Medication
Operative Treatment Operative treatment of Achilles tendinosis involves the removal of abnormal tissues and lesions, fenestration of the tendon through multiple longitudinal creations, and possibly stripping the paratenon.
Procedures
Sclerosing injections. After treating 400 Achilles tendons, we have had two complications that may be related to treatment. One patient who was treated in the Achilles tendon insertion sustained a total rupture in the proximal part of the tendon at the end of an 800 m track race 8 weeks after the treatment.
Therapy
Sclerotherapy is most often used to treat varicose veins. Varicose veins are also known as chronic venous insufficiency. Varicose veins occur when the veins swell and bulge, usually in the legs. This is due to weak vein walls that, in turn, weaken the vein valves.
Self-care
Small skin incisions are made and an arthroscopic shaver is introduced into the Achilles tendon to debris the peritenon. This procedure produces decreased postoperative complication thus allowing the patient early return to previous activity.
Nutrition
See more
How is Achilles tendinosis treated?
What are the possible complications of sclerosing injections for Achilles tendons?
What is sclerotherapy used to treat?
What is the Achilles tendon Shaver procedure?

Does Achilles Tendonosis ever go away?
It is important to remember that it may take at least two to three months for the pain of Achilles tendonitis to go away. If your pain does not improve, you may need surgery to remove inflamed tissue and abnormal areas of the tendon.
What is the best treatment for Achilles tendon?
How are Achilles tendon injuries treated?Rest.Ice.Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief, such as ibuprofen or naproxen.Specific exercises to strengthen your calf muscles.Physical therapy.Eccentric strength training. ... Low-impact activities, such as swimming.More items...
How long does Achilles tendinosis take to heal?
Treatment. Achilles Tendinitis generally takes 6-8 weeks to improve and early activity on a healing tendon can result in a setback in recovery. Non-compliance can double the recovery time and can be very frustrating for patients.
What is PRP treatment for Achilles tendonitis?
PRP injections are thought to promote tendon repair by introducing a high concentration of growth factors (produced from whole blood) directly at the site of degeneration to enhance regeneration. However, randomized trial evidence for PRP to treat midportion Achilles tendinopathy is limited.
Is walking good for Achilles tendonitis?
Even fast walking would likely be ok - but if too painful, try using an insert in the heel (available at most drug stores). This shortens the length of the Achilles tendon and relieves some of the stress.
How do you fix your Achilles tendon without surgery?
You can treat an Achilles tendon rupture with surgery or by using a cast, splint, brace, walking boot, or other device that will keep your lower leg and ankle from moving (immobilization). Both surgery and immobilization are usually successful.
Is tendonosis permanent?
Tendinosis can be cured, but it takes a long time—somewhere between three and six months—to heal completely. However, treatments can help speed up the healing process and improve outcomes.
How do you get rid of tendonosis?
How is tendonosis treated?resting the affected tendon.taking a break every 15 minutes if your work involves performing a repetitive task.applying ice for 15 to 20 minutes, several times a day.using ergonomic keyboards and chairs.wearing braces or tape for support of the affected tendon.More items...
What is the difference between Achilles tendonitis and tendonosis?
It is important to distinguish between Achilles Tendonitis and Achilles Tendonosis. Achilles Tendonitis is the painful inflammation, swelling and irritation of the Achilles tendon. In contrast, Tendonosis is caused by chronic overuse, repeated injury and not allowing sufficient time for the tendon to heal.
Can you walk after PRP injection?
Rest for the first 24-48 hours, but do not lie sedentary. We encourage light movement and range of motion after your injections. Use crutches or a walker for a lower extremity joint, and a sling if necessary for shoulders. You should gradually increase activities using discomfort as a guideline.
How long does it take for PRP to work on Achilles?
published their results of treating 26 patients with recalcitrant Achilles tendinopathy with one injection of autologous-conditioned plasma combined with exercise and therapeutic ultrasonography. At the short-term evaluation at 6 weeks, the patients were found to have had a significant clinical improvement.
What happens after PRP injection in Achilles tendon?
A: There may be some mild soreness after the procedure, so a prescription for pain medications is usually provided after the procedure. Patients are placed in a boot for 1-2 weeks and will require somebody to drive them home.
What is the pain at the insertion of the Achilles tendon to the calcaneus?
