
What is Reverse Osmosis?
- Understanding Reverse Osmosis. Reverse Osmosis, commonly referred to as RO, is a process where you demineralize or deionize water by pushing it under pressure through a semi-permeable Reverse Osmosis Membrane.
- Osmosis. ...
- Reverse Osmosis Performance & Design Calculations. ...
Full Answer
Which reverse osmosis system wastes the least amount of water?
Reverse osmosis is a process which uses a membrane under pressure to separate relatively pure water (or other solvent) from a less pure solution.
What water problems does reverse osmosis remove?
Apr 11, 2022 · Reverse osmosis is a highly effective method for getting rid of salts and other dissolved solids that are oftentimes present in water. While there are many other water treatment techniques that you can use, reverse osmosis systems have proven to be more effective and more affordable than the alternatives.
What contaminants will reverse osmosis remove from water?
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a water purification methodology that removes ions, molecules and other larger particles from drinking water using a semipermeable membrane. The process of removing salt from seawater or desalination is done by reverse osmosis. History of …
Does reverse osmosis water filter really work?
A reverse osmosis water system removes dissolved contaminants that you can't see but that could make you sick. Reverse osmosis does work for your kidneys by filtering water before it enters your body. It also removes beneficial minerals like calcium and magnesium from water, but that does not make reverse osmosis water bad for you.
Can you drink reverse osmosis water?
The short answer to the question, “is reverse osmosis water safe?” is that reverse osmosis water is safe to drink. Though reverse osmosis removes hard minerals from water, it also removes a wide range of other contaminants which can have a negative health impact.
What is reverse osmosis in simple words?
Definition of reverse osmosis : the movement of fresh water through a semipermeable membrane when pressure is applied to a solution (such as seawater) on one side of it.
Why is reverse osmosis used?
Reverse osmosis helps in improving the quality and safety of water for domestic as well as for industrial use. It is widely used to desalinate the sea water. Reverse osmosis helps in removing many types of suspended and dissolved species from water. It helps in removing bacteria and removes the impurity of the water.Nov 26, 2016
Why is it called reverse osmosis?
When pressure is added, to the higher level side, that is greater than the current osmotic pressure the flow will be reversed. This reversal allows the contaminant solution to be further concentrated and produces purified water. The adding of pressure to enact the reversal is called Reverse Osmosis or RO.
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis ( RO) is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane to separate ions, unwanted molecules and larger particles from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome osmotic pressure, a colligative property that is driven by chemical potential differences of the solvent, ...
Why is pretreatment important in reverse osmosis?
Pretreatment is important when working with reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes due to the nature of their spiral-wound design. The material is engineered in such a fashion as to allow only one-way flow through the system. As such, the spiral-wound design does not allow for backpulsing with water or air agitation to scour its surface and remove solids. Since accumulated material cannot be removed from the membrane surface systems, they are highly susceptible to fouling (loss of production capacity). Therefore, pretreatment is a necessity for any reverse osmosis or nanofiltration system. Pretreatment in sea water reverse osmosis systems has four major components:
How many desalination plants are there in the world?
Almost all commercial reverse-osmosis membrane is now made by this method. By 2019, there were approximately 16,000 desalination plants operating around the world, producing around 95 million cubic metres per day (25 billion US gallons per day) of desalinated water for human use.
When was osmosis first discovered?
A process of osmosis through semipermeable membranes was first observed in 1748 by Jean-Antoine Nollet. For the following 200 years, osmosis was only a phenomenon observed in the laboratory. In 1950, the University of California at Los Angeles first investigated desalination of seawater using semipermeable membranes. Researchers from both University of California at Los Angeles and the University of Florida successfully produced fresh water from seawater in the mid-1950s, but the flux was too low to be commercially viable until the discovery at University of California at Los Angeles by Sidney Loeb and Srinivasa Sourirajan at the National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, of techniques for making asymmetric membranes characterized by an effectively thin "skin" layer supported atop a highly porous and much thicker substrate region of the membrane. John Cadotte, of FilmTec Corporation, discovered that membranes with particularly high flux and low salt passage could be made by interfacial polymerization of m -phenylene diamine and trimesoyl chloride. Cadotte's patent on this process was the subject of litigation and has since expired. Almost all commercial reverse-osmosis membrane is now made by this method. By 2019, there were approximately 16,000 desalination plants operating around the world, producing around 95 million cubic metres per day (25 billion US gallons per day) of desalinated water for human use. Around half of this capacity was in the Middle East and North Africa region.
What is the purpose of drinking water purification?
Around the world, household drinking water purification systems, including a reverse osmosis step, are commonly used for improving water for drinking and cooking. Such systems typically include a number of steps: a sediment filter to trap particles, including rust and calcium carbonate.
How does solar desalination work?
