
In haemophilia, prophylaxis can be defined as the administration of clotting factor concentrate in anticipation of or to prevent bleeding.
What is hemophilia prophylaxis?
Home » Hemophilia Treatments » Prophylaxis. Prophylaxis is commonly referred to as a preventive measure in hemophilia of regularly infusing blood clotting factor concentrates to avoid bleeding.
How do medications treat hemophilia A?
In some forms of mild hemophilia, this hormone can stimulate the body to release more clotting factor. It can be injected slowly into a vein or used as a nasal spray. Emicizumab (Hemlibra). This is a newer drug that doesn't include clotting factors. This drug can help prevent bleeding episodes in people with hemophilia A.
Why choose at-home hemophilia treatment?
Giving factor treatment products at home means that bleeds can be treated quicker, resulting in less serious bleeding and fewer side effects. Hemophilia is a complex disorder.
What are the benefits of factor treatment products for hemophilia?
Giving factor treatment products at home means that bleeds can be treated quicker, resulting in less serious bleeding and fewer side effects. Hemophilia is a complex disorder. Good quality medical care from doctors and nurses who know a lot about the disorder can help people with hemophilia prevent some serious problems.
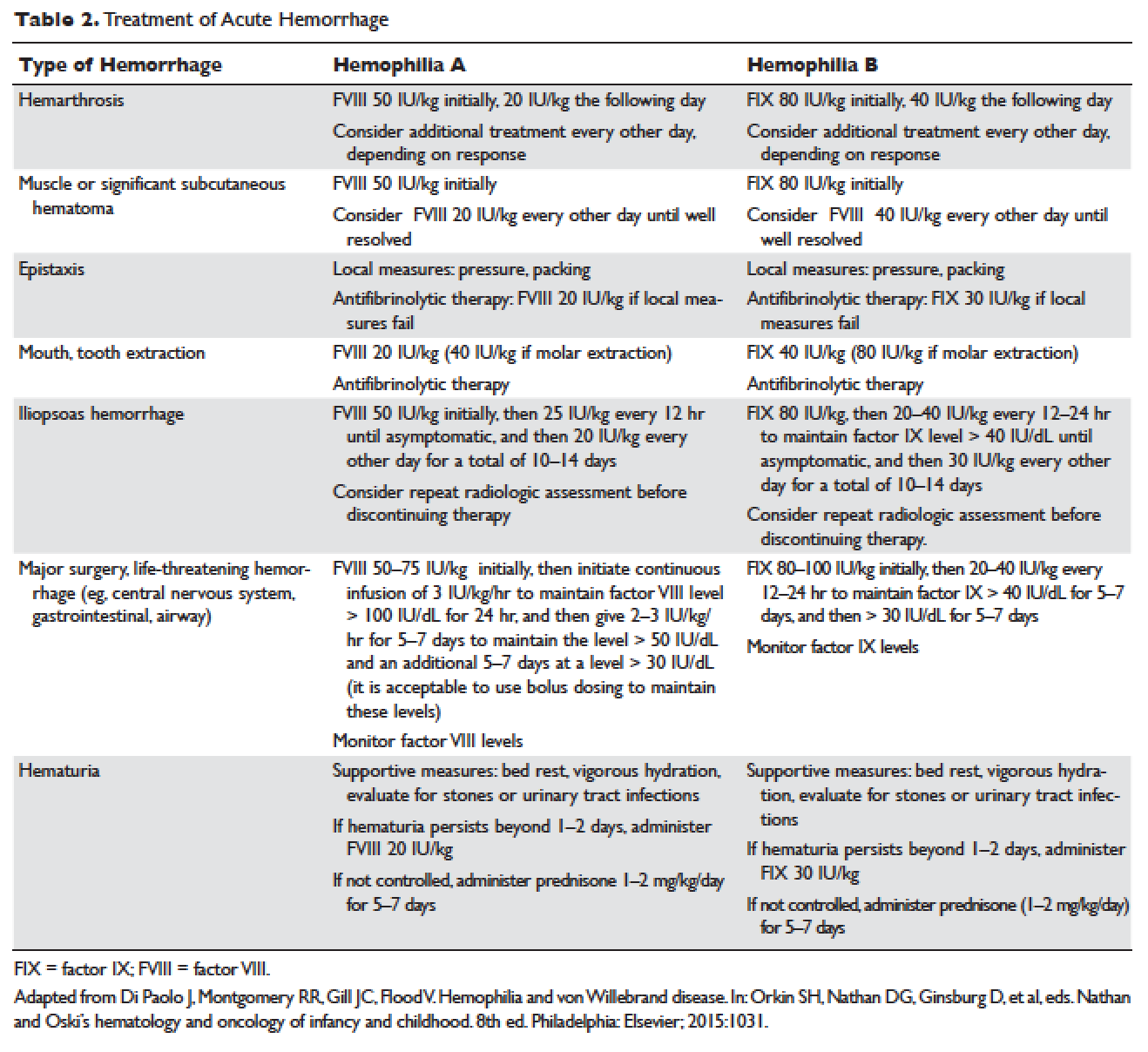
What is the difference between on demand vs prophylactically treating hemophilia?
