
Medication
This should include:
- Brushing – brush your teeth every day after each meal. ...
- Flossing – you need to remove the food particles that get stuck between your teeth after each meal as they are breeding grounds for toxic bacteria. ...
- Rinsing – the final step in your daily routine should be using a mouthwash to rinse away the left over bacteria. ...
Procedures
The good news is that it is possible to cure periodontal disease. Below are some of the aspects of periodontal disease treatment that can be expected. Behavior Change. This is one of the first things the dentist will recommend as part of your treatment. Because plaque is the root cause of periodontal disease, it is essential that it is removed every day.
Self-care
To use a salt water rinse:
- Add 1/2 to 3/4 teaspoon of salt to a glass of lukewarm water and mix well.
- Swish the solution in your mouth for up to 30 seconds.
- Spit out the solution.
- Repeat two to three times per day.
Nutrition
What you need to do:
- Swish sesame oil (one tablespoon) around in the mouth and through the teeth.
- Do this for at least 10 minutes.
- Spit it out and then wash your mouth with water.
How to reverse periodontal disease naturally without surgery?
Is it possible to cure periodontal disease?
How to cure periodontitis naturally?
How to treat periodontitis disease at home?
What is periodontal disease?
Periodontal diseases are infections in the structures around the teeth, but not in the actual teeth themselves. These structures include the: It can progress from gingivitis, which is the first stage of periodontal disease and only affects the gums, to the other structures. Periodontal diseases are caused most often by a combination ...
How to get rid of bacteria in teeth?
Your dentist will carefully detail the oral hygiene practices you need to follow, including brushing your teeth properly and flossing daily. Clean your teeth carefully, making sure not to miss any of the hard-to-reach spots, and use mouthwash to help kill off any leftover bacteria.
How much does it cost to remove tartar from a tooth?
The gums will then be sutured to fit more tightly around the tooth. This procedure typically costs between $1000 and $3000 without insurance.
What is scaling in dental?
Procedures called “scaling” and “root planing” will also happen during this stage, where the dentist will clean your teeth deeply and remove plaque and calculus. Medications may also be prescribed.
Can periodontal disease cause tooth extraction?
Periodontal disease can increase your risk for conditions like stroke, heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory diseases. Untreated, it can also result in tooth extraction. It’s exceptionally important to treat it. If you start early, it can even save you from needing more invasive treatments in the long run.
Can you get implants if you have teeth removed?
Some individuals may also enter a restorative phase if extensive surgery was needed. Implants or prosthetics may be inserted if teeth were extracted or if a large amount of tissue or bone had to be removed . Orthodontic treatment can also help align your teeth properly, making them easier to care for.
Is it better to start your periodontal treatment early?
If you start early, it can even save you from needing more invasive treatments in the long run. Periodontal therapies and treatments are often exceptionally effective, and as long as you follow the instructions your dentist provides you during the maintenance stage, your risk of recurrence is low.
Treatment for Periodontal Disease
Periodontal treatment methods depend upon the type and severity of the disease. Your dentist and dental hygienist will evaluate for periodontal disease and recommend the appropriate treatment. There are many surgical and nonsurgical treatments the periodontics may choose to perform, depending upon the exact condition of the teeth, gums and jawbone.
Here are some of the more common treatments for periodontal disease
Scaling and root planing – In order to preserve the health of the gum tissue, the bacteria and calculus (tartar) which initially caused the infection, must be removed. The gum pockets will be cleaned and treated with antibiotics as necessary to help alleviate the infection. A prescription mouthwash may be incorporated into daily cleaning routines.
What is the best way to treat periodontal disease?
Your dentist or periodontist may determine that antibiotics are necessary to treat your periodontal disease. After root planing, he may insert antibiotic chips in the gum pockets that will slowly dissolve and release medication to kill bacteria in a small area without influencing your entire body.
How to get rid of a periodontal infection?
Apply antibiotic gel, if prescribed. Your dentist or periodontist may prescribe you antibiotic gel to apply to your gums twice daily after brushing, flossing, and irrigation. This gel kills bacteria, and will help get your periodontal infection under control.
