What is a natural substitute for antibiotic?
Use in humans?
- Oregano oil. Its use for chickens was mentioned above and in the laboratory, it has also been studied in mice. ...
- Mustard oil. Oregano isn’t the only one on this list. ...
- Cinnamon. A search for the two words “cinnamon antibiotic” on PubMed yields over 100 results. ...
- Colloidal silver. ...
- Goldenseal. ...
- Echinacea. ...
- Andrographis. ...
- Garlic. ...
- Coconut oil. ...
- Grapefruit seed extract. ...
What antibiotic is best for infection?
Please give an overall site rating:
What is a good substitute for amoxicillin?
Top seven safe, effective natural antibiotics
- Seven best natural antibiotics. Garlic may be an effective treatment against bacteria. ...
- Risks of natural antibiotics. Just because something is labeled natural, it is not necessarily safe. ...
- When to use prescribed antibiotics. Antibiotics may be prescribed to speed recovery from illness or to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
- Outlook. ...
Is there any alternative for antibiotics?
- Bactroban
- Nitrofurazone
- Nystatin (mentioned above for denture stomatitis)
- Silvadene
- Sulfamylon
What antibiotics are used for treating?
Antibiotics are a group of medicines that are used to treat infections caused by some germs (bacteria and certain parasites). They do not work against infections that are caused by viruses - for example, the common cold or flu.
What are the 3 main antibiotics?
What are the most common antibiotics?Penicillins. Penicillins are a common treatment for a variety of skin conditions. ... Cephalosporins. Cephalosporins often treat gonorrhea, pelvic inflammatory disease, and sinusitis. ... Tetracyclines. ... Macrolides. ... Fluoroquinolones. ... Sulfonamides. ... Glycopeptides.
What is the best antibiotic medicine?
Top 10 List of Brand Name AntibioticsAugmentin.Flagyl, Flagyl ER.Amoxil.Cipro.Keflex.Bactrim, Bactrim DS.Levaquin.Zithromax.More items...•
What are the 7 types of antibiotics?
In this portal, antibiotics are classified into one of the following classes: penicillins, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, macrolides, beta-lactams with increased activity (e.g. amoxicillin-clavulanate), tetracyclines, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, lincosamides (e.g. clindamycin), urinary anti-infectives, and other ...
What are the 4 types of infections?
The four different categories of infectious agents are bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. When studying these agents, researchers isolate them using certain characteristics: Size of the infectious agent.
What is the safest antibiotic?
Penicillins are the oldest of the antibiotics and are generally safe (but they can cause side effects such as diarrhea, skin rash, fever and more). FQs are the newest group of antibiotics.
When do I need antibiotics?
When do we need antibiotics? Antibiotics are for bacterial infections only. This includes infections such as bloodstream infections, skin abscess/impetigo, bacterial pneumonia, urinary tract infections, streptococcal pharyngitis and some middle ear infections.
Are antibiotics harmful?
They are very helpful in fighting disease, but sometimes antibiotics can actually be harmful. Key facts to know about antibiotic safety: Antibiotics can have side effects including allergic reactions and serious, possibly life-threatening diarrhea caused by the bacteria (germ) Clostridium difficile (C. diff).
What are the most common antibiotics?
Penicillin is the most widely prescribed of all antibiotics, usually in the form of amoxicillin.
What are the 5 antibiotics?
7 Types of AntibioticsPenicillins such as penicillin and amoxicillin.Cephalosporins such as cephalexin (Keflex)Macrolides such as erythromycin (E-Mycin), clarithromycin (Biaxin), and azithromycin (Zithromax)Fluoroquinolones such as ciprofolxacin (Cipro), levofloxacin (Levaquin), and ofloxacin (Floxin)More items...
What is antibiotic and example?
Antibiotics are chemical substances produced by a living organism that kill or stop the growth of disease-causing micro-organisms such as fungi and bacteria. Examples of antibiotics: Penicillin. Streptomycin.