Prophylaxis regimen was found to have significantly better bleeding outcomes than on-demand regimen in spite of heterogeneity in study design and populations. Joint outcomes were not reported uniformly but were found to be better for patients on the prophylaxis regimen than on-demand regimen.
Is there a prevention for hemophilia?
Because it's a genetic condition someone is born with, there is currently no way to prevent the disease, so scientists are constantly investigating ways that the disease can be stopped before it passes to the next generation.
What is secondary prophylaxis in hemophilia?
Secondary prophylaxis can also be used as a short-term treatment following a major hemorrhage. Its purpose is to allow the joint or muscle to heal, absorb the blood in that joint or muscle, and prevent further bleeding.
What are the two types of prophylaxis?
The different types of prophylaxis include:Primary Prophylaxis: This means preventing or increasing resistance to a disease that you don't have. ... Secondary Prophylaxis: Measures are taken to prevent a medical problem or injury from happening again.More items...•
What does treatment of hemophilia often involve?
The main treatment for hemophilia is called replacement therapy. Concentrates of clotting factor VIII (for hemophilia A) or clotting factor IX (for hemophilia B) are slowly dripped or injected into a vein. These infusions help replace the clotting factor that's missing or low.
How do you stop haemophilia from bleeding?
Apply pressure to the bleeding area. Use an ice pop or piece of ice on the area. When the bleeding stops, help your child avoid hard or hot foods because they can restart the bleeding. If the bleeding does not stop within 20 minutes, call your care team.
What does prophylactic use mean?
1 : guarding from or preventing the spread or occurrence of disease or infection prophylactic therapy. 2 : tending to prevent or ward off : preventive. Other Words from prophylactic. prophylactically \ -ti-k(ə-)lē \ adverb. prophylactic.
Which drug is used for prophylaxis?
Prophylactic agents include the following: Beta-blockers - Propranolol and nadolol. Tricyclics - Amitriptyline. Antiepileptic drugs - Valproic acid, topiramate, and zonisamide.
What is called prophylaxis?
: measures designed to preserve health (as of an individual or of society) and prevent the spread of disease.
What is the difference between prophylaxis and prophylactic?
Prophylaxis is a Greek word and concept. It means any action taken to guard or prevent beforehand. The corresponding adjective is prophylactic.
What is difference between treatment and prophylaxis?
Therefore, if the drug is administered before disease onset, it is considered prophylactic, otherwise it is considered therapeutic. Therapeutic group are the subjects on treatment of existing disease, while prophylatic group are subjects receiving preventive measures.
What is the best treatment for hemophilia?
Often the best choice for care is at a comprehensive hemophilia treatment center (HTC). An HTC provides patients with the care and education to address all issues related to the disorder. The team consists of physicians (hematologists or blood specialists), nurses, social workers, physical therapists, and other healthcare providers who are specialized in the care of people with bleeding disorders.
How to treat hemophilia?
Treatment of Hemophilia. The best way to treat hemophilia is to replace the missing blood clotting factor so that the blood can clot properly. This is typically done by injecting treatment products, called clotting factor concentrates, into a person’s vein. Clinicians typically prescribe treatment products for episodic care or prophylactic care.
