Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Wastewater Treatment: How Do They Work?
- Primary Wastewater Treatment. Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. ...
- Secondary Wastewater Treatment. Secondary treatment of wastewater makes use of oxidation to further purify wastewater. ...
- Tertiary Wastewater Treatment. ...
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
May 31, 2009 · Primary waste water treatment uses simple mechanical & physical processes to remove nearly half of the solid contaminants from waste water. Primary treatment consists of units like coarse screening, grit removal, communicator, flow equalization and primary sedimentation tanks. The schematic diagram of primary treatment with commonly used units.
What is removed during primary wastewater treatment?
wastewater treatment - Primary treatment | Britannica Primary treatment Primary treatment removes material that will either float or readily settle out by gravity. It includes the physical processes of screening, comminution, grit removal, and sedimentation. Screens are made of long, closely spaced, narrow metal bars.
What is the primary treatment of wastewater?
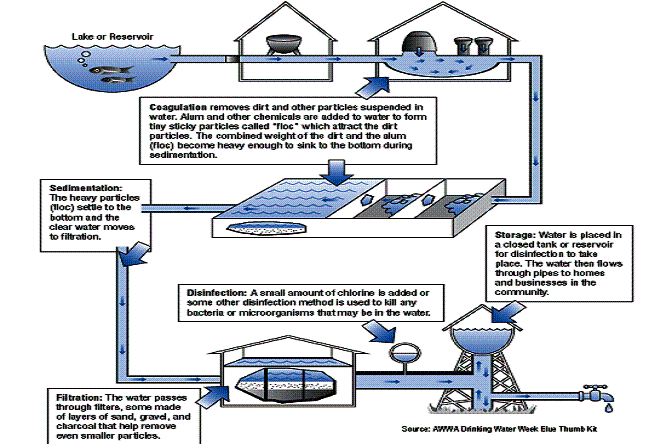
a common water treatment plant involves the following processes: (1) pretreatment to remove big objects that can be found in the pipelines that transport water from the supply to the treatment plant, (2) softening and/or coagulation for the removal of hardness and/or suspended particles, (3) filtering through sand beds to remove any fine …
What are the steps of the water treatment process?
Jun 27, 2017 · Primary Wastewater Treatment. Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. This is done after filtering out larger contaminants within the water. Wastewater is passed through several …

What is primary treatment in water treatment?
Primary treatment removes material that will either float or readily settle out by gravity. It includes the physical processes of screening, comminution, grit removal, and sedimentation. Screens are made of long, closely spaced, narrow metal bars.
What is primary and secondary water treatment?
In the primary stage, solids are allowed to settle and removed from wastewater. The secondary stage uses biological processes to further purify wastewater. Sometimes, these stages are combined into one operation.
What is the primary treatment?
(PRY-mayr-ee TREET-ment) The first treatment given for a disease. It is often part of a standard set of treatments, such as surgery followed by chemotherapy and radiation. When used by itself, primary treatment is the one accepted as the best treatment.
What is primary and secondary treatment?
Primary treatment works on sedimentation, where solids separate from the water through several different tanks. In contrast, secondary treatment uses aeration, biofiltration and the interaction of waste throughout its process.Nov 19, 2020
What is meant by secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment is the second step in most waste treatment systems during which bacteria consume the organic parts of the wastes. This is accomplished by bringing the sewage, bacteria and oxygen together in trickling filters or within an activated sludge process.Mar 13, 2003
What is secondary treatment of water?
Secondary treatment is the removal of biodegradable organic matter (in solution or suspension) from sewage or similar kinds of wastewater. The aim is to achieve a certain degree of effluent quality in a sewage treatment plant suitable for the intended disposal or reuse option.
What are the 3 stages of water treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What is the purpose of primary treatment in wastewater?
The objective of primary treatment is the removal of settleable organic and inorganic solids by sedimentation, and the removal of materials that will float (scum) by skimming.
What is the key difference between primary and secondary?
Primary sources can be described as those sources that are closest to the origin of the information. They contain raw information and thus, must be interpreted by researchers. Secondary sources are closely related to primary sources and often interpret them.Oct 21, 2021
What is the difference between primary and secondary sludge?
Primary sludge is generated from chemical precipitation, sedimentation, and other primary processes, whereas secondary sludge is the activated waste biomass resulting from biological treatments. Some sewage plants also receive septage or septic tank solids from household on-site wastewater treatment systems.
What is secondary treatment in a wastewater treatment process?
Secondary wastewater treatment processes use microorganisms to biologically remove contaminants from wastewater. Secondary biological processes can be aerobic or anaerobic, each process utilizing a different type of bacterial community.
