Treatments can include: Receiving blood transfusions Drinking lots of water (8 to 10 glasses of water each day) Receiving IV (intravenous) therapy (fluids given into a vein) Taking medications to help with pain For severe SCD An inherited blood disorder where red blood cells (RBCs) become sickle/crescent shaped.Sickle Cell Anemia
Hydroxycarbamide
Hydroxycarbamide, also known as hydroxyurea, is a medication used in sickle-cell disease, chronic myelogenous leukemia, cervical cancer, and polycythemia vera. In sickle-cell disease it increases hemoglobin and decreases the number of attacks. It is taken by mouth.
Full Answer
Can you cure sickle cell?
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited blood disorder ... severe tiredness and delayed growth or puberty. Treatment typically focuses on controlling symptoms and may include pain medicines during ...
Which medications are used to treat sickle cell disease (SCD)?
- Stroke
- Elevated TCD velocity
- Recurrent acute chest syndrome despite supportive care
- Recurrent severe VOC despite supportive care
- Red cell alloimmunization despite intervention plus established indication for chronic transfusion therapy
- Pulmonary hypertension
Can stem cells help reverse sickle cell disease?
Experts say that editing specific blood stem cells can help reverse symptoms of blood disorders, including sickle cell disease, a hereditary condition that makes your red blood cells look like sickles. Read on to know more about this condition. Your blood is the fuel that runs your whole body. Any problem with it can affect total health.
Is there a cure for sickle cell disease (SCD)?
To date, the only cure for SCD is a bone marrow or stem cell transplant. • A bone marrow or stem cell transplant is a procedure that takes healthy stem cells from a donor and puts them into someone whose bone marrow is not working properly. These healthy stem cells cause the bone marrow to make new healthy cells.

What is the known treatment for sickle cell disease?
Stem cell or bone marrow transplants are the only cure for sickle cell disease, but they're not done very often because of the significant risks involved. Stem cells are special cells produced by bone marrow, a spongy tissue found in the centre of some bones. They can turn into different types of blood cells.
What are the types of sickle?
The four main types of sickle cell anemia are caused by different mutations in these genes.Hemoglobin SS disease. ... Hemoglobin SC disease. ... Hemoglobin SB+ (beta) thalassemia. ... Hemoglobin SB 0 (Beta-zero) thalassemia. ... Hemoglobin SD, hemoglobin SE, and hemoglobin SO. ... Sickle cell trait.
What are the 3 types of sickle cell?
There are several types of sickle cell disease. The most common are: Sickle Cell Anemia (SS), Sickle Hemoglobin-C Disease (SC), Sickle Beta-Plus Thalassemia and Sickle Beta-Zero Thalassemia.
What are the four types of sickle cell crisis?
Four major types of crises are recognised in sickle cell anaemia: aplastic, acute sequestration, hyper-haemolytic, and vaso-occlusive crises.
What is the most common type of sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell anemia (HbSS) Sickle cell anemia is the most common and severe type of SCD. It happens when a person inherits 2 genes for hemoglobin S (1 from each parent). Hemoglobin S clumps together inside red blood cells. This makes red blood cells rigid and sickle-shaped.
What is the difference between sickle cell SS and SC?
Hemoglobinopathies (structural defects in hemoglobin) Unlike Hb SS, Hb SC usually does not produce significant symptoms until the teenage years. Hb SC disease may cause all the vasoocclusive complications of sickle cell anemia, but episodes are less frequent and damage is less disabling.
How can I change my genotype from as to AA?
Genotype CompatibilityTypes of Genotype. The genotypes in humans are AA, AS, AC, SS. They refer to the hemoglobin gene constituents on the red blood cells. ... Compatible genotypes for marriage are: AA marries an AA. ... Solution. The only thing that can change the genotype is the bone marrow transplant (BMT).
How many types of hemoglobin are there?
Four different hemoglobin species are commonly recognized: oxyhemoglobin (oxy-Hb), deoxyhemoglobin (deoxy-Hb), methemoglobin (met-Hb), and hemichromes, whose structures appear below. Following this evolutionary transition methemoglobin and hemichromes are enzymatically cleaved into multiple small fragments.
Can AS and ac get married?
Originally Answered: Can AA and AC genotypes get married? Yes. The offspring of an AA x AC will be 50% AA and 50% AC but all would be phenotypically hemoglobin A.
What are 5 symptoms of a sickle cell crisis?
