase that should be considered carefully.
What is radiosurgery for acoustic neuroma?
Radiosurgery is a non-invasive treatment that uses precisely focused, narrow beams of radiation to both treat the acoustic neuroma and to reduce the dose of radiation delivered to the surrounding tissues including the hearing, balance and facial nerves .
How many operative approaches are there for acoustic neuromas?
Microsurgical resection of acoustic neuromas can be accomplished using one of three operative approaches. Microsurgical resection of acoustic neuromas can be accomplished through three different operative approaches to the tumor.
How long does radiation last?
Few studies to date have documented the effects of radiation beyond 5 years. Moreover, there now exist several reports of malignancies (cancers) developing within the field of radiation treatment for acoustic neuroma.
Can you preserve hearing after acoustic neuroma surgery?
Hearing preservation after surgery for acoustic neuroma varies between reported groups of patients. However, a general rule is that roughly half of patients with small tumors who have useful hearing prior to surgery will maintain useful hearing following surgery.
Can acoustic neuromas be treated with MRI?
Controversy exists regarding the optimal form of treatment for the acoustic neuromas. Small tumors that do not pose a risk to brain function and do not produce symptoms, may be watched with follow-up MRI scans to insure "control". This is most often an attractive option in older individuals with small tumors.
How many acoustic neuromas have been removed from the Mayo Clinic?
Over the past 26 years, it has been used at Mayo Clinic's campus in Minnesota to treat approximately 1,000 acoustic neuromas. In addition, Mayo Clinic neurosurgeons have surgically removed thousands of acoustic neuromas. Otolaryngologists work with neurosurgeons on each case.
How many people have acoustic neuromas?
Acoustic neuromas, which develop in only two to four people per 100,000, are typically discovered on MRI after patients present with unilateral hearing loss, tinnitus, and sometimes dizziness or headache. Surgical removal was once standard treatment; however, reduced tolerance of post-treatment morbidity has resulted in a greater proportion of patients undergoing observation or stereotactic radiosurgery.
What is intraoperative monitoring?
Otolaryngologists work with neurosurgeons on each case. Intraoperative monitoring is used to avoid damaging auditory, facial and other cranial nerves. "We think it's important to take out all of the tumor. But sometimes we do a less than complete resection to keep the facial nerve intact," Dr. Link says.
Can acoustic neuromas affect quality of life?
Although acoustic neuromas are benign, they can severely affect quality of life. Unilateral hearing loss and tinnitus are common symptoms, and hearing loss can persist after treatment. Observation might be a valid treatment strategy for small, slow-growing acoustic neuromas; however, patients can experience significant anxiety after ...
Does acoustic neuroma shrink over time?
In a study published in the September 2015 issue of Otolaryngology — Head and Neck Surgery, Mayo Clinic researchers found that although the incidence of acoustic neuroma has remained steady over time, tumor size at time of diagnosis has decreased. The researchers also noted a clear, recent evolution in the United States toward managing acoustic ...
What is the treatment for acoustic neuroma?
The treatments for acoustic neuroma, in fact, include surgical removal, radiation therapy, regular monitoring and more. MRI and monitoring: this is beneficial since there is some acoustic neuroma that does not grow. Thus, continuous monitoring is a must. Radiosurgery: it delivers radiation straight through the tumor.
How do you know if you have acoustic neuroma?
Some other symptoms of an acoustic neuroma include: Confusion. Unsteadiness or clumsiness. Headaches. Hoarseness and difficulty in swallowing. Taste changes. Facial weakness. Facial numbness as well as tingling which can be constant or may come and go. The feeling like the world is spinning or vertigo.
What nerve is responsible for acoustic neuroma?
3 Causes of Acoustic Neuroma. 4 Treatments for Acoustic Neuroma. Acoustic neuroma is actually a non-cancerous growth, which develops on the eighth cranial nerv e. This is also known as the vestibular nerve, which connects the inner ear with the brain.
What is the condition that affects the sense of hearing?
There are various conditions that may affect the sense of hearing. And one of which is the acoustic neuroma. Acoustic neuroma is actually a benign tumor that mainly affects the nerves that run through the inner ear through the brain.
What percentage of acoustic neuroma cases are not known?
the exact cause of the condition is not yet clear even up to this date. In fact, according to a certain research, there is about 95 percent of the cases that have no known cause. However, there are some factors that may increase the risk of acoustic neuroma. These include:
Why is it important to see a doctor for balance issues?
Problems with balance. It is very important to see your doctor if you already have these symptoms. Furthermore, mental confusion, as well as clumsiness, may be an indication of more serious problems which may require urgent treatments.
Does vestibular nerve cause tinnitus?
