Table 1. Common methods for treating and stabilizing sewage sludge.
| Treatment method | Description¹ | Effects on sludge |
| Thickening | Sludge solids are concentrated either by ... | Sludge retains the properties of a liqui ... |
| Dewatering | Several processes are used: air drying o ... | Increases solids content to 15 to 30% Ai ... |
| Anaerobic digestion | One of the most widely used methods for ... | Increases solids content Reduces odors D ... |
Full Answer
What is sludge and how it is treated?
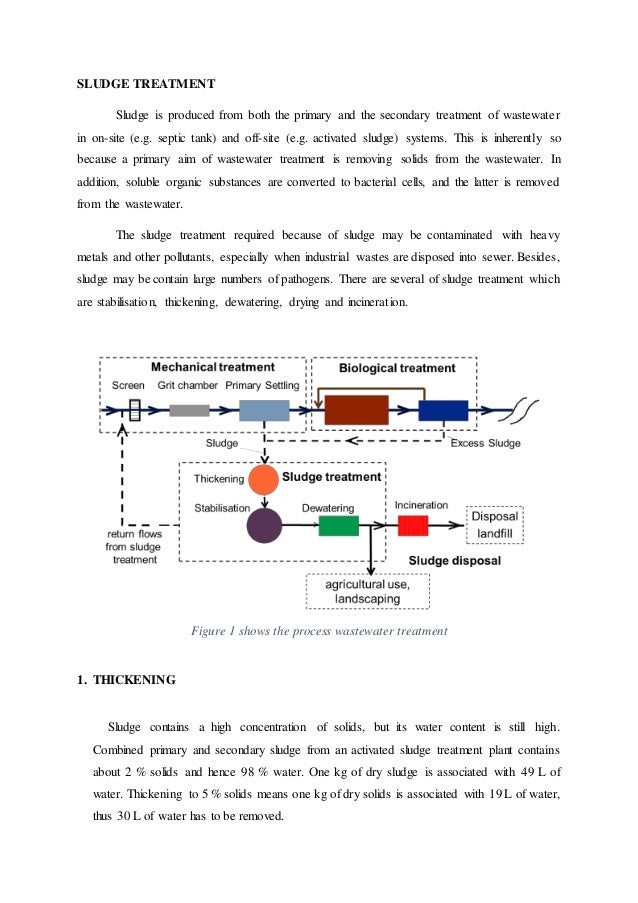
Dec 15, 2021 · Treatment is one of the most important parts of wastewater processing, as it alters the sewage sludge to minimize environmental hazards as well as safety and health concerns. Sludge Treatment Process. The sludge treatment process incorporates these four stages: 1. Sludge Thickening. One way to help control sewage sludge is to thicken it.
How to treat and dispose sludge?
Sludge Treatment: The range of processes used to reduce or remove potential health risks, remove water from sludge & reduce its weight and volume, thus reducing disposal costs. Furthermore, it attempts to discuss the main stages involved in the sludge treatment process in sludge management.
What happens to sludge from a wastewater treatment facility?
Mar 03, 2021 · Sludge treatment is an undeniably important part of treating wastewater and ensuring our activities as a society are not a net negative on the environment.
What are the methods of sludge disposal?
Explain how it is treated Sludge is the human waste that is present in the waste water which is left during the sewage treatment. It is used in the production of biogas and manure. This is because it is an organic waste. Treatment: Sludge is collected and decomposed using an anaerobic bacterium. The biogas then produced is used as a fuel.

How is sludge treated?
Thickening is usually the first step in sludge treatment because it is impractical to handle thin sludge, a slurry of solids suspended in water. Thickening is usually accomplished in a tank called a gravity thickener. A thickener can reduce the total volume of sludge to less than half the original volume.
What is a sludge process?
The activated sludge process is a type of wastewater treatment process for treating sewage or industrial wastewaters using aeration and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoa.
What are the three methods of treating sludge?
4-Step Wastewater Sludge Treatment ProcessStep 1 – Sludge Thickening. The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. ... Step 2 – Sludge Digestion. After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. ... Step 3 – Dewatering. ... Step 4 – Disposal.Apr 3, 2018
What is sludge How is it treated in Short answer?
