Tax Rules for an Inherited Nonqualified Annuity
- Nonqualified. Investors can open annuities as a qualified retirement plan, such as an individual retirement annuity.
- Tax Treatment of Gain. Although some annuities operate as managed investment accounts, payments from annuities are treated as ordinary income for tax purposes.
- Estate Tax. ...
- Inheritance Tax. ...
- Return of Principal. ...
How are non qualified annuities taxed to beneficiaries?
- Non-Qualified Annuity Beneficiary Options: Stretch Provisions. ...
- Considering the Beneficiary of Your Annuity: Spouses and Non-spouses. ...
- Annuity Maximization: Strategies Beyond Non-Qualified Annuities to Maximize Wealth and Minimize Taxes. ...
What is non - tax qualified annuity?
What Is an Inherited Non-Qualified Annuity?
- A financial advisor can help you handle an inherited annuity, whether it’s qualified or not. Find an advisor now.
- Annuity Basics. Annuities are contracts between insurance companies and individuals that are often used in funding retirement.
- Comparing Qualified and Non-Qualified Annuities. ...
Is non qualified annuity taxable?
Non-qualified annuity premiums are not deductible from gross income, meaning any earnings on the investment will be taxable. Pre-Tax Contributions or After-Tax Contributions? Non-qualified annuities are an option for more conservative investors who want the potential of tax-deferred earnings and predictable retirement income.
How to calculate taxes on an annuity?
Key Takeaways
- Taxation varies, depending on the type of retirement income you receive.
- You may pay taxes on Social Security benefits if you have other sources of income.
- Income from pensions, traditional IRAs, 401 (k)s, and similar plans are taxed as ordinary income.
- You'll pay taxes on investment income, including capital gains taxes if applicable.

At what point are a nonqualified annuity earnings subject to income tax?
It is taxed only when you begin to receive the funds from the annuity, usually in retirement. With a non-qualified annuity, your purchase is made with money on which you have paid income or other applicable taxes already.
Is a non-qualified annuity considered income?
A non-qualified annuity is funded with after-tax dollars, meaning you have already paid taxes on the money before it goes into the annuity. When you take money out, only the earnings are taxable as ordinary income.
Which of the following correctly describes the basic income tax treatment of nonqualified annuities?
The correct answer is: Contributions are not tax-deductible, but benefits are received tax-free. A nonqualified annuity: Interest earned in a nonqualified annuity is tax-deferred until distributions are made.
Are loans from non-qualified annuities taxable?
When a non-qualified annuity is used as collateral, the IRS considers the loan to be a withdrawal, or non-periodic distribution, from the annuity. Here's the problem: Non-periodic distributions from annuities are taxable up to the amount of gains that have been accumulated. The taxes are paid at ordinary income rates.
How are non-qualified accounts taxed?
The amount of money you invest into a non-qualified account is considered the cost basis of that account. When you withdraw the cost basis, you are not taxed on it again, as you already paid income tax on it. The value in your account that is above the cost basis represents a stock appreciation.
How are distributions from a non-qualified account taxed?
There are no taxes on the principal when money is taken via a penalty-free withdrawal or lifetime withdrawals from a non-qualified annuity. You have to pay taxes only if there are earnings and interest. You will follow the “last-in-first-out” (LIFO) protocol of the IRS if it's a non-qualified annuity distribution.
Do non-qualified annuities get a step up in basis?
Similar to U.S. savings bonds, traditional IRAs, 401(k)s, 403(b)s and other retirement plans, there is no step-up on nonqualified annuities. Annuities provide tax deferred, not tax-free income.
What does tax status Non-qualified mean?
Funds in qualified plans are taxable as ordinary income when they are withdrawn. A non-qualified retirement plan, on the other hand, is funded with money that has already been taxed. Like qualified plans, funds in non-qualified plans grow on a tax-deferred basis.
Are non-qualified annuities subject to RMD?
Annuities are subject to the same RMD requirements if they are held inside an IRA. Nonqualified annuities (those held outside a retirement account) generally have no obligation to withdraw funds at any age unless required by the annuity contract itself.
What can I do with a non-qualified annuity?