And these branches directly influence the balance as well as the hearing. Not only that, the pressure that comes from the acoustic neuroma may also cause tinnitus or the ring ing in the ear, unsteadiness, as well as hearing loss.
What Is The Best Treatment for Acoustic Neuroma?
Due to its slow-growing and non-malignant properties, these tumors do not require any form of treatment for them. The growth sometimes becomes so slow that people often survive a lifetime without even experiencing any symptoms and tumor is detected after death during the autopsy.
Conclusion
Waiting approach is usually applied in non-symptomatic patients of acoustic neuroma. Initial treatment would be supportive with the target towards symptomatic relief to the patients. Hearing ability can a by the use of hearing aids in the management of early symptoms or after the operation.
What is the major focus of acoustic neuroma surgery?
One of the major recent focuses of acoustic neuroma surgery is the preservation of hearing. Major strides have been made in recent years in terms of improving the results of hearing preservation with surgery. Much like facial nerve results, the size of tumor is an influential factor.
Why are acoustic neuromas so difficult to treat?
Acoustic neuromas, because of their location in proximity to delicate brain structures and cranial nerves , are a complicated treatment problem.
Why do people lose hearing?
Patients lose hearing due to these tumors from pressure effects of the tumor on the auditory nerve, as well as, invasion of the auditory nerve by the tumor. Similarly, the tumor can cause an obstruction of blood flow to the auditory nerve and the cochlea which results in hearing loss.
What is an acoustic neuroma?
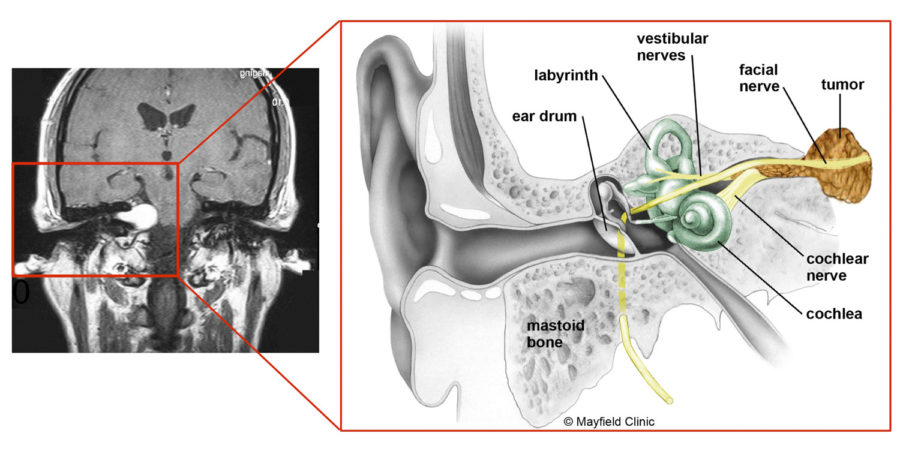
Acoustic neuromas are benign fibrous growths that arise from the balance nerve, also called the eighth cranial nerve or vestibulocochlear nerve. (Figure A) These tumors are non-malignant, meaning that they do not spread or metastasize to other parts of the body.
What nerve travels in the inner ear?
Illustration of the anatomy of the temporal bone and inner ear structures. The vestibulocochlear (VIIIth cranial nerve) nerve travels in a bony canal, the internal auditory canal, with the facial nerve. The brain stem and its vital structures are adjacent to this region.
Why is it necessary to sacrifice hearing in order to completely remove neuroma?
In some cases, because of invasion of the auditory nerve by the tumor, it is necessary to sacrifice hearing in order to completely remove the neuroma. The success of hearing preservation in these cases is largely dependent upon the size of the tumor and the condition of the auditory nerve in relation to the tumor.
What percentage of brain tumors are acoustic?
Acoustic Neuromas: What You Should Know. Acoustic neuromas, also known as vestibular schwannomas, constitute approximately six percent (6%) of all brain tumors. These tumors occur in all races of people and have a very slight predilection for women over men. In the United States, approximately ten (10) people per million, ...
What is acoustic neuroma?
Acoustic (bilateral) neuroma is a benign tumor that develops in the auditory nerve, which is also called an acoustic nerve. The acoustic nerve is responsible for transmitting the acoustic information to the brain and it is located in the inner ear. The incidence rate of acoustic neuroma is two cases per 200,000 population. This tumor occupies 11 - 12% of all brain cancers. Generally the disease is more likely to appear among the individuals between 35 and 45 years. There has never been cases of acoustic neuroma among children and teenagers.
What is the difference between hearing test and electronystagmography?