Solution 1 Semi-solids such as faeces that settle down during wastewater treatment are called sludge. This sludge is removed using a scraper and then transferred to a tank where it is decomposed by anaerobic bacteria to produce biogas. This biogas is used as a low-cost fuel for heating, cooking, etc.
What activated sludge removes?
The activated sludge is a process with high concentration of microorganisms, basically bacteria, protozoa and fungi, which are present as loose clumped mass of fine particles that are kept in suspension by stirring, with the aim of removing organic matter from wastewater.
What is the first step in the sludge treatment process?
Explanation: Thickening is often the first step in a sludge treatment process. Primary or secondary clarifier sludge may be stirred (often after addition of clarifying agents) to form larger, more rapidly settling aggregates. 9. What is the percentage of thickness that can be achieved for primary sludge?
How is sludge removed from water?
Primary treatment involves gravity sedimentation and flotation processes that remove approximately half of the solid material that enters this stage. Solid material (both organic and inorganic) that settles out during this stage of treatment is drawn from the bottom and constitutes the primary sludge.Sep 15, 2010
How do you reduce sludge volume?
2) reduction of dry mass of sludge. The increase of the solid content in sludge by dewatering significantly reduces the volume of wet sludge for disposal.
How does activated sludge treatment help in secondary treatment?
Activated sludge is a common suspended-growth method of secondary treatment. Activated sludge plants encompass a variety of mechanisms and processes using dissolved oxygen to promote growth of biological floc that substantially removes organic material.
Why do we need to treat sludge?
Today, however, sludge is increasingly seen as a resource. This is because treating sludge through a process called “anaerobic digestion” allows water companies to recover biogas out of the material and make the biosolids a nutrient-rich soil product.
What is sludge in wastewater treatment class 7?
Sludge is the collected solid waste from the wastewater during the treatment in water treatment plant. Sludge is decomposed in a separate tank by the anaerobic bacteria. Activated sludge is used as manure.Sep 25, 2019
What decomposes sludge?
sludge is decomposed by Aerobic bacteria(Aerobic digestion is a bacterial process occurring in the presence of oxygen resembling a continuation of the activated sludge process.Jun 1, 2017
How does sludge dry?
These areas are called sludge-drying beds. The sludge dries through evaporation and sometimes drainage is installed under the sand to pump the water as well.
What is primary sludge?
Primary sludge is generated from chemical precipitation, sedimentation and primary processes. Primary processes refer to treatment methods that perform the initial filtration of wastewater such as screening, comminutor and the grit chamber.
Why is wastewater treatment important?
Wastewater treatment is an important process in modern societies to minimise our impact on the environment. It involves the removal of contaminants and converting wastewater into effluent to be returned to the water cycle. The treatment of wastewater creates a byproduct called sludge, which must also be treated and disposed of responsibly.
What is the byproduct of wastewater treatment?
The treatment of wastewater creates a byproduct called sludge, which must also be treated and disposed of responsibly. Sludge is essentially a combination of organic and inorganic materials, chemicals and pathogens. It has a semisolid, slurry consistency and is typically brown in colour. The goal of sludge treatment is to reduce its volume ...
How does a sludge thickener work?
To make treatment and processing easier, sludge is typically thickened in a dissolved-air flotation tank or gravity thickener. A dissolved-air flotation tank thickens the sludge by using air bubbles to carry the solids to the surface, forming a layer of thickened sludge on the top. A gravity thickener works in reverse, ...
How does anaerobic digestion work?
This biological process called anaerobic digestion destroys pathogens, making sludge safer to handle, less offensive, easier to dewater and reduces the total mass of solids. Sludge digestion happens in two-stages. In the first stage, the sludge is heated and mixed in a close tank for several days.
Can sludge be disposed of?
After sludge has been digested and dewatered, it is finally able to be disposed of safely. The disposal method chosen is dependent on the available land and toxicity level of the sludge.
How is sludge concentrated?
Sludge solids are concentrated either by settling due to gravity or by introducing air, which causes sludge solids to float. Sludge retains the properties of a liquid, but solids content is increased to 5 to 6%. Dewatering. Several processes are used: air drying on sand beds.