SymptomsAnemia. Sickle cells break apart easily and die. ... Episodes of pain. Periodic episodes of extreme pain, called pain crises, are a major symptom of sickle cell anemia. ... Swelling of hands and feet. ... Frequent infections. ... Delayed growth or puberty. ... Vision problems.
What is SC in sickle cell?
Summary. Hemoglobin SC disease, is a type of sickle cell disease, which means it affects the shape of the red blood cells. Red blood cells contain a protein called hemoglobin, which is responsible for carrying blood throughout the body.
What blood type carries sickle cell?
Sickle cell trait (AS) is not a “type” of sickle cell disease. It is an inherited condition in which both hemoglobin A and S are produced in the red blood cells, always more A than S. Individuals with sickle cell trait are generally healthy.
What is the procedure to replace sickle cell anemia?
Stem cell transplant. Also known as bone marrow transplant, this procedure involves replacing bone marrow affected by sickle cell anemia with healthy bone marrow from a donor. The procedure usually uses a matched donor, such as a sibling, who doesn't have sickle cell anemia.
How to prevent sickle cell?
Drink plenty of water. Dehydration can increase your risk of a sickle cell crisis. Drink water throughout your day, aiming for about eight glasses a day. Increase the amount of water you drink if you exercise or spend time in a hot, dry climate. Avoid temperature extremes.
Why is sickle cell anemia important?
They're even more important for children with sickle cell anemia because their infections can be severe. Your child's doctor will ensure that your child receives all of the recommended childhood vaccinations, as well vaccines against pneumonia and meningitis and an annual flu shot.
How to diagnose sickle cell anemia?
Sickle cell anemia is usually diagnosed through genetic screening done when a baby is born. Those test results will likely be given to your family doctor or pediatrician. He or she will likely refer you to a doctor who specializes in blood disorders (hematologist) or a pediatric hematologist.
How old do you have to be to take penicillin for sickle cell anemia?
Children with sickle cell anemia might receive penicillin between the ages of about 2 months old until at least age 5. Doing so helps prevent infections, such as pneumonia, which can be life-threatening to children with sickle cell anemia.
How to test for sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell disease can be diagnosed in an unborn baby by sampling some of the fluid surrounding the baby in the mother's womb (amniotic fluid). If you or your partner has sickle cell anemia or the sickle cell trait, ask your doctor about this screening.
What to do if your child has sickle cell anemia?
If you or your child has sickle cell anemia, your doctor might suggest additional tests to check for possible complications of the disease. If you or your child carries the sickle cell gene, you'll likely be referred to a genetic counselor.
What is a sickle cell?
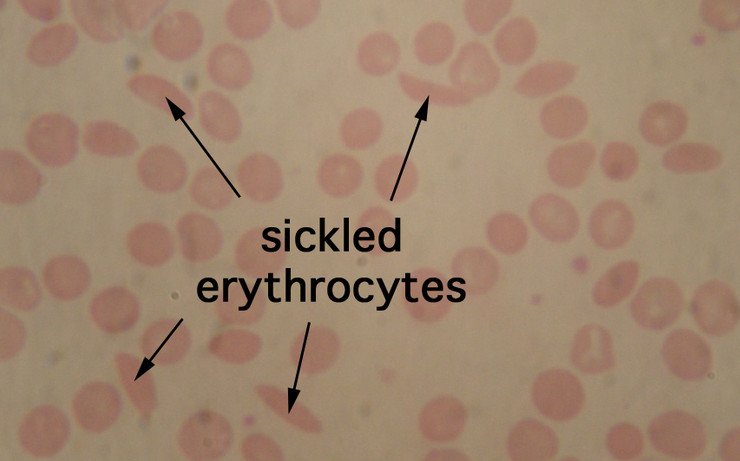
What is Sickle Cell Disease? SCD is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. Healthy red blood cells are round, and they move through small blood vessels to carry oxygen to all parts of the body. In someone who has SCD, the red blood cells become hard and sticky and look like a C-shaped farm tool called a “sickle”.
Why do sickle cells die?
The sickle cells die early, which causes a constant shortage of red blood cells. Also, when they travel through small blood vessels, they get stuck and clog the blood flow. This can cause pain and other serious problems such infection, acute chest syndrome and stroke.
How many sickle cell genes are there?
People who have this form of SCD inherit two sickle cell genes (“S”), one from each parent. This is commonly called sickle cell anemia and is usually the most severe form of the disease.
What is SCD in children?
