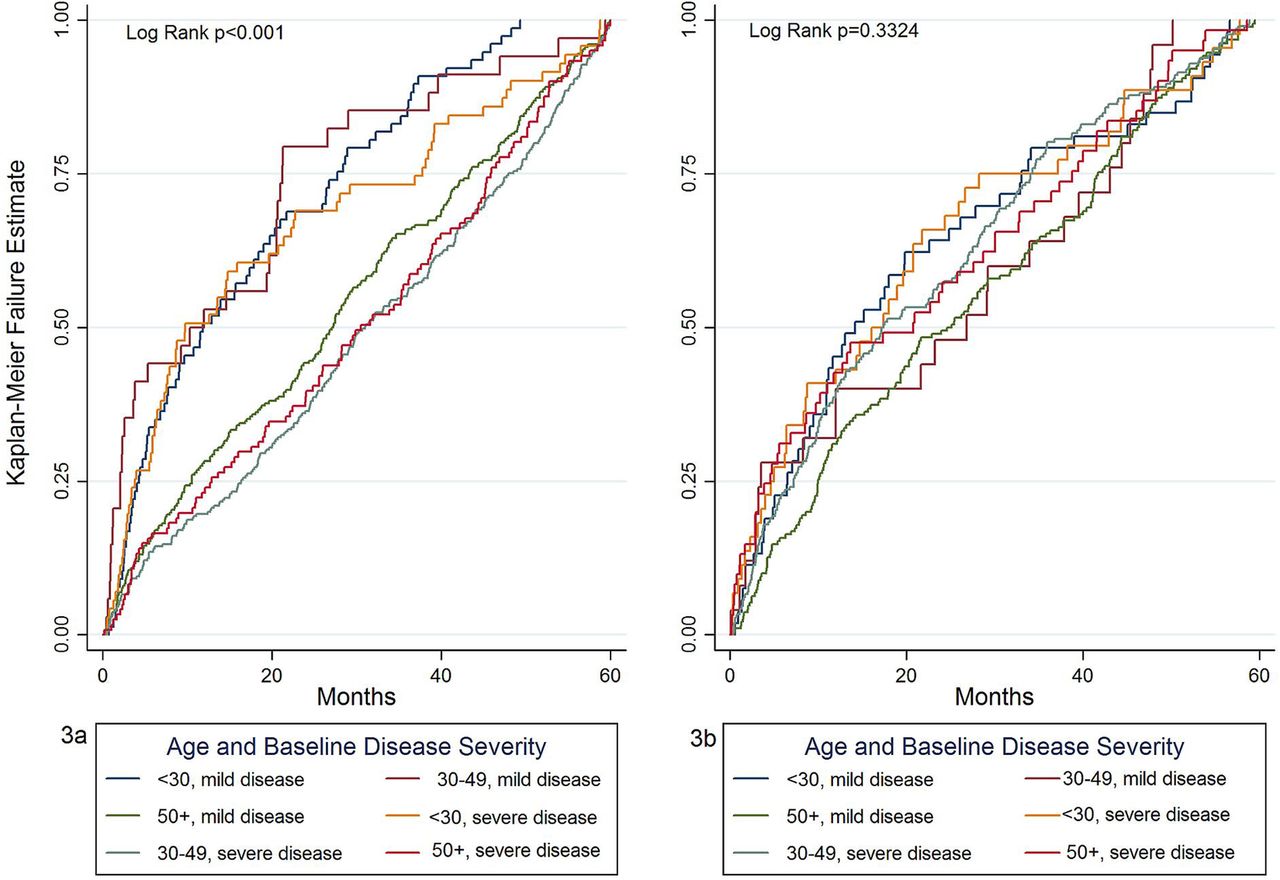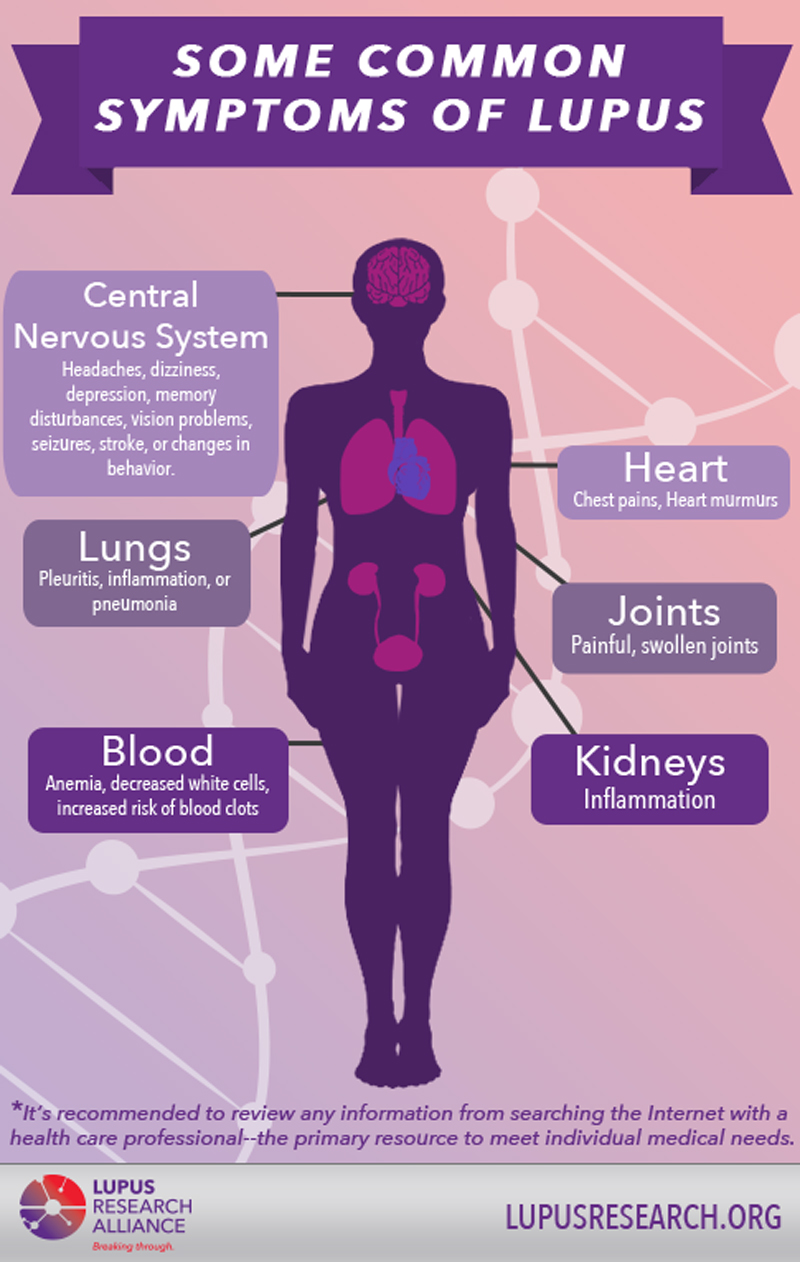
How to cure SLE?
Mar 05, 2021 · What's New in the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Abstract. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune multisystem disease with a variable presentation... The Cellular Approach. The B cell, as a major component of the adaptive immune system, may mediate autoimmune disease. ...
How is SLE treated?
Nov 23, 2021 · Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus) Doctors treat lupus based on your symptoms. The goal of treatment is to: Manage symptoms. Prevent, limit, and stop flares. Maintain the lowest level of disease activity, and, if possible, achieve complete remission. Prevent or slow organ damage. Improve your quality of life.
What does SLE stand for medical?
Oct 17, 2018 · SLE treatment consists primarily of immunosuppressive drugs that inhibit activity of the immune system. Hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) are often used to treat SLE. The FDA approved belimumab in 2011, the …
How to treat SLE?
These include: aspirin warfarin (Coumadin) heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin (Lovenox or Fragmin)

What is the best treatment for SLE?
The medications most commonly used to control lupus include: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Over-the-counter NSAIDs , such as naproxen sodium (Aleve) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), may be used to treat pain, swelling and fever associated with lupus.Jan 27, 2021
What is standard treatment for SLE?
Nowadays, antimalarials are the basic treatment for every patient with SLE, whereas glucocorticoids should only be used when acutely indicated. If reduction or tapering of glucocorticoids proves impossible, extended immunosuppression with azathioprine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil is recommended.
