Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Wastewater Treatment: How Do They Work?
- Primary Wastewater Treatment. Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. ...
- Secondary Wastewater Treatment. Secondary treatment of wastewater makes use of oxidation to further purify wastewater. ...
- Tertiary Wastewater Treatment. ...
What is the best water treatment?
Jun 26, 2018 · The initial and primary water treatment process removes large matter from wastewater while the secondary treatment will remove smaller particles already dissolved or suspended. Sedimentation and filtration are the processes involved in the primary treatment method while biological breakdown occurs through aerobic or anaerobic units in secondary …
What is secondary treatment of wastewater in a treatment plant?
Jun 27, 2017 · The resulting “sludge” is then fed into a digester, in which further processing takes place. This primary batch of sludge contains nearly 50% of suspended solids within wastewater. Secondary Wastewater Treatment. Secondary treatment of wastewater makes use of oxidation to further purify wastewater. This can be done in one of three ways: Biofiltration
What is the secondary treatment of wastewater?
The primary treatment of sour water contaminated with oils and solid particles involve the stripping of dissolved H 2 S using steam, float/sink density separation for skimming the floating oil, and the settling tanks to separate heavier oil and solids, usually in multiple stages, before the treated water can be directed to public treatment facilities. The secondary treatment uses …
Do it yourself water treatment?
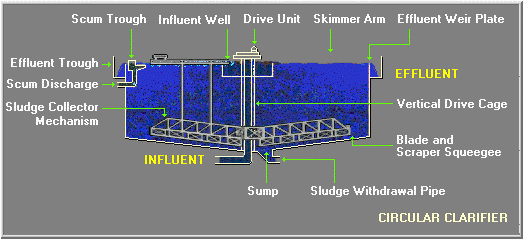
The Secondary Clarifiers are identical to the Primary Clarifiers; materials in the wastewater sink and float and rotating arms remove this material from the water. After treatment in the Secondary Clarifiers, the wastewater is now ready to be released to the Napa River, or further treated to produce recycled water.
What is primary water treatment?
The purpose of primary treatment is to settle material by gravity, removing floatable objects,and reducing the pollution to ease secondary treatment. Primary Treatment aims to reduce the Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Total Suspended Solids (TSS) in the wastewater.
What is primary and secondary treatment?
The main difference is the way each respective treatment is processed. Primary treatment works on sedimentation, where solids separate from the water through several different tanks. In contrast, secondary treatment uses aeration, biofiltration and the interaction of waste throughout its process.Nov 19, 2020
What is secondary treated water?
Secondary treatment removes the soluble organic matter that escapes primary treatment. It also removes more of the suspended solids. Removal is usually accomplished by biological processes in which microbes consume the organic impurities as food, converting them into carbon dioxide, water, and energy…
What is the difference between primary and secondary water?
The initial and primary water treatment process removes large matter from wastewater while the secondary treatment will remove smaller particles already dissolved or suspended.Jun 26, 2018
What is meant by secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment is the second step in most waste treatment systems during which bacteria consume the organic parts of the wastes. This is accomplished by bringing the sewage, bacteria and oxygen together in trickling filters or within an activated sludge process.Mar 13, 2003
What are the 3 stages of water treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What is the difference between primary and secondary sludge?
Primary sludge is generated from chemical precipitation, sedimentation, and other primary processes, whereas secondary sludge is the activated waste biomass resulting from biological treatments. Some sewage plants also receive septage or septic tank solids from household on-site wastewater treatment systems.
What is the purpose of primary treatment in wastewater?
The objective of primary treatment is the removal of settleable organic and inorganic solids by sedimentation, and the removal of materials that will float (scum) by skimming.
What is secondary treatment of water explain various kind of secondary treatment processes?
The secondary stage of treatment removes about 85 percent of the organic matter in sewage by making use of the bacteria in it. The principal secondary treatment techniques used in secondary treatment are the trickling filter and the activated sludge process.
What is secondary treatment in a wastewater treatment process?
Secondary treatment is the removal of biodegradable organic matter (in solution or suspension) from sewage or similar kinds of wastewater. The aim is to achieve a certain degree of effluent quality in a sewage treatment plant suitable for the intended disposal or reuse option.
What is the key difference between primary and secondary?
Primary sources can be described as those sources that are closest to the origin of the information. They contain raw information and thus, must be interpreted by researchers. Secondary sources are closely related to primary sources and often interpret them.Oct 21, 2021
What are the main difference observed in primary and secondary treatment in STP?
2) Primary treatment involves in removal of large particles and floating materials such as leaves, papers, rags, solids such as sand, grit and oily substances whereas Secondary treatment involves the removal of fine suspended and dissolved organic matter.Aug 27, 2018
What is the most effective method of secondary treatment of wastewater?