Why do you need to see your dentist after a periodontal cleaning?
After your deep cleaning, you will need to see your dentist more frequently so that she can measure the periodontal disease pockets and ensure that they are healing. If the disease is not improving sufficiently, she will then make recommendations for further treatment.
How to diagnose periodontal disease?
1. Visit your dentist for an exam. Your dentists will examine your teeth and gums, take x-rays, and assess the extent of your gum disease by measuring the depth of periodontal pocket. She will then have you schedule a deep cleaning and give you instructions on oral hygiene and home care leading up to that appointment.
What happens if you leave periodontal disease untreated?
Periodontal disease is a serious bacterial infection of the gums that, if left untreated, will eventually destroy the gums, ligaments and bones supporting your teeth, leading to tooth loss.
How to floss your teeth?
Floss your teeth at least once a day. Begin with an 18-inch piece of floss. Wrap it around your two middle fingers leaving a gap of 1 to 2 inches in between. Then slide the floss between two teeth, and wiggle it up and down and back and forth, several times. Keep in mind that plaque and food can get stuck under the gum line, so this is what you want to target with the floss. Be sure to wrap the floss around each tooth, and floss all the way to your gums, extending as far as you can without causing discomfort. Then repeat the process on the next tooth, moving to a new section of the floss, as it becomes soiled or frayed. Make sure that once you have placed the floss between two teeth you are flossing two surfaces. Once you have this down, the entire process should only take two or three minutes per day.
What is the procedure called when you have to remove tartar from your gums?
The most basic surgical option is called flap surgery, in which your dentist or periodontist will make an incision in your gums, lifting them back to clean and remove the tartar, infected bone, and necrotic cementum underneath. The flap is then sutured back into place, up against your teeth.
What are the signs of periodontal disease?
The following are warning signs of periodontal disease: Bad breath or bad taste that won’t go away. Red or swollen gums. Tender or bleeding gums. Painful chewing. Loose teeth. Sensitive teeth. Gums that have pulled away from your teeth. Any change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite.
How many people have periodontal disease?
47.2% of adults aged 30 years and older have some form of periodontal disease . Periodontal disease increases with age, 70.1% of adults 65 years and older have periodontal disease. This condition is more common in men than women (56.4% vs 38.4%), those living below the federal poverty level (65.4%), those with less than a high school education ...
Why do my gums bleed?
Periodontal diseases are mainly the result of infections and inflammation of the gums and bone that surround and support the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums can become swollen and red, and they may bleed.
What is the most serious form of tooth decay?
In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or even fall out. Periodontal disease is mostly seen in adults. Periodontal disease and tooth decay are the two biggest threats to dental health.
What happens when bacteria in your mouth is on your teeth?
Bacteria in the mouth infect tissue surrounding the tooth, causing inflammation around the tooth leading to periodontal disease. When bacteria stay on the teeth long enough, they form a film called plaque, which eventually hardens to tartar, also called calculus.
Can periodontal disease be treated?
More severe forms of periodontal disease can also be treated successfully but may require more extensive treatment. Such treatment might include deep cleaning of the tooth root surfaces below the gums, medications prescribed to take by mouth or placed directly under the gums, and sometimes corrective surgery.
Can tartar build up on gums be removed?
Tartar build-up can spread below the gum line, which makes the teeth harder to clean. Then, only a dental health professional can remove the tartar and stop the periodontal disease process.
What are the different types of periodontal disease?
There are different forms of periodontal disease, but the following are the most common: 1 Chronic gingivitis. A reversible, milder form of periodontal disease, marked by inflammation, redness, and bleeding gums. There is no bone loss with gingivitis, and as noted, it is easily preventable! 2 Aggressive periodontitis. A rapid loss of gum attachment and bone destruction in a short period. 3 Chronic periodontitis. The most common form of periodontitis. It progresses slowly. 4 Necrotizing periodontal disease. An infection resulting from the death of gum tissue surrounding the tooth and connecting bone. Its common symptoms are a foul odor and painful bleeding gums.