What is primary treatment?
Primary treatment. Primary treatment removes material that will either float or readily settle out by gravity. It includes the physical processes of screening, comminution, grit removal, and sedimentation. Screens are made of long, closely spaced, narrow metal bars. They block floating debris such as wood, rags, ...
What is the purpose of sewage treatment plant?
The sewage treatment plant provides a suitable environment , albeit of steel and concrete , for this natural biological process. Removal of soluble organic matter at the treatment plant helps to protect the dissolved oxygen balance of a receiving stream, river, or lake.
What is activated sludge?
activated sludge process. Primary and secondary treatment of sewage, using the activated sludge process. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Grit chambers are long narrow tanks that are designed to slow down the flow so that solids such as sand, coffee grounds, and eggshells will settle out of the water. Grit causes excessive wear and tear on pumps ...
How long does it take for a primary clarifier to settle?
These tanks, also called primary clarifiers, provide about two hours of detention time for gravity settling to take place. As the sewage flows through them slowly, the solids gradually sink to the bottom. The settled solids—known as raw or primary sludge —are moved along the tank bottom by mechanical scrapers.
How is sludge moved?
The settled solids—known as raw or primary sludge —are moved along the tank bottom by mechanical scrapers. Sludge is collected in a hopper, where it is pumped out for removal. Mechanical surface-skimming devices remove grease and other floating materials.
How does a trickling filter work?
A trickling filter is simply a tank filled with a deep bed of stones. Settled se wage is sprayed continuously over the top of the stones and trickles to the bottom , where it is collected for further treatment. As the wastewater trickles down, bacteria gather and multiply on the stones. The steady flow of sewage over these growths allows the microbes to absorb the dissolved organics, thus lowering the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) of the sewage. Air circulating upward through the spaces among the stones provides sufficient oxygen for the metabolic processes.
What is the purpose of a secondary clarifier?
Air circulating upward through the spaces among the stones provides sufficient oxygen for the metabolic processes. Settling tanks, called secondary clarifiers, follow the trickling filters. These clarifiers remove microbes that are washed off the rocks by the flow of wastewater.
Why is water treatment important?
Water treatment is performed in order to improve water quality. The processes employed for water treatment depend on the quality of the water supply. In all cases, water has to be disinfected in order to deactivate any existing microorganisms present in water. So far, this technique was proved to be the most important for the protection ...
What is biological waste water treatment?
Biological waste water treatment is the primary method of preparing food-processing waste water flows for return to the environment. Increasing waste water loads on existing plants and more stringent government discharge requirements have put considerable pressure on the food-processing industry to refine and understand better the design and management of biological waste water treatment processes. Though activated sludge and other biological treatment processes are still frequently operated by general guidelines and ‘rules of thumb,’ facility design and operation must be guided by consideration of both the physical and biological aspects of waste water treatment. Various modifications and combinations of aerobic and anaerobic biological treatment processes are commonly used in the food-processing industry.
What will the future of brewing water systems be like?
Brewery water treatment systems of the future will be very flexible, allowing breweries to tailor-make their water for different products. At the same time, these future water treatment systems will aim to achieve optimum efficiency in terms of operating cost and especially wastewater produced. The advances in analysis techniques will inevitably lead to further challenges, as it will be possible to detect certain components that are not an issue today but will then need to be removed. It will also continue to be vital for brewers to pay attention to their water supply to avoid surprising and unexpected quality defects in the finished product.
How to remove hardness from water?
Softening is another technique commonly used to remove hardness in case water is hard, which is performed by the addition of lime and subsequent precipitation of calcium as calcium carbonate and magnesium as magnesium hydroxide.
What is membrane technology?
The development of large-scale modules with lower-energy consumption reduced costs significantly. Especially in the water industry, membrane technology has grown much more than coagulation and ozonation, since membranes require minimal addition of aggressive chemical reagents and produce no by-products.
How to improve the taste of water?
1. Understand the treatment need: For many consumers, simply improving the taste of the water is their primary treatment need. For some, there may be health contaminants that must be treated. And others may have very hard water, causing issues with lime scale around fixtures and possibly damaging appliances. 2.
Is bioremediation a good technique?
Bioremediation appears as a promising technique; moreover, recent studies indicate that use of enzymes for rapid degradation and removal of phenolic pollutants is an alternative to the traditional methods as well as microbial treatment that create some serious limitations ( Chen & Lin, 2007 ).
