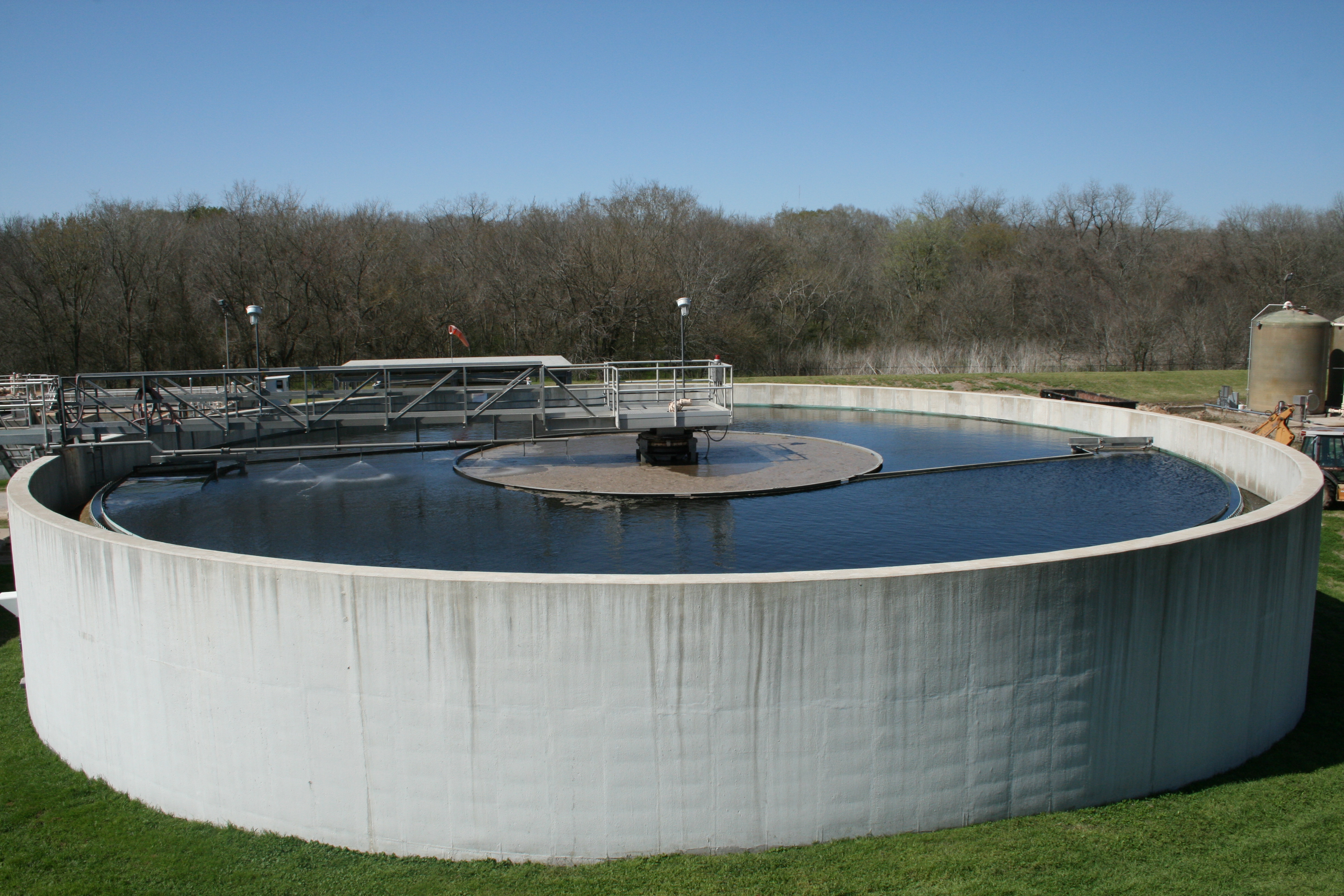

What is a primary clarifier?
