Explore
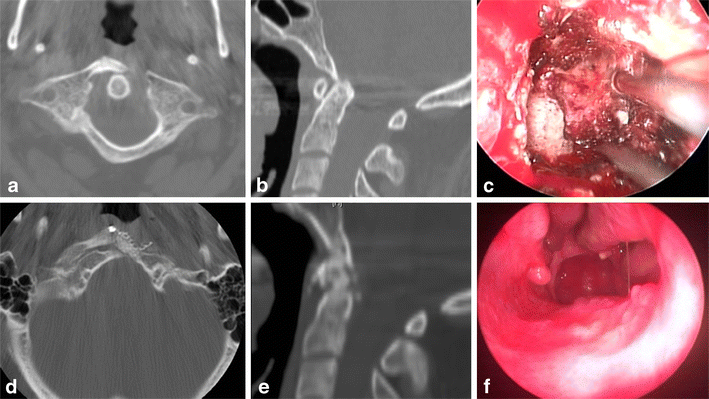
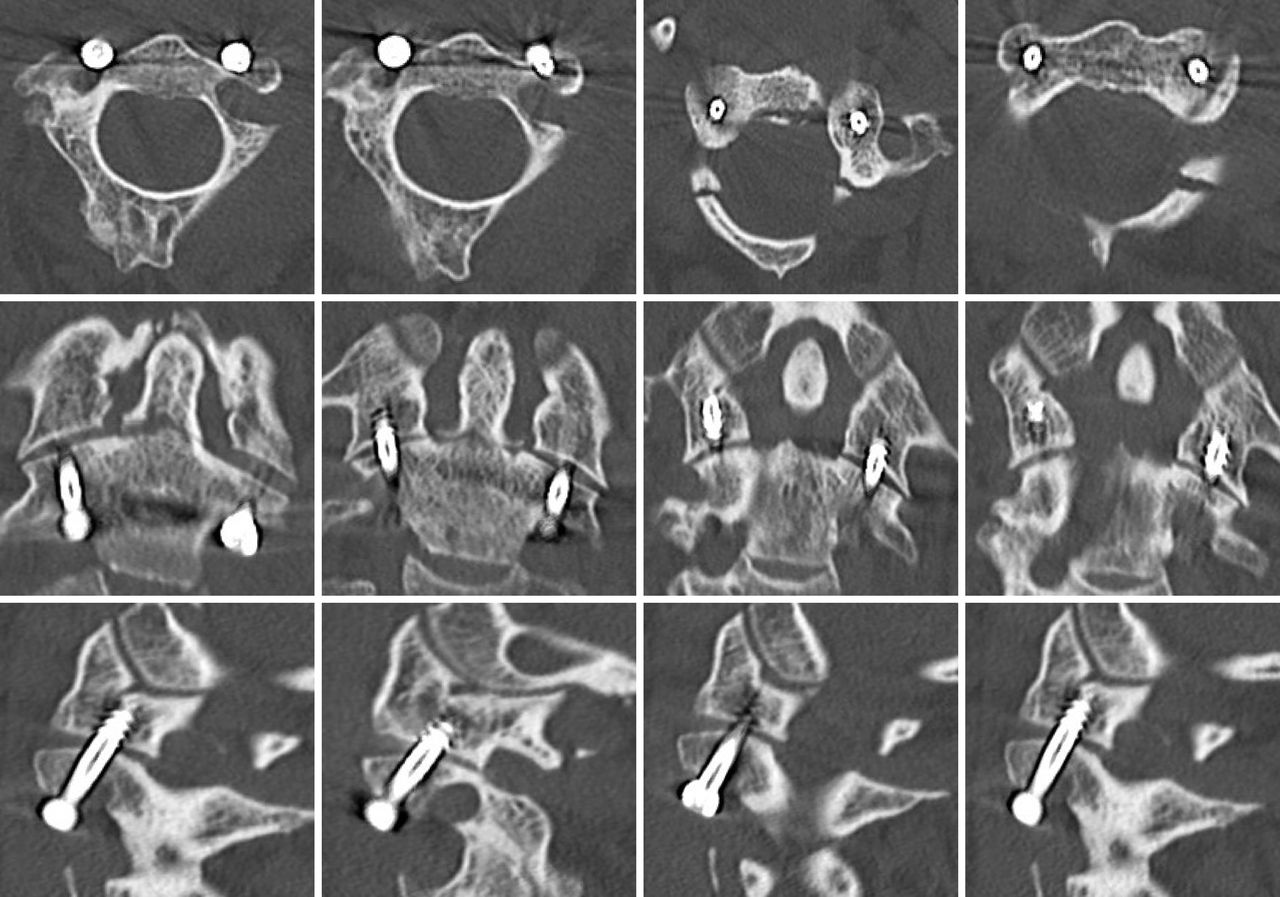
The patient underwent surgery to perform laminectomy C4-C5-C6, partial facet joint resection C6 and posterior lateral mass fixation C4-C5 and transfacet T1-T2 screws obtaining a reduction of subluxation of C6, improving of the alignment in saggital plane and the neurological deficit of the 4 limbs.
