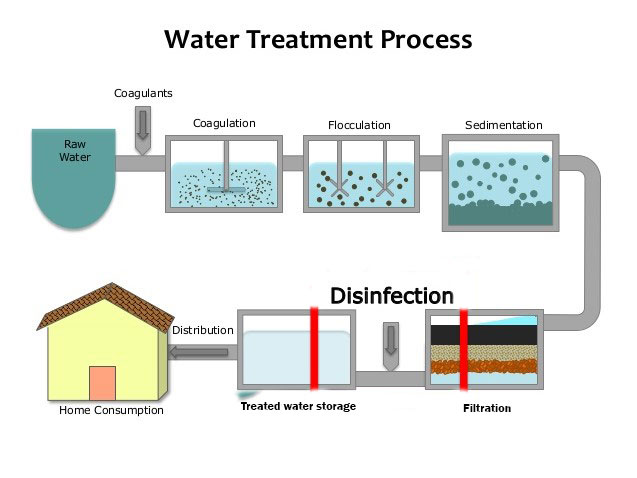
Simply put, sedimentation is the process of removing solids from water and wastewater. It is typically the first treatment performed after the water or wastewater is screened to remove debris and other large objects. By first removing solids, other treatment processes can then be performed more effectively.
What is a sedimentation tank in wastewater treatment?
May 01, 2018 · A sedimentation tank in wastewater treatment removes particles from the water. The accumulated solids, or sludge, form at the bottom of the sedimentation tank and are removed periodically. Coagulants are typically added to the water before sedimentation to aid in the settling process. After sedimentation, there are often other treatment steps.
How is sedimentation used to clean water?
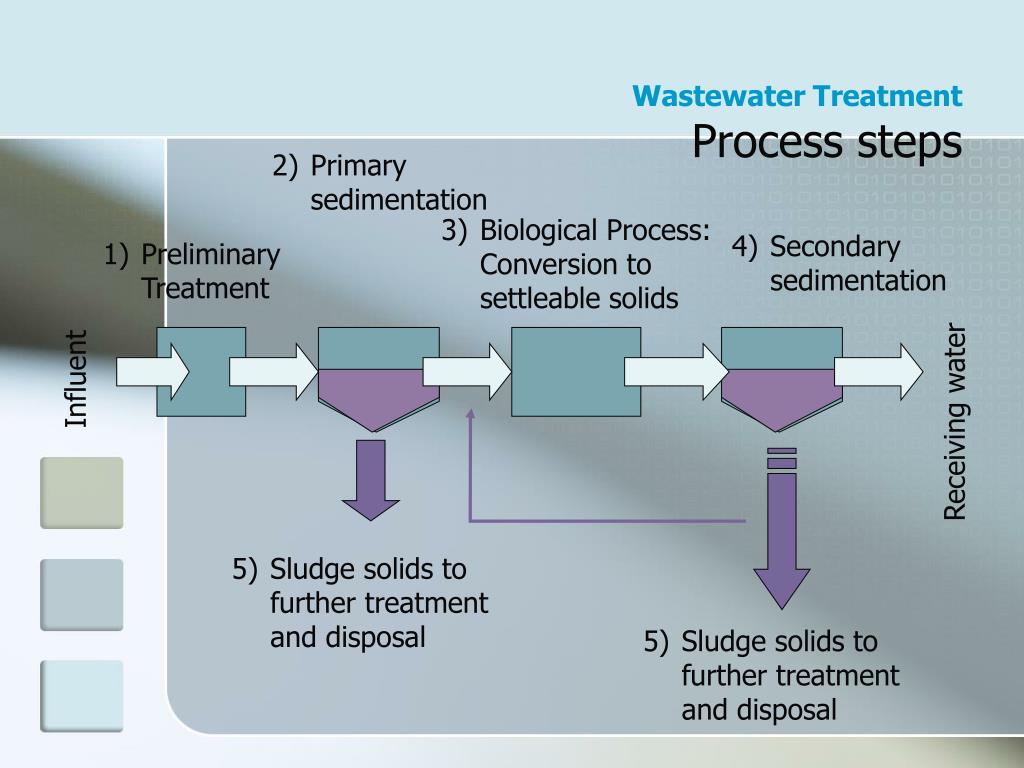
Primary sedimentation is usually the second stage of the Wastewater Treatment (WWT) process. It occurs after the water passes through the Inlet Works/Screening process where all non-organic solids such as non-dissolved materials, wet-pipes and debris are removed from the water.
What is sedimentation?
A sedimentation tank enables suspended particles in water or wastewater to settle out as it flows slowly through the tank, providing some level of purification. At the bottom of the tank, a layer of accumulated solids known as sludge forms and is eliminated. Coagulants are added to the water prior to sedimentation to aid in the settling process, which is then followed by filtration and …
What is the treatment of wastewater?
Jan 07, 2022 · Sedimentation is the most common physical unit operation in wastewater treatment, more so in primary treatment where sedimentation is the workhorse of the treatment. The term sedimentation is also called settling in some literature. Sedimentation is, in a nutshell, a process by which the suspended solids, which have higher densities than that of water, are re-.