An isolated pain at the insertion of the Achilles tendon to the calcaneus due to an intratendinous degeneration is referred to as insertional Achilles tendinosis, while a non-insertional (mid-portion) Achilles tendinosis occurs in the main body of the Achilles tendon.
What causes Achilles tendonitis?
The etiology behind an Achilles tendinosis remains unclear but there are many theories as to the cause of the disease which include overuse, decreased blood supply and tensile strength with aging, muscle imbalance or weakness, insufficient flexibility, and even malalignment such as hyperpronation.
What is Achilles tendinopathy?
Achilles tendinopathy is a painful condition that occurs commonly in active and inactive individuals. 1)It was initially reported to be a tendon disorder which has multiple suggested pathology which are based on poor scientific evidence as explained by Lake and Ishikawa.
What is the first line of treatment for any kind of disease?
The first line of treatment for any kind of disease is still the non-invasive methods such as activity modification, orthotics, heel lifts, massage, hot and cold compresses, strengthening exercises, ultrasound, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) or oral corticosteroid.
How is microtrauma produced?
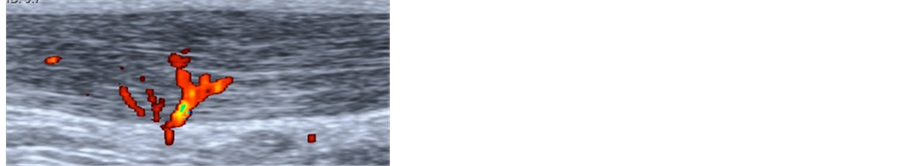
Microtrauma is produced by the repeated shock wave to the affected area which then stimulates neovascularization (Fig. 1). It is this new blood flow that promotes tissue healing and relief from pain. It can also inhibit afferent pain receptor function and produce a high number of nitric oxide synthase.
Where is the ethibond thread inserted?
A number 1 Ethibond thread is inserted at the 2 proximal incisions over the anterior aspect of the Achilles tendon. Ends of the Ethibond are then retrieved from the distal incisions. The Ethibond is then slid onto the tendon, causing it to be stripped and freed from adhesions at the anterior surface of the tendon.
Can a pes cavus cause Achilles tendonitis?
4)One study even suggests that having a pes cavus could also cause Achilles tendinosis. Since there is no gold standard treatment for the Achilles tendinosis, this paper aims to describe the various treatment options for the disorder, conservative as well as surgical treatments. CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT.
Abstract
Sclerosing injections under ultrasonographic guidance is a new method of treatment for persistent pain in Achilles tendinosis. Good results, even superior to those of surgery, have been described. We report the outcome of 25 patients with midportion tendinosis receiving sclerosing treatment.
Introduction
Achilles tendinosis is a common disorder among athletes and sedentary people alike, characterized by a structural changes, local neovascularisation, hyperemia and edema of the tendon tissue [ 6, 12 ].
Patients and methods
Patients referred during the period November 2004 to November 2005 because of chronic Achilles pain were identified in the database of the department for radiology, Malmö University Hospital. Radiology reports were reviewed.
Results
In total, 28 patients (29 tendons) with changes typical of midportion tendinosis such as irregular fiber structure and hypoechoic areas corresponding to a painful nodulus in the tendon were identified. Three tendons had no or very few detectable neovessels and were excluded from treatment.
Discussion
Surgical excision of the lesion or scarification of the tendon has long been the gold standard in treating chronic painful Achilles midportion tendinosis. In total, 70–80% of the patients are able to return to unrestricted activity with minor or no remaining symptoms [ 10, 15, 18, 19 ].
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Jeanette Nilsson for practical assistance. The investigation was financed by: ALF, Herman Järnhardt foundation, Konung Gustav V 80års fond.
What is sclerotherapy used for?
Sclerotherapy is also used to treat some other conditions, including: Malformed lymph vessels.
What are the different types of sclerotherapy?
Sclerotherapy is also used to treat some other conditions, including: 1 Malformed lymph vessels. These are vessels that carry lymphatic fluid or lymph, which helps the immune system fight infections. 2 Hemorrhoids. Sclerotherapy may be used when other treatments fail. Hemorrhoids occur when blood vessels, surrounding the rectum, swell and become irritated, causing pain and making bowel movements uncomfortable. 3 Hydroceles. A hydrocele is an unhealthy development of fluid in a body cavity. Hydroceles are common in the testicles.