Is paracetamol an antibiotic?
Paracetamol is a common painkiller used to treat aches and pain. It can also be used to reduce a high temperature. It's available combined with other painkillers and anti-sickness medicines.
When Not to Use Antibiotics
Antibiotics are not the correct choice for all infections. For example, most sore throats, cough and colds, flu or acute sinusitis are viral in ori...
Top 10 List of Common Infections Treated With Antibiotics
1. Acne 2. Bronchitis 3. Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye) 4. Otitis Media (Ear Infection) 5. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD’s) 6. Skin or Soft Tissue...
Top 10 List of Generic Antibiotics
1. amoxicillin 2. doxycycline 3. cephalexin 4. ciprofloxacin 5. clindamycin 6. metronidazole 7. azithromycin 8. sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim 9. am...
Top 10 List of Brand Name Antibiotics
1. Augmentin 2. Flagyl, Flagyl ER 3. Amoxil 4. Cipro 5. Keflex 6. Bactrim, Bactrim DS 7. Levaquin 8. Zithromax 9. Avelox 10. Cleocin
Top 10 List of Antibiotic Classes (Types of Antibiotics)
1. Penicillins 2. Tetracyclines 3. Cephalosporins 4. Quinolones 5. Lincomycins 6. Macrolides 7. Sulfonamides 8. Glycopeptides 9. Aminoglycosides 10...
Are There Any Over-The-Counter Antibiotics?
Over-the-counter (OTC) oral antibiotics are not approved in the U.S. A bacterial infection is best treated with a prescription antibiotic that is s...
Need-To-Know: Trending Antibiotic Articles
Patients frequently have questions about specific topics with antibiotics. Here are some articles that address common questions you may have about...
When should antibiotics be given?
Antibiotics are given as soon as the patient can tolerate oral medication. The choice of antibiotic should be informed by local antibiotic susceptibility patterns.
When were antibiotics used for cholera?
Antibiotics have been used as an adjunct to hydration treatment for cholera since 1964. Findings from randomized controlled trials evaluated the effectiveness of selected antibiotics on three main outcomes: stool output, duration of diarrhea, and bacterial shedding. These studies compared outcomes for cholera patients who were given both ...
How much does doxycycline cost?
Doxycycline costs approximately $0.02 per 100-mg tablet. Azithromycin costs approximately $0.16 per 250-mg tablet. Antibiotics can cause nausea and vomiting.
What are the alternatives to doxycycline?
If resistance to doxycycline is documented, azithromycin and ciprofloxacin are alternative options. During an epidemic or outbreak, antibiotic susceptibility should be monitored through regular testing of sample isolates from various geographic areas.
What is the best treatment for cholera?
Oral or intravenous hydration is the primary treatment for cholera. In conjunction with hydration, treatment with antibiotics is recommended for severely ill patients. It is also recommended for patients who have severe or some dehydration and continue to pass a large volume of stool during rehydration treatment.
What is the risk factor for antimicrobial resistance?
A likely risk factor for antimicrobial resistance is widespread use of antibiotics, including mass distribution for prophylaxis in asymptomatic individuals. Antibiotic resistance emerged in previous epidemics in the context of antibiotic prophylaxis for household contacts of cholera patients. Unanswered questions.
Is tetracycline a good antibiotic for cholera?
Antibiotic regimens for the treatment of cholera. Tetracycline has been shown to be an effective treatment for cholera and is superior to furazolidone, cholamphenicol,and sulfaguanidine in reducing cholera morbidity. Treatment with a single 300-mg dose of doxycycline has been shown to be equivalent to tetracycline treatment ...
What to do if your doctor says antibiotics are the best treatment?
If your doctor decides an antibiotic is the best treatment when you’re sick: Take them exactly as your doctor tells you. Do not share your antibiotics with others. Do not save them for later. Talk to your pharmacist about safely discarding leftover medicines. Do not take antibiotics prescribed for someone else.