Hearing test is a diagnostic procedure of the acoustic (bilateral) neuroma that measures hearing in both ears. Electronystagmography is a test, during which the cold and warm water are poured into the ear canal and the results of dizziness and of eye movements are recorded and analyzed.
How many departments does University Hospital Ulm have?
The hospital is famous for its numerous discoveries and the world-class achievements in medicine and pharmaceuticals. The medical facility has 29 specialized departments a
When was the University Hospital Tuebingen founded?
According to the prestigious medical publication Focus, the University Hospital Tuebingen ranks among the top five German hospitals! The hospital was founded in 1805, therefore it is proud of its long history, unique experience, and outstanding achievements in the field of medical care, as well as research and teaching activitie
Is University Hospital Hamburg Eppendorf a top ten hospital in Germany?
According to the Focus magazine, the University Hospital Hamburg-E ppendorf ranks among the top ten hospitals in Germany! Since its foundation in 1889, the hospital has taken a leading position in the European medical arena and still occupies it until today. A highly competent medical team of more than 11,000 employees takes care
Is University Hospital Würzburg a German hospital?
According to the Focus magazine in 2019, the University Hospital Würzburg ranks among the top national German hospitals! The hospital is one of the oldest medical facilities in Germany. The centuries-old traditions of first-class treatment are combined with the very latest achievements of modern evidence-based medicine and
What is the University Hospital Marburg?
The University Hospital Marburg UKGM offers patients modern diagnostics and comprehensive therapy at the international level. As a maximum care hospital, the medical facility specializes in all fields of modern medicine ranging from ophthalmology to traumatology and dentistry. The main areas of specialization of the hospital are
What is the best way to detect vestibular schwannoma?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are critical in the early detection of a vestibular schwannoma and are helpful in determining the location and size of a tumor and in planning its microsurgical removal.
What is the name of the tumor that develops from the balance and hearing nerves supplying the inner ear?
A vestibular schwannoma (also known as acoustic neuroma, acoustic neurinoma, or acoustic neurilemoma) is a benign, usually slow-growing tumor that develops from the balance and hearing nerves supplying the inner ear. The tumor comes from an overproduction of Schwann cells—the cells that normally wrap around nerve fibers like onion skin ...
What nerves do vestibular schwannoma affect?
As the vestibular schwannoma grows, it affects the hearing and balance nerves, usually causing unilateral (one-sided) or asymmetric hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ear), and dizziness/loss of balance. As the tumor grows, it can interfere with the face sensation nerve (the trigeminal nerve), causing facial numbness.
How many people develop vestibular schwannoma?
Approximately one out of every 100,000 individuals per year develops a vestibular schwannoma . Bilateral vestibular schwannomas affect both hearing nerves and are usually associated with a genetic disorder called neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). Half of affected individuals have inherited the disorder from an affected parent ...
What is the name of the tumor in the inner ear?
Inner ear with vestibular schwannoma (tumor) A vestibular schwannoma (also known as acoustic neuroma, acoustic neurinoma, or acoustic neurilemoma) is a benign, usually slow-growing tumor that develops from the balance and hearing nerves supplying the inner ear. Source: NIH/NIDCD. A vestibular schwannoma (also known as acoustic neuroma, ...
How many ear tumors are there in the skull?
Unilateral vestibular schwannomas affect only one ear. They account for approximately 8 percent of all tumors inside the skull; approximately one out of every 100,000 individuals per year develops a vestibular schwannoma. Symptoms may develop at any age but usually occur between the ages of 30 and 60 years.
Why is it so difficult to remove a tumor?
As the tumor grows larger, surgical removal is more complicated because the tumor may have damaged the nerves that control facial movement, hearing, and balance and may also have affected other nerves and structures of the brain. The removal of tumors affecting the hearing, balance, or facial nerves can sometimes make the patient’s symptoms worse ...
What is the treatment for acoustic neuroma?
Radiation therapy is another treatment option for acoustic neuromas. Typically for acoustic neuromas, stereotactic radiation is used because this allows the radiation to be delivered with increased precision to the tumor while minimizing the radiation exposure to the normal, healthy tissues surrounding the acoustic neuroma such as the brainstem, ...
How long after radiation treatment for acoustic neuroma?
Once radiation has been used to treat the acoustic neuroma, surveillance imaging, typically with MRI scans, should be performed for at least 10 years after the treatment to ensure that the tumor does not continue to show any signs of growth that would require further treatment.
What is the treatment team for stereotactic neuromas?
The treatment team should consist of a neurosurgeon and/or a neurotologist and a radiation oncologist.
How does stereotactic radiation work?
Stereotactic radiation can either be delivered as single-fraction radiosurgery (SRS) or by dividing the radiation dose over multiple sessions which is termed fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (FRS). Both forms of radiation (SRS and FSR) work similarly by damaging the DNA within the tumor cells. The cells can no longer divide and eventually die ...