What are the surgical options for subluxation of C6?
C1 and C2 subluxation symptoms: Consequently, most medical professionals consider injuries to the first and second vertebrae in the cervical spine to be the most serious type of spinal cord injury. This is because severe damage to the C1 or C2 commonly causes full paralysis or death.
What is C1 and C2 subluxation?
Treatment for subluxations often includes resetting the joint, pain relief, rehabilitation therapy, and in severe cases, surgery. Some of the common symptoms of a joint subluxation include: 1 If your injury is serious, you should either call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room.
What is the treatment for a joint subluxation?
Treatment for type I C2 (axis) fractures is hard-collar immobilization for 6-8 weeks, which usually is quite successful. Type II fractures can be managed conservatively or surgically. Treatment options include the following: Halo immobilization. Internal fixation (odontoid screw fixation) Posterior atlantoaxial arthrodesis.
What are the treatment options for a C2 fracture?
How do you fix C2 subluxation?
The treatment of pain that stems from C1-C2 in the upper neck is usually nonsurgical....Nonsurgical Treatment for C1-C2Medication. ... Immobilization. ... Physical therapy. ... Chiropractic manipulation. ... Traction refers to stretching and/or realigning the spine to relieve direct nerve pressure and stress on the vertebral levels.More items...
How is cervical subluxation treated?
Objective The recommended treatment of cervical subluxation is currently closed or open reduction. These treatments are better accomplished in the acute setting, when muscular and ligamentous laxity allows the required maneuvers to realign the dislocated segments.
How do you fix C1-C2 instability?
Surgery is often aimed at fixing the instability by fusing vertebral segments together. In the case of C1-C2 instability, these two vertebrae are fused posteriorly to limit their amount of movement. However, it may limit motion so much that patients become completely unable to move that portion of their neck.
How do you treat AAI?
Unless symptoms of spinal cord compression occur, AAI requires no treatment. Once symptoms arise, cervical spine stabilization is indicated until surgical stabilization is performed.
Is cervical subluxation serious?
The subluxation of the cervical spine and the associated complications can have negative impacts on patients' functionality and their quality of life. [17] Most of the patients with poor neurological status are dependent upon their care providers even for their activities of daily living.
What causes C1 C2 subluxation?
Rotational subluxation or dislocation of C1 on C2. Can develop from osseous or ligamentous abnormalities resulting from acquired or congenital disorders. As a result of instability, excessive motion and spinal cord compression may occur at the atlantoaxial joint.
What kind of doctor treats cervical instability?
If you are experiencing any symptoms of cervical instability, contact your doctor or chiropractor right away. This is a manageable disorder, but only with high-quality treatment, such as physical therapy or chiropractic adjustments.
How long does it take for neck surgery to heal?
It will take between 4 and 6 weeks before light work can be accomplished, while full recovery usually takes between 2 and 3 months. If necessary your doctor may suggest physical therapy sessions to aid recovery.
Can cervical neck instability be cured?
There are a number of treatment modalities for the management of chronic neck pain and cervical instability, including injection therapy, nerve blocks, mobilization, manipulation, alternative medicine, behavioral therapy, fusion, and pharmacologic agents such as NSAIDs and opiates.
How is atlantoaxial subluxation treated?
Treatment of Atlantoaxial Subluxation Treatment includes symptomatic measures and cervical immobilization, usually beginning with a rigid cervical collar. Urgency of treatment is generally based on symptoms or presence of cord abnormalities on MRI in susceptible patients.
What does atlantoaxial instability look like?
“The neurologic manifestations of symptomatic AAI include easy fatiguability, difficulties in walking, abnormal gait, neck pain, limited neck mobility, torticollis (head tilt), incoordination and clumsiness, sensory deficits, spasticity, hyperreflexia…and (other spinal cord) signs and symptoms.
What is subluxation of C1 and C2?
Atlanto-axial subluxation is a disorder of C1-C2 causing impairment in rotation of the neck. The anterior facet of C1 is fixed on the facet of C2. It may be associated with dislocation of the lateral mass of C1 on C2.
What is bilateral facet dislocation?
Bilateral facet dislocation is the most severe injury of the flexion-distraction spectrum, causing complete disruption of facet joint capsule and interspinous ligament, ligament flavum,supraspinous ligament in all cases. The posterior longitudinal ligament disruption is also described in 40-100 % of cases with bilateral facet joint dislocation. Traumatic disc herniation with posterior annulus disruption is described in 56% of unilateral and 82.5% of bilateral facet dislocations [8].
What approach is used by Surgeos?