How to prevent tooth decay?
Avoid sugary foods and drinks as they contribute to tooth decay. Instead, build a well-balanced diet. It should consist of plenty of hydration, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, meats, and dairy to make a robust immune system ready to fight disease!
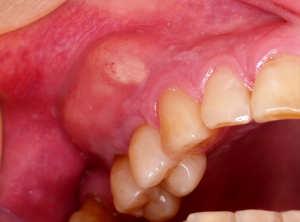
What does it mean when your gums are red?
A periodontal abscess can sometimes occur from advanced gum disease. This abscess appears as a red, swollen lesion on the gumline. If you suddenly feel a sharp pain in your gums, it's best to see a dentist quickly, as the sooner an abscess gets treatment, the better!
Why do teeth get loose?
Toxins from this buildup of bacterial plaque affect your gum tissue and the bone and ligaments that support your teeth. As the infection causes periodontitis to spread to the bone and supporting tissues, your teeth may become loose and need removal. But even advanced cases of periodontal disease don't have to progress to this point.
Why do dentists cover roots?
Your dental professional takes gum tissue from your palate or another source and uses it to cover the roots of one or more teeth. Covering exposed roots helps reduce sensitivity and protects your roots from decay while stopping further gum recession and bone loss.
What is the sign of gum disease?
Gingivitis to Periodontitis. A significant indicator of gum disease is inflammation, which is the body's way of shielding, guarding, and protecting itself from infection. Think of it as a blowfish puffing up to scare away predators!
What is the first stage of gum disease?
Gum disease is a sneaky, progressive disease. Here's why: the first stage, called gingivitis, occurs when bacterial plaque is not thoroughly removed from your teeth.
What is periodontal disease?
With the busy pace of life, sometimes it can be easy to let oral hygiene slip. But taking care of your oral health is key to keeping your entire body healthy. Like any disease, oral diseases such as gum disease can be harmful to the body. If your gums are not taken care of, an advanced stage of gum disease can occur known as periodontal disease.
What are the stages of periodontitis?
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that can become progressively worse if not treated. The early stage of gum disease is known as gingivitis, which is often characterized by signs of bleeding and inflamed gums.
Symptoms of periodontitis
Symptoms of periodontitis may vary for each individual. Some individuals are asymptomatic early on, while others may experience oral pain and sensitivity. In addition, gum recession, loose teeth, trouble chewing, bad breath, altered taste, and inflamed or bleeding gums are other common signs and symptoms of periodontitis.
Causes of Periodontitis
Poor oral hygiene is one of the most common causes of periodontitis. Lacking good oral hygiene allows bacteria to thrive and wreak havoc in your mouth as a result of plaque buildup. Thankfully, taking good care of your teeth and gums can help you prevent periodontitis.
How to prevent Periodontitis?
Periodontitis can be prevented with good lifestyle choices. Focus on perfecting your oral hygiene routine by brushing your teeth at least twice a day for two minutes each time, and don’t skip out on flossing at least once a day.
Diagnosis of periodontitis
Confirming a diagnosis of periodontitis first typically starts with a thorough dental examination performed by your dental professionals. They will review your medical and dental history, take X-rays of your teeth to check for tooth decay and examine your bone levels, and probe the gums surrounding each tooth.
What are the complications of periodontitis?
Periodontitis can lead to permanent negative changes in your mouth if untreated. Common complications of periodontitis include:
What Is Periodontal Disease?
Causes
Warning Signs
Risk Factors
Specialist to consult
Prevention and Treatment
- To determine whether you have periodontitis and how severe it is, your dentist may: 1. Review your medical historyto identify any factors that could be contributing to your symptoms, such as smoking or taking certain medications that cause dry mouth. 2. Examine your mouthto look for …
What Is The CDC Doing About Periodontal Disease?
Podcasts About Periodontal Disease and Diabetes
Additional Resources
Reference