What is first line treatment for SLE?
Hydroxychloroquine is first-line treatment unless contraindicated and is useful in almost all manifestations of lupus. Other treatments are titrated against type and severity of organ involvement.Jun 2, 2020
Can SLE be cured completely?
There is no cure for SLE. The goal of treatment is to control symptoms. Severe symptoms that involve the heart, lungs, kidneys, and other organs often need treatment by specialists.Jan 21, 2020
What is latest treatment of SLE?
A new biologic for systemic lupus erythematosus may help reduce corticosteroid use. People living with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have a new drug option. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved anifrolumab (Saphnelo) in early August — the first new drug approved for SLE in 10 years.
What are the top 5 signs of lupus?
Lupus facial rashFatigue.Fever.Joint pain, stiffness and swelling.Butterfly-shaped rash on the face that covers the cheeks and bridge of the nose or rashes elsewhere on the body.Skin lesions that appear or worsen with sun exposure.Fingers and toes that turn white or blue when exposed to cold or during stressful periods.More items...•Jan 27, 2021
What is the most common treatment for lupus?
Types of medicines commonly used to treat lupus include:Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). ... Corticosteroids. ... Antimalarial drugs. ... BLyS-specific inhibitors. ... Immunosuppressive agents/chemotherapy. ... Other medicines.Oct 17, 2018
Is lupus curable or treatable?
Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus) Lupus is an autoimmune disease that can cause joint pain, fever, skin rashes and organ damage. There's currently no cure for lupus and it requires life-long management.Apr 19, 2021
Is dapsone used to treat lupus?
Small series have reported that dapsone, which has been used in the treatment of lupus since 1978, can ameliorate vasculitis, bullae, urticaria, oral ulcerations, thrombocytopenia, lupus panniculitis, and subacute cutaneous lupus. Dapsone may be steroid-sparing and can be effective in lupus resistant to chloroquine.
Is SLE lupus serious?
SLE is the most common and most serious type of lupus. Other types of lupus include the following: Cutaneous lupus (skin lupus) is lupus that affects the skin in the form of a rash or lesions. This type of lupus can occur on any part of the body, but usually appears where the skin is exposed to sunlight.
Can SLE get pregnant?
Pregnancy and lupus. Women with lupus can safely get pregnant and most will have normal pregnancies and healthy babies.Oct 17, 2018
What is the difference between lupus and SLE?
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is the most common form of lupus. When people talk about lupus in general, this is the type they're most likely referring to. SLE affects many organs, especially skin, joints and kidneys.
What is lupus?
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), commonly known as lupus, is an autoimmune illness that affects all parts of the body. The term "lupus" is also...
What causes lupus?
The exact cause of lupus is unknown, but most scientists believe that genetics, combined with outside triggers – such as infections, medications or...
What are the different types of lupus?
There are five recognized forms of lupus: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is the disease most commonly mentioned, and the most serious since it...
What are the risk factors for lupus?
Gender, race and ethnicity, and age are all key factors. Younger women, and especially younger women of color, are most at risk.
If I have lupus, do I have a greater risk of getting the COVID-19 coronavirus?
People with rheumatic diseases and suppressed immune systems, such as lupus patients, may be more vulnerable to the disease known as COVID-19, whic...
What are the symptoms of lupus?
Symptoms vary from person to person, but the typical lupus patient is a young woman who develops arthritis of the fingers, wrists or other small jo...
How is lupus diagnosed?
A diagnosis for lupus is generally based on laboratory tests that exclude other diseases which may have similar symptoms (such as Lyme disease), an...
What is the treatment for lupus?
Depending on the symptoms, blood test results and the particular organs involved, a person with lupus may receive one or more of the following: non...
What are the health complications of lupus?
The severity of lupus varies from mild to life-threatening. After many years of having lupus, patients may develop: osteoporosis (especially in tho...
Are people with lupus at a higher risk for blood clots?
Lupus patients who are positive for antiphospholipid antibody (aPL) can develop blood clots and heart valve disease and may require additional medi...
What is SLE in medical terms?
What is SLE? Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is the most common type of lupus. SLE is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks its own tissues, causing widespread inflammation and tissue damage in the affected organs. It can affect the joints, skin, brain, lungs, kidneys, and blood vessels.