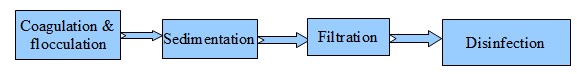
Screening – Primary treatment for waste water
The first process in Primary Treatment for Wastewater is screening. I will show you the screening process and different types of screens used in primary wastewater treatment.
Flow Equalisation – Primary treatment for waste water
Under uniform flow rates, clarifiers and mechanised secondary treatment are more efficient.
Sedimentation – Primary treatment for wastewater
The wastewater, then moves to sedimentation ponds, settling tanks, or clarifiers after the removal of settled grit. The sedimentation process removes the settleable solids by gravitational settling under quiescent conditions.
Flocculation
Flocculation is a water treatment process to remove small suspended solids which don’t settle in the sedimentation tank. In this process solids form larger clusters, or flocs on the addition of a flocculent like aluminium sulphate.
Scum Removal
Lighter materials rise to the surface as sludge settles to the bottom of the sedimentation tanks. The constituents of ‘scum’ are grease, oils, plastics, and soap. Scum is skimmed off the surface of the wastewater by slow-moving rakes. Scum is thickened before being poured into the digesters with the sludge.
What is primary treatment of wastewater?
Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. This is done after filtering out larger contaminants within the water. Wastewater is passed through several tanks and filters that separate water from contaminants.
What is the most effective method of secondary treatment of wastewater?
This method of secondary treatment of wastewater employs sand filters, contact filters, or trickling filters to ensure that additional sediment is removed from wastewater. Of the three filters, trickling filters are typically the most effective for small-batch wastewater treatment.
What is the third step in wastewater management?
This third and last step in the basic wastewater management system is mostly comprised of removing phosphates and nitrates from the water supply. Substances like activates carbon and sand are among the most commonly used materials that assist in this process.
How long does it take for a wastewater solution to be aerated?
The resulting mixture is then aerated for up to 30 hours at a time to ensure results.
What is primary treatment wastewater?
Primary Treatment Wastewater is a plain sedimentation process to remove suspended organic solids from the sewage. Chemical are sometimes used to remove finely divided and colloidal solids.
What is the primary objective of wastewater treatment?
The main objectives of primary treatment of wastewater are: To reduce the strength of sewage to the extent 30% to 50%. To remove settleable solids by 80% to 90%. To reduce BOD by 30% to 35%. To make the sewage fit for further treatment process.
What is primary sedimentation tank?
Primary sedimentation tank is also known as primary clarifier and is located just after grit chamber. It may be rectangular, circular or square shape. The principle and construction details are same as that of plain sedimentation tank W.T.P.
Screening – Primary Treatment For Waste Water
- The first process in Primary Treatment for Wastewater is screening. I will show you the screening process and different types of screens used in primary wastewater treatment. In addition to dissolved and suspended impurities, stone, rocks, and even dead animals are among the components of the treatment plant’s wastewater. These solid materials, which make up about a …
Flow Equalisation – Primary Treatment For Waste Water
- Under uniform flow rates, clarifiers and mechanised secondary treatment are more efficient.
- Equalization basins store diurnal or wet-weather flow peaks temporarily and make the water flow rate uniform.
- Basins serve as a temporary holding area for the incoming wastewater during temporary plant shut down and maintenance.
- Under uniform flow rates, clarifiers and mechanised secondary treatment are more efficient.
- Equalization basins store diurnal or wet-weather flow peaks temporarily and make the water flow rate uniform.
- Basins serve as a temporary holding area for the incoming wastewater during temporary plant shut down and maintenance.
- It acts as a means of diluting and distributing hazardous or high-strength waste into batches.
Sedimentation – Primary Treatment For Wastewater
- The wastewater, then moves to sedimentation ponds, settling tanks, or clarifiers after the removal of settled grit. The sedimentation process removes the settleable solids by gravitational settling under quiescent conditions. On proper adjustment of water flow in the sedimentation tank, the suspended particles begin to fall to the bottom and form a solid mass. Raw primary biosolids, al…
Flocculation
- Flocculation is a water treatment process to remove small suspended solids which don’t settle in the sedimentation tank. In this process solids form larger clusters, or flocs on the addition of a flocculent like aluminium sulphate. The coagulant molecules have a positive charge. Hence, they can neutralize the negatively charged solid particles that are suspended in the water. Neutralizat…
Scum Removal
- Lighter materials rise to the surface as sludge settles to the bottom of the sedimentation tanks. The constituents of ‘scum’ are grease, oils, plastics, and soap. Scum is skimmed off the surface of the wastewater by slow-moving rakes. Scum is thickened before being poured into the digesters with the sludge. Primary treatment removes about 60% of the total suspended solids and nearly …