Cause of SCD. SCD is a genetic condition that is present at birth. It is inherited when a child receives two sickle cell genes—one from each parent.
Can a person with SCT inherit a normal gene?
HbAS. People who have SCT inherit one sickle cell gene (“S”) from one parent and one normal gene (“A”) from the other parent. This is called sickle cell trait (SCT). People with SCT usually do not have any of the signs of the disease and live a normal life, but they can pass the trait on to their children.
What is the type of sickle cell disease?
Types of Sickle Cell. Sickle cell disease is a group of inherited disorders. The specific type of SCD a person has depends on which HBB gene mutations they inherited from their parents. The HBB gene gives instructions for a part of hemoglobin, which is the protein that travels through the blood to deliver oxygen throughout the body. 1.
What is the sickle cell trait?
Sickle cell trait (HbAS) When someone inherits 1 gene for hemoglobin S and 1 gene for normal hemoglobin A , they have sickle cell trait. They usually do not have any signs of the disease and live a normal life. However, they can pass on the hemoglobin S gene to their children. 4.
What is the most common type of SCD?
Sickle cell anemia (HbSS) Sickle cell anemia is the most common and severe type of SCD. It happens when a person inherits 2 genes for hemoglobin S (1 from each parent). Hemoglobin S clumps together inside red blood cells.
What are the different types of SCD?
Less common types of SCD include HbSD, HbSE, and HbSO. These happen when someone inherits 1 gene for hemoglobin S from 1 parent and a gene for another abnormal hemoglobin (D, E, or O) from the other parent. 2. People with HbSD have moderate anemia and occasional pain episodes.
Can sickle cell patients pass on hemoglobin?
However, they can pass on the hemoglobin S gene to their children. 4. People with sickle cell trait have enough normal hemoglobin to prevent red blood cells from sickling. This means they will usually not experience any complications. In rare cases, people with sickle cell trait may experience pain crises.
Can SCD be severe?
Some types of SCD may show more severe symptoms. However, severity also varies within each type because of other genetic and environmental factors. A simple blood test can determine what type of SCD you have.
Is HBS beta plus thalassemia mild?
People with HbS beta zero thalassemia show similar complications as people with sickle cell anemia. People with HbS beta plus thalassemia usually show milder symptoms. Severe and moderate forms are most common in the eastern Mediterranean region and parts of India. Milder forms are common in populations of African ancestry. 3
What is a sickle cell?
Treatments. Pregnancy. Lifestyle measures. Outlook. Sickle cell disease refers to a group of genetic disorders that affect hemoglobin. These disorders can be life threatening, but there are ways to manage the symptoms. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which is a molecule that delivers oxygen to the body’s tissues.
What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
a higher risk of infections, which may have severe symptoms. fever. The following list will provide more detail about some of the main symptoms and complications of sickle cell disease: Pain: During a pain episode, sickle cells get stuck and prevent blood from flowing to a part of the body.
Why is sickle cell disease present before birth?
Because a person inherits it, sickle cell disease is present before birth. A routine blood test at birth will show whether or not the condition is present.
What is the best powder for sickle cells?
L-glutamine oral powder (Endari): This helps reduce the number of sickle cells. It is suitable from the age of 5 years.
When to do a sickle cell test for newborn?
Tests are also available before birth, starting from weeks 8–10. Trusted Source.
Where does sickle cell disease come from?
According to Genetics Home Reference, sickle cell disease disproportionately affects “people whose ancestors come from Africa; Mediterranean countries such as Greece, Turkey, and Italy; the Arabian Peninsula; India, and Spanish-speaking regions in South America, Central America, and parts of the Caribbean.”
Which ethnicity has the highest rate of sickle cell disease?
People of Mediterranean, South American, Middle Eastern, and South Asian ancestry also have higher rates of sickle cell disease. in the United States have sickle cell disease. Around 1 in 365 Black Americans are born with the disease, and 1 in 13 are born with the trait.
What are the different types of sickle cell disease?
Types of Sickle Cell Disease. There are several types of sickle cell disease. The most common are: Sickle Beta-Zero Thalassemia. *The majority of individuals with sickle cell disease have hemoglobin S, but some make a different type of abnormal hemoglobin like hemoglobin C, hemoglobin D, or hemoglobin E.
What is sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder that affects red blood cells. People with sickle cell disease have red blood cells that contain mostly hemoglobin S, an abnormal type of hemoglobin.
What happens when sickle cells block blood vessels?
