
Medication
Here’s a list of the major treatments available for people with psoriatic disease: Topicals. Phototherapy. Systemics (including biologics and oral treatments) Complementary and integrative medicine. Last updated on 10/14/20 by the National Psoriasis Foundation.
Therapy
Your treatment plan may include medication you apply to your skin, advice to help you care for your skin, and tips to help prevent flare-ups. To control psoriasis, some people also need light treatments or medication that works throughout the body.
Nutrition
The treatment of psoriasis usually depends on how much skin is affected, how bad the disease is (e.g., having many or painful skin patches), or the location (especially the face). Treatments range from creams and ointments applied to the affected areas to ultraviolet light therapy to drugs (such as methotrexate).
What are the topical therapies used to treat psoriasis?
Mar 23, 2019 · Interestingly, psoriasis treatment leads to improvement in anxiety symptoms [51,52]. 2. Pathogenesis The hallmark of psoriasis is sustained inflammation that leads to uncontrolled keratinocyte proliferation and dysfunctional differentiation.
Which is the best treatment for psorisis?
May 02, 2020 · Psoriasis is a common, long-term (chronic) disease with no cure. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Treatments are available to help you manage symptoms. And you can incorporate lifestyle habits and coping strategies to help you live better with psoriasis.
How to cure psoriasis permanently?
Jun 08, 2021 · Fish oil, vitamin D, milk thistle, aloe vera, Oregon grape, and evening primrose oil have all been reported to help ease mild symptoms of psoriasis, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
How to find the best doctor for your psoriasis?

What is the best treatment of psoriasis?
Steroid creams or ointments (topical corticosteroids) are commonly used to treat mild to moderate psoriasis in most areas of the body. The treatment works by reducing inflammation. This slows the production of skin cells and reduces itching. Topical corticosteroids range in strength from mild to very strong.
What is the main cause of psoriasis?
Common psoriasis triggers include: Infections, such as strep throat or skin infections. Weather, especially cold, dry conditions. Injury to the skin, such as a cut or scrape, a bug bite, or a severe sunburn.May 2, 2020
How do I get rid of psoriasis fast?
Here are 12 ways to manage mild symptoms at home.Take dietary supplements. Dietary supplements may help ease psoriasis symptoms from the inside. ... Prevent dry skin. Use a humidifier to keep the air in your home or office moist. ... Try aloe. ... Avoid fragrances. ... Eat healthfully. ... Soak your body. ... Get some rays. ... Reduce stress.More items...
Is psoriasis is curable or not?
Although there is no cure, there are more effective treatments for psoriasis today than ever before. Treating psoriasis can help improve symptoms as well as lower the risk of developing other health conditions such as psoriatic arthritis, heart disease, obesity, diabetes and depression.Nov 19, 2021
How long can psoriasis last?
At times, treatment can lead to clear skin and no psoriasis symptoms. The medical term for this is “remission.” A remission can last for months or years; however, most last from 1 to 12 months. Psoriasis is notoriously unpredictable, so it's impossible to know who will have a remission and how long it will last.
How serious is psoriasis?
Psoriasis is not generally considered life-threatening, except in cases of erythrodermic psoriasis. This rare type of psoriasis can affect the entire body. Erythrodermic psoriasis can cause shivering and fluid retention, and may increase the risk of pneumonia and heart failure.Jun 29, 2021
Is Vaseline good for psoriasis?
Petroleum jelly (such as Vaseline) and vegetable shortening (such as Crisco) also work. If you have psoriasis on your scalp, use a shampoo with salicylic acid, such as Sebcur. Avoid harsh skin products, such as those that contain alcohol.
How do you stop psoriasis from spreading?
Still, you can do a lot on your own to help control and prevent flare-ups.Use Moisturizing Lotions. ... Take Care of Your Skin and Scalp. ... Avoid Dry, Cold Weather. ... Use a Humidifier. ... Avoid Medications That Cause Flare-Ups. ... Avoid Scrapes, Cuts, Bumps, and Infections. ... Get Some Sun, But Not Too Much. ... Zap Stress.More items...•Sep 14, 2020
What cream is good for psoriasis?