A solar-powered desalination unit produces potable water from saline water by using a photovoltaic system that converts solar power into the required energy for reverse osmosis. Due to the extensive availability of sunlight across different geographies, solar-powered reverse osmosis lends itself well to drinking water purification in remote settings lacking an electricity grid. Moreover, solar energy overcomes the usually high-energy operating costs as well as greenhouse emissions of conventional reverse osmosis systems, making it a sustainable freshwater solution compatible to developing contexts. For example, a solar-powered desalination unit designed for remote communities has been successfully tested in the Northern Territory of Australia.
When did maple syrup start using reverse osmosis?
In 1946, some maple syrup producers started using reverse osmosis to remove water from sap before the sap is boiled down to syrup. The use of reverse osmosis allows about 75–90% of the water to be removed from the sap, reducing energy consumption and exposure of the syrup to high temperatures.
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse Osmosis: Water Treatment Process. Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a water purification methodology that removes ions, molecules and other larger particles from drinking water using a semipermeable membrane. The process of removing salt from seawater or desalination is done by reverse osmosis.
When was reverse osmosis first discovered?
The process of Reverse Osmosis by using semipermeable membrane was observed first in 1748 by a French clergyman and physicist Jean Antoine Nollet. The University of California at Los Angeles was the first to investigate in 1950, desalination of seawater using semipermeable membranes.
What is a ROWPU?
The reverse osmosis water purification unit (ROWPU) is designed for military use, which is a self-contained water treatment unit providing potable water from almost any source of water.
What is RO in water?
Formally, RO is the process of forcing a solvent to a region of low soluble concentration from high solute concentration region through a semipermeable membrane by applying pressure . Intake: To set up RO system you need an intake pump at the source of the water to be purified.
What is the pressure of brackish water?
Pressure for brackish water typically ranges from 225 to 376 psi and in the case of seawater it ranges from 800-1180 psi. Membrane: In membrane assembly there is a pressure vessel with a membrane, allowing feed water to be pressed against the membrane.
What is the best way to clean windows?
Window cleaning: An increasingly popular technique of cleaning windows is “water-fed pole” system. With this system windows are scrubbed with purified water, using a brush on the end of a long pole, wielded from the ground level.
How does maple syrup work?
Maple syrup and hydrogen production: A maple syrup producer uses this process to remove water from the sap before boiling it down into syrup. The use of reverse osmosis process lets 75-90% of the water to be removed from the sap, resulting in reduced energy consumption. Sometimes reverse osmosis is used in small-scale hydrogen production ...
What is the purpose of reverse osmosis?
A reverse osmosis system removes dissolved solids like arsenic and fluoride through the RO membrane. An RO system also includes sediment and carbon filtration for a broad spectrum of reduction. The carbon filters in an RO system remove chlorine and bad taste and odors, and the sediment filter removes dirt and debris.
Why is reverse osmosis used in commercial water systems?
Commercial or industrial reverse osmosis systems are common because commercial units allow drain water to be sent back into the feed supply. Reverse osmosis removes paints, dyes, and other industrial contaminants well.
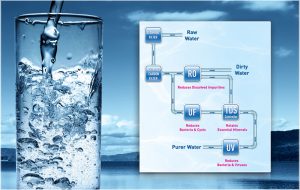
What is the RO membrane?
The RO membrane is the focal point of a reverse osmosis system, but an RO system also includes other types of filtration. RO systems are made up of 3, 4, or 5 stages of filtration. Every reverse osmosis water system contains a sediment filter and a carbon filter in addition to the RO membrane. The filters are called either prefilters ...
Where is reverse osmosis installed?
Reverse osmosis is most commonly installed at the point of use (POU), like under a kitchen or bathroom sink. A point-of-use RO system could also be mounted in a cabinet or remotely in the garage or basement.
What is a semi-permeable membrane?
Semi-permeable membrane: Removes up to 98% of total dissolved solids (TDS) When water first enters an RO system, it goes through prefiltration. Prefiltration typically includes a carbon filter and a sediment filter to remove sediment and chlorine that could clog or damage the RO membrane.
Can you install an under sink in an apartment?
One point-of-entry unit usually supplies water to an apartment building or condominium, and installing an under-sink system is often not allowed. A countertop filter system is the best option in an apartment.
Can RVs have RO systems?
A reverse osmosis system can be very helpful for those whose RV adventures take them into more remote, wilderness locations. A combination of RO and ultraviolet disinfection can make sure the water you are drinking is free from harmful bacteria and parti culate matter.
What is reverse osmosis?
Image source: thrillist.com. Reverse osmosis is one of the essential tools humanity has for turning out abundant-yet-undrinkable oceans into potable water. While residential uses are the most oft-thought-of, it is used at broad scales too.
How much water does reverse osmosis filter waste?
You may have heard statistics about how it filters “waste” roughly four gallons of water for every gallon they produce.
What is hydroponics water?
hydroponics. These are all activities that would traditionally require “new” water from your faucet or a hose. By using your system’s reject water for these tasks instead, you’ll save on two fronts. First, you’ll put the “wastewater” to good use.
Do reverse osmosis filters use force?
You’ll recall that in our “Reverse Osmosis: Explained” section, we mentioned that these filters use force to pass your water through a series of membranes. Well, that force doesn’t just exist on its own! This system needs additional water to facilitate the process.