What is sclerototherapy for spider veins?
Takeaway. Sclerotherapy is a form of treatment where a doctor injects medicine into blood vessels or lymph vessels that causes them to shrink. It is commonly used to treat varicose veins or so-called spider veins. The procedure is non-surgical, requiring only an injection.
Why do veins swell?
Varicose veins occur when the veins swell and bulge, usually in the legs. This is due to weak vein walls that , in turn, weaken the vein valves. As a result, blood pools up the veins, causing them to swell and look different. Varicose veins may be painful and can cause skin issues, including rashes.
When to use sclerotomy?
Sclerotherapy may be used when other treatments fail. Hemorrhoids occur when blood vessels, surrounding the rectum, swell and become irritated, causing pain and making bowel movements uncomfortable. Hydroceles. Trusted Source. .
What are the negative effects of sclerotherapy?
The most common negative reactions to sclerotherapy include bruising, redness, and pain near the injected vein. About a third of people develop small branches of blood vessels surrounding the injected vein. These vessels usually disappear on their own.
What does it feel like to have a vein injected?
The doctor injects the vein with an irritating solution. The individual may feel burning, tingling, or nothing at all. When the injection is complete, the doctor will massage the area to prevent blood from re-entering the vein. The individual may need to wear a pad or compression stockings in the area.
What is the treatment for varicose veins?
Overview. Sclerotherapy effectively treats varicose and spider veins. It's often considered the treatment of choice for small varicose veins. Sclerotherapy involves injecting a solution directly into the vein. The sclerotherapy solution causes the vein to scar, forcing blood to reroute through healthier veins.
How long does it take for veins to fade after sclerotherapy?
After sclerotherapy, treated veins tend to fade within a few weeks, although occasionally it may take a month or more to see the full results. In some instances, several sclerotherapy treatments may be needed.
How long does it take for spider veins to heal?
If you were treated for small varicose veins or spider veins, you can usually expect to see definitive results in three to six weeks. Larger veins may require three to four months. However, multiple treatments may be needed to achieve the results you want.
Why do veins return blood to the heart?
To return blood to your heart, the veins in your legs must work against gravity. Varicose veins may be caused by weakened valves (incompetent valves) within the veins that allow blood to pool in your veins instead of traveling to your heart.
What is the procedure to check veins in legs?
Ultrasound. Depending on which veins are involved, your doctor may request ultrasound imaging on the veins in your legs. Ultrasound is a painless procedure that uses sound waves to produce images of structures inside the body.
What is the risk of pulmonary embolism?
Deep vein thrombosis carries a risk of pulmonary embolism (a very rare complication of sclerotherapy), an emergency situation where the clot travels from your leg to your lungs and blocks a vital artery. Seek immediate medical care if you experience difficulty breathing, chest pain or dizziness, or you cough up blood.
Why does my vein feel like foam?
Foam tends to cover more surface area than liquid. Some people experience minor stinging or cramps when the needle is inserted into the vein. If you have a lot of pain, tell your doctor. Pain may occur if the solution leaks from the vein into surrounding tissue.
What is the first line of treatment for sclerosing cholangitis?
Bile acid sequestrants. Medications that bind to bile acids — the substances thought to cause itching in liver disease — are the first line treatment for itching in primary sclerosing cholangitis.
What is a liver biopsy?
A liver biopsy is a procedure to remove a piece of liver tissue for laboratory testing. Your doctor inserts a needle through your skin and into your liver to extract a tissue sample. A liver biopsy can help determine the extent of damage to your liver. The test is used only when the diagnosis of primary sclerosing cholangitis is still uncertain ...
What test is used to diagnose sclerosing cholangitis?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose primary sclerosing cholangitis include: Liver function blood test. A blood test to check your liver function, including levels of your liver enzymes, can give your doctor clues about your diagnosis. MRI of your bile ducts.
What is the procedure to remove a small sample of liver tissue for laboratory testing?
Liver biopsy. A liver biopsy is a procedure to remove a small sample of liver tissue for laboratory testing. Liver biopsy is commonly performed by inserting a thin needle through your skin and into your liver. Tests and procedures used to diagnose primary sclerosing cholangitis include: Liver function blood test.
How does a balloon dilation work?
