What are the side effects of taking post-exposure prophylaxis?
Apr 28, 2021 · PEP, or post-exposure prophylaxis, is a short course of HIV medicines taken very soon after a possible exposure to HIV to prevent the virus from taking hold in your body. You must start it within 72 hours (3 days) after a possible exposure to HIV, or it won’t work. Every hour counts! PEP should be used only in emergency situations.
How do you prevent HIV after exposure?
PEP is the use of antiretroviral medication to prevent HIV infection in an HIV-negative person who has had a specific high-risk exposure to HIV. Such an exposure typically occurs through sex or sharing syringes (or other injection equipment) with someone who has or might have HIV. Exposure to HIV is a medical emergency, because HIV establishes infection very quickly, often …
What is the risk of HIV post exposure?
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) PEP is the use of antiretroviral drugs after a single high-risk event to stop HIV seroconversion. PEP must be started as soon as possible to be effective—and always within 72 hours of a possible exposure. Resources for Consumers Basic PEP Q&As – learn the basics about PEP and if it’s right for you.
How much does post exposure prophylaxis cost?
May 25, 2021 · PEP (post-exposure prophylaxis) means taking medicine to prevent HIV after a possible exposure. PEP should be used only in emergency situations and must be started within 72 hours after a recent possible exposure to HIV. This section answers some of the most common questions about PEP. You can also download PEP materials to share.
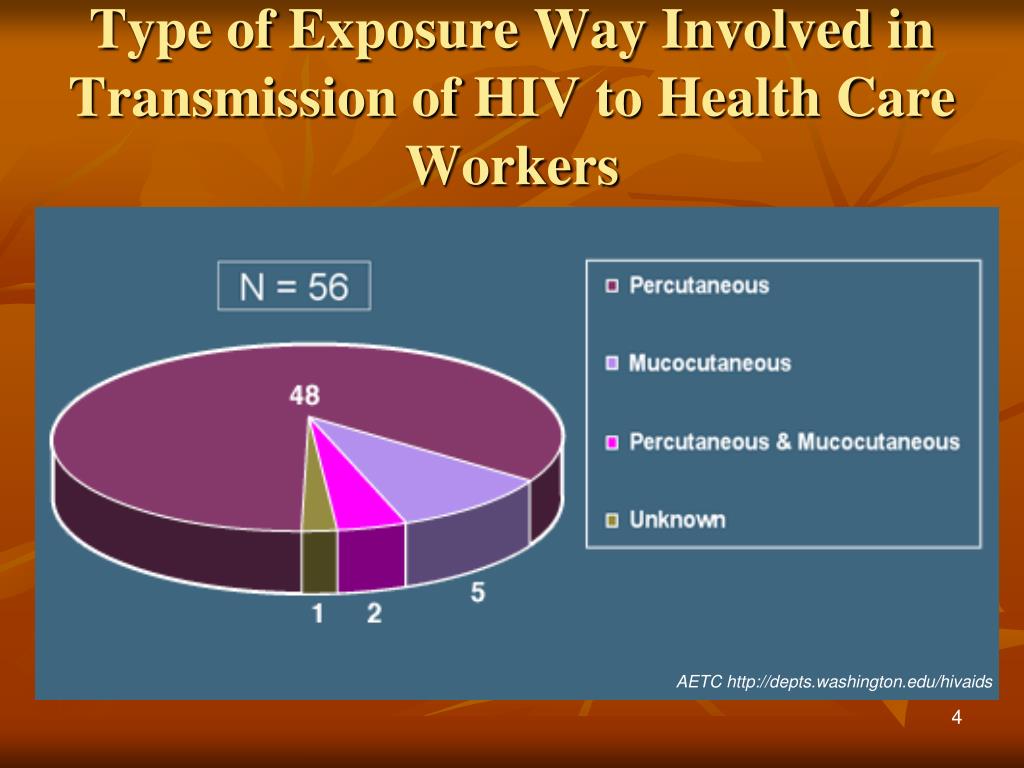
What is the difference between pre and post-exposure prophylaxis for HIV?
PrEP is daily medicine that can reduce this risk. With PrEP, if you do get exposed to HIV, the medicine can stop HIV from taking hold and spreading throughout your body. PEP stands for post-exposure prophylaxis. PEP is for people who have possibly been exposed to HIV.Oct 13, 2021
When should you take PEP?
PEP needs to be taken as soon as possible after you have been exposed, ideally within 2 hours and not later than 72 hours (three days). The sooner PEP is taken, the more likely it is to stop HIV infection. Your doctor will talk to you about whether PEP is right for you.
What medication is used for PEP?
The medication now used for PEP is a single tablet called Truvada and two tablets of raltegravir.
Can I stop PEP after 5 days?
In practice, after a needlestick risk. most health workers report stopping PEP within a week or two. Either way, holding back a few days of PEP does makes practical sense, especially when health services generally – certainly in the UK – keep people waiting for at least four hours, if not considerably longer.Mar 12, 2022
Is PEP effective after 3 days?
PEP is a series of pills you can start taking very soon after you've been exposed to HIV that lowers your chances of getting it. But you have to start PEP within 72 hours, or 3 days, after you were exposed to HIV, or it won't work. The sooner you start, the better it works — every hour matters.
Is PEP and PrEP the same drug?
PrEP stands for pre-exposure prophylaxis and PEP stands for post-exposure prophylaxis. Prophylaxis means “treatment or actions taken to prevent a disease.” PrEP is a treatment plan to prevent HIV before a person is exposed while PEP is a treatment plan for after a person is exposed.May 12, 2020
Does post-exposure prophylaxis work?
How well does PEP work? If taken within 72 hours after possible exposure, PEP is highly effective in preventing HIV. But to be safe, you should take other actions to protect your partners while you are taking PEP.
