
What happens to sludge from a wastewater treatment facility?
Nov 24, 2010 · Sewage sludge is, in this document, considered a type of biowaste. In the case of biowaste stabilization installations, special attention is paid for odor emissions, including measures that can be taken to reduce odor nuisance.
What are the disadvantages of a waste water treatment plant?
Sewage sludge is a product of wastewater treatment. Wastewater and stormwater enter the sewage system and flow into wastewater treatment facilities, where the solid wastes are separated from the liquid wastes through settling. At this point, they are processed and “digested,” or decomposed by bacteria. These separated processed solids – sewage sludge – contain …
Does the wastewater treatment plant smell bad?
Sewage sludge is the semisolid, solid, or slurry waste material generated as a by-product of sewage treatment processes. However, this residue is often classified as primary & secondary sludge. Primary sludge is produced from sedimentation, chemical precipitation, & other primary processes, while secondary sludge is the activated litter biomass arising from biological …
What is the purpose of a waste water treatment plant?
Aug 27, 2020 · Sludge or sewage sludge can be defined as the residue or the by-product which is left after the wastewater treatment processes are carried out in the wastewater treatment plants. The solid, semi-solid, and slurry residue is a combination of various components like organic and inorganic materials, plant nutrients, chemicals, and disease-causing pathogens.
What is in sewage sludge?
Sewage sludge is a mud-like residue resulting from wastewater treatment. Sewage sludge contains heavy metals and pathogens such as viruses and bacteria. It also contains valuable organic matter and nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus, and can therefore be very useful as a fertilizer or soil improver.
What is meant by sludge in wastewater treatment?
The residue that accumulates in sewage treatment plants is called sludge (or biosolids). Sewage sludge is the solid, semisolid, or slurry residual material that is produced as a by-product of wastewater treatment processes. This residue is commonly classified as primary and secondary sludge.
Is sewage sludge toxic?
Sewage sludge as a waste (by-product) from the wastewater treatment process for many years has been mainly utilized by landfarming or/and landfilling. Due to the increasing content of toxic pollutants in many countries the sewage sludge has been found as hazardous waste and often incinerated.
What do you mean by sludge?
Definition of sludge 1 : mud, mire especially : a muddy deposit (as on a riverbed) : ooze. 2 : a muddy or slushy mass, deposit, or sediment: such as. a : precipitated solid matter produced by water and sewage treatment processes.
What is sludge example?
Sludge definition Sludge is a substance that is between solid and liquid form. An example of sludge is a mass of mud formed in a river bed after a flood. An example of sludge is the treated material from a sewage plant.
What is the sludge process?
The activated sludge process is a means of treating both municipal and industrial wastewater. The activated sludge process is a multi-chamber reactor unit that uses highly concentrated microorganisms to degrade organics and remove nutrients from wastewater, producing quality effluent.Feb 10, 2021
Is sewage sludge a good fertilizer?
Simply put, the group says that it is not safe to grow food in sewage sludge. Why isn't it safe? Sewage sludge regularly tests positive for a host of heavy metals, flame retardants, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, pharmaceuticals, phthalates, dioxins, and a host of other chemicals and organisms.Oct 4, 2010
What happens to sludge from a sewage treatment plant?
Once treated, sewage sludge is then dried and added to a landfill, applied to agricultural cropland as fertilizer, or bagged with other materials and marketed as “biosolid compost” for use in agriculture and landscaping.
Where does human waste go after a sewage treatment plant?
The treated wastewater is released into local waterways where it's used again for any number of purposes, such as supplying drinking water, irrigating crops, and sustaining aquatic life.