In this case the patient presented distractive flexion injury. In the literature the posterior approach is the most used by surgeos in this kind of injuries. An adequate realignment and improvement of the neurological status was obtained due to the short time between his arrival at the hospital, diagnosis and medical treatment.
What are the goals of surgery?
The goals of surgery are realignment and cervical balance, decompression of the neural elements and instrumented stabilization with a solid construct. We present a case of male 62 years old with subluxation of c6-c7 cused by trauma and and his surgical treatment.
Can axial CT diagnose facet joint dislocation?
The axial CT are not very useful to diagnose facet joint dislocation, there are several signs of diagnosing facet joint dislocation including the naked facet sign, the reverse “hamburger bun” and the “headphones sign” Pre-operative cervical MRI needs for the treatment decision in patients with unilateral or bilateral facet joint dislocation and look for intervertebral disc disruption [9-11].
What does spinal subluxation mean?
In general, most chiropractors believe that spinal subluxation is a process that negatively impacts an individual as their tissues undergo constant and steady changes, rather than being from a sudden jolt or traumatic injury. However, several things that chiropractors widely believe can come with spinal subluxation include but are not limited to:
What causes spinal subluxation?
Constant and repeated trauma could also play a part in spinal subluxation. For example, if you carry a heavy bag on one shoulder every day, or if you sit at a desk a certain way. This could cause a slow and gradual shift in your spine's natural alignment.
How to keep your spine in proper alignment?
Starting an exercise routine can help you strengthen your muscles and tendons to help keep your spine in proper alignment. You want to focus on a mix of strength training and cardio to help you improve your flexibility, build muscle, tone muscle, and improve your posture. It's best to start out slow and build your way up. Enlisting the help of a personal trainer can help motivate you.
How many categories of spinal subluxation are there?
To make it slightly more complicated, there are four broad categories that encompass different types of spinal subluxation. Each category has several subcategories, and this is why it can take a while to get a concrete diagnosis.
What is the term for the separation of the ribs?
Costovertebral or costotransverse separation (joints that connect your ribs to the spine)
What is secondary to structural asymmetries?
Scoliosis and/or curve alteration secondary to any structural asymmetries
Can a car accident cause spinal subluxation?
Although a sudden onset of spinal subluxation is rare, it can happen. It's usually the result of some form of traumatic event that jolted your spine or caused injuries to the muscles or tendons in your back. For example, a car accident can cause whiplash. This results in muscle spasms, tightness and back pain that can cause misalignment.
What is anterior subluxation?
Anterior subluxation of the cervical spine , also known as hyperflexion sprain, is a ligamentous injury of the cervical spine.
What causes anterior subluxation of the cervical spine?
Anterior subluxation of the cervical spine results from posterior ligamentous complex injury , however, there may be an associated posterior intervertebral disc injury and compression fractures of the anterior vertebral bodies 1-3 .
What is the treatment for subluxation of ligaments?
The treatment for subluxations may include resetting the joint, pain relief, rehabilitation therapy, and, in severe cases, surgery. Verywell / JR Bee.
What causes joint subluxation?
Traumatic causes of joint subluxation include: 1 Blunt force injuries: Including motor vehicle accidents, sports injuries, or a severe fall 2 Overuse injuries: Including those associated with medial epicondylitis (golfer's elbow) or patellar tendonitis (jumper's knee) 3 Joint hyperextension: An injury that occurs when a joint is hyperextended (extended beyond its normal range of motion) 10
What is the procedure to repair a dislocated joint?
Surgery may involve grafting bone or connective tissues into the joint space, debriding (removing) cartilage or bone to improve joint mobility, or repairing torn ligaments or tendons. 15
What to do if your joint feels loose?
Even if a joint injury doesn't appear all that serious but is limiting motion or "feels loose," it is important to make an appointment with your doctor immediately. During the appointment, your doctor will examine the injured joint to check of any visible damage, such as swelling and bruising.
How does placing a joint above the heart help?
Elevation: Placing the joint above the heart can also alleviate pain and inflammation by reducing blood flow and pressure to the joint. 2
What to do if you have a joint injury?
If the joint injury is serious, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room. Signs of an emergency include severe pain, loss of sensation, or the inability to move a joint or bear weight on it. 2
Can subluxations occur in loose joints?
Subluxations can also occur as a result of loose joints. For example, people with generalized joint laxity and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome have joints that are overly flexible. Individuals with these conditions are prone to subluxations, often without any instigating trauma or injury. 11
How long does it take to treat a C2 fracture?
Treatment for type I C2 (axis) fractures is hard-collar immobilization for 6-8 weeks, which usually is quite successful.
What is the treatment for type IIA fracture?