What is sludge dewatering?
Sludge is dewatered to increase solids content to around 20%, then mixed with a high-carbon organic material such as sawdust. The mix is composted under aerobic conditions at temperatures of at least 131°F for several days during the composting process. Volume reduction of sludge. Reduces odors.
What was the result of the 1950s?
In response to concerns about water quality degradation, thousands of communities throughout the United States constructed wastewater treatment systems during the 1950s and 1960s. This resulted in greatly improved stream and river water quality, but created another material to deal with: sewage sludge. Approximately 99% of the wastewater stream that enters a treatment plant is discharged as rejuvenated water. The remainder is a dilute suspension of solids that has been captured by the treatment process. These wastewater treatment solids are commonly referred to as sewage sludge.
What is biosolids in wastewater treatment?
The industry defines biosolids as sewage sludge that has undergone sufficient treatment for stabilization and pathogen reduction, and that is of sufficiently high quality to be land applied. The term is intended to distinguish high-quality, treated sewage sludge from raw sewage sludge and from sewage sludge that contains large quantities of environmental pollutants. The term "biosolids" also helps to distinguish sewage sludge from industrial sludge by emphasizing that the former is produced by a biological process. The term has been criticized by some as an attempt to disguise the real nature of sewage sludge, thereby making land application of this material less objectionable to the general public. Although "biosolids" undoubtedly does not conjure up the same negative images as does "sewage sludge" or simply "sludge," it is a legitimate and functional term when correctly used to make the distinction described above. In this document, "sewage sludge" will be used to refer to wastewater treatment solids generally, and "biosolids" will be used to refer specifically to material that is suitable for land application.
How long does sludge stay in the air?
One of the most widely used methods for sludge treatment. Sludge is held in the absence of air for 15 to 60 days at temperatures of 68 to 131°F. Anaerobic bacteria feed on the sludge, producing methane and carbon dioxide. In some treatment plants, the methane is collected and burned to maintain the treatment temperature.
Is landfilling a good solution?
From a management and materials handling perspective, landfilling is perhaps the simplest solution. From an economic standpoint, landfilling presently compares favorably with other options. This undoubtedly will change, however, as landfill space becomes more limited and tipping fees (waste-dumping costs) increase. From an environmental standpoint, landfilling prevents the release of any sludge-borne pollutants or pathogens by concentrating the sludge into a single location. If the landfill is properly constructed and maintained, environmental risks are minimal.
What is biosolids in sewage?
The term "biosolids" also helps to distinguish sewage sludge from industrial sludge by emphasizing that the former is produced by a biological process.
How is sludge collected?
Sludge is collected and decomposed using an anaerobic bacterium. The biogas then produced is used as a fuel. After an aerator tank, microbes and human waste settle down, forming an activated sludge. The activated sludge contains 97% water, which is dried by sand. The dried sludge is used as a manure.
What is sludge in chemistry?
What is sludge? Explain how it is treated. Sludge is the human waste that is present in the waste water which is left during the sewage treatment. It is used in the production of biogas and manure. This is because it is an organic waste. Treatment:
What is sludge in sewage treatment?
The residue that accumulates in sewage treatment plants is called sludge (or biosolids). Sewage sludge is the solid, semisolid, or slurry residual material that is produced as a by-product of wastewater treatment processes . This residue is commonly classified as primary and secondary sludge. Primary sludge is generated from chemical precipitation, sedimentation, and other primary processes, whereas secondary sludge is the activated waste biomass resulting from biological treatments. Some sewage plants also receive septage or septic tank solids from household on-site wastewater treatment systems. Quite often the sludges are combined together for further treatment and disposal.
What is the first step in sludge treatment?
Thickening. Thickening is usually the first step in sludge treatment because it is impractical to handle thin sludge, a slurry of solids suspended in water. Thickening is usually accomplished in a tank called a gravity thickener. A thickener can reduce the total volume of sludge to less than half the original volume.
How does a thickener work?
A thickener can reduce the total volume of sludge to less than half the original volume. An alternative to gravity thickening is dissolved-air flotation. In this method, air bubbles carry the solids to the surface, where a layer of thickened sludge forms.
What is secondary sludge?