CeraVe Psoriasis Cream. ... Curél Hydra Therapy Wet Skin Moisturizer. ... Dermarest Psoriasis Medicated Treatment Gel. ... Eucerin Skin Calming Itch Relief Treatment. ... Gold Bond: Multi-Symptom Psoriasis Relief Cream. ... Lubriderm Intense Skin Repair Lotion. ... MG217 Medicated Salicylic Acid Cream.More items...•Jun 4, 2019
Is psoriasis transmitted?
Psoriasis causes red, scaly patches to appear on the skin. It can look like a rash, so you may worry that you could get it from someone else or pass it to others. But rest easy: It's not contagious. You cannot catch the disease by touching someone who has it.Jul 26, 2021
What organs can be affected by psoriasis?
Living with psoriasis can be difficult enough, but new research suggests sufferers may be at a higher risk for other serious diseases affecting vital organs like the heart, lungs and kidneys.Aug 7, 2013
Can psoriasis cause death?
Conclusions. Severe psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of death from a variety of causes with cardiovascular death being the most common etiology. These patients were also at increased risk of death from causes not previously reported such as infection, kidney disease, and dementia.
What is the treatment plan for psoriasis?
To create this plan, your dermatologist will consider the: Your treatment plan may include medication you apply to your skin, advice to help you care for your skin, and tips to help prevent flare-ups.
How to diagnose psoriasis?
To diagnose psoriasis, a dermatologist will examine your skin, nails, and scalp for signs of this condition. Your dermatologist will also ask if you have any: Joint problems, such as pain and swelling or stiffness when you wake up. Recent changes in your life, such as an illness or increased stress.
What kind of doctor treats psoriasis?
Dermatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating diseases that affect the skin, hair, and nails. If you have psoriasis, your dermatologist can create a treatment plan that meets your individual needs. This type of treatment plan has many benefits. It can relieve symptoms like itch.
Can psoriasis be cured?
It’s important to understand that treatment can control psoriasis, but it cannot cure psoriasis. Because psoriasis cannot be cured, most people live with this condition for the rest of their lives. Knowledge is the key to living well with psoriasis.
What is the best treatment for psoriasis?
Topical treatments for psoriasis come as ointments, creams, or foam and include: Steroid creams. These slow down immune cells in your skin. They can ease swelling and redness. Mild steroid creams are available over the counter. You’ll need a prescription from your doctor for something stronger.
How to treat psoriasis with oatmeal?
Colloidal oatmeal. Some people say their skin is less red and itchy when they soak in an oatmeal bath or apply a paste to their skin. There’s not much evidence to show it treats psoriasis. Aloe vera.
What are the side effects of phototherapy?
Phototherapy can cause short and long-term side effects. It may make you feel like you have sunburn and raise your risk of getting skin cancer. It’s not recommended if: 1 You’ve had skin cancer 2 You have a medical condition that raises your chances of getting skin cancer 3 You have a medical condition or take medicine that makes you more sensitive to UV light
Why do people take retinoids?
They think it’s because retinoids affect how fast skin cells grow. Oral retinoids are often used to treat pustular psoriasis. But they can cause unwanted side effects, including hair loss and liver or bone problems. Your doctor may lower your dose once your symptoms get better.
What to do if you are sensitive to UV light?
You have a medical condition or take medicine that makes you more sensitive to UV light. Systemic Treatments. Immunosuppressants. If other treatments don’t work or you have moderate to severe psoriasis, your doctor might give you drugs to slow down your entire immune system.
Does coal tar cause itching?
Your doctor might give you these to use on sensitive areas such as your face, groin, or skin folds. Coal tar ointment and shampoo. Coal tar is known to ease psoriasis-related inflammation, itching, and scales. But it can cause side effects such as skin redness and dryness.