What is sedimentation in waste water treatment?
What is sedimentation and settling?
What is sedimentation caused by?
What is sedimentation short answer?
What is sedimentation example?
How is sedimentation used?
How do you reduce sedimentation in waterways?
Why is sedimentation bad?
What happens sedimentation?
What is sedimentation and filtration?
What is sedimentation explain with diagram?
What is difference between sedimentation and decantation?
What is sedimentation in wastewater treatment?
Sedimentation is the most common physical unit operation in wastewater treatment, more so in primary treatment where sedimentation is the workhorse of the treatment . The term sedimentation is also called settling in some literature. Sedimentation is, in a nutshell, a process by which the suspended solids, which have higher densities than that ...
What is sedimentation used for?
Sedimentation is a very important primary treatment process; it is, however, also used in the biological treatment, such as activated sludge and trickling filters for solid removal. The settling characteristics of the solids are determined by the types of the settling solids and their concentrations. Sedimentation has four distinct types of ...
What is sediment basin?
Sedimentation basins are usually rectangular or circular with a radial or upward water flow pattern. Sedimentation is not limited to primary treatment; there is also secondary sedimentation by which settleable solids in the biological secondary treatment processes are removed.
What is zone settling?
Zone settling, also called hindered settling, acquires its name from the fact that aggregated particulates of a concentrated suspension (activated sludge or flocculated colloids) in the sedimentation basin tend to form a massive blanketlike suspension with a distinct interface.
Why is sedimentation important?
The advantage of sedimentation is that it minimizes the need for coagulation and flocculation. Typically, chemicals are needed for coagulation and flocculation, but improved sedimentation controls the need for additional chemicals.
What are the advantages of sedimentation?
The advantage of sedimentation is that it minimizes the need for coagulation and flocculation. Typically, chemicals are needed for coagulation and flocculation, but improved sedimentation controls the need for additional chemicals. Additionally, sedimentation can be used after coagulation to increase the effectiveness of ongoing filtration in ...
What is water treatment?
Water treatment is the process of making water ready for human use. While there are several critical aspects, sedimentation water treatment is of particular importance. It is essential to understand the whole water treatment process in order to ensure the process is completed safely and efficiently for the general public.
What is a scada system?
SCADA is a supervisory computer system that continuously collects and analyzes data.
How does Sirofloc work?
In a Sirofloc® process, fine magnetite is prepared with high acidity. This attracts certain particles in the water. As water is passed through a magnetic field, the magnetite particles start to clump together. Then, the water is passed through a radial flow tank to allow the magnetite to be collected.
What is the process of sedimentation in water treatment?
Sedimentation in potable water treatment generally follows a step of chemical coagulation and flocculation, which allows grouping particles together into flocs of a bigger size. This increases the settling speed of suspended solids and allows settling colloids.
What is sedimentation in water?
Water treatment process using gravity to remove suspended solids from water. Sedimentation is a physical water treatment process using gravity to remove suspended solids from water.
What is a settling basin?
Settling basins are ponds constructed for the purpose of removing entrained solids by sediment ation. Clarifiers are tanks built with mechanical means for continuous removal of solids being deposited by sedimentation. Clarification does not remove dissolved species. Sedimentation is the act of depositing sediment.
What is suspended solid?
Suspended solids (or SS), is the mass of dry solids retained by a filter of a given porosity related to the volume of the water sample. This includes particles 10 μm and greater.
What is the effect of particles in suspension?
This results in a reduced particle-settling velocity and the effect is known as hindered settling.
How do settling particles contact each other?
The settling particles can contact each other and arise when approaching the floor of the sedimentation tanks at very high particle concentration. So that further settling will only occur in adjust matrix as the sedimentation rate decreasing. This is can be illustrated by the lower region of the zone-settling diagram (Figure 3). In Compression zone, the settled solids are compressed by gravity (the weight of solids), as the settled solids are compressed under the weight of overlying solids, and water is squeezed out while the space gets smaller.
What is the primary treatment for sewage?
Sedimentation has been used to treat wastewater for millennia. Primary treatment of sewage is removal of floating and settleable solids through sedimentation. Primary clarifiers reduce the content of suspended solids as well as the pollutant embedded in the suspended solids.
What is sedimentation used for?
Sedimentation is used in primary treatment, secondary treatment, and advanced wastewater treatment processes to remove solids. Primary sedimentation occurs in either long rectangular tanks or circular tanks, usually called primary clarifiers. After wastewater enters a settling tank or basin, velocity reduces to about 1 ft/min.
What is primary sedimentation?
The objective of primary sedimentation is the removal of settleable organic solids and floating organic material (called scum) in order to reduce the suspended solids load for downstream treatment processes. Scum is usually disposed separately or in combination with sludge/biosolids in wastewater treatment plants.
What is primary effluent?