When sickle-shaped cells block small blood vessels, less blood can reach that part of the body. Parts of the body that don’t receive a normal blood flow eventually become damaged. This is what causes the complications of sickle cell disease although some individuals may be eligible for a curative bone marrow transplant.
How are sickle cell diseases inherited?
Sickle cell conditions are inherited from parents in much the same way as blood type, hair color and texture, eye color and other physical traits. The types of hemoglobin a person makes in the red blood cells depend upon what hemoglobin genes the person inherits from his or her parents.
How long does hemoglobin S last in sickle cell?
Red blood cells containing mostly hemoglobin S do not live as long as normal red blood cells (normally about 16 days).
What are the treatments for sickle cell disease?
These agents have the potential to improve survival and quality of life for individuals with sickle cell disease. Also discussed is stem cell transplantation that, to date, is the only curative approach for this disease, as well as the current status of gene therapy.
Where do sickle cell diseases occur?
Those affected by the disease live in areas of sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, India, the Caribbean, South and Central America, some countries along the Mediterranean Sea, as well as in the United States and Europe.16The disease has, at times, through forced and unforced migration, been introduced to areas in which it was not endemic.17In the United States, 80,000-100,000 individuals are affected by the disorder; worldwide, more than 300,000 children are estimated to be born annually with sickle cell disease.18-20This number includes approximately 3,000 children born with the disease each year in the United States.18
What happens to sickle hemoglobin after deoxygenation?
Upon deoxygenation, the sickle hemoglobin is insoluble and undergoes polymerization and aggregation of the polymers into tubulin fibers that then produce sickling.43,44Because of their rigid shape, the cells are prone to being trapped in the microcirculation, while tissues downstream of this blockage are deprived of blood flow and oxygen and suffer ischemic damage or death. This blood flow deprivation in turn leads to tissue necrosis or reperfusion injury.
What is the pathophysiology of sickle cell anemia?
Schematic representation of the pathophysiology (in part) of sickle cell anemia. A single gene mutation (GAG→GTG and CTC→CAC) results in a defective hemoglobin that when exposed to deoxygenation (depicted in the right half of the diagram) polymerizes (upper right of the diagram), resulting in the formation of sickle cells. Vaso-occlusion can then occur. The disorder is also characterized by abnormal adhesive properties of sickle cells; peripheral blood mononuclear cells (depicted in light blue; shown as the large cells under the sickle cells) and platelets (depicted in dark blue; shown as the dark circular shapes on the mononuclear cells) adhere to the sickled erythrocytes. This aggregate is labeled 1. The mononuclear cells have receptors (eg, CD44 [labeled 3 and depicted in dark green on the cell surface]) that bind to ligands, such as P-selectin (labeled 2 and shown on the endothelial surface), that are upregulated. The sickle erythrocytes can also adhere directly to the endothelium. Abnormal movement or rolling and slowing of cells in the blood also can occur. These changes result in endothelial damage. The sickled red cells also become dehydrated as a result of abnormalities in the Gardos channel. Hemolysis contributes to oxidative stress and dysregulation of arginine metabolism, both of which lead to a decrease in nitric oxide (NO) that, in turn, contributes to the vasculopathy that characterizes sickle cell disease.
What are the adhesion receptors in sickle cells?
The abnormal adhesive properties of the sickle erythrocyte can lead to activation of adhesion receptors, such as those of the intercellular adhesion molecule-4.57Similar ly, the glycoprotein basal cell adhesion molecule (Lutheran blood group), a transmembrane adhesion molecule found in the vascular endothelium, interacts with the unique integrin alpha 4 beta 1 expressed on sickle cells, mediating their adhesion to the endothelium.58,59The result is abnormal interactions between red cells, leukocytes, platelets, endothelium, and extracellular matrix proteins. Such abnormal cell-cell interactions lead to a steady process of adherent interactions, driving endothelial cell expression of procoagulant proteins. The mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK 1/2 and the upstream kinase responsible for its activation, MEK 1/2, are constitutively activated in sickle red cells, leading to increased adhesion.60-62The selectins E-selectin and P-selectin are upregulated in sickle cell disease and also mediate adhesion, with the degree of red cell adhesion correlating with greater severity of disease.63
How does sickle cell disease affect the world?
Sickle cell disease causes significant morbidity and mortality and affects the economic and healthcare status of many countries . Yet historically, the disease has not had commensurate outlays of funds that have been aimed at research and development of drugs and treatment procedures for other diseases.