What are the side effects of antibiotics?
Common side effects range from minor to very severe health problems and can include: Rash. Nausea.
Can antibiotics help with sickness?
Antibiotics aren’t always the answer when you’re sick. Sometimes, the best treatment when you’re sick may be over-the-counter medication. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for tips on how to feel better while your body fights off an infection.
Do you need antibiotics for sinus infections?
Antibiotics also ARE NOT needed for some common bacterial infections, including: Many sinus infections. Some ear infections. Taking antibiotics when they’re not needed won’t help you, and their side effects can still cause harm. Your doctor can decide the best treatment for you when you’re sick.
Do antibiotics help with resistance?
Antibiotic Do’s & Don’ts. Smart use of antibiotics is the best care. Here are some steps you can take to use antibiotics appropriately so you can get the best treatment when you’re sick, protect yourself from harms caused by unnecessary antibiotic use, and combat antibiotic resistance.
What is the purpose of antibiotics?
Antibiotics are medications used to fight infections caused by bacteria. They’re also called antibacterials. They treat infections by killing or decreasing the growth of bacteria. The first modern-day antibiotic was used in 1936. Before antibiotics, 30 percent.
Why are antibiotics used for treating infections?
Antibiotics are used for treating infections caused by bacteria. Sometimes it’s difficult to determine if your infection is caused by bacteria or a virus because the symptoms are often very similar. Your healthcare provider will evaluate your symptoms and conduct a physical exam to determine the cause of your infection.
Why are antibiotics less effective than they once were?
However, some antibiotics are now less useful than they once were due to an increase in antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria can no longer be controlled or killed by certain antibiotics.
Why are antibiotics unnecessary?
of antibiotic use is thought to be unnecessary. This is because antibiotics are often prescribed when they aren’t needed. Several important steps can be taken to decrease inappropriate antibiotic use: Take antibiotics only for bacterial infections.
How long does it take for antibiotics to work?
How quickly you get better after antibiotic treatment varies. It also depends on the type of infection you’re treating. Most antibiotics should be taken for 7 to 14 days.
What is a CRE infection?
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) This class of bacteria are resistant to a lot of other antibiotics. CRE infections typically occur in people in hospitals and who are on a mechanical ventilator or have indwelling catheters.
How effective are antibiotics?
Antibiotics are most effective when used appropriately. This starts with ensuring that you really need the antibiotic. Only use antibiotics prescribed by your doctor for a bacterial infection. Talk with your doctor or pharmacist about the best way to take your antibiotic.
What is the first line of antibiotics?
First-line options are usually selected from nitrofurantoin, fosfomycin and sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim. Amoxicillin/clavulanate ( Augmentin) and certain cephalosporins, for example cefpodoxime, cefdinir, or cefaclor may be appropriate options when first-line options cannot be used.
How long should you take antibiotics for a recurrent UTI?
For recurrent UTIs, there are several antibiotic options for prevention: A shorter course (3 days) of antibiotics at the first sign of UTI symptoms; a prescription may be given to you to keep at home, but testing should be done at least once to confirm you have a UTI and not another problem.
How much does a UTI cost?
Roughly 40% of women experience a UTI at some time, and in women, it is the most common infection. Healthcare costs related to UTIs exceed $1.6 billion per year. A urinary tract infection (UTI) can happen anywhere along your urinary tract, which includes the kidneys (the organ that filters the blood to make urine), ...
What is it called when bacteria get into the bladder?
A lower urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria gets into the urethra and is deposited up into the bladder -- this is called cystitis . Infections that get past the bladder and up into the kidneys are called pyelonephritis.
How long does it take to get rid of cystitis?
Length of treatment for cystitis can range from a single, one-time dose, to a course of medication over 5 to 7 days. Kidney infections may require injectable treatment, hospitalization, as well as a longer course of antibiotic, depending upon severity of the infection.
