
Wastewater Wastewater, also written as waste water, is any water that has been adversely affected in quality by anthropogenic influence. Wastewater can originate from a combination of domestic, industrial, commercial or agricultural activities, surface runoff or stormwater, and from sewer inf…Wastewater
Effluent
Effluent is an outflowing of water or gas from a natural body of water, or from a manmade structure. Effluent, in engineering, is the stream exiting a chemical reactor. Effluent is defined by the United States Environmental Protection Agency as "wastewater-treated or untreated-that …
Full Answer
What are the main steps in sewage treatment?
What is the first step in sewage treatment?
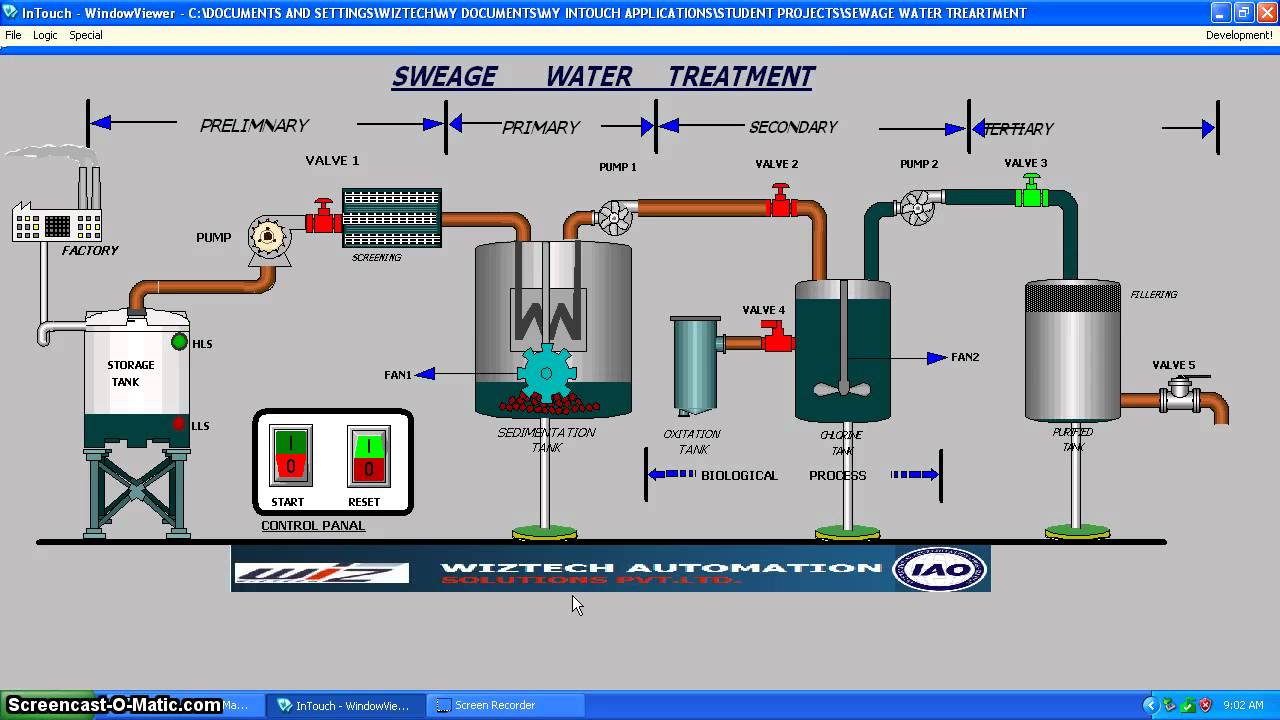
- Step 1: Screening and Pumping. The incoming wastewater passes through screening equipment where objects such as rags, wood fragments, plastics, and grease are removed.
- Step 2: Grit Removal.
- Step 3: Primary Settling.
- Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge.
- Step 5: Secondary Settling.
- Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
- Sludge Treatment.
What is sewage and how is it treated?
Sewage treatment refers to the process of removing microorganisms and other types of contaminants from wastewater. In more developed countries, most domestic waste is collected in a sewer system and sent through pipelines to a central sewage treatment plant. At these plants, sewage treatment in done in a multi-step process that removes or changes different types of material in stages, so that the end product, or effluent, is safe to return into the environment.
What are the primary stages of sewage treatment?
There are four major processes under the tertiary treatment:
- Solids removal
- Biological nitrogen removal
- Biological phosphorus removal
- Disinfection.