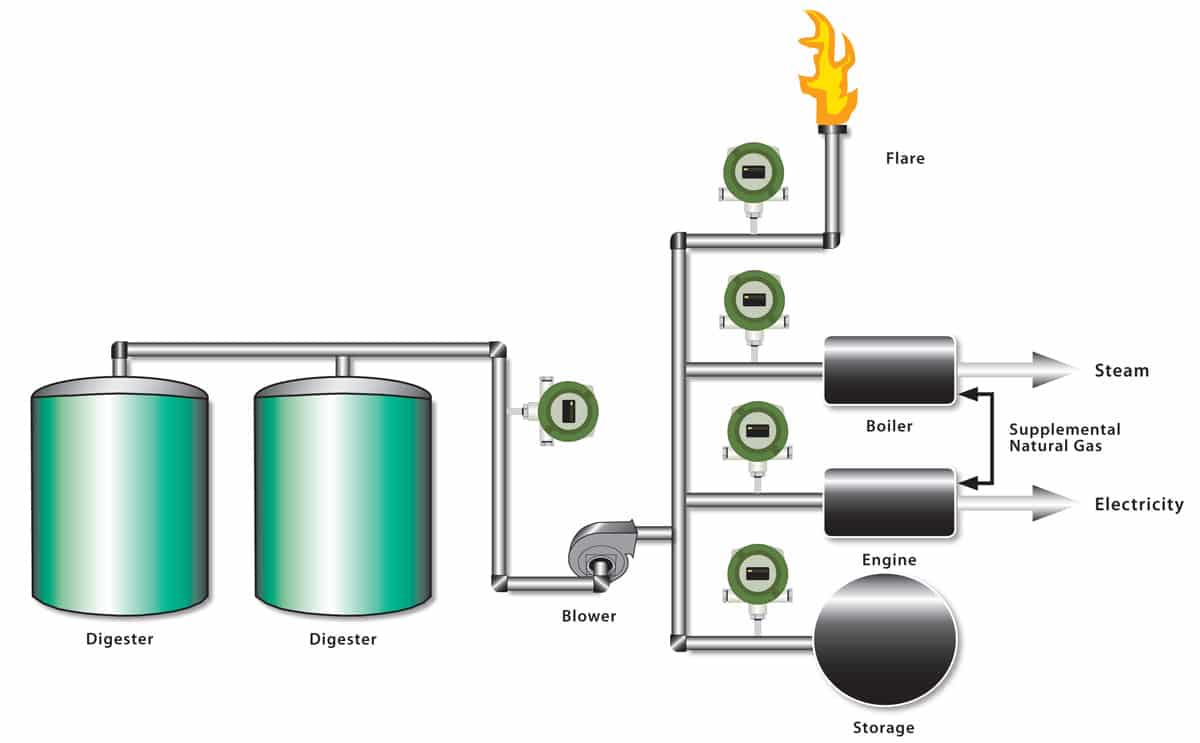
What is sludge in biogas plant?
Sewage sludge also includes toxic and hazardous organic and inorganic pollutants sources. The digestion of municipal sewage sludge (MSS) occurs in three basic steps: acidogen, methanogens, and methanogens. During a 30-day digestion period, 80–85% of the biogas is produced in the first 15–18 days.Oct 4, 2016
How many types of sludge are there?
In the present paper an alternative approach has been followed. A mathematical model was proposed and identified on a set of six different types of sludge (primary, secondary and mixed sludge from both urban and industrial WWTP).
How is sludge useful?
Uses of SludgeFor Agricultural Purposes. Treated sludge can be used for agricultural practices in home gardening, forestry, and parks. ... Helpful in Controlling Soil Erosion. ... Landscaping. ... Used as an Alternative Fuel Source in the Cement Industry. ... Domestic Use for Heating and Cooking.
What is sewage sludge?
The combination of primary and secondary sludge is termed ‘sewage sludge’. Sewage sludge contains 1–5% solids, 60% of which is nontoxic organic matter, as well as nitrogen and phosphorus containing components, toxic organic and inorganic pollutants, pathogens and other microbial vectors, and inorganic components.
Where is sludge used in agriculture?
In EU countries, the agricultural use of sludge is widespread in the Czech Republic, France, Hungary, Portugal, Italy, Slovakia, Spain, and the United Kingdom. It is not popular in such countries as Austria, Belgium, Finland, Greece, Romania, Slovenia, and Switzerland ( Mininni and Dentel, 2013 ).
What is the Directive 2009/28/EC?
The Directive of the European Parliament and Council 2009/28/EC on the promotion of energy from renewable sources ( Directive 2009/28/EC, 2009) amends, and as a consequence abates, Directive 2009/28/EC indicating compulsory energy levels to be derived from renewable energy sources .
What is hydrothermal torrefaction?