Primary sludge is generated from chemical precipitation, sedimentation, and other primary processes, whereas secondary sludge is the activated waste biomass resulting from biological treatments. Some sewage plants also receive septage or septic tank solids from household on-site ...
What is sludge digestion?
Sludge digestion is a biological process in which organic solids are decomposed into stable substances. Digestion reduces the total mass of solids, destroys pathogens, and makes it easier to dewater or dry the sludge. Digested sludge is inoffensive, having the appearance and characteristics of a rich potting soil.
Is methane a fuel?
Methane is combustible and is used as a fuel to heat the first digestion tank as well as to generate electricity for the plant. Anaerobic digestion is very sensitive to temperature, acidity, and other factors. It requires careful monitoring and control.
How to prevent gallbladder sludge?
To prevent gallbladder sludge, try to eat a healthy, well-balanced diet low in sodium, fats, and cholesterol. Last medically reviewed on May 3, 2017.
What happens if your gallbladder doesn't empty?
If the gallbladder doesn’t empty completely, particles in the bile — like cholesterol or calcium salts — can thicken as a result of remaining in the gallbladder for too long. They eventually become biliary sludge, which is commonly referred to as gallbladder sludge.
Can gallstones cause cholecystitis?
This is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. Gallbladder sludge can cause or contribute to cholecystitis, or an inflamed gallbladder. If your gallbladder causes frequent or chronic pain, your doctor will likely recommend removing the gallbladder entirely.
What are the symptoms of gallbladder stones?
Others will experience symptoms consistent with an inflamed gallbladder or gallbladder stones. The primary symptom is often abdominal pain, especially on your upper right side under the ribs. This pain may increase shortly after a meal. Other symptoms can include: chest pain. right shoulder pain. nausea and vomiting.
Can you get gallbladder sludge while pregnant?
While gallbladder sludge is not a common problem, there are certain people who have a higher risk for developing it.

Overview of Sludge Processing
Sludge Processing Methods
- There are essentially two methods by which the volume of sludge is reduced: 1. consolidation, which reduces the sludge volume by removing the water along with the associated dissolved solids, and 2. destruction, in which the organic carbon component of the sludge is either oxidised, ultimately to carbon dioxide, or reduced, predominantly to methane...
Sludge as A Resource
- While sludge is essentially a waste product, there is increasing focus on its potential as a resource (i.e. sludge valorisation), specifically with reference to its: 1. latent energy (or calorific content, which can be used to quantify its potential for methane and/or hydrogen production), and 2. nutrient content (phosphate and nitrate). There is also significant interest in, and increasing i…
Introduction
- Before 1950, most communities in the United States discharged their wastewater, or sewage, into streams and rivers with little if any treatment. As urban populations increased, the natural ability of streams and rivers to handle the wastewater was overwhelmed and caused water quality to deteriorate in many regions. In response to concerns about water quality degradation, thousand…
Production of Municipal Sewage Sludge
- Municipal wastewater, or sewage, refers to water that has been used in urban and suburban area homes or businesses for washing, bathing, and flushing toilets. Municipal wastewater also may include water from industrial sources. To remove chemicals or pollutants resulting from industrial processes, industrial contributors to municipal wastewater systems must pretreat their wastew…
Options For Dealing with Sewage Sludge
- Sewage sludge can be viewed either as an organic and nutrient resource to be used beneficially or as a waste material to be disposed of. Before 1991, large amounts of sewage sludge, including some from Pennsylvania, were disposed of by ocean dumping. Concerns about excess nutrient loading of ocean waters led to the banning of this practice. At pres...
Regulation of Land-Applied Biosolids
- The current regulations for land application of biosolids were established by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (E.P.A.) in 1993. In 1997, Pennsylvania revised its regulations for land application of biosolids by largely adopting the technical aspects of the Federal regulations and by adding several requirements specific to Pennsylvania. The underlying premis…
What Does This Mean For Pennsylvania?
- The question that confronts municipalities, farmers, and rural communities in Pennsylvania is whether or not biosolids can be applied to land without creating undue risk to human health and the environment. When considering this question, it is helpful to separate short-term and long-term risk. In the short term, the risk from land application of biosolids can be maintained at very …