Can you use UV light on psoriasis?
Phototherapy for Psoriasis. Sunlight has been used to treat skin conditions for thousands of years. Now doctors use machines to shine ultraviolet (UV) rays directly on your skin. Light therapy can slow down fast-growing skin cells in people who have psoriasis.
What is the treatment for psoriatic arthritis?
The treatment of psoriatic arthritis usually involves the use of drugs (such as methotrexate). Psoriatic disease (when a person has psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis) may be treated with drugs (such as methotrexate) or a combination of drugs and creams or ointments.
What is psoriasis skin?
What is Psoriasis? Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disease that speeds up the growth cycle of skin cells.
What is the best doctor for psoriasis?
Psoriatic arthritis has many of the same symptoms as other types of arthritis, so a rheumatologist (arthritis doctor) is often the best doctor to diagnose it.
What is the pathogenesis of psoriasis?
In the past 15 years, breakthroughs in the understanding of the pathogenesis of psoriasis have been translated into targeted and highly effective therapies providing fundamental insights into the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases with a dominant IL-23/Th17 axis. This review discusses the mechanisms involved in the initiation and development of the disease, as well as the therapeutic options that have arisen from the dissection of the inflammatory psoriatic pathways. Our discussion begins by addressing the inflammatory pathways and key cell types initiating and perpetuating psoriatic inflammation. Next, we describe the role of genetics, associated epigenetic mechanisms, and the interaction of the skin flora in the pathophysiology of psoriasis. Finally, we include a comprehensive review of well-established widely available therapies and novel targeted drugs.
What is the most common type of psoriasis?
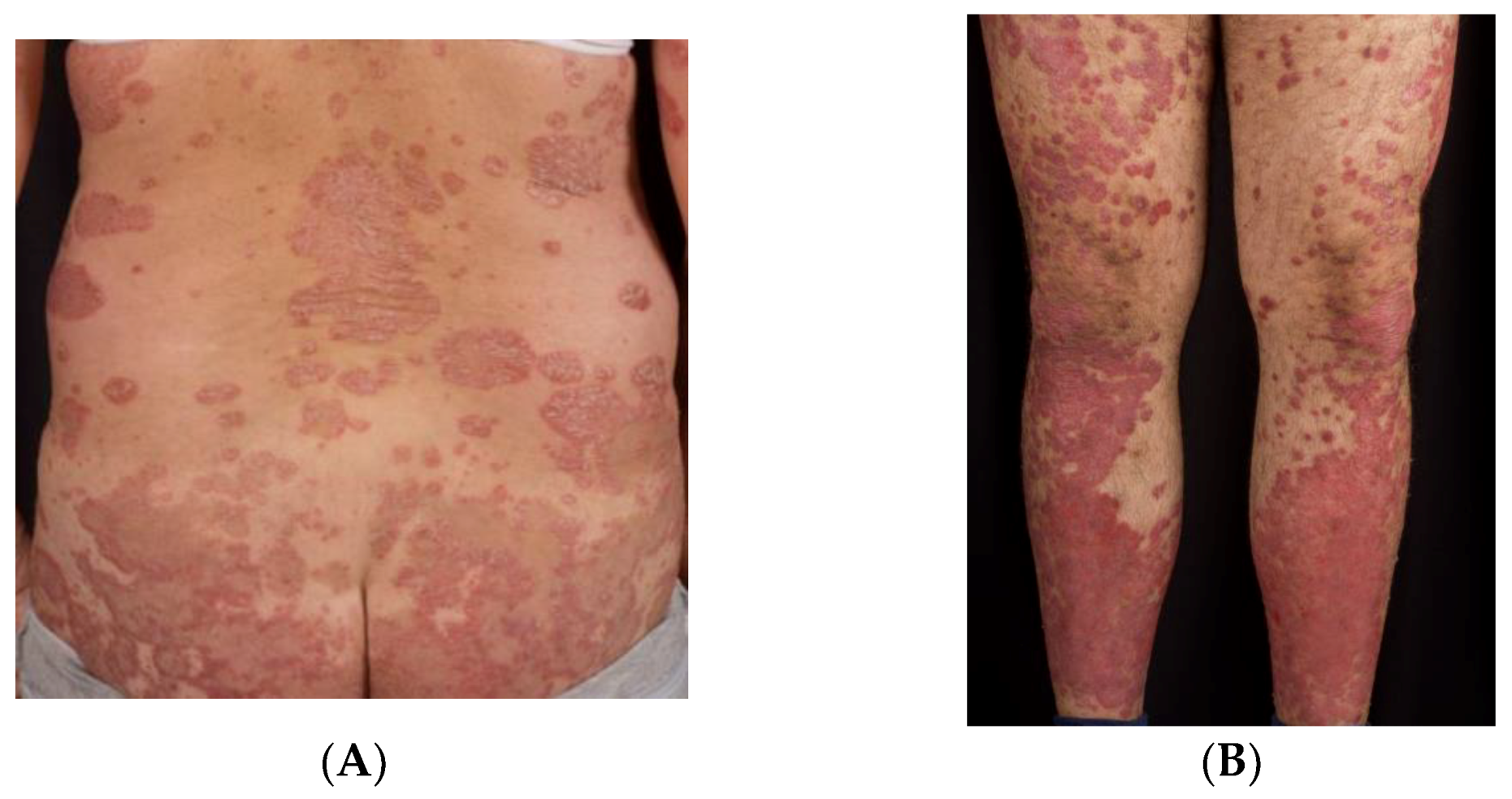
The dermatologic manifestations of psoriasis are varied; psoriasis vulgaris is also called plaque-type psoriasis, and is the most prevalent type. The terms psoriasis and psoriasis vulgaris are used interchangeably in the scientific literature; nonetheless, there are important distinctions among the different clinical subtypes (See Figure 1 ).