Can antibiotics cause yeast infections?
However, there are side effects that are common to most antibiotics, regardless of class or drug: Vaginal yeast infections or oral thrush (candida species): Antibiotics may change the normal balance in the vagina and lead to a fungal overgrowth.
How are antibiotics given?
Before surgery, a healthcare provider usually gives antibiotics through a tube that they have inserted into one of your veins. Or they may prescribe a pill.
Why do we need antibiotics?
Antibiotic prophylaxis is the use of antibiotics before surgery or a dental procedure to prevent a bacterial infection. This practice isn’t as widespread as it was even 10 years ago. This is due to: 1 the increase in the resistance of bacteria to antibiotics 2 the change in bacteria that cause infections 3 improvements in technology that can detect infections
Why do we use antibiotics before surgery?
Antibiotic prophylaxis is the use of antibiotics before surgery or a dental procedure to prevent a bacterial infection. This practice isn’t as widespread as it was even 10 years ago. This is due to: the increase in the resistance of bacteria to antibiotics. improvements in technology that can detect infections.
What are the factors that affect antibiotic prophylaxis?
These factors include: very young or very old age. poor nutrition. obesity. diabetes. smoking, including a history of smoking.
Can antibiotics detect infections?
improvements in technology that can detect infections. However, antibiotic prophylaxis is still used in people who have certain risk factors for bacterial infection. Professional guidelines recommend using antibiotics before procedures that have a high risk of bacterial infection. These include:
Can you take antibiotics before dental surgery?
If you forget to fill your prescription or to take your pills before your appointment, your dentist may give you antibiotics during or after the procedure.
Can antibiotics cause death?
Untreated infections can lead to longer recovery times. In very rare cases, they can cause death.
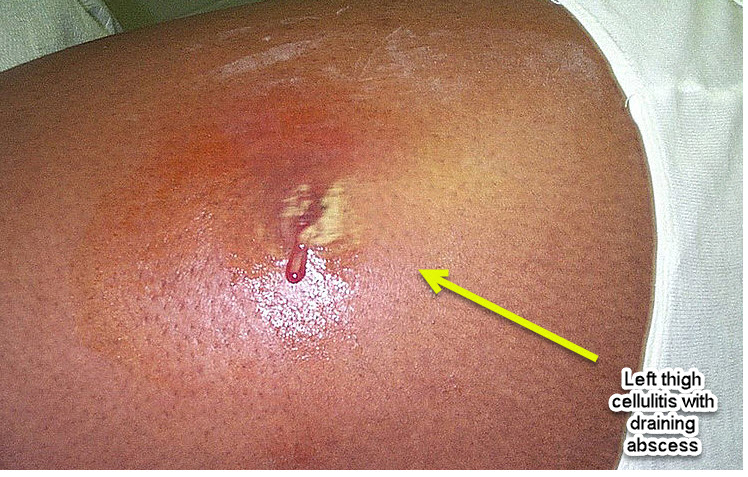
What antibiotics are prescribed for cellulitis?
Depending on how advanced the infection is, these may include: Your doctor may prescribe dicloxacillin, cephalexin, trimethoprim with sulfamethoxazole, clindamycin, or doxycycline antibiotic s.
What is the best antibiotic for cellulitis?
The best antibiotic to treat cellulitis include dicloxacillin, cephalexin, trimethoprim with sulfamethoxazole, clindamycin, or doxycycline antibiotics. Cellulitis is a deep skin infection that spreads quickly. It is a common skin condition, but it can be serious if you don’t treat cellulitis early with an antibiotic.
What is the bacteria that can enter the skin?
These are usually Staphylococcus or Streptococcus bacteria. These and other bacteria can enter the skin through cuts, burns, skin abscesses, surgery, animal bites, fungal infections like Athlete’s foot, and skin disorders like eczema. When the bacteria enter the skin, they grow and cause an infection.