In balloon dilation, your doctor runs a slender tube with an inflatable balloon at its tip (balloon catheter) through an endoscope and into a blocked bile duct. Once the balloon catheter is in place, the balloon is inflated. Stent placement.
What is an ERCP test?
An ERCP is the test of choice if signs and symptoms persist despite no abnormalities on an MRI. An ERCP is often the initial test if you're unable to have an MRI because of a metal implant in your body. Liver biopsy. A liver biopsy is a procedure to remove a piece of liver tissue for laboratory testing.
Why is a bile duct test rarely used?
But this test is rarely used for diagnosis because of the risk of complications. To make your bile ducts visible on an X-ray, your doctor uses a flexible tube passed down your throat to inject dye into the area of your small intestine where your bile ducts empty.
What is polidocanol foam?
Polidocanol Foam is a synthetic long chain fatty alcohol approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a sclerosing therapy for the treatment of uncomplicated varicose veins up to 3 mm in diameter. Research done with macaques in 2014 produced bilateral tubal occlusion, when multiple treatments of 5% polidocanol foam were administered transcervically [ 18 ]. In later research with baboons – which have a straighter cervical canal, as humans do – a single treatment with 5% polidocanol foam resulted in complete tubal occlusion [ 19 ]. In a histological examination of the tissue samples collected from these studies, both macaques and baboons, collagen accumulation showed the formation of a lasting blockade in the tube. Further study is recommended by the research team to evaluate the possibility of using this approach as a permanent contraceptive method for women [ 20 ].
How to treat hemorrhoids?
Various surgical and nonsurgical methods of treating hemorrhoids exist, the choice of which often depends on the stage of the hemorrhoid and the expertise of the physician. Stage I or II hemorrhoids can often be managed medically, especially if they are acute. Herbal rectal suppositories, along with the indicated homeopathic medicine, often aid in quick resolution of the flare-up. In uncomplicated cases of stage I or II hemorrhoids, unless the patient is exhibiting symptoms, treatment is usually not recommended except for increasing dietary fiber and addressing the patient’s dietary choices.
What is the treatment for Achilles tendonitis?
Other treatment modalities suggested for Achilles tendinopathy include platelet-rich plasma injection, sclerosing therapy, electrocoagulation, topical glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), aprotinin injections, extracorporeal shock wave therapy, and prolotherapy. Because of the potential morbidity and complications associated with surgical treatment, these modalities are often attempted prior to surgery in the face of recalcitrant Achilles tendinopathy. A recent Cochrane Database Review revealed inconclusive evidence and that few well-designed studies are available for review ( Kearney, 2015 ). Larger studies with longer follow-up are needed to prove the benefits of these methods.
Does sclerosing help with Achilles tendonitis?
Sclerosing therapy for chronic Achilles tendinosis is based on the premise that the process of neovascularization in the damaged tendon is the source of the patient's pain. Studies in the European literature have implicated neurovascularization as possible pain generators in Achilles tendinopathy, possibly because of the sensory nerves linked to the vessels, and these findings led to the hypothesis that destruction of the vessels and nerves leads to pain relief.
PSC Treatment: Medication
There is no medication proven to be effective in the treatment of PSC. However, ursodeoxycholic acid is a treatment that improves abnormal biochemical tests. It works by increasing the bile flow as well as preventing damage to liver cells, but it does not appear to affect survival or the need for liver transplantation.
PSC Treatment: Endoscopic Therapy
Endoscopic therapy is used to dilate the strictures in order to increase bile flow. This improves jaundice and decreases the number of episodes of cholangitis. Doctors at The Johns Hopkins Hospital have decades of experience using aggressive endoscopic therapy in patients who have strictures but not cirrhosis.
PSC Treatment: Percutaneous Therapy
Like endoscopic therapy, percutaneous therapy dilates the biliary tree and improves bile flow. Percutaneous therapy may be used in conjunction with an endoscopic or surgical approach. Just like an endoscopic procedure, your doctor will dilate a balloon in the ducts.
PSC Treatment: Surgery
Surgery is performed to improve bile flow, reduce jaundice and prevent further episodes of cholangitis. Non-transplant surgical approaches include resecting the part of the hepatic bile duct that is outside the liver, called the extrahepatic bile ducts. Your doctor may decide to permanently stent the bile ducts.