What are AMPs in psoriasis?
Among the most studied psoriasis-associated AMPs are LL37, β-defensins, and S100 proteins [56].
How does the skin microbiome affect the immune system?
The skin microbiome exerts an active role in immune regulation and pathogen defense by stimulating the production of antibacterial peptides and through biofilm formation. A differential colonizing microbiota in comparison to healthy skin has been found in several dermatologic diseases, including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and acne vulgaris [ 150, 151 ]. It is hypothesized that an aberrant immune activation triggered by skin microbiota is involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. For instance, there is growing evidence that the steady-state microbiome plays a role in autoimmune diseases such as in inflammatory bowel disease [ 152 ].
Which axis plays a central role in T cell-mediated plaque psoriasis?
Whereas the TNFα–IL23–Th17 axis plays a central role in T cell-mediated plaque psoriasis, the innate immune system appears to play a more prominent role in the pustular variants of psoriasis [ 55 ]. Different pathomechanisms are associated with distinct psoriasis subtypes.
Is psoriasis an autoantigen?
Psoriasis shows clear autoimmune-related pathomechanisms. This very important area of research will allow for a deeper understanding of to which extent autoantigen-specific T cells contribute to the development, chronification, and overall course of the disease.
Is psoriasis a genetic disorder?
Psoriasis has a genetic component that is supported by patterns of familial aggregation. First and second-degree relatives of psoriasis patients have an increased incidence of developing psoriasis, while monozygotic twins have a two to threefold increased risk compared to dizygotic twins [ 82, 83 ]. Determining the precise effect of genetics in shaping innate and adaptive immune responses has proven problematic for psoriasis and other numerous immune-mediated diseases [ 84, 85 ]. The genetic variants associated with psoriasis are involved in different biological processes, including immune functions such as antigen presentation, inflammation, and keratinocyte biology [ 55 ].
What happens if you have psoriasis?