How big is acoustic neuroma?
Typically, acoustic neuromas that are greater than 2.5 – 3cm in size are not considered ideal candidates for radiation therapy as these larger tumors often compress the surrounding brainstem and the potential for side effects from the radiation is increased.
How does a linear accelerator work?
Linear Accelerator (LINAC) machines work by accelerating electrons to produce high-energy X-rays. The beam of X-rays (photons) is then shaped to the tumor as it exits the machine using a series of collimators and by rotating either the patient or the machine.
Does radiation kill acoustic neuroma?
Although radiation effectively kills the acoustic neuro ma by altering the individual tumor cell DNA, the incidence of transforming the acoustic neuroma from a benign to a malignant tumor (i.e., malignant transformation) as a result of DNA mutation has fortunately been extremely rare.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
Treatment
- Your acoustic neuroma treatment may vary, depending on: 1. The size and growth of the acoustic neuroma 2. Your overall health 3. Severity of symptoms To treat acoustic neuroma, your doctor may suggest one or more of three potential options: monitoring, surgery or radiation therapy.
Future
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Clinical significance
- Dealing with the possibility of hearing loss and facial paralysis and deciding which treatment would be best for you can be quite stressful. Here are some suggestions you may find helpful: 1. Educate yourself about acoustic neuroma.The more you know, the better prepared you'll be to make good choices about treatment. Besides talking to your doctor and your audiologist, you m…
Introduction
- You're likely to start by seeing your family doctor or a general practitioner. Your doctor may then refer you to a doctor trained in ear, nose and throat conditions or a doctor trained in brain and nervous system surgery (neurosurgeon). Because there's often a lot to talk about during your appointment, it's a good idea to be well prepared. Here's some information to help you get ready …
Selected publications
- As discussed below, the therapeutic options for acoustic neuromas include observation, surgery and radiosurgery. The optimal treatment varies according to whether the tumor is large or small, whether it has caused neurologic damage prior to treatment and on patient factors. Because acoustic neuromas are usually slow-growing, immediate intervention ...
Diagnosis
- Currently, long-term follow-up after treatment that documents a high cure rate is only available for surgical removal, and only when the vast majority of the tumor is completely resected. (There is a suggestion that small \"flecks\" of tumor may be left without risk of regrowth, but significant portions of the tumor left behind present a significant risk of regrowth). In some cases, however…
Risks
- The skull base team may favor the translabyrinthine approach for removal of the acoustic neuroma as it offers early visualization of the seventh nerve. This approach results, however, in complete loss of ipsilateral hearing in virtually all patients. The middle fossa approach has been used for small intracanalicular acoustic neuromas in patients with intact hearing. This approach…
Pathophysiology
- Image-guided surgery brings together the skills of experienced surgeons with 2- and 3-dimensional images of the skull base obtained using CT or MRI scans. Graphic displays in the operating room link those images to the sterile instruments used by the surgeons, so that the instrument tips in real space also appear in the virtual space of the CT or MRI images. The virtua…
Prognosis
- Most modern surgical series report complete tumor removal with both anatomic and functional preservation of the facial nerve in over 90% of patients having surgery for the acoustic neuromas (Buchman CA, Chen DA, Flannagan P, Wilberger JE, Maroon JC. The learning curve for acoustic tumor surgery. Laryngoscope 1996;106:1406-1411; Sampath P. Facial nerve injury in acoustic ne…
Individualized Treatment Decisions
- To review complications that occur during the course of acoustic neuroma surgery a retrospective case review was published (Otol Neurotol 2001 Nov;22(6):895-902 Perioperative morbidity of acoustic neuroma surgery. Slattery WH 3rd, Francis S, House KC). A series of 1,687 patients undergoing acoustic neuroma surgery between 1987 and 1997 included 822 male and 865 fema…
Expertise with Radiation and Surgery
- The surgical removal of Acoustic Neuromas that grow after radiotherapy presents a unique set of challenges. Acoustic neuromas that grow despite radiotherapy present either as active growth demonstrated on MRI scans (after radiation) or neurologic deficits, particularly facial muscle weakness and spasm that slowly worsen. In such cases, repeated radiation is not thought to be …
For More Information
- A recent study based at Johns Hopkins documented the experience of removing acoustic neuromas that grow after radiation therapy (Lee, Westra, Staecker, Long, Niparko: Clinical and histopathological features of recurrent acoustic neuroma following stereotactic radiosurgery. Otology & Neurotology, in press, 2003). As stereotactic radiosurgery for acoustic neuroma entail…