What are the effects of SLE?
Poor access to care, late diagnosis, less effective treatments, and poor adherence to therapeutic regimens may increase the damaging effects of SLE, causing more complications and an increased risk of death. 1. SLE can limit a person’s physical, mental, and social functioning.
Why is it important to see a rheumatologist?
Because diagnosis can be challenging, it is important to see a doctor specializing in rheumatology for a final diagnosis. Rheumatologists sometimes use specific criteria. to classify SLE for research purposes. Learn more about lupus diagnosis and treatment.
How long does it take for lupus to go away?
Drug-induced lupus is similar to SLE, but occurs as the result of an overreaction to certain medications. Symptoms usually occur 3 to 6 months after starting a medication, and disappear once the medicine is stopped. 14 Learn more about drug-induced lupus on the Medline Plus website. External.
What are the symptoms of Lupus?
Other symptoms can include sun sensitivity, oral ulcers, arthritis, lung problems, heart problems, kidney problems, seizures, psychosis, and blood cell and immunological abnormalities. Learn more about lupus symptoms. Learn more about lupus triggers and how to control your symptoms on the Managing Lupus page. Top of Page.
What is the name of the rash that affects the skin?
Other types of lupus include the following: Cutaneous lupus (skin lupus) is lupus that affects the skin in the form of a rash or lesions. This type of lupus can occur on any part of the body, but usually appears where the skin is exposed to sunlight.
When was belimumab approved?
The FDA approved belimumab in 2011, the first new drug for SLE in more than 50 years. SLE also may occur with other autoimmune conditions that require additional treatments, like Sjogren’s syndrome, antiphospholipid syndrome, thyroiditis, hemolytic anemia, and idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura. 1.
What is lupus erythematosus?
What is lupus? Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), commonly known as lupus, is an autoimmune illness that affects many organs and systems in the body. Lupus is a chronic condition, but symptoms tend to cycle in alternate periods of "flares" (or "flares-ups") and remissions.
What tests are used to diagnose lupus?
A diagnosis for lupus is generally based on laboratory tests that exclude other diseases which may have similar symptoms (such as Lyme disease), and specific serologic tests – blood tests that determine the presence of certain antibodies.
How old do you have to be to get Lupus?
Age: Symptoms that lead to a lupus diagnosis most commonly appear in people between 15 and 44 years of age.
What is a discoid rash?
Discoid lupus is a skin-only illness in which a specific rash, mostly a scarring rash of circular-shaped lesions, occurs without other symptoms (SLE patients sometimes have the same rash). Subacute cutaneous lupus involves a more widespread rash that is often worsened by sun exposure.
Is lupus a rare disease?
It is associated with a limited form of SLE in about 50% of cases. Drug-induced lupus is relatively rare and is triggered by certain drugs, such as hydralazine and some anti-seizure drugs. Drug-induced lupus causes joint pain in about 90% of cases, rash in 20%, and inflammation of the lining of the heart or lung in 15%.
What are the symptoms of Lupus?
Symptoms vary from person to person, but the typical lupus patient is a young woman who develops arthritis of the fingers, wrists or other small joints, hair loss, a rash (often on the face, in butterfly pattern over the nose and cheeks).
Do women of color have lupus?
Race and ethnicity: Women of color have higher incidences of lupus than do Caucasian women of primarily Northern European descent. The incidences of lupus in women of African descent is three times that of incidences in Caucasian women. The incidences of lupus in women of Asian descent are twice that of incidences in Caucasian women.
What is the musculoskeletal system?
The musculoskeletal system is involved in around 90% of patients with SLE. In addition to myalgia and arthralgia, arthritis of small and large joints may occur (2). Tendovaginitis and synovitis can be detected by sonography and/or magnetic resonance imaging.
Can you take hydroxychloroquine while pregnant?
Based on the experience of experts, the continuation of hydroxychloroquine treatment during pregnancy is recommended, as SLE patients on hydroxychloroquine show lower disease activity and fewer exacerbations and need lower doses of glucocorticoids at the time of birth (26, e20).
Is chloroquine good for SLE?
Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine are licensed for the treatment of SLE. Apart from their good efficacy against arthritis and LE-specific skin lesions (8), antimalarials maintain SLE in remission, are associated with fewer disease flares, and reduce damage in the course of the disease (23, e18).