The primary clarifiers are used to separate settle able solids from the raw incoming wastewater. These are located on the downstream of the plant. The major function of the primary clarifier is the removal of all settle able and floating solid waste which have a high oxygen demand – BOD.
What is a secondary clarifier?
The secondary clarifier can be described as a circular basin where effluent from the activated sludge process is held. The biomass of microorganisms settles to the bottom in the form of activated sludge. After settling over a period of time, this biomass of microorganisms is returned to the first aeration tank.
What causes pin floc in clarifier?
- Check to see if the clarifier is level in both planes, front to back and side to side. ...
- When was the last time the settling plates were cleaned? ...
- When was the last time the entire clarifier was cleaned? ...
- Have you checked to make sure your flocculant or polymer dosage is not excessive? ...
What is removed during primary wastewater treatment?
The initial and primary water treatment process removes large matter from wastewater while the secondary treatment will remove smaller particles already dissolved or suspended. Sedimentation and filtration are the processes involved in the primary treatment method while biological breakdown occurs through aerobic or anaerobic units in secondary processes.
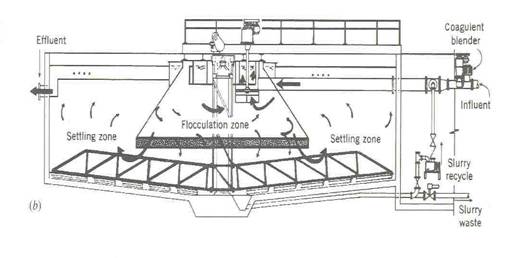
What is a primary clarifier?
A circular tank in which wastewater is held for a period of time to allow heavier solids to settle to the bottom as sludge and lighter materials to float to the water surface as scum.
What is the difference between primary and secondary clarifier?
What is the main difference between the sludge from primary and secondary clarifiers? Sludge from primary clarifiers is more dense than from secondary clarifiers (because it is from the first round of settling).
What is secondary clarifier in wastewater treatment?
secondary clarifiers is to separate biological floc from the treated liquid waste stream. Secondary clarifiers are most often discussed in conjunction with suspended growth biological wastewater treatment systems.
What do primary clarifiers remove?
Answer: Primary clarifiers are very effective at removing floatable and settleable solids from the wastewater flow stream, so the answer is A, settleable and floatable. Floatable solids include objects and debris that are positively buoyant, meaning they float.
What is a final clarifier?
Final Clarifier. The Final Clarifiers are designed to allow sludge to settle while the clean water is discharged to the receiving stream. We have three finals, and they operate in parallel fashion. Like the aeration basins, there is a splitter that divides the stream equally.
What is primary and secondary treatment?
There are two basic stages in the treat- ment of wastes, primary and secondary, which are outlined here. In the primary stage, solids are allowed to settle and removed from wastewater. The secondary stage uses biological processes to further purify wastewater. Sometimes, these stages are combined into one operation.
What is the primary function of secondary clarifier?
Secondary clarifiers are used to remove the settlable suspended solids created in biological treatment processes such as the activated sludge and trickling filter process.
How many types of clarifier are there?
There are three key types of clarifiers (although, as we will note, clarifiers deployed in the field may be hybrids of more than one type).
Why is secondary clarifier important?
The function of the secondary clarifier is to separate the activated sludge solids from the mixed liquor. These solids represent the colloidal and dissolved solids that were originally present in the wastewater. In the aeration unit they were incorporated into the activated sludge floc, which are settleable solids.
What is the purpose of clarifier?
A clarifier is generally used to remove solid particulates or suspended solids from liquid for clarification and (or) thickening. Concentrated impurities, discharged from the bottom of the tank are known as sludge, while the particles that float to the surface of the liquid are called scum.
Where does effluent from a primary clarifier go?
Aeration BasinsFrom the Primary Clarifiers, the wastewater flows into large, rectangular tanks called Aeration Basins, where a biological treatment called the “activated sludge process” occurs. The wastewater flows slowing through a series of chambers as large volumes of air are bubbled up through the water.