Is PEP effective after 48 hours?
Thus, even though PEP is often offered for up to 72 hours after exposure, it should be initiated as early as possible. After 72 hours, PEP is not effective, and there are gradations in efficacy from 24 hours postexposure, to 36, 48, and 72 hours.
What is PEP?
PEP (post-exposure prophylaxis) means taking medicine to prevent HIV after a possible exposure. PEP Must Be Started Within 72 Hours of Possible Exp...
How well does PEP work?
If taken within 72 hours after possible exposure, PEP is highly effective in preventing HIV. But to be safe, you should take other actions to prote...
Are there any side effects?
PEP is safe but may cause side effects like nausea in some people. In almost all cases, these side effects can be treated and aren’t life-threatening.
How to start a PEP?
Guidelines recommend the following baseline screening before initiating PEP: 1 HIV rapid test at baseline. If baseline rapid test indicates existing HIV infection, PEP should not be started. However, if rapid HIV baseline test is not available, there should be no delay in starting PEP. Oral HIV tests are not recommended for use among persons being evaluated for PEP. 2 Pregnancy test (if a woman is of reproductive age, not using highly effective contraception, eg IUDs or other long-active reversible contraceptives (LARCs), oral contraceptives, or properly used condoms, and with vaginal exposure to semen). 3 Serum liver enzymes 4 BUN/creatinine 5 STI screening#N#Persons being evaluated for PEP because of a sexual encounter should have STI-specific nucleic acid amplification (NAAT testing) for chlamydia and gonorrhea, and a blood test for syphilis 6 Hepatitis B testing, including hepatitis B surface antigen, surface antibody, and core antibody 7 Hepatitis C (HCV) antibody
Is PEP effective for HIV?
PEP is only indicated for potentially exposed people without HIV infection. PEP is unlikely to be effective in people who have been exposed more than 72 hours before seeking medical assistance. PEP should be provided only for infrequent exposures.
What is a pregnancy test?
Pregnancy test (if a woman is of reproductive age, not using highly effective contraception, eg IUDs or other long-active reversible contraceptives (LARCs), oral contraceptives, or properly used condoms, and with vaginal exposure to semen). Serum liver enzymes. BUN/creatinine.
New (September 17, 2018)
Guidance for Non-HIV-Specialized Providers Caring for Persons with HIV Who Have been Displaced by Disasters (such as a Hurricane)#N#external icon
Update (May 23, 2018)
Interim Statement Regarding Potential Fetal Harm from Exposure to Dolutegravir – Implications for HIV Post-exposure Prophylaxis (PEP). Please see attached PDF#N#pdf icon#N#[PDF – 104 KB].
Resources for Consumers
Basic PEP Q&As – learn the basics about PEP and if it’s right for you.
Resources for Providers
Visit the Prescribe HIV Prevention website to learn about using PrEP and PEP to reduce new HIV infections.
What is a PEP?
PEP is for Emergency Situations 1 PEP is given after a possible exposure to HIV. 2 PEP is not a substitute for regular use of other HIV prevention. 3 PEP is not the right choice for people who may be exposed to HIV frequently. 4 If you are at ongoing risk for HIV, such as through repeated exposures to HIV, talk to your health care provider about PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis).
What is PEP for HIV?
PEP is given after a possible exposure to HIV. PEP is not a substitute for regular use of other HIV prevention. PEP is not the right choice for people who may be exposed to HIV frequently. If you are at ongoing risk for HIV, such as through repeated exposures to HIV, talk to your health care provider about PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis).
How long does it take to get a PEP?
PEP Must Be Started Within 72 Hours of Possible Exposure to HIV. Talk right away (within 72 hours) to your health care provider, an emergency room doctor, or an urgent care provider about PEP if you think you’ve recently been exposed to HIV: during sex (for example, if the condom broke),
Is PEP safe for HIV?
PEP is safe but may cause side effects like nausea in some people. In almost all cases, these side effects can be treated and aren’t life-threatening. YouTube. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) 538K subscribers. HIV Prevention – Let’s Talk About PEP. Watch later. Share. Info.
How to prevent HIV transmission?
Other than PEP, HIV transmission can also be prevented by: Using condoms (including female or internal condoms) with water or silicone-based lubricant during anal or vaginal sex. Using clean, sterile injecting equipment.
What is PEP in HIV?
PEP is taken after a known or suspected exposure to HIV to prevent HIV transmission. Examples of known or suspected exposure to HIV may include: Condom -less sex with a person whose HIV status you don’t know or who is HIV-positive and not on treatment. Where a condom has broken or failed during sex.
How effective is PrEP?
PrEP is a pill taken once a day and is 99% effective at preventing HIV transmission if taken consistently as prescribed. For more information visit or call the Victorian PrEP Service, Alfred Health on 1800 889 887.
What is PEP treatment?
What is PEP? PEP (post-exposure prophylaxis) is a course of antiviral medication you can take to prevent HIV infection if you have potentially been exposed to the virus. It must be started within 72 hours of an exposure to HIV and be taken correctly over a 28-day treatment period. PEP can be 1 tablet taken daily or a combination ...
How long does it take for PEP to work?
PEP must be started within 72 hours of an exposure to HIV and be taken correctly over a 28-day treatment period to be effective.
Does PEP protect against STI?
Can cause severe side effects in some people – such as nausea and vomiting, headaches, an upset stomach, diarrhoea or tiredness. PEP does not protect against other sexually transmissible infections (STI) such as: syphilis. gonorrhoea.
Is it safe to take PEP if you have HIV?
If your exposure to HIV is through a person with HIV who has an undetectable viral load, PEP is not recommended, as there is no risk of transmission.