A non-qualified annuity is an annuity bought with after-tax dollars, whereas a qualified annuity is an annuity bought with pretax dollars, in most cases. Non-qualified annuities can help reduce your taxable income when you retire and provide tax-deferral on earnings until then.
What is the difference between a qualified and nonqualified annuity?
A qualified annuity is a retirement savings plan that is funded with pre-tax dollars. A non-qualified annuity is funded with post-tax dollars. To be clear, the terminology comes from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
Is nonqualified interest taxable?
Generally Yes. Non-qualified interest is interest which is generally associated with an investment vehicle which is for some reason not qualified for a current tax deferral. It is reported on a 1099-INT and should be reported to the IRS even if you do not get a 1099-INT.
What is the tax treatment on the payout of a non qualified variable annuity quizlet?
[D] It will be taxed partly as ordinary income and partly as return of capital. A non-tax qualified annuity is an annuity where after tax dollars are contributed by the investor, upon retirement only the excess of the amount contributed is taxed.
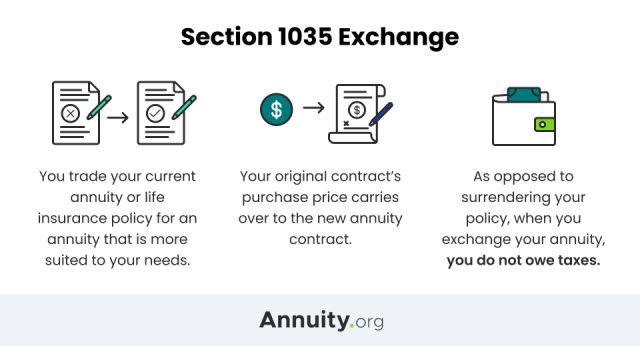
Is a section 1035 exchange taxable?
Can the insured be changed during a tax-free 1035 Exchange? No, this is treated as a taxable exchange which is taxed in the same manner as a surrender of the original contract and the issuance of a new one.
What are annuitization options?
What Is an Annuitization Method? The term annuitization method refers to an annuity distribution structure. Annuities are financial contracts distributed by financial institutions that allow individuals to invest money over a period of time to give them a source of income in the future—normally during retirement.
Which of the following is not included in an annuity contract?
Which of the following is NOT included in an annuity contract? AD&D rider. ( All of these are included in an annuity contract EXCEPT an Accidental Death & Dismemberment (AD&D) rider.
Do you pay taxes on annuities?
You do not owe income taxes on your annuity until you withdraw money or begin receiving payments. Upon a withdrawal, the money will be taxed as inc...
Do beneficiaries pay tax on inherited annuities?
Inherited annuity earnings are subject to taxation. The taxed amount depends on the payout structure and the beneficiary’s relationship with the an...
How much tax should you withhold from your annuity?
Taxes are deferred until you begin receiving your distributions or stream of income from the annuity. Then, your income will be taxable based on wh...
What is a 1035 exchange?
So-called Section 1035 exchanges cover the trading of life insurance policies and annuity contracts, and the tax-law provision allows such exchanges without having to recognize capital gain. Downsides of non-qualified annuity taxation. Investors face a trade-off with non-qualified annuities.
Why do investors choose annuities?
These contracts have tax considerations you have to keep in mind. One of the reasons why investors choose annuities is that they carry some favorable tax traits. Even if you don't hold an annuity in a qualified retirement account like an IRA, some of the tax laws that apply to annuities closely resemble how retirement money gets treated.
What is the biggest benefit of an annuity?
The biggest benefit of an annuity is that your investment can grow on a tax-deferred basis. As long as your money remains invested in the annuity contract, you don't have to pay any taxes on any income or gains that the annuity produces. Because annuity contributions aren't eligible for any sort of tax deduction, ...
Is an annuity taxable if you take a withdrawal?
For most annuities, if you just take a withdrawal, it will be deemed to have come first from earnings, meaning that the entire amount is taxable until the value of the annuity contract falls below the total of the premium payments you initially invested.
Can you hold an annuity in an IRA?
Even if you don't hold an annuity in a qualified retirement account like an IRA, some of the tax laws that apply to annuities closely resemble how retirement money gets treated. The fact that the IRS largely treats non-qualified annuities in a similar manner to tax-favored retirement accounts has some pros and cons.
Is a non-qualified annuity taxable?