Torrefaction, a pretreatment of biomass (see Chapter 4) to produce solid feedstock, is generally carried out in an inert gaseous environment within a small temperature window of 200–300°C. The same process could use even a lower temperature window of 180–260°C if subcritical water is used instead as the inert medium. Hydrothermal torrefaction or carbonization (HTC) produces gases, aqueous chemicals, and solid product, hydrochar. Some of the inorganic products of the process dissolves in hot compressed water. As a result, it produces solid fuels with reduced ash content. Additionally, the water from hydrothermal process contains a host of organic and inorganic materials. Some of these are important value-added chemicals that can be recovered through downstream processing ( Gullón et al., 2012). Alkali metals in biomass are major contributors to fouling when it is burnt. In hydrothermal torrefaction these are leached in water resulting in reduced ash as well as reduced alkali in treated biomass. The leachate from sewage sludge treatment could allow recovery nutrients especially potassium, opening up another feed benefits. Compared to dry torrefaction, hydrothermal torrefaction has relatively short residence time for a given level of solid yield or higher mass yield at a given residence time and temperature. Compared to dry torrefied biomass, high temperature carbonized biomass exhibits lower H/C, O/C ratio, and brings them closer to coal or lignite (Kambo and Dutta, 2014 ). The most important benefit of hydrothermal torrefaction is that it could avoid the energy intensive process of drying of biomass, which is especially expensive for very wet biomass. This option is thus effective for very wet biomass such as animal manures, human waste, sewage sludge ( He et al., 2013 ), municipal solid waste (MSW), and algae residues.
Is biomass a fossil fuel?
Biomass in general contains substantially more moisture than do a fossil fuel like coal. Some aquatic species, such as water hyacinth, algae, or raw sewage, can have water contents exceeding 90%. Thermal gasification, where air, oxygen, or subcritical steam is the gasification medium, is very effective for dry biomass, but it becomes very inefficient for a high-moisture biomass because the moisture in feed must be substantially driven away before thermal gasification can begin, and it takes a large amount of the extra energy (∼2242 kJ/kg moisture) just for evaporation alone.
What can accumulate in AD broth?
Ammonia, sulfides, and VFAs can accumulate in AD broth, which can inhibit the methanogenesis process and also result in reactor instability. Treatment of AD effluent in MFC could lower the inhibitory concentration of ammonium. In an MFC having a cation exchange membrane the accumulated ammonium in anolyte would transfer to the cathode side, which results in ammonia removal in continuous and selective fashion from the digestate. This approach has been applied in a number of studies using several waste streams such as synthetic wastewater, AD digestate, urine, and effluent from sewage sludge treatment (Desloover et al., 2012; Kim et al., 2015 ). In this process the potential difference developed between anode and cathode of MFC creates a net flux of ammonium ions from the waste stream at anode compartment to the counter stream at the cathode compartment ( Cheng et al., 2013 ). Principally, when the ammonium ions reach the cathode compartment crossing the cation exchange membrane, an alkaline catholyte of pH>9.2 transforms ammonium to volatile ammonia due to the acid dissociation constant (p K a value) of 9.25 (at 25°C) for ammonium and removed from the catholyte by the volatilization. The recovery of ammonia is carried out by dissolving in acids separately. The use of MFC in ammonia stripping from anaerobic digester is an attractive approach for ammonia inhibition and enhancing AD performance; in addition, it recovers nutrients from the anaerobic digestate and generates electricity.
Is sewage sludge bad for soil?
It is, however, necessary to control concentrations of heavy metals in sewage sludge and soil. Sewage sludge use is prohibited when the concentration of heavy metals in sludge and soil exceeds limits given in the directive.
What is sewage sludge used for?
Once treated, sewage sludge is then dried and added to a landfill, applied to agricultural cropland as fertilizer, or bagged with other materials and marketed as “biosolid compost” for use in agriculture and landscaping.
What is sludge in a sewage system?
Sewage sludge is a product of wastewater treatment. Wastewater and stormwater enter the sewage system and flow into wastewater treatment facilities, where the solid wastes are separated from the liquid wastes through settling. At this point, they are processed and “digested,” or decomposed by bacteria.
Who is the chair of the Senate Environment and Public Works Committee?