What is a primary sludge?
Primary sludge is produced through the mechanical wastewater treatment process. It occurs after the screen and the grit chamber and consists of unsolved wastewater contaminations. The sludge amassing at the bottom of the primary sedimentation basin is also called primary sludge.
Drives and Sludge Collection
Monroe Environmental incorporates durable drives and bottom scraping rakes that will continuously remove settled sludge. The rake employs multiple bottom scraping blades that are angled to ensure that all settling sludge is captured and brought to the central sludge well.
Clarifier Effluent
Monroe worked with consulting engineers to provide two 30′ Primary Circular Clarifiers capable of processing over 1.25 million gallons per day for a snack food producer.
Primary and secondary clarifying
Both the primary and secondary phases of the process rely on clarifier equipment to get the job done in the right way, but each phase has its own objective.
Key types of clarifiers
There are three key types of clarifiers (although, as we will note, clarifiers deployed in the field may be hybrids of more than one type). Read on to discover more about each.
Clarifier tank structures
While we have already covered the main types of wastewater clarifiers, there is something else left to discuss — the structure of the clarifier tank itself. These structures come in two basic types: pre-fab and concrete cylinder.
Learn about this topic in these articles
These tanks, also called primary clarifiers, provide about two hours of detention time for gravity settling to take place. As the sewage flows through them slowly, the solids gradually sink to the bottom. The settled solids—known as raw or primary sludge—are moved along the tank bottom by mechanical scrapers.…
sewage treatment facilities
These tanks, also called primary clarifiers, provide about two hours of detention time for gravity settling to take place. As the sewage flows through them slowly, the solids gradually sink to the bottom. The settled solids—known as raw or primary sludge—are moved along the tank bottom by mechanical scrapers.…
What is a primary clarifier?
Primary Clarifiers- How they often impact the process negatively when they are overlooked. Primary wastewater treatment systems may include both clarification and physical-chemical treatment equipment, depending on the components in the wastewater.
How long does it take for a clarifier to settle?
Usually, clarifier design allows for detention times ranging between 2 to 3 hours, however, it may be as long as 4 to 5 hours.
Can chlorination cause filaments to grow back?
Chlorination is only a quick fix. Without process changes, filaments will grow back after chlorination. Wastewater Biomass Analyses and Cooling Tower Analyses also available.
How The Clarification Occurs
Coagulation and flocculation reagents, such as polyelectrolytes and ferric are added before the water enters the clarifier to cause finely suspended particles to clump together and form larger and denser particles, called flocs.
Sedimentation Tanks or Secondary Clarifiers
Sedimentation tanks or secondary clarifiers remove flocs of biological growth created in some methods of secondary treatment including activated sludge and rotating biological processes.
Municipal Clarification
WesTech’s primary and secondary clarifiers are synonymous with innovative solutions that provide the flocculation, sedimentation, and clarification processes necessary to produce quality effluent that meets your applications’ needs and regulatory requirements.
Primary Clarification
In primary clarification, a portion of the suspended solids and organic matter is removed from the wastewater. This removal is usually accomplished with physical operations such as sedimentation. The effluent from primary clarification will ordinarily contain organic matter and have notable BOD.
Secondary Clarification
We offer a variety of options for secondary clarification – a necessary step for municipal applications where organic matter and BOD in waters from primary clarifiers must be removed.

Primary and Secondary Clarifying
- Both the primary and secondary phases of the process rely on clarifier equipment to get the job done in the right way, but each phase has its own objective.
Key Types of Clarifiers
- There are three key types of clarifiers (although, as we will note, clarifiers deployed in the field may be hybrids of more than one type). Read on to discover more about each.
Clarifier Tank Structures
- While we have already covered the main types of wastewater clarifiers, there is something else left to discuss — the structure of the clarifier tank itself. These structures come in two basic types: pre-fab and concrete cylinder.