After preliminary treatment and primary sedimentation, the waste stream (cleaned of large debris, grit, and many settleable materials) is now called primary effluent. Primary effluent still contains large amounts of dissolved food, waste, and other chemicals (nutrients), and is usually cloudy and gray in color. Flotation.
What is a rectangular basin?
Rectangular basins are the simplest design, allowing water to flow horizontally through a long tank. This type of basin is usually found in large-scale water treatment plants. Rectangular basins have a variety of advantages - predictability, cost-effectiveness, and low maintenance.
What is primary sedimentation?
The objective of primary sedimentation (also known as primary treatment) is the removal of settleable organic solids and floating organic material (called scum) in order to reduce the suspended solids load for downstream treatment processes ( Metcalf and Eddy/AECOM, 2014 )). Scum is usually disposed separately or in combination with sludge/biosolids in wastewater treatment plants. No literature data were found on pathogen concentrations in scum, but it can be assumed to have significant concentrations and should be handled accordingly. Primary sedimentation is a form of centralized or semi-centralized wastewater treatment and is an integral part of conventional wastewater treatment (primary and secondary treatment) as developed historically and practiced today (Figures 7 and 8). Primary sedimentation tanks can be rectangular or circular, and typically operate with a hydraulic detention time of 1.5-3 hours based on the average daily flowrate (Figures 9 and 10). The settled primary sludge solids, which are highly putrescible, must be continuously removed from the bottom of the sedimentation tank and stabilized, usually by anaerobic digestion and less frequently by aerobic digestion (see Chapter on Sludge Management). Primary sludge typically contains 2 to 5% total solids with 60 to 80% organic content.#N#Typical performance data for the removal of total suspended solids (TSS) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD 5) in primary sedimentation tanks are shown in Figure 11. Primary treatment can remove up to 70% TSS and 45% BOD 5 ( Metcalf and Eddy/AECOM, 2014 )). Primary effluent requires downstream secondary treatment for further removal of organic matter, usually aerobic technologies (e.g., chapter on Activated Sludge, chapter on Media Filters such as a trickling filter) or natural system technologies (e.g., chapter on Constructed Wetlands).
What are the factors that affect sedimentation?
3.0 Factors Affecting Pathogens in Primary Sedimentation Processes 1 Design overflow rates and corresponding settling velocities for primary sedimentation tanks are much greater than that required for pathogen removal by sedimentation, including those with the highest settling velocities (helminth ova). 2 The fraction of pathogens associated with settleable solids has a direct effect on removal.
What is the mechanism of retention in settling flocs?
As a result, it is assumed that retention in settling floc particles is similar to the processes forming the flocs, which includes ( Metcalf and Eddy/AECOM, 2014 ): (1) coalescence of fine particles, which gradually form settleable flocs, and (2) rate of coalescence, which is a function of the concentration of particles and their natural ability to coalesce upon collision. CEPT/APT processes enhance floc formation of fine particles and, as a result, more pathogens, especially large ones such as helminth eggs, will coalesce into the settleable floc particles.
What is primary treatment?
Primary treatment (also called primary sedimentation) is a sanitation technology that removes suspended solids and floating organic material (called scum) to reduce the suspended solids load for subsequent treatment processes.
What is tertiary wastewater treatment?
In tertiary treatment, harmful microbiological matter is rendered killed or inactive so that it will not cause sickness to those organisim that encounter it . These wastewater treatment methods, are coagulation and disinfection respectively. Each of these processes has multiple ways that they can be accomplished, ...
What are the two most common disinfection methods used in wastewater treatment?
There are several wastewater treatment methods of disinfection available, but the two most commonly used are chlorine and ultraviolet light.
What is the process of coagulation?
Chemical coagulation is a well known method of particle coagulation. This process warrants the addition of a number of chemical additives to achieve the desired destabilized state. Alum, Ferric chloride, Ferric sulfate, Ferrous sulfate, and Lime are some of the additives used to neutralize the charged particles. Other supplements include polymers, which act as an aid for the aggregation of solids.
Is coagulation an additive process?
Chemical coagulation is, at its core, an additive process. Though it can reduce the amounts of solids in a solution, it still requires the addition of chemicals to achieve this. Adding these substances can be quite complex and require extensive jar testing. The dosages need to be fairly exact in order to properly process the influent optimally. Dosage can require continuous adjustment based on the varying composition of the wastewater source.
Is electrocoagulation a straight forward process?
Electrocoagulation is a straight forward process. It has few moving parts, thus it can be remotely monitored with reduced oversight and maintenance. The process can also typically be adjusted to accommodate for differing amounts of particles without much effort if required.
What is EC process?
The EC process is also able to target multiple contaminants using a single system and in certain cases with a single treatment pass. Its lack of typical chemical addition, produces smaller volumes of sludge that are typically non-hazardous, easily dewatered, and less expensive to process and dispose of.
How does chlorine kill organisms?
Chlorine is a toxic agent to biological organisms and kills them by oxidation. It penetrates the surface of pathogens and once inside, begins to interact with intracellular enzymes and proteins, rendering them nonfunctional. The micro-organism will either die or fail to reproduce.