On April 15th the Senate Environment and Public Works Committee, chaired by Senator Barbara Boxer, will be holding hearings on recent studies documenting pharmaceuticals found in…. Read More. Sludge victims tell their stories to the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works.
What is sludge in sewage treatment?
The residue that piles up in sewage treatment plants is known as sludge. Sewage sludge is the semisolid, solid, or slurry waste material generated as a by-product of sewage treatment processes. However, this residue is often classified as primary & secondary sludge.
What is the first stage of sludge treatment?
Thickening is the first stage in sludge treatment as it is impractical to handle fine sludge. Usually, thickening is accomplished in a tank known as a gravity thickener. However, a gravity thickener can minimize the sludge’s total volume to less than half the initial volume. A substitute for gravity thickening is dissolved-air flotation. Here, air bubbles take the solids to the surface, where a thickened sludge layer is formed.
What is water treatment plant?
Water treatment plants are plants that need to be installed for the recycling of water that could be beneficial to several domestic purposes. Now let’s learn more about it in brief before opting for Plantas Piloto de tratamiento de agua.
What is the process of sludge digestion?
After piling up all the solids from the wastewater, sludge begins the process of sludge digestion. Digestion is a biological method in which the organic solids in the sludge are decomposed into static substances. However, this process also helps minimize the overall mass of solids while eliminating any present pathogens to allow easy dewatering.
Can sludge be incinerated?
Since sludge might contain harmful industrial chemicals, it’s not spread on the ground where crops are harvested. When a suitable place for land disposal is not accessible, as, in urban regions, sludge can be incinerated, incineration evaporates the moisture & turns the organic solids into plain ash.
What is sewage sludge?
Sludge or sewage sludge can be defined as the residue or the by-product which is left after the wastewater treatment processes are carried out in the wastewater treatment plants. The solid, semi-solid, and slurry residue is a combination of various components like organic and inorganic materials, plant nutrients, chemicals, ...
How to manage sewage sludge?
Composting is one of the other ways to manage sewage sludge in treatment plants. In this method, dewatering is done which is followed by mixing the mostly solid sludge with high carbon organic material. The mix is laid for composting under aerobic conditions for a duration of time. ...
Why is wastewater treatment important?
Treatment is important because sludge emanates toxic gases and it can act as a health hazard. There are several treatment methods used to treat sewage sludge.
What is wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment plants collect a large amount of domestic waste, industrial waste, agricultural waste, and waste from commercial spaces and provide treatment. This involves primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment of wastewater which uses physical, biological, and chemical means to purify the wastewater.
What is the primary treatment of wastewater?
The primary treatment of wastewater plants involves various processes like filtering of solid particles like wood, paper, plastic, vegetable matter, etc. Also, oil and grease are removed during this process. Gravity sedimentation, flotation processes, chemical precipitation, sedimentation leads to the generation of primary sludge which is settled ...
What is the process of sludge?
In the aerobic process, the sludge is supplied with oxygen which produces carbon dioxide. The biological processes ably reduce sludge volume, eliminates pathogens, and even makes it easy to dry the sludge. It converts organic sludge into liquids and gases.
What is sludge treatment?
There are now strong biological solutions that help in wastewater and sludge treatment.
How does sewage sludge digest?
After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. This is a biological process in which the organic solids present in the sludge are decomposed into stable substances. This process also helps reduce the total mass of solids, while destroying any present pathogens to enable easy dewatering. The sludge digestion process is a two-phase process. In the first stage, the dry solid sludge is heated and mixed in a closed tank to enable anaerobic digestion by acid-forming bacteria. These bacteria hydrolyze the large molecules of proteins and lipids present in the sludge and break them down into smaller water-soluble molecules, which they then ferment into various fatty acids. The sludge then flows into the second tank where it is converted by other bacteria to produce a mixture of carbon dioxide (CO 2) and methane, after which the methane is collected and reused to power the digestion tank and generate power (depending on the quantity retrieved).
How is sewage treated?
While sewage sludge is usually treated using a standard plan of action , it is extremely important to factor in aspects like the origin of the sewage, the treatment process used to reduce the sewage to sludge, as well as the possible byproducts that can be retrieved from it for further use before choosing a sludge treatment plan.
Why is it important to treat sludge?