How does hemlibra work?
Hemlibra ® works by replacing the function of factor VIII (8) , rather than replacing the missing clotting factor VIII directly. It can be used to either prevent or reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes in people with hemophilia A. This treatment product can be given by injection under the skin. Patients who use Hemlibra ® for prophylaxis and use clotting factor concentrates to treat breakthrough bleeds, can still develop an inhibitor. Traditional laboratory inhibitor testing methods do not work when testing for inhibitors in patients on Hemlibra ®; as such, a specialized testing method called the chromogenic Bethesda assay is needed.
Why is cryoprecipitate not used?
However, because there is no method to kill viruses, such as HIV and hepatitis, in cryopreci pitate, it is no longer used as the current standard of treatment in the United States.
What is the best age to start prophylactic treatment for hemophilia?
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the World Federation of Hemophilia advise parents of children with hemophilia to initiate prophylactic treatment at an early age to achieve optimal results for a child with a severe form of the bleeding disorder.
What is the purpose of prophylaxis?
Prophylaxis is commonly referred to as a preventive measure in hemophilia of regularly infusing blood clotting factor concentrates to avoid bleeding. This approach stemmed from research that patients with mild-to-moderate hemophilia (or those who have clotting factor levels of 1 percent or more) rarely experience spontaneous bleeds ...
What is hemophilia news?
Hemophilia News Today is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Why do prophylactics need to be tailored?
But because each patient has different clotting factor levels, prophylactic dosage intervals should be tailored individually, depending on the aim of the treatment, bleeding phenotype, the patient’s daily activities, and cost efficacy.
How to treat hemophilia A?
This is done by infusing (giving medication into a vein) a FVIII product into the affected person. When you infuse, FVIII concentrate, the FVIII is immediately available in the bloodstream, and your body can use it to stop or prevent the bleeding.
When did cloning of FVIII and FIX occur?
In the early 1980s, the cloning of FVIII and FIX and subsequent expression of functional proteins occurred. This was during the “bad blood” era (when many individuals with hemophilia being treated with plasma-derived clotting factor were infected with HIV and/or HCV). This led to the development and commercialization of recombinant clotting factors. These initial products were manufactured using Chinese hamster ovary cells or baby mouse kidney cells. Manufacturers injected these cells with the factor gene so that large amounts of the factor protein could be produced. Since the proteins are extracted from animal cells, they are not at risk for containing human viruses. Some factor concentrate products are stabilized using human albumin, while others are stabilized using sucrose. This was life-changing for many with hemophilia, allowing for prophylactic (or preventive) treatment. Some companies are now using human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells to grow the factor.
What is a broviac catheter?
BROVIAC® catheters and HICKMAN® catheters (often referred to as “broviacs”) are similar to a PICC line. However, A BROVIAC® catheter is placed directly into a central vein and threaded to a position just above the heart. It is tunneled under the skin and brought out away from the site where it enters the vein to theoretically prevent bacteria from gaining access to the central portion of the catheter. BROVIAC® catheters contain a “cuff” that is under the skin. As the skin grows into this “cuff,” the catheter becomes more stable, reducing the chance of it becoming pulled out. Like the PICC line, his device is easy to use and does not require sticks into the person’s skin. The difference is that these catheters can last for a prolonged period of time. The most common long-term complications of this type of central line are infection, movement that takes the catheter out of the proper position, and damage to the catheter.
What is a butterfly needle used for?
Peripheral venous access, where a butterfly needle is inserted directly into a vein and is used to infuse FVIII into the bloodstream, is commonly used by those who infuse at home but do not have a venous access device , such as a port, PICC line, or BROVIAC®. Below are some considerations regarding this type of access:
Can you infuse FVIII into bloodstream?
All FVIII products need to be infused directly into the bloodstream. There are several ways to infuse FVIII, and each has its advantages and disadvantages. These include peripheral infusion (accessing a vein with a butterfly needle), port-a-catheter (also called a port), a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line, or a BROVIAC® or HICKMAN® catheter.
Does hemophilia have an inhibitor?