This method of secondary treatment of wastewater employs sand filters, contact filters, or trickling filters to ensure that additional sediment is removed from wastewater. Of the three filters, trickling filters are typically the most effective for small-batch wastewater treatment.
What is primary treatment of wastewater?
Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. This is done after filtering out larger contaminants within the water. Wastewater is passed through several tanks and filters that separate water from contaminants.
What is the third step in wastewater management?
This third and last step in the basic wastewater management system is mostly comprised of removing phosphates and nitrates from the water supply. Substances like activates carbon and sand are among the most commonly used materials that assist in this process.
How long does it take for a wastewater solution to be aerated?
The resulting mixture is then aerated for up to 30 hours at a time to ensure results.
What is considered preliminary treatment?
Preliminary Treatment: Physical. When wastewater arrives at the treatment plant, it contains many solids that cannot be removed by the wastewater treatment process. This can include rags, paper, wood, food particles, egg shells, plastic, and even toys and money.
What happens when wastewater enters the secondary clarifier?
When the wastewater enters the two Secondary Clarifiers, it still contains lots of microorganisms from the Aeration Basins and looks brown and murky. The Secondary Clarifiers are identical to the Primary Clarifiers; materials in the wastewater sink and float and rotating arms remove this material from the water.
How much water does a secondary clarifier hold?
The Secondary Clarifiers each hold 800,000 gallons of water.
What is the process of aeration of wastewater?
From the Primary Clarifiers, the wastewater flows into large, rectangular tanks called Aeration Basins, where a biological treatment called the “activated sludge process” occurs. The wastewater flows slowing through a series of chambers as large volumes of air are bubbled up through the water. There is so much air added that it looks as if the water is boiling. In these basins, the wastewater is mixed with the “activated sludge;” hundreds of millions of actively growing single-celled microorganisms (mostly bacteria and protozoa) referred to as “bugs.”
How many gallons of water can a primary clarifier hold?
Primary Clarifiers: Physical. From the Headworks, the wastewater flows into two huge circular tanks called Primary Clarifiers. These tanks can hold 600,000 gallons of water each. Here the wastewater slows down and remains in the tanks for about two hours.
How long does it take for wastewater to leave the aeration basin?
When all of the food (waste) is gone, after about eight hours, the wastewater leaves the Aeration Basins.
What is the EPA drinking water standards?
EPA Primary and Secondary Drinking Water Standards. The US national Primary Drinking Water Regulations establish standards for water purity that apply to public water systems.*. The standards define a permitted "maximum contaminant level" (MCL) for various minerals, chemicals and other pollutants that has been arrived at by weighing health risks, ...
How many contaminants are in the EPA drinking water standards?
In addition to the primary standards, the EPA has established national Secondary Drinking Water Regulations that set non-mandatory water quality standards for 15 contaminants.
What is secondary treatment?
The secondary treatment is designed to remove soluble organics from the wastewater. Secondary treatment consists of a biological process and secondary settling is designed to substantially degrade the biological content of the sewage such as are derived from human waste, food waste, soaps and detergent.
What is the purpose of sewage treatment?
The purpose of the sewage treatment is to remove the solids present in the sewage. ROLE OF MICROORGANISMS. Microorganisms are unicellular microscopic living things. They multiply by binary division of cells within 10 to 20 minutes. They require oxygen for their respiration.
What is activated sludge?
The activated sludge process (ASP) is an aerobic biological wastewater treatment process that uses microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, to speed up decomposition of organic matter requiring oxygen for treatment.
What are the end products of anaerobic and aerobic processes?
Under aerobic conditions, if completely oxidized, organic matter is transformed into non-hazardous products. But an anaerobic process can produce methane (CH 4 ), which is explosive, and ammonia (NH 3) and hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S), which are toxic.
What are the two types of biological processes?
TYPES OF BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES. There are two types of biological treatment process; aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic process means that oxygen is present for the microbes for respiration. Anaerobic process means that the process proceeds in the absence of DO.
What are the two types of solids in sewage?
SOLIDS IN SEWAGE. The solids present in the sewage are of two types viz., Organic solids, and. Inorganic solids. Organic solids are the substances derived from living things like produces from plant and animal. Examples of organic solids are carbohydrate, protein, and fat.
How is DO supplied in biological treatment?
In the biological treatment processes the DO is supplied either through natural means or by mechanical means by agitation. Anaerobic organisms can multiply in the absence of DO and do the decomposition, but the end products are undesirable fowl smelling gases like H 2 S, CH, etc.