Therefore, it is extremely important to properly treat such sludge in order to minimize its environmental repercussions.
What is the first step in sewage treatment?
The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. In this step, the sewage sludge is thickened in a gravity thickener to reduce its overall volume, thus enabling the easy handling of the sludge.
What is the process of sludge digestion?
The sludge digestion process is a two-phase process. In the first stage, the dry solid sludge is heated and mixed in a closed tank to enable anaerobic digestion by acid-forming bacteria.
How much water is in dewatered sludge?
In most cases, dewatered sludge usually contains a significant amount of water, as much as 70 percent, in spite of its solidified state. Therefore, it is important to dry and dewater the sludge beforehand.
How long does it take to dry sludge?
While using sludge-drying beds is the most common way to carry out this process, it is extremely time-consuming and may take weeks before the process is complete . In order to quicken these processes, waste management plans are also employing solid-liquid separation devices to carry out this process.
What are the chemicals in sewage sludge?
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB), dioxin, brominated flame retardants and pesticides have all been found in sewage sludge. The use of sewage sludge on any open land means that America’s toxic waste may be absorbed by crops and find their way up the food chain and into human diets.
Why is sewage sludge used as fertilizer?
Sewage sludge is falsely marketed to farmers as a fertilizer because it has measurable amounts of Nitrogen and Phosphorous. By accepting the sewage sludge, the farmer can save thousands of dollars normally spent on synthetic fertilizer. As the sludge industry participates in conservation and zoning plans, hosting farm appreciation gatherings and making huge financial displays of ‘affection’ in the farm community, farmers are lured into trusting the big business of the sludge industry. These corporations understand how to pose as ‘a wolf in sheep’s clothing’.
Why is California using recycled water?
The push on California farmlands and vineyards to use recycled water is the result of disposal challenges of sewage waste water effluent that does not and cannot meet water quality standard for being released into rivers and streams. This water is also used to irrigate the lawns of schools, playgrounds and parks.
What foods contain cadmium?
Cadmium and lead, heavy metals linked to intestinal and kidney damage, have been found to be easily taken up in food products like carrots, potatoes, lettuce, spinach and grains. Sensitivity levels to heavy metals vary depending on the plant.
What are the contaminants of greatest concern?
The contaminants of greatest concern are the heavy metals, toxic organic compounds, and pathogenic microorganisms…” . Common sense, apparently lacking in the bureaucracies charged with protecting our health and safety, dictates that foods grown in contaminated soil and water become contaminated.
Is dioxin in breast milk?
Studies show that PCB’s, dioxin and flame retardants all concentrate in breast milk and are extremely accessible to the nursing baby. Milk in general collects and accumulates dioxin, but testing of the human breast milk that a nursing mother provides and the effect on their babies has not been gathered.
Can you grow food on sewage sludge?
Human and animal foods are allowed to be grown on land where sewage sludge has been applied. Cattle and other livestock may also be set to graze on pastures with sludge ‘top dressing’ – spraying sludge on top of the foliage of a grazing field without plowing into the soil.

Introduction
- Before 1950, most communities in the United States discharged their wastewater, or sewage, into streams and rivers with little if any treatment. As urban populations increased, the natural ability of streams and rivers to handle the wastewater was overwhelmed and caused water quality to d…
Options For Dealing with Sewage Sludge
- Sewage sludge can be viewed either as an organic and nutrient resource to be used beneficially or as a waste material to be disposed of. Before 1991, large amounts of sewage sludge, including some from Pennsylvania, were disposed of by ocean dumping. Concerns about excess nutrient loading of ocean waters led to the banning of this practice. At present, almost all sewage sludg…
Regulation of Land-Applied Biosolids
- The current regulations for land application of biosolids were established by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (E.P.A.) in 1993. In 1997, Pennsylvania revised its regulations for land application of biosolids by largely adopting the technical aspects of the Federal regulations and by adding several requirements specific to Pennsylvania. The underlying premis…
What Does This Mean For Pennsylvania?
- The question that confronts municipalities, farmers, and rural communities in Pennsylvania is whether or not biosolids can be applied to land without creating undue risk to human health and the environment. When considering this question, it is helpful to separate short-term and long-term risk. In the short term, the risk from land application of biosolids can be maintained at very …