What is the process that the sewage treatment goes through?
Treatment Steps. Step 1: Screening and Pumping. The incoming wastewater passes through screening equipment where objects such as rags, wood fragments, plastics, and grease are removed. The material removed is washed and pressed and disposed of in a landfill. The screened wastewater is then pumped to the next step: grit removal.
What is wastewater?
Wastewater is the polluted form of water generated from rainwater runoff and human activities. It is also called sewage. It is typically categorize...
How is wastewater generated?
Domestic wastewater results from water use in residences, businesses, and restaurants.Industrial wastewater comes from discharges by manufacturing...
What are the common pollutants present in wastewater?
Wastewater contains a wide range of contaminants. The quantities and concentrations of these substances depend upon their source. Pollutants are ty...
How is wastewater processed at a sewage treatment facility?
Sewage treatment facilities use physical, chemical, and biological processes for water purification. The processes used in these facilities are als...
Why is wastewater resource recovery important?
Wastewater is a complex blend of metals, nutrients, and specialized chemicals. Recovery of these valuable materials can help to offset a community’...
Why Treat Wastewater?
It's a matter of caring for our environment and for our own health. There are a lot of good reasons why keeping our water clean is an important priority:
Wastewater treatment
The major aim of wastewater treatment is to remove as much of the suspended solids as possible before the remaining water, called effluent, is discharged back to the environment. As solid material decays, it uses up oxygen, which is needed by the plants and animals living in the water.
What is wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment, also called sewage treatment, the removal of impurities from wastewater, or sewage, before it reaches aquifers or natural bodies of water such as rivers, lakes, estuaries, and oceans.
What are the processes used in wastewater treatment?
Sewage treatment facilities use physical, chemical, and biological processes for water purification. The processes used in these facilities are also categorized as preliminary, primary, secondary, and tertiary. Preliminary and primary stages remove rags and suspended solids. Secondary processes mainly remove suspended and dissolved organics.
What is the polluted form of water generated from rainwater runoff and human activities?
Wastewater is the polluted form of water generated from rainwater runoff and human activities. It is also called sewage. It is typically categorized by the manner in which it is generated—specifically, as domestic sewage, industrial sewage, or storm sewage (stormwater).
What was the drainage system of ancient Rome?
It included many surface conduits that were connected to a large vaulted channel called the Cloaca Maxima (“Great Sewer”), which carried drainage water to the Tiber River. Built of stone and on a grand scale, the Cloaca Maxima is one of the oldest existing monuments of Roman engineering.
Why is water polluted?
In broad terms, water is said to be polluted when it contains enough impurities to make it unfit for a particular use, such as drinking, swimming, or fishing. Although water quality is affected by natural conditions, the word pollution usually implies human activity as the source of contamination. Water pollution, therefore, is caused primarily by ...
Why is pretreatment important in wastewater treatment?
For example, pretreatment of industrial wastewater, with the aim of preventing toxic chemicals from interfering with the biological processes used at sewage treatment plants, often became a necessity.
Where does industrial wastewater come from?
Industrial wastewater comes from discharges by manufacturing and chemical industries. Rainwater in urban and agricultural areas picks up debris, grit, nutrients, and various chemicals, thus contaminating surface runoff water. Read more below: Sources of water pollution.
What is wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment is the process of converting wastewater into water that can be discharged back into the environment. According to the U.S. EPA, one of the most common forms of pollution control in the U.S. is wastewater treatment. The purpose of wastewater treatment is to speed up the natural processes by which water is purified.
What is the primary stage of wastewater treatment?
In the primary stage, solids are allowed to settle and be removed from wastewater. The secondary stage uses biological processes to further purify wastewater. Sometimes these stages are combined, and in some cases additional treatment such as tertiary treatment and advanced wastewater treatment are used.
What is activated sludge?
People tend to use the activated sludge process instead of trickling filters, since the activated sludge process speeds up the work of the bacteria. After the sewage leaves the settling tank in the primary stage, it is pumped into an aeration tank.
How is wastewater formed?
Wastewater is formed by a number of activities such as bathing, washing, using the toilet, and rainwater runoff. Wastewater is essentially used water that has been affected by domestic, industrial and commercial use. Some wastewaters are more difficult to treat than others, according to the Safe Drinking Water Foundation.
What is the process of removing chlorine from sedimentation tanks?
Many states now also require the removal of excess chlorine before discharge to surface waters by a process called dechlorination, according to the EPA.