Is reverse osmosis wastewater lost forever?
Even if the worst-case-scenario parroted by skeptics were true (that is, reverse osmosis wastewater is lost forever), this would still be preferable from an environmental standpoint to the alternative of drinking water from plastic bottles.
Is reverse osmosis water bad for you?
While many skeptics are also quick to point out that reverse osmosis water is terrible for you to health-wise due to its absence of minerals (read more against this argument here ), this is also untrue.
Is reverse osmosis water filtration effective?
Reverse osmosis is one of the most effective water filtration methods available. While skeptics raise concerns about its potential for “wasting water,” these are generally overstated. These systems don’t waste water as much as they use it as part of the purification process.
Why is reverse osmosis important?
It is very important to the water absorption processes of plants. Reverse osmosis is a process which uses a semipermeable membrane which retains both salt and impurities from seawater while allowing water molecules to pass. Filtration of up to 90% is possible making the produced water unsuitable for boiler feed without further conditioning.
What is the purpose of seawater feed for reverse osmosis?
The scale inhibitors such as sodium hexa meta phosphate/ sodium hexa phosphate use to assist wash through of salt deposits on the surface of the elements , and the seawater sterilised to remove bacteria which could otherwise become resident in the filter.
What is a semi-permeable membrane?
The semi-permeable membrane typically makes of polyamide membrane sheets wrapped in a spiral form around a perforated tube resembling a loosely wound toilet roll.
What temperature should a plant be to remove calcium carbonate scale?
Use low-pressure evaporation plant-Operating at a temperature below 80oC so that calcium Carbonate scale predominates. That is a soft scale which can easily remove and not such a poor conductor of heat.
What is magnetic treatment?
Use magnetic ” treatment-A unit consisting of permanent magnets, preceded by a filter. It installed in the evaporator feed line. The water passes through a strong magnetic field which alters the charge on the salts. So that amalgamation of the salt crystals, formed during precipitation in the evaporator, can prevent.
What temperature does a low pressure plant boil?
If it boiled at temperatures above 75 C most of the bacteria will not die-most of the low-pressure plants operate at temperatures ranging from 40°C to 60C#N#Additives to diesel engine cooling water are not harmful. Those not-allowed for health reasons are the chromates.#N#Sometimes inhibitors add to seawater systems to prevent fouling by the growth of marine organisms. It must not use if the seawater used in part for supplying the evaporator.#N#The evaporator is not operating within the limits from the coastline to about 20 to 50 miles from it.
What is storage tank?
Storage tanks and delivery systems intended for drinking or washing water- It is preferable that systems use for drinking and washing keep isolated from the system supplying such circuits as jacket water and oil purifier seal water. Where this is impractical then effort must put by the fitting of efficient non-return valves or an air break in the pipework to prevent back contamination.
Overview
Fresh water applications
Around the world, household drinking water purification systems, including a reverse osmosis step, are commonly used for improving water for drinking and cooking.
Such systems typically include a number of steps:
• a sediment filter to trap particles, including rust and calcium carbonate
History
A process of osmosis through semipermeable membranes was first observed in 1748 by Jean-Antoine Nollet. For the following 200 years, osmosis was only a phenomenon observed in the laboratory. In 1950, the University of California at Los Angeles first investigated desalinationof seawater using semipermeable membranes. Researchers from both University of California at Los Angeles an…
Landfill leachate purification
Treatment with reverse osmosis is limited, resulting in low recoveries on high concentration (measured with electrical conductivity) and fouling of the RO membranes. Reverse osmosis applicability is limited by conductivity, organics, and scaling inorganic elements such as CaSO4, Si, Fe and Ba. Low organic scaling can use two different technologies, one is using spiral wound membra…
Desalination
Areas that have either no or limited surface water or groundwater may choose to desalinate. Reverse osmosis is an increasingly common method of desalination, because of its relatively low energy consumption.
In recent years, energy consumption has dropped to around 3 kWh/m , with the development of more efficient energy recoverydevices and improved membran…
Disadvantages
Household reverse-osmosis units use a lot of water because they have low back pressure. Earlier they used to recover only 5 to 15% of the water entering the system. However, the latest RO water purifiers can recover 40 to 55% of water. The remainder is discharged as waste water. Because waste water carries with it the rejected contaminants, methods to recover this water are not practical for household systems. Wastewater is typically connected to the house drains and will …
New developments
Since the 1970s, prefiltration of high-fouling waters with another larger-pore membrane, with less hydraulic energy requirement, has been evaluated and sometimes used. However, this means that the water passes through two membranes and is often repressurized, which requires more energy to be put into the system, and thus increases the cost.
Other recent developmental work has focused on integrating reverse osmosis with electrodialysisto …
See also
• Electrodeionization
• ERDLator
• Forward osmosis
• Microfiltration
• Reverse osmosis plant
• Electrodeionization
• ERDLator
• Forward osmosis
• Microfiltration
• Reverse osmosis plant