While anyone with a bleeding disorder can develop an inhibitor to clotting factor, those with hemophilia A develop inhibitors more often than the other bleeding disorders. Inhibitors are antibodies that the immune system develops because it perceives the infused FVIII as a foreign substance that needs to be destroyed. Antibodies are proteins that eat up the FVIII before it has time to stop the bleeding.
What is the standard of care for a patient with severe hemophilia?
Early long-term prophylaxis is the standard of care to prevent joint bleeding and chronic arthropathy in patients with severe hemophilia. Areas covered: Despite the obvious prophylaxis advantages upon the clinical outcomes, there are still several drawbacks to be addressed for the optimal patients' compliance.
What is early long term prophylaxis?
Early long-term prophylaxis is the standard of care to prevent joint bleeding and chronic arthropathy in patients with severe hemophilia. Areas covered: Despite the obvious prophylaxis advantages upon the clinical outcomes, there are still several drawbacks to be addressed for the optimal patients' …. Prophylactic versus on-demand treatments ...
How to prevent hemophilia?
Lifestyle and home remedies. To avoid excessive bleeding and protect your joints: Exercise regularly. Activities such as swimming, bicycle riding and walking can build up muscles while protecting joints. Contact sports — such as football, hockey or wrestling — are not safe for people with hemophilia.
How to help a child with hemophilia?
To help you and your child cope with hemophilia: Get a medical alert bracelet. This bracelet lets medical personnel know that you or your child has hemophilia, and the type of clotting factor that's best in case of an emergency. Talk with a counselor.
What is a recombinant clotting factor?
Similar products, called recombinant clotting factors, are manufactured in a laboratory and aren't made from human blood. Other therapies may include: Desmopressin. In some forms of mild hemophilia, this hormone can stimulate your body to release more clotting factor.
What is the best way to prevent clots from breaking down?
It can be injected slowly into a vein or provided as a nasal spray. Clot-preserving medications. These medications help prevent clots from breaking down. Fibrin sealants. These medications can be applied directly to wound sites to promote clotting and healing. Fibrin sealants are especially useful in dental therapy.
How to treat internal bleeding?
If internal bleeding has caused severe damage, you may need surgery. First aid for minor cuts. Using pressure and a bandage will generally take care of the bleeding. For small areas of bleeding beneath the skin, use an ice pack.
When is hemophilia diagnosed?
Depending on the severity of the deficiency, hemophilia symptoms can first arise at various ages. Severe cases of hemophilia usually are diagnosed within the first year of life.
Can you use Tylenol for hemophilia?
Avoid certain pain medications. Drugs that can aggravate bleeding include aspirin and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others). Instead, use acetaminophen (Ty lenol, others), which is a safer alternative for mild pain relief.
How to treat bleeding disorders?
Treatment Options for Bleeding Disorders 1 Standard half-life therapies: Standard half-life therapies are used to treat hemophilia A and B, some types of von Willebrand disease, and some rare factor disorders. Dosing can be anywhere from three times a week to every day, depending on the person. 2 Extended half-life (EHL) therapies: EHL contains a molecule that has been modified in some way to delay the breaking down of factor in the body. This results in higher levels of factor in the body lasting for longer, resulting in less frequent infusions. How long the factor is effective in the body depends on the person. Extended half-life therapies are mostly used to treat hemophilia A and B. 3 Bypassing agents are used to treat bleeds in people with hemophilia with inhibitors. These treatments contain other factors that can stimulate the formation of a clot and stop bleeding.
What is EHL therapy?
Extended half-life (EHL) therapies: EHL contains a molecule that has been modified in some way to delay the breaking down of factor in the body. This results in higher levels of factor in the body lasting for longer, resulting in less frequent infusions. How long the factor is effective in the body depends on the person.
What is extended half life therapy?
Extended half-life therapies are mostly used to treat hemophilia A and B. Bypassing agents are used to treat bleeds in people with hemophilia with inhibitors. These treatments contain other factors that can stimulate the formation of a clot and stop bleeding.
What is non factor replacement therapy?
Non-factor replacement therapies include: Emicizumab (Hemlibra) is a therapy used to treat hemophilia A, to prevent bleeding episodes in people both with and without inhibitors. It is known as a factor VIII (8) mimetic because it mimics, or imitates, the way factor VIII (8) works.