Just like a retirement account, withdrawals from a non-qualified annuity result in taxable income in the year in which you take money out of the contract. Exactly how much of your withdrawal is subject to tax can get tricky.
What happens if you gift an annuity to another party?
When an annuity is gifted to another party, the transaction triggers a taxable event for the donor. Any relevant capital gains will be taxed at the current owner’s tax bracket. And, should the gift occur prior to the annuity owner’s age of 59 ½, the transaction will be subject to a 10% IRS early withdrawal penalty.
What are the phases of an annuity?
There are two distinct phases of the annuity contract: the accumulation phase and the annuitization phase. During the accumulation phase, the owner generally is not taxed on the earnings credited to the cash value of the annuity contract unless a distribution is received. The accumulation phase continues until the annuity contract is terminated ...
What happens to an annuity if the owner dies?
If the owner of the annuity is a non-natural owner, then the annuitant's death triggers the distribution at death rules. In addition, the distribution at death rules are also triggered by a change in the annuitant on an annuity contract owned by a non-natural person. Income Tax. Unlike death benefits paid from life insurance policies, ...
What age can you withdraw from an annuity?
Annuities are designed to function as retirement investment vehicles, placing withdrawals after the attained age of 59 1/2. Should the annuity owner begin withdrawals following this age and assuming that they have satisfied any relevant surrender schedule, they will not be assessed fees outside of their tax liabilities. However, should the annuity owner opt to receive withdrawals prior to reaching the age of 59 ½, they may be subject to a 10% IRS penalty on any gains posted to-date. One exception to this rule is if the annuity owner has established an agreement with the IRS, referred to as substantially equal periodic payments (SEPP). Under this agreement, equal withdrawal payments can begin prior to the annuity owner’s age of 59 ½ without penalty as long as they continue to the agreed upon future date, which at a minimum is the later of age 59 ½ or a 5 year period.
Why are non-qualified annuities so popular?
Annuities have become increasingly popular. Tax deferred growth is arguably the most appealing feature of a non-qualified annuity. This permits earnings on premiums to avoid income taxation until distribution. Long-term savings advantages and the ability to insure an income stream for life add to annuities' increasing appeal.
What is aggregation in annuity?
Purchasing several individual annuity contracts from a single insurance company within the same calendar year is often referred to as aggregation. In this scenario, the IRS treats these purchases as a single transaction in order to prevent the owner of the policies from manipulating the basis in each contract. Aggregation can result in an unexpected tax liability for the annuity owner. This rule does not apply when contracts are purchased from different insurance companies or if one annuity is deferred and another is immediate.
Is an annuity a trust?
Classification of the Annuity’s Owner as a Trust. When the owner of a nonqualified annuity is a non-natural person, such as a trust, it is taxed on an annual basis and is ineligible for tax deferral benefits. One exception does exist; should the trust act in an agent capacity.
What is the exclusion ratio on an annuity?
Non-qualified annuities require tax payments on only the earnings. The amount of taxes on non-qualified annuities is determined by something called the exclusion ratio. The exclusion ratio is used to determine what percentage of annuity income payments is taxable and how much is not. The idea is to determine the amount of a withdrawal ...
How long does an annuity last?
Your life expectancy is 10 years at retirement. You have an annuity purchased for $40,000 with after-tax money. Annual payments of $4,000 – 10 percent of your original investment – is non-taxable. You live longer than 10 years. The money you receive beyond that 10-year-life expectation will be taxed as income.
What is the rest of an annuity?
The rest is the taxable balance, or the earnings. When you receive income payments from your annuity, as opposed to withdrawals, the idea is to evenly divide the principal amount — and its tax exclusions — out over the expected number of payments.
What happens if you withdraw money from an annuity?
In general, if you withdraw money from your annuity before you turn 59 ½, you may owe a 10 percent penalty on the taxable portion of the withdrawal. After that age, taking your withdrawal as a lump sum rather than an income stream will trigger the tax on your earnings.
What are the tax advantages of annuities?
One of the main tax advantages of annuities is they allow investments to grow tax-free until the funds are withdrawn. This includes dividends, interest and capital gains, all of which may be fully reinvested while they remain in the annuity. This allows your investment to grow without being reduced by tax payments.