Why are sickle cells prone to dehydration?
These sickle cells are also prone to dehydration because of abnormalities in the Gardos channel. 13,45,46These cells are characterized by abnormal activation of intracellular signaling pathways and have less nitric oxide47and adenosine triphosphate content.48These cells also have less antioxidant capacity.49,50As a result, many of the cellular components may have oxidative damage.51Oxidative damage to the cellular membrane proteins and aggregation of proteins along the inner surface of plasma membranes can lead to intracellular abnormalities at the red cell surface; such changes lead ultimately to increased phosphatidylserine exposure and the formation of microparticles that allow procoagulant activity by the red cell itself.52
What is the only medicine that can treat sickle cell disease?
For about 20 years, the only medicine available to treat sickle cell disease (SCD) was hydroxyurea. Since 2017, 3 new medicines – Endari, Adakveo, and Oxbryta – have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). These all reduce the number of pain crises and hospitalizations. These newer drugs can all be used alone or in combination with hydroxyurea. Access, adherence (taking medicine as prescribed), and cost remain issues with these medications.
What is the best treatment for SCD?
Pain is the most common symptom of SCD. It is most often treated at home with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or diclofenac. When home management with pain medications and hydration does not relieve pain, treatment in an ER is necessary. Doctors may administer stronger pain medications, such as opioids or ketamine. 1,4
How old do you have to be to get penicillin for SCD?
Treatments to prevent and manage infections have greatly improved childhood survival rates. This usually includes daily penicillin from 2 months old to 5 years old. It also includes all routine vaccinations, as well as the pneumococcal and meningococcal vaccines. 12,13
Does hydroxurea help with sickle hemoglobin?
Hydroxyurea treats SCD in multiple ways. Most importantly, it increases your amount of fetal hemoglobin. This type of hemoglobin is normally only present in newborns. It transports oxygen well and can counteract the negative effects of sickle hemoglobin. 2,4
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Management of sickle cell anemia is usually aimed at avoiding pain episodes, relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Treatments might include medications and blood transfusions. For some children and teenagers, a stem cell transplant might cure the disease.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Taking the following steps to stay healthy might help you avoid complications of sickle cell anemia: 1. Take folic acid supplements daily and choose a healthy diet.Bone marrow needs folic acid and other vitamins to make new red blood cells. Ask your doctor about a folic acid supplement and other vitamins. Eat a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, as well as whole g…
Coping and Support
- If you or someone in your family has sickle cell anemia, you might consider the following to help you cope: 1. Finding someone to talk with.Living with a chronic illness is stressful. Consider consulting a mental health professional, such as a psychologist, counselor or social worker, to help you cope. 2. Join a support group.Ask your health care provider about support groups for fa…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Sickle cell anemia is usually diagnosed through genetic screening done when a baby is born. Those test results will likely be given to your family doctor or pediatrician. He or she will likely refer you to a doctor who specializes in blood disorders (hematologist) or a pediatric hematologist. Here's information to help you get ready for your appointment.
Types of SCD
Sickle Cell Trait
- People who have SCT inherit one sickle cell gene (“S”) from one parent and one normal gene (“A”) from the other parent. This is called sickle cell trait(SCT). People with SCT usually do not have any of the signs of the disease and live a normal life, but they can pass the trait on to their children. Additionally, there are a few, uncommon health problems that may potentially be related to sickl…
Cause of SCD
- SCD is a genetic condition that is present at birth. It is inherited when a child receives two sickle cell genes—one from each parent.
Diagnosis
- SCD is diagnosed with a simple blood test. It most often is found at birth during routine newborn screening tests at the hospital. In addition, SCD can be diagnosed before birth. Because children with SCD are at an increased risk of infection and other health problems, early diagnosis and treatment are important. You can call your local sickle cell organization to find out how to get te…
Complications and Treatments
- People with SCD start to have signs of the disease during the first year of life, usually around 5 months of age. Symptoms and complications of SCD are different for each person and can range from mild to severe. There is no single best treatment for all people with SCD. Treatment options are different for each person depending on the symptoms. Learn about complications and treat…
Cure
- The only cure for SCD is bone marrow or stem cell transplant. Bone marrow is a soft, fatty tissue inside the center of the bones where blood cells are made. A bone marrow or stem cell transplant is a procedure that takes healthy cells that form blood from one person—the donor—and puts them into someone whose bone marrow is not working properly. Bon...