Also, talk to your doctor if your psoriasis: Becomes severe or widespread. Causes you discomfort and pain. Causes you concern about the appearance of your skin. Leads to joint problems, such as pain, swelling or inability to perform daily tasks.
What is the most common type of psoriasis?
Plaque psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis. It usually causes dry, red skin lesions (plaques) covered with silvery scales. Guttate psoriasis, more common in children and adults younger than 30, appears as small, water-drop-shaped lesions on the trunk, arms, legs and scalp.
Why does my skin turn red?
Causes. Psoriasis is thought to be an immune system problem that causes the skin to regenerate at faster than normal rates. In the most common type of psoriasis, known as plaque psoriasis, this rapid turnover of cells results in scales and red patches.
What causes red patches on the scalp?
Psoriasis is a skin disease that causes red, itchy scaly patches, most commonly on the knees, elbows, trunk and scalp. Psoriasis is a common, long-term (chronic) disease with no cure. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Treatments are available to help you manage ...
Where is psoriasis most commonly found?
The most commonly affected areas are the lower back, elbows, knees, legs, soles of the feet, scalp, face and palms.
What is the name of the small water drop shaped lesions on the trunk, arms, legs and scalp?
Guttate psoriasis, more common in children and adults younger than 30, appears as small, water-drop-shaped lesions on the trunk, arms, legs and scalp. The lesions are typically covered by a fine scale. Scalp psoriasis. Open pop-up dialog box. Close.
What is the name of the condition that causes blisters on the skin?
Pustular psoriasis. Pustular psoriasis generally develops quickly, with pus-filled blisters appearing just hours after your skin becomes red and tender. It can occur in widespread patches or in smaller areas on your hands, feet or fingertips. Erythrodermic psoriasis.
What is the best treatment for psoriasis?
Try massaging a few tablespoons on your scalp to help loosen troublesome plaques during your next shower. Apple cider vinegar has also been found to be a good detoxifier for the body.
How to get rid of psoriasis on the inside?
1. Take dietary supplements. Dietary supplements may help ease psoriasis symptoms from the inside. Fish oil, vitamin D, milk thistle, aloe vera, Oregon grape, and evening primrose oil have all been reported to help ease mild symptoms of psoriasis, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
Why are T cells important for psoriasis?
T cells are designed to protect the body from infection and disease. When these cells mistakenly become active and set off other immune responses, it can lead to psoriasis symptoms. Even though there’s no cure, many treatments exist to ease the symptoms of psoriasis. Here are 12 ways to manage mild symptoms at home. 1.
What is the cause of red patches on the skin?
Treating psoriasis. Psoriasis is a recurring autoimmune disorder characterized by red, flaky patches on the skin. Even though it affects your skin, psoriasis actually begins deep inside your body in your immune system. It comes from your T cells, a type of white blood cell.
What foods can help with psoriasis flare ups?
Eliminating red meat, saturated fats, refined sugars, carbohydrates, and alcohol may help reduce flare-ups triggered by such foods. Cold water fish, seeds, nuts, and omega-3 fatty acids are known for their ability to reduce inflammation. This can be helpful for managing psoriasis symptoms.
How to stop psoriasis from growing?
Get some rays. Light therapy involves exposing your skin to ultraviolet light under the supervision of a doctor. Ultraviolet light can help slow the growth of skin cells triggered by psoriasis. This therapy often requires consistent and frequent sessions.
Can alcohol cause psoriasis?
Alcohol is a trigger for many people who have psoriasis. A study in 2015 found an increased risk of psoriasis among women who drank nonlight beer. Those who drank at least five nonlight beers per week were nearly twice as likely to develop psoriasis compared to women who didn’t drink. 10. Try turmeric.
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Psoriasis treatments aim to stop skin cells from growing so quickly and to remove scales. Options include creams and ointments (topical therapy), light therapy (phototherapy), and oral or injected medication. Which treatments you use depends on how severe the psoriasis is and ho…