Is an annuity payment taxable?
If an annuitant lives longer than his or her actuarial life expectancy, any annuity payments received after that age are fully taxable. That’s because the exclusion ratio is calculated to spread principal withdrawals over the annuitant’s life expectancy.
What is annuity.org?
Annuity.org writers ad here to strict sourcing guidelines and use only credible sources of information, including authoritative financial publications, academic organizations, peer-reviewed journals, highly regarded nonprofit organizations, government reports, court records and interviews with qualified experts . You can read more about our commitment to accuracy, fairness and transparency in our editorial guidelines.
How are non qualified annuities taxed?
How is a Non-Qualified Annuity Taxed? All annuities are allowed to grow tax-deferred. This means any earned money on the investment is not taxed until it is paid out to the annuity owner. However, there are differences in how taxes are taken out in non-qualified annuities.
What is 1035 exchange?
A 1035 annuity exchange is a rule under Section 1035 of the Internal Revenue Code that allows for a tax-free exchange of a life insurance or annuity policy for a different annuity contract better suited to an owner’s needs. When transferring from one plan to another via a 1035 exchange, the transfer must be “like-to-like.”.
What is LIFO in annuities?
Last-In-First-Out ( LIFO) means any taxable earnings and interest is distributed to the annuity holder first. Once the interest and earnings are depleted, there are no taxes due. Traditional Withdrawals = Last-In, First-Out. Lifetime Income = Last-In, First-Out.
What is a non qualified annuity?
Non-Qualified Annuity Features and Benefits. A non-qualified annuity is a type of investment you buy with the money you have already been taxed on. It is not connected to any retirement account, such as an IRA or 401K.
What does an annuity owner want?
An annuity owner might want a higher interest rate or premium bonus. The insurance company may not be financially strong. A new annuity contract may offer desirable features such as an enhanced death benefit or guaranteed lifetime income. A new annuity could provide more upside potential or more guaranteed income.
Can annuities be changed after 1035 exchange?
This means the annuity owner, annuitant, and the beneficiary must be the same during the exchange. Changes to the annuity contract can be changed AFTER the 1035 exchange is completed. Annuity companies make this transfer easy for applicants by filling out a 1035 exchange form.
Is an annuity income taxed?
When you withdraw money from a qualified annuity, all of it is taxed as regular income. But if you withdraw money from a non-qualified annuity, only the earnings are taxed as regular income.
What is non qualified annuity?
A non-qualified annuity is purchased with after-tax dollars that were not from a tax-favored retirement plan. Non-qualified annuity premiums are not deductible from gross income. All annuities are allowed to grow tax-deferred. This means any earnings on the investment are not taxed until they are paid out to the annuity holder.
What is the difference between qualified and non qualified annuities?
These differences come down to whether the annuity is considered qualified or non-qualified. Qualified annuities are purchased with pre-tax funds, while non-qualified annuities are funded with money on which ...
What is a 1035 exchange?
These transfers are known as 1035 exchanges. With qualified annuities, such transfers can take place, but the transfers are limited to funds in the annuity that are considered tax-deferred. Possible reasons for such transfers could be: A fixed annuity owner might want an annuity with a higher interest rate.
When is an annuity considered taxable income?
So, for example, if your calculated life expectancy is 85 years old, then the exclusion ratio will determine how much of each payment from your non-qualified annuity will be considered taxable earnings until you turn 85. After the age of 85, all payouts from the annuity are considered taxable income.
What is annuity.org?
Annuity.org writers adhere to strict sourcing guidelines and use only credible sources of information, including authoritative financial publications, academic organizations, peer-reviewed journals, highly regarded nonprofit organizations, government reports, court records and interviews with qualified experts.
Is an annuity tax favored?
Qualified Annuities and Retirement Plans. Qualified annuities are treated like tax-favored retirement plans. In fact, they are often purchased through an employer tax-favored retirement plan. They’re also purchased with money from an IRA, 401 (k), or another account that is tax deferred.
Can you transfer an annuity without penalty?
With non-qualified annuities, you can transfer the funds between different kinds of annuities, such as fixed and variable, without facing an early-withdrawal penalty because the exchanges are covered by Section 1035 of the Internal Revenue Code. These transfers are known as 1035 exchanges.