What is primary treatment?
Primary Treatment. Primary treatment removes material that will either float or readily settle out by gravity. This treatment includes the physical processes of screening, comminution—the act of reducing a material to minute particles or fragments—grit removal and sedimentation. As wastewater enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen.
What happens if wastewater is not treated?
If wastewater is not properly treated, then the environment and human health can be negatively impacted, reported the United States Geological Survey (USGS). Among the impacts are harm to fish and wildlife populations, oxygen depletion, beach closures and other restrictions on recreational water use. Advertisement.
What is sewage in a toilet?
There are two types of sewage: blackwater, or wastewater from toilets, and graywater, which is wastewater from all domestic sources except toilets. Blackwater and graywater have different characteristics, but both contain pollutants and disease-causing agents that require treatment.
Why is extra treatment required for industrial wastewater?
For this reason, extra treatment steps are often required to remove inorganic materials from industrial wastewater sources . For example, heavy metals which are discharged with many types of industrial wastewaters, are difficult to remove by conventional treatment methods.
Why is Oxymem used in wastewater treatment?
Because OxyMem uses gas permeable membranes, this allows oxygen to be transferred directly to the wastewater treating micro-organisms. Therefore, it is possible to deliver the oxygen required to maintain the populations in a much more cost effective manner.
Why is there an excess of nutrients in wastewater?
In severe cases, excessive nutrients in receiving waters cause algae and other plants to grow quickly depleting oxygen in the water.
What are some examples of wastewater?
Dairy plants and breweries are perfect examples of this. To combat any issues these types of wastewater sources tend to provide their own treatment or preliminary treatment to protect the main wastewater treatment system.
What diseases can be caused by wastewater?
Other important wastewater-related diseases include hepatitis A, typhoid, polio, cholera, and dysentery.
Is stormwater treated separately?
For example, to prevent flooding of treatment plants during bad weather, stormwater should be collected separately. Screens often remove rubbish and other large solids from storm sewers. In addition, many industries produce ...
What is wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment (WWT) is a process to remove harmful contaminants from wastewater or sewage produced by households and industrial facilities. Wastewater is full of contaminants including bacteria, chemicals, and other toxins and nutrients.
How does wastewater reduce the amount of waste?
Waste Reduction: Through the treatment of wastewater, the amount of harmful waste that is usually released into the environment is reduced. By doing so, companies can reduce the health risks associated with environmental pollution, as well as reduce the water loss induced through water pollution.
What temperature is sludge treated?
It is treated with anaerobic bacteria in special fully-enclosed digesters that are heated to 35 degrees Celsius.
What is wastewater used for?
Wastewater is used water that has been affected by domestic, industrial and commercial use . The composition of all wastewaters is thus constantly changing and highly variable, which is why it is so difficult to pinpoint a singular definition of the word itself. The composition of wastewater is 99.9% water and the remaining 0.1% is what is removed.
What is the composition of wastewater?
The composition of wastewater is 99.9% water and the remaining 0.1% is what is removed. This 0.1% contains organic matter, microorganisms and inorganic compounds. Wastewater effluents are released to a variety of environments, such as lakes, ponds, streams, rivers, estuaries and oceans.
What are the minerals in wastewater?
Inorganic matter. Inorganic minerals, metals and compounds, such as sodium, copper, lead and zinc are common in wastewater from both sewage and wastewater. They can originate from industrial and commercial sources, stormwater, and inflow and infiltration from cracked pipes.
What is the organic content of wastewater?
The organic content of wastewater is made up of human feces, protein, fat, vegetable and sugar material from food preparation, as well as soaps. Some of this organic content is dissolved into the water and some exist as separate particles. The portion of organic material that does not dissolve ...
What is the portion of organic material that does not dissolve but remains suspended in the water?
The portion of organic material that does not dissolve but remains suspended in the water is known as suspended solids. Wastewater is treated to remove as much organic material as possible. Advertisement.
Where does domestic wastewater come from?
Domestic wastewater originates from activities such as restroom usage, bathing, food preparation and laundry. Commercial wastewater from non-domestic sources, such as beauty salons or auto body repair shops, for example. This wastewater may contain hazardous materials and requires special treatment or disposal.
Is wastewater a pollutant?
Other wastewater pollutants. Bacteria, viruses and disease-causing pathogens in wastewater can pollute beaches and contaminate shellfish populations. Fecal coliform bacteria in human waste is typically harmless, but there are pathogens that can negatively impact human health.