Is hydroxychloroquine good for Lupus?
In particular, hydroxychloroquine is associated with a higher rate of remission, fewer relapses, and reduced damage in the course of the disease, even in lupus nephritis.
What is SLE treatment?
ABSTRACT: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease presenting with varying degrees of organ and system involvement. Treatment currently includes antimalarials, glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, and biologics. Delayed diagnosis of SLE and decreased quality of life warrant an improvement in classification as well as in treatment.
What are the current treatments for SLE?
However, many agents have come and gone from pipelines without gaining approval. As of early 2019, rigerimod (Lupuzor), interferon-alpha (IFN) kinoid, atacicept, and obexelimab are in various stages of phase III investigations, and their approvals are highly anticipated. Targets for new drug development include major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II receptors, IFN-alpha, BLyS/a proliferation–inducing ligand (APRIL), and CD19/FcyRIIb receptors. Additional potential novel products that are already approved in the United States but not currently indicated for SLE include ustekinumab and baricitinib, which target interleukin (IL)-12/IL-23 and Janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK2 inhibitors, respectively. Further investigation of these agents is warranted.
What is the inflammation of the kidneys called?
The inflammation of the kidneys, referred to as lupus nephritis (LN), can damage the kidney and its ability to filter blood; 35% of SLE patients are found to have LN at SLE diagnosis and 50% to 60% develop LN within 10 years of SLE diagnosis.
What drugs cause lupus erythematosus?
Drugs that commonly cause DILE include hydralazine, procainamide, isoniazid, minocycline, diltiazem, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors.
What are the complications of SLE?
Other complications associated with the disease include vasculitis, alopecia, mouth ulcerations, nephritis, pericarditis, peripheral neuropathy, cognitive impairment, anxiety, and depression. 2,3. Severe SLE can lead to inflammation of vital organs such as the brain and kidneys.
How common is SLE in the world?
Incidence rates of SLE around the world are approximately 1 to 10 per 100,000 person/years, and prevalence rates range from 20 to 70 per 100,000 person/years. Persons of African, Asian, or Hispanic descent are at a higher risk of presenting with SLE than persons of European descent. 1.
What are the biological agents used for SLE?
Biological Agents: Biological agents used in the treatment of SLE include rituximab and belimumab, both monoclonal antibodies. Rituximab targets B cells and is used to treat renal and CNS presentations of SLE. This agent is recognized as a second- or third-line agent for active disease.
What is the treatment for SLE?
The treatments may include: anti-inflammatory medications for joint pain and stiffness, such as these options available online. steroid creams for rashes.
What are the complications of SLE?
Possible complications may include: blood clots and inflammation of blood vessels or vasculitis. inflammation of the heart, or pericarditis. a heart attack. a stroke. memory changes. behavioral changes. seizures.
Why does autoimmune disease occur?
An autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system attacks the body because it confuses it for something foreign. There are many autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The term lupus has been used to identify a number of immune diseases that have similar clinical presentations and laboratory features, ...
What does it mean when your fingers turn blue?
blood-clotting problems. fingers turning white or blue and tingling when cold, which is known as Raynaud’s phenomenon. Other symptoms depend on the part of the body the disease is attacking, such as the digestive tract, the heart, or the skin. Lupus symptoms are also symptoms of many other diseases, which makes diagnosis tricky.
How many people have SLE?
Most people with SLE are able to live a normal life with treatment. According to the Lupus Foundation of America, at least 1.5 million Americans are living with diagnosed lupus. The foundation believes that the number ...
What are the symptoms of Lupus?
Your doctor will do a physical exam to check for typical signs and symptoms of lupus, including: sun sensitivity rashes, such as a malar or butterfly rash. mucous membrane ulcers, which may occur in the mouth or nose. arthritis, which is swelling or tenderness of the small joints of the hands, feet, knees, and wrists.
What are the symptoms of Raynaud's disease?
Symptoms can vary and can change over time. Common symptoms include: fingers turning white or blue and tingling when cold, which is known as Raynaud’s phenomenon. Other symptoms depend on the part of the body the disease is attacking, such as the digestive tract, the heart, or the skin.