How to treat cellulitis at home?
These can include: Elevating the affected part of your body to reduce swelling. Regularly moving the joint near the affected area, such as your ankle, to prevent stiffness. Drinking plenty of fluids.
Can tea tree oil help with cellulitis?
Tea tree oil. You should not only use herbal supplements or plant oils to treat cellulitis. Although they can help kill bacteria on the skin and be useful if your cellulitis is resistant to treatment, they may also interact negatively with your medications.
Can you treat cellulitis with antibiotics?
You should not treat cellulitis with alternative therapies alone. Cellulitis can be very serious and potentially life-threatening, so you will need antibiotics. Your doctor may recommend alternative therapies alongside antibiotics to strengthen a weak immune system, or if you have antibiotic-resistant bacteria.

Overview
Causes
Clinical significance
- A lower urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria gets into the urethra and is deposited up into the bladder -- this is called cystitis. Infections that get past the bladder and up into the kidneys are called pyelonephritis . An infection of the tube that empties urine from the bladder to the outside is called urethritis. UTI symptoms in women and men are similar.
Symptoms
- Urinary tract infection symptoms may include: Upper UTIs which include the kidney may also have symptoms of fever, back pain, and nausea or vomiting.
Epidemiology
- Urinary tract infections occur more frequently in women than in men because a womans urethra is shorter and closer to the anus than in men, allowing easier entry of bacteria into the urethra. Women are also more likely to get an infection after sexual activity or when using a diaphragm for birth control. Menopause also increases the risk of a UTI.
Treatment
- There are multiple types of antibiotics used to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs). Most UTIs (75-95%) in women are caused by a bacteria known as Escherichia coli (E. coli). Other Enterobacteriaceae types of bacteria may infrequently be present. Different treatments may be recommended in different areas of the country based on regional patterns ...
Diagnosis
- Most patients with an uncomplicated UTI will begin treatment without any special diagnostic test, although a urinalysis may be performed by taking a urine sample. In a urinalysis, chemical components of the urine are determined, and the doctor may look at urine color, clarity, and a view a sample under the microscope. A urine culture may be order, too, but is not always needed to st…
Results
- Symptoms like burning while urinating will usually clear up in within one to two days after starting treatment. Be sure to finish your entire course of medication. If symptoms are still present after 2 to 3 days, contact your healthcare provider
Medical uses
- The fluoroquinolones, such as ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and levofloxacin (Levaquin) have also been commonly used for uncomplicated cystitis; however, July 2016 FDA recommendations strongly suggest that the fluoroquinolone class be reserved for more serious infections, and only be used if other appropriate antibiotics are not an option.
Safety
- An FDA safety review found that both oral and injectable fluoroquinolones (also called \"quinolones\") are associated with disabling side effects involving tendons, muscles, joints, nerves and the central nervous system. These adverse effects can occur soon after administration to weeks after exposure, and may potentially be permanent. Patients should disc…
Prognosis
- Resistance rates for antibiotics are always variable based on local patterns in the community and specific risk factors for patients, such as recent antibiotic use or travel.
Uses
- Some patients may want to use cranberry or cranberry juice as a home remedy to treat a UTI. Cranberry juice has not been shown to cure an ongoing bacterial infection in the bladder or kidney.
Research
- Cranberry has been studied as a preventive maintenance agent for UTIs. According to one expert, the active ingredient in cranberries -- A-type proanthocyanidins (PACs) -- is effective against UTI-causing bacteria, but is only in highly concentrated cranberry capsules, not in cranberry juice. Cranberry seems to work by preventing bacteria from sticking to the inside of the bladder; howe…
Risks
- The effectiveness of many herbal or home remedies may not have been scientifically tested to the same degree as prescription medications -- or at all. Over-the-counter herbal products and dietary supplements are not regulated by the FDA. Side effects and drug interactions may still occur with alternative treatments. Always check with your health care professional before using an alternati…