Treatment options for type IIA fractures include both conservative and surgical measures. Conservative treatment consists of closed reduction that is obtained under fluoroscopic guidance via application of compression and extension and is followed by halo-vest immobilization. Repeated imaging is used to monitor the healing process with a variable time course. Surgical options include C2 transpedicular screws and anterior cervical plating. Conservative and surgical treatments typically yield very good results. Malunion is a potential complication.
What type of fracture is treated with halo immobilization?
Type III fractures are treated with halo immobilization, odontoid screw fixation, or C1-C2 arthrodesis.
How long should you take antibiotics after surgery?
Osteomyelitis is a rare, but not unknown, complication. Some authors recommend the use of prophylactic antibiotics for up to 72 hours following surgery, and continuation if there is evidence of an infection.
What is a clay shoveler fracture?
(A) Lateral view of this fracture caused by a flexion mechanism shows that it is stable and represents an avulsion fracture of the base of the spinous process near the supraspinous ligament. (B) Anteroposterior view shows the vertically split appearance of the spinous process.
Is anterior subluxation stable in extension?
Anterior subluxation with a flexion mechanism is stable in extension but potentially unstable in flexion.
What does it feel like to have a C6 subluxation?
Victims will feel a numbness or tingling in their fingers, hands, or arms. Additionally, pressure on the C6 nerve can cause problems with muscle control in the forearms and wrists.
What are the symptoms of C3 vertebrae?
The symptoms of C3 vertebra damage, can range from severe to potentially unnoticeable, for example: Limited range of motion. Loss of diaphragm function. Requirement of a ventilator for breathing. Paralysis in arms, hands, torso, and legs. Trouble controlling bladder and bowel function. Neuralgia.
Is C3 vertebral damage more severe?
The C3 vertebra is slightly less fragile than the first two, but severe injuries can still occur if badly damaged. Individuals who experience spinal cord damage in this area usually suffer from limited mobility with the "flexion and extension" movement of the neck.
Can C5 subluxation cause paralysis?
C5 subluxation symptoms: C5 vertebral damage does not usually cause paralysis or the inability to breathe or speak on one's own. However, some symptoms of a C5 spinal cord injury can still be traumatic and take time to heal and recover fully. Some of the most common symptoms patients experience are:

Abstract
Keywords
- Cervical subluxation; bilateral facet joint dislocation; cervical trauma; cervical injury; cervical stabilization.
Introduction
- Car accidents, firearm injuries and sports activities are the most common cause of cervical spine injury [1,2]. Sub-axial cervical spine, defined as C3 to C7 is vulnerable to traumatic injury, 65% of the fractures and more tan 75% of all dislocations in spine most often C5-C7 . These cervical spine injuries may associated with a severe permanent disability caused by spinal cord injury. M…
Case Report
- A 62-year-old man falls presenting a hyperflexion of the neck and sudden quadriparesis. He was taken to the emergency department within the first 8 hrs after the fall where the cervicothoracic CT scan and MRI done and revealed C6–C7 bilateral facet joint dislocation and anterior translation of C6 over C7 (Figure 1). The patient underwent surgery to perform laminectomy C4-…
Discussion
- Allen-Ferguson classify in 6 types the cervical injuries: compression-flexion, vertical compression, distraction-flexion, compression-extension, distraction-extension, and lateral flexion; however it is no longer used. The AO classification of fractures of subaxial cervical spine consists of three types A: compression; B: distraction; C: rotation, while the groups and subgroups define the mor…
Conclusion
- In this case the patient presented distractive flexion injury. In the literature the posterior approach is the most used by surgeos in this kind of injuries. An adequate realignment and improvement of the neurological status was obtained due to the short time between his arrival at the hospital, diagnosis and medical treatment. Decide the conservative or surgical treatment in a precise wa…
References
- Blackmore CC, Emerson SS, Mann FA, Koepsell TD (1999) Cervical spine imaging in patients with trauma: determination of fracture risk to optimize use. Radiology 211: 759-765. [Crossref]
- National Spinal Cord Injury Association Resource Center (2013) www.sci-info-pages.com/factsheets.html. Accessed 12 April 2013
- Goldberg W, Mueller C, Panacek E, Tigges S, Hoffman JR, et al. (2001) Distribution and patter…
- Blackmore CC, Emerson SS, Mann FA, Koepsell TD (1999) Cervical spine imaging in patients with trauma: determination of fracture risk to optimize use. Radiology 211: 759-765. [Crossref]
- National Spinal Cord Injury Association Resource Center (2013) www.sci-info-pages.com/factsheets.html. Accessed 12 April 2013
- Goldberg W, Mueller C, Panacek E, Tigges S, Hoffman JR, et al. (2001) Distribution and patterns of blunt traumatic cervical spine injury. Ann Emerg Med 38: 17-21. [Crossref]
- Zaveri G, Das G (2017) Management of Sub-axial Cervical Spine Injuries. Indian J Orthop